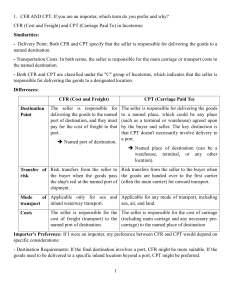
FINANCING INTERNATIONAL TRADE PROFESSOR DR. MD. AMINUL ISLAM F A C U LT Y O F A P P L I E D A N D H U M A N SCIENCES U N I V E R S I T I M A L AY S I A P E R L I S VISITING PROGFESSOR D A F F O D I L I N T E R N AT I O N A L U N I V E R S I T Y aminsazea@gmail.com WhatsApp: +60164049087 Knowledge Sincerity MY YOUTUBE CHANNEL: P L AT F O R M F O R R E S E A R C H A N D Excellence DEVELOPMENT UniMAP LEARNING OUTCOMES After this session participants will be able to: Describe methods of payment for international trade Explain common trade finance methods Describe the major agencies that facilitate international trade with export insurance and/or loan programs Payment Methods for International Trade 1. Prepayment a. Same as cash in advance b. Payment usually by wire transfer c. Method offers exporter greatest degree of protection d. Usually requested when 1.) First time buyer 2.) Danger of pre shipment cancellation 3.) Importer country has high political risk Payment Methods for International Trade 2. Letters of Credit (L/C) a. An instrument issued by a bank b. on behalf of the importer (buyer) c. promising to pay the exporter (beneficiary) upon presentation of shipping documents in compliance with the terms stipulated therein. e. In effect, the bank is substituting its credit for that of the buyer. Payment Methods for International Trade 3. Drafts (or bill of exchange) a. An unconditional promise drawn by one party, usually the exporter, b. instructing the buyer to pay the face amount of the draft upon presentation. c. draft represents the exporter’s formal demand for payment from the buyer. d. draft affords the exporter less protection than an L/C because the banks are not obligated to honor payments on the buyer’s behalf. Payment Methods for International Trade 4. Consignment a. exporter ships the goods to the importer while still retaining actual title to the merchandise. b. The importer has access to the inventory but does not have to pay for the goods until they have been sold to a third party. c. The exporter is trusting the importer to remit payment for the goods sold at that time. d. If the importer fails to pay, the exporter has limited recourse because no draft is involved and the goods have already been sold. Payment Methods for International Trade 5. Open Account a. The opposite of prepayment - the exporter ships the merchandise and expects the buyer to remit payment according to the agreed upon terms. b. The exporter is relying fully upon the financial creditworthiness, integrity, and reputation of the buyer. c. method is used when the seller and buyer have mutual trust and a great deal of experience with each other. Trade Finance Methods 1. Accounts Receivable Financing a. could take the form of an open account shipment or a time draft b. the bank will provide a loan to the exporter secured by an assignment of the account receivable. 2. Factoring Receivables the exporter sells the accounts receivable without recourse. Trade Finance Methods 3. Letters of Credit ( L/C ) a. Types of Letters of Credit b. Use of Drafts c. Bill of Lading: Key Document d. Commercial Invoice (currency) The Credit Procedure Trade Finance Methods 4. Banker’s Acceptance Bill of exchange, or time draft, drawn on and accepted by a bank. It is the accepting bank’s obligation to pay the holder of the draft at maturity. 5. Working Capital Financing 6. Medium-Term Capital Goods Financing (Forfaiting) Similar to factoring in that the forfaiter (or factor) assumes responsibility for the collection of payment from the buyer, the underlying credit risk, and the risk pertaining to the countries Involved. Life Cycle of a Typical Banker’s Acceptance (B/A) Trade Finance Methods 7. Countertrade a. Denotes all types of foreign trade transactions in which the sale of goods to one country is linked to the purchase or exchange of goods from that same country. b. Some types of countertrade, such as barter, have been in existence for thousands of years. c. Recently countertrade gained popularity and importance. Agencies That Motivate International Trade 1. Export-Import Banks b. Its mission today is to finance and facilitate the export of goods and services c. Maintain the competitiveness of companies in overseas markets. d. Programs that are classified as 1.) guarantees 2.) loans 3.) bank insurance 4.) export credit insurance. Agencies That Motivate International Trade 2. Private Export Funding Co. (PEFCO) a. Is owned by a consortium of commercial banks and industrial companies. b. Provides medium and long-term fixed rate financing to foreign buyers. 3. Overseas Private Investment Corporation (OPIC) A self-sustaining federal agency responsible for insuring direct investments in foreign countries against the risks of currency inconvertibility, expropriation, and other political risks. Knowledge Sincerity Excellence UniMAP