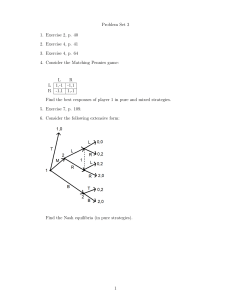
3/17/2020 Project Management BA023IU Recap of Session 4 Conflict resolution Negotiation Case: “Habitat for Humanity Wins a Big One” Agenda Session 5 Project Organization Why project organization matters? Three major project organization forms Selecting appropriate organization form Project management office and project team Lecturer: Tung Nhu Nguyen 1. The importance of project organization Remember in Session 1, what made project emerged as an important alternative: Skills and knowledge specification, knowledge explosion Demands for more complex and customized goods and services, increased customer focus, compressed product life cycle Evolution of larger and more sophisticated markets, global competition Project-oriented organization Has the advantages in terms of Response to market The traditional way The project way Diverse specialized knowledge required Manufactured goods vs. agricultural goods Software: graphics vs. logical design vs. programming Films 1 3/17/2020 Project-oriented organization Responsive to organizational changes 2. Different ways in organizing projects Those happen more and more frequently: companies buying other companies, or product lines When new management trends emerged: applying corporate reengineering, CRM… Communicating with single project managers rather than to multiple functional managers on complicated matters 2.1 Project as part of a functional department Level of independence Deciding on project design is usually the responsibility of senior management, PMs can give comments or be involved 2.1 Project as part of a functional department Advantages President Marketing Market research project Z Launching Brand X Finance HR 2.1 Project as part of a functional department Pure project Matrix Functional Enable total-control, one-stop contact point of organizational issues. As a part of functional department Pure project organization Matrix organization Flexibility of staff, of resources Better use of resources for multiple projects inside the department Exchange of ideas, knowledge, assistance among experts inside the department Retain knowledge and know-how inside department and organization; continuity Incubator for potential experts 2.2 Pure project organization Disadvantages Project may not received focus needed inside functional dept., when other daily activities are going on, slow response to project issues Discipline oriented rather than problem oriented No dedicated PM may result in chaos More priorities are given to tasks related to the department Lack of motivation, as project staff are not “seen” Lack of holistic view to address problems or better serve the clients President Program manager Vice President marketing Project 2 Project 1 Vice President HR Project … Marketing Marketing Design Design Finance Finance 2 3/17/2020 2.2 Pure project organization Organization consists of many projects and no official functional department Each project has “everything”: manager, staff of different specialization, resources, office For instance Resources and efforts, not shared but duplicated and wasted Excess resources tend to be stored idle in individual projects to be ready “when necessary” Project technical staff might become outdated with technical advancement, lack of a breadth of knowledge as they are away from functional dept. Technical procedure not strictly followed Mental issues: rivalries among projects, anxiety for life after projects finished 2.3 Matrix organization Advantages The PM has total authority, single boss The staff are also responsible to one boss only Communications are streamlined, decision making is quicker, better responses to changes or Project identity is promoted Better commitment and motivation Structure is easily understood, better working atmosphere in general Problems are solved with a holistic approach 2.3 Matrix organization Disadvantages An IT outsourcing company organizes project as nucleus of operation A research lab that has various projects on some breakthrough products 2.2 Pure project organization 2.2 Pure project organization Matrix = Pure + Functional Different levels of matrix exist The roles of PMs: when and what tasks to be finished The roles of functional managers: who to send and how tasks to be finished For instance: The project to design, produce and introduce a new homepage of the university President Manufacturing Marketing HR Finance Project 1 - Mfg Project 1 – Mar. Project 1 – HR Project 1 – Fin Project 2 - Mfg Project 2 – Mar. Project 2 – HR Project 2 – Fin Project 3 - Mfg Project 3 – Mar. Project 3 – HR Project 3 – Fin 2.3 Matrix organization Advantages Better identity, better focus, better commitment Flexibility prevails, resources shared, waste and duplication reduced Less anxiety when projects end as staff still belong to functional departments Administrative and technical procedures tend to be followed more strictly Loads tend to be more balanced or optimized among projects, problems holistically addressed 3 3/17/2020 2.3 Matrix organization Variations of matrix org. Disadvantages Conflict between project manager and functional manager: who is in charge? (WHO?) PMs tend to have strong negotiating skills to succeed In times of success, who is the creditor? in times of difficulties, who is the culprit? Conflicts among project managers as they compete to secure resources for one’s own project Staff have to work under two bosses Weak matrix (functional matrix) Variations of matrix org. Balanced matrix Variations of matrix org. When a functional group is to serve several similar projects A person is assigned to oversee the project and interact on an equal basis with functional managers. This person and the functional managers jointly direct workflow segments and approve technical and operational decisions. Organization structure influences on projects A person is formally designated to oversee the project across different functional areas. This person has limited authority over functional people involved and serve primarily to plan and coordinate the project. The functional managers retain primary responsibility for their specific segments of the project. Share capacity rather than dedicated expert Strong matrix (project matrix) A person is assigned to oversee the project and is responsible for the completion of the project. The functional managers involvement is limited to assigning personnel as needed and providing advisory expertise. 3. Selecting an appropriate project organization form Situation determined Each form has pros and cons No one form is best for all projects, or even best for one project throughout its entire life cycle. Source: PMI 4 3/17/2020 3. Selecting an appropriate project organization form What to consider: The nature of the project Importance Size, budget, time constraints Innovation involved Options from organizational point of view Resources available, stability of supplies, potential problems… Attitudes of management Experience Freedom given to PM Then, decide 3. Selecting an appropriate project organization form Examples: A construction company won a tender and to build a theatre A supermarket to use new shelves and change the arrangement of the floor A bank to implement a customer relationship management system 3. Selecting an appropriate project organization form Common sense: 4.1 Project Management Office Role: 4.1 Project Management Office Tasks Which form is appropriate? Establish processes Develop management system Help with administrative details Conducting review, audit Report progress Serve as a place for PMs to exchange Facilitator for project management tasks Not project implementation Responsibilities Functional project: Technology driven, building, equipment, large capital investment Pure project: Many similar projects (construction), control required, specific, unique (to market a new product) Matrix: when?? Improve efficiency of project implementation Promote good practices Data and information streamlines Communication with stakeholders about progress 4.2 Project Team The PM and his key members Typical key members of a project may include: Project engineer Manufacturing engineer Field manager Contract administrator Project controller Support service manager 5 3/17/2020 Quiz 4.2 Project Team Issues in managing project team Perfectionism Motivating the team Participatory approach Empowerment Delegation Conflict resolution 6