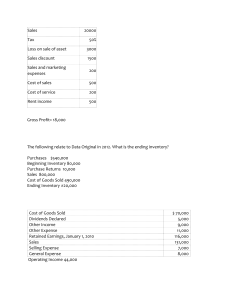
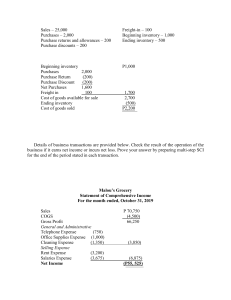
lOMoARcPSD|30612575 480429767 9 Accounting for Merchandising Operations Long Accountancy (University of Northern Philippines) Studocu is not sponsored or endorsed by any college or university Downloaded by Sunflower (flauviablythe@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|30612575 ACCOUNTING FOR MERCHANDISING OPERATIONS Merchandising - a business activity of buying and selling of goods. The goods that a merchandising company sells to its customers are called Merchandise Inventory, or simply, Inventory. - examples: grocery, department store, appliance stores Operating Cycle Gross Invoice Price In Accounting for Merchandising Operations, we always record the Gross Invoice Price in the books. Merchandises are always quoted in the original price, called List Price and deductions are given by the seller to encourage the buyer to buy more, called Trade Discounts. Gross List Trade Invoice = Price Discount Price List Price Trade Discount Gross Invoice Price = 1. Find the amount that will be recorded in the books of Jimin Trading regarding their purchase of merchandise, listed as P6,000 and is given a trade discount of 20% Given List Price Trade Discount Gross Invoice Price Amount 6,000 20% ? 6,000 x 20% = 1, 200 = 6,000 1,200 4,800 2. Find the amount that will be recorded in the books of Jimin Trading regarding their purchase of merchandise, listed as P7,000 and is given chain discounts of 30% and 25%. Given List Price Trade Discount (Chain) Gross Invoice Price Downloaded by Sunflower (flauviablythe@gmail.com) Amount 7,000 30% 25% ? lOMoARcPSD|30612575 Sales, whether in cash or account, are sometimes returned to seller because of wrong color, wrong size, inferior quality, and many other reasons. 7,000 x 30% = 2,100 = 7,000 2,100 4,900 Sales Returns --- merchandise returned to the seller, which Implies a cancellation of sale 4,900 x 25% = 1,225 = Sales Allowances --- granted to customers if customers keep the merchandise although unsatisfied with what they bought Sales Returns and Allowances --- account name used to record these types of transactions 4,900 1,225 3,675 Sales In a sales transaction, the legal ownership of goods is transferred from the seller of the goods to the buyer of the merchandise. When you purchase a flat-screen television from an appliance center. The appliance center first had he ownership of the television when hey bought it from the supplier. The appliance center then sells you the television and transfer the ownership o you in the sales transaction. Revenue is earned each time sale is made. Sales can be accepted in cash or on account. Credit Term --- when goods are sold on account, the terms of payment must be specified on the invoice (sales invoice) Terms of Payment --- conditions of payment agreed between a a buyer and a seller for goods sold or services rendered --- examples: 2/10, n/30 2/15, 5/10, n/60 5/10, n/EOM 1. The following transactions were dealt by Lisa Merchandising: a) April 1, sold merchandise to Jennie Company with a price of P12,000, cash on delivery. b) April 2, sold merchandise to Rose Company with a price of P8,000, terms 2/10, n/30 c) April 5, Jennie returned P3,000 worth of defective merchandise. Cash refund was granted. d) April 11, Rose Company paid their account balance. 2020 01 Cash April 12,000 Sales Accounts 02 Receivable – Rose Company Sales 12,000 8,000 8,000 05 Sales Returns and Allowances Cash 3,000 11 Cash Sales Discount Accounts Receivable Kim Company 7,840 160 Downloaded by Sunflower (flauviablythe@gmail.com) 3,000 8,000 lOMoARcPSD|30612575 Rose Company Given Item Price Terms of Payment Amount 8,000 2/10 n/30 8,000 x 2% = 160 = 8,000 160 7,840 Purchases The cash collected will then be used to purchase goods that will then be used to purchase goods that will be sold by the firm. Merchandising entities need to purchase inventory in order to be able to sell and gain profit. the account contains deductions from purchases for items returned to suppliers, as well as deductions allowed by suppliers for goods that are not returned. 1. The following transactions were dealt by Lisa Merchandising: a) May 1, purchased merchandise from M Company amounting to P15,000, cash on delivery. b) May 2, purchased merchandise from Kim Company amounting to P6,000, terms 5/10, n/EOM c) May 7, Lisa returned P3,000 worth of merchandise to M Company, cash refund was granted. d) May 10, Lisa Company paid their account balance to Kim Company. 2020 01 Purchases May Cash 15,000 15,000 We can say that Purchases are also sales transactions. However, the viewpoint here is that the company that accounts for the transaction will be the buyer of merchandise. 02 Purchases Accounts Payable - Kim Company 6,000 Periodic Inventory System - under this system, no detailed record of inventory is being maintained during the year - an actual physical count of the goods remaining on hand is required at the end of each period - form of inventory valuation where the inventory account is updated at the end of an accounting period rather than after every sale and purchase - the method allows a business to track its beginning inventory and ending inventory within an accounting period. 07 Cash 3,000 6,000 Purchase Returns and Allowances 10 Accounts Payable – Kim Company Cash Purchase Discount Purchase Returns and Allowances - an account that is paired with and offsets the purchases account in a periodic inventory system Downloaded by Sunflower (flauviablythe@gmail.com) 3,000 6,000 5,700 300 lOMoARcPSD|30612575 Lisa Company Merchandise Transportation Given Item Price Terms of Payment Freight Terms Amount 6,000 5/10 n/EOM 6,000 x 5% = 300 = 6,000 300 5,700 Sales and Purchases 1. Gabb Company has gross sales of P400,000, sales discount of P10,000, and sales returns and allowances of P12,000. Also, Gabb has purchased P200,000 worth of inventory, purchase discount of P8,000 and purchase returns and allowances of P5,000. Compute for net sales and net purchases. Net Sales: Gross Sales Less: Sales Discount Sales Returns and Allowances Net Sales ₱ 400,000 (10,000) (12,000) ₱ 378,000 Net Purchases: Gross Purchases Less: Purchase Discount Purchase Returns and Allowances Net Purchases ₱ 200,000 (8,000) (5,000) ₱ 187,000 Free on Board Shipping Point --- title of the goods (ownership) passes to the buyer as soon as the shipment leaves the seller’s warehouse (or shipping dock) --- the seller should record the sale when the goods leave warehouse VS Free on Board Destination Point --- the buyer owns the title of the goods (ownership) once it arrives at the buyer’s dock --- the ownership title rests with the seller during the transit Who is the owner by December 31? Buyer 1. Goods shipped FOB Shipping Point on December 28, received by the buyer on December 30. 2. Goods shipped FOB Shipping Point on December 28, received by the buyer on January 3. 3. Goods shipped FOB Destination on December 28, received by the buyer on December 30. 4. Goods shipped FOB Destination Point on December 28, received by the buyer on January 3. Freight Prepaid --- fare paid in advance, which means that the seller will pay the fare --- carriers collect the freight charges before performing the contract of carriage, usually from the shipper Downloaded by Sunflower (flauviablythe@gmail.com) VS Seller ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ Freight Collect --- the consignee or receiver is responsible for the freight charges --- carriers collect the freight charges after performing the contract of carriage, usually from the shipper lOMoARcPSD|30612575 Freight-In --- buyer pays for the freight charges --- it is an adjunct account to purchases and thus added as cost of inventory in bringing it to its present location and condition VS Freight-Out --- seller pays for the freight charges --- recorded by the seller as an operating expense, under the selling expense line item What will be the entry for the following? 1. ABC Company purchased merchandise worth P15,000 with terms 5/10, n/30. Freight charges paid by ABC amounts to P3,000. Purchases Freight-In Cash Accounts Payable 15,000 3,000 3,000 15,000 2. DEF Company sold merchandise priced at P8,000 with terms 2/10, n/30. Freight charges paid by DEF amounts to P2,000 and will not be reimbursed by their buyer. Accounts Receivable Freight-out/Delivery Expense Sales Cash Income Statement Adjusting Entries To close beginning inventory… Profit or Loss Summary Merchandise Inventory (Beginning) xxx To record ending inventory… Merchandise Inventory (Ending) Profit or Loss Summary xxx xxx Net Sales Less: Cost of Goods Sold Gross Profit Add: Other Income Total Revenue Less: Operating Expenses Net Income ₱ Gross Sales Less: Sales Discount Sales Returns and Allowances Net Sales ₱ xxx (xxx) (xxx) ₱ xxx Beginning Inventory Add: Net Purchases Cost of Goods Available for Sale Less: Ending Inventory Cost of Goods Sold ₱ xxx xxx Gross Purchases Add: Freight-In Total Purchases Less: Purchase Discount Purchase Returns and Allowances Net Purchases ₱ xxx xxx xxx (xxx) (xxx) ₱ xxx 8,000 2,000 8,000 2,000 xxx Downloaded by Sunflower (flauviablythe@gmail.com) ₱ xxx (xxx) xxx xxx xxx (xxx) xxx xxx ₱ (xxx) xxx lOMoARcPSD|30612575 Two Methods of Presenting the Income Statement Function of Expense Nature of Expense VS Method Method --- classifies expenses --- expenses are according to their aggregated function as cost of according to their goods sold nature and not by function Function of Expense Method Prepare Excellent Retail Company’s Income Statement for the month of April under: a) Function of Expense Method b) Nature of Expense Method c) Functional Multi-Step Presentation Note 2 – Net Purchases Gross Purchases Add: Freight-In Total Purchases Less: Purchase Discount Purchase Returns and Allowances Net Purchases Sales and Other Income Gross Sales Sales Returns and Allowances Sales Discount Other Income Purchase and Freight Gross Purchases Freight-In Purchase Returns and Allowances Purchase Discount Operating Expenses Salaries Expense Utilities Expense Rent Expense Depreciation Expense Inventory Beginning Inventory Ending Inventory 900,000 15,000 10,000 45,000 300,000 80,000 20,000 10,000 70,000 60,000 50,000 40,000 120,000 150,000 Note 1 – Net Sales Gross Sales Less: Sales Discount Sales Returns and Allowances Net Sales ₱ 900,000 (10,000) (15,000) (25,000) ₱ 875,000 ₱ 300,000 80,000 380,000 (10,000) (20,000) Note 3 – Cost of Goods Sold Beginning Inventory Add: Net Purchases Cost of Goods Available for Sale Less: Ending Inventory Cost of Goods Sold (30,000) ₱ 350,000 ₱ 120,000 350,000 470,000 (150,000) ₱ 320,000 Note 4 – Operating Expenses Salaries Expense Utilities Expense Rent Expense Depreciation Expense Total Operating Expenses ₱ 70,000 60,000 50,000 40,000 ₱ 220,000 EXCELLENT RETAIL COMPANY Income Statement For the Month Ended April 30, 2020 Net Sales (Note 1) ₱ Less: Cost of Goods Sold (Note 3) Gross Profit Add: Other Income Total Revenue Less: Operating Expenses (Note 4) Net Income ₱ Downloaded by Sunflower (flauviablythe@gmail.com) 875,000 (320,000) 555,000 45,000 600,000 (220,000) 380,000 lOMoARcPSD|30612575 Nature of Expense Method Note 1 – Net Sales Gross Sales Less: Sales Discount Sales Returns and Allowances Net Sales Note 2 – Net Purchases Gross Purchases Add: Freight-In Total Purchases Less: Purchase Discount Purchase Returns and Allowances Net Purchases ₱ 900,000 (10,000) (15,000) (25,000) ₱ 875,000 ₱ 300,000 80,000 380,000 (10,000) (20,000) (30,000) ₱ 350,000 EXCELLENT RETAIL COMPANY Income Statement For the Month Ended April 30, 2020 REVENUES Net Sales (Note 1) Other Income Total Revenue DEDUCTION AND EXPENSES Increase in Merchandise Inventory Net Purchases (Note 2) Salaries Expense Utilities Expense Rent Expense Depreciation Expense Total Deductions and Expenses NET INCOME ₱ 875,000 45,000 920,000 - ₱ 30,000 350,000 70,000 60,000 50,000 40,000 540,000 380,000 Downloaded by Sunflower (flauviablythe@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|30612575 Functional Multi-Step Presentation EXCELLENT RETAIL COMPANY Income Statement For the Month Ended April 30, 2020 Gross Sales Less: Sales Returns and Allowances Sale Discount Net Sales Beginning Inventory Gross Purchases Add: Freight-In Total Purchases Less: Purchase Returns and Allowances Purchase Discount Net Purchases Cost of Goods Available for Sale Less: Ending Inventory Cost of Goods Sold Gross Profit Add: Other Income Total Revenue Less: Operating Expenses Salaries Expense Utilities Expense Rent Expense Depreciation Expense Net Income ₱ ₱ 900,000 15,000 10,000 - 25,000 875,000 - 320,000 555,000 45,0000 600,000 - 220,000 380,000 120,000 ₱ ₱ 300,000 80,000 380,000 20,000 10,000 - 30,000 - 350,000 470,000 150,000 70,000 60,000 50,000 40,000 ₱ Downloaded by Sunflower (flauviablythe@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|30612575 Closing Entries Dec 31 Sales Purchase Returns and Allowances Interest Revenue Profit or Loss Summary 31 Profit or Loss Summary Sales Returns and Allowances Purchases Freight-In Sales Salaries Expense Store Supplies Expense Advertising Expense xxx xxx Office Supplies Expense Depreciation Expense – Equipment Rent Expense Auditing Expense Miscellaneous Expense Insurance Expense Interest Expense xxx xxx xxx xxx xxx xxx xxx xxx xxx 31 Profit or Loss Summary Schiffman, Capital Downloaded by Sunflower (flauviablythe@gmail.com) xxx xxx xxx xxx xxx xxx xxx xxx xxx