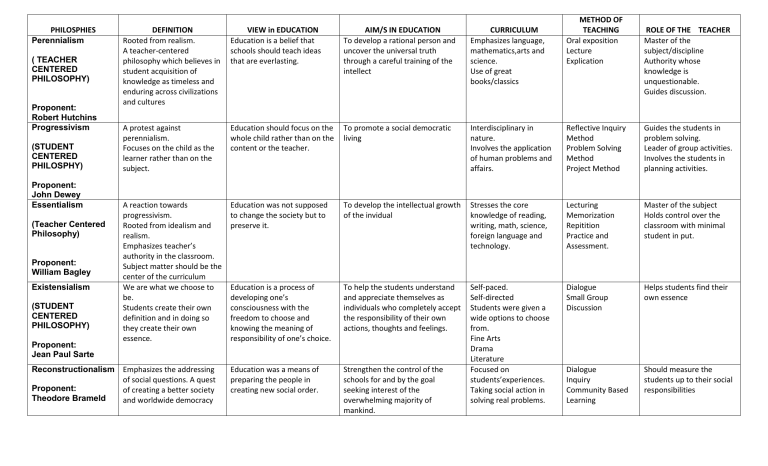
PHILOSPHIES Perennialism ( TEACHER CENTERED PHILOSOPHY) Proponent: Robert Hutchins Progressivism (STUDENT CENTERED PHILOSPHY) Proponent: John Dewey Essentialism (Teacher Centered Philosophy) Proponent: William Bagley Existensialism (STUDENT CENTERED PHILOSOPHY) Proponent: Jean Paul Sarte METHOD OF TEACHING Oral exposition Lecture Explication DEFINITION Rooted from realism. A teacher-centered philosophy which believes in student acquisition of knowledge as timeless and enduring across civilizations and cultures VIEW in EDUCATION Education is a belief that schools should teach ideas that are everlasting. AIM/S IN EDUCATION To develop a rational person and uncover the universal truth through a careful training of the intellect CURRICULUM Emphasizes language, mathematics,arts and science. Use of great books/classics A protest against perennialism. Focuses on the child as the learner rather than on the subject. Education should focus on the whole child rather than on the content or the teacher. To promote a social democratic living Interdisciplinary in nature. Involves the application of human problems and affairs. Reflective Inquiry Method Problem Solving Method Project Method Guides the students in problem solving. Leader of group activities. Involves the students in planning activities. A reaction towards progressivism. Rooted from idealism and realism. Emphasizes teacher’s authority in the classroom. Subject matter should be the center of the curriculum We are what we choose to be. Students create their own definition and in doing so they create their own essence. Education was not supposed to change the society but to preserve it. To develop the intellectual growth of the invidual Stresses the core knowledge of reading, writing, math, science, foreign language and technology. Lecturing Memorization Repitition Practice and Assessment. Master of the subject Holds control over the classroom with minimal student in put. Education is a process of developing one’s consciousness with the freedom to choose and knowing the meaning of responsibility of one’s choice. To help the students understand and appreciate themselves as individuals who completely accept the responsibility of their own actions, thoughts and feelings. Dialogue Small Group Discussion Helps students find their own essence Education was a means of preparing the people in creating new social order. Strengthen the control of the schools for and by the goal seeking interest of the overwhelming majority of mankind. Self-paced. Self-directed Students were given a wide options to choose from. Fine Arts Drama Literature Focused on students’experiences. Taking social action in solving real problems. Dialogue Inquiry Community Based Learning Should measure the students up to their social responsibilities Reconstructionalism Emphasizes the addressing of social questions. A quest Proponent: of creating a better society Theodore Brameld and worldwide democracy ROLE OF THE TEACHER Master of the subject/discipline Authority whose knowledge is unquestionable. Guides discussion. PHILOSPHIES REALISM Proponent: John Locke Naturalism (Child Centered Philosophy) VIEW OF EDUCATION Education should be concerned with the actualization of life. AIM/S IN EDUCATION A happy and integrated life. CURRICULUM Science and vocational subjects are in predominant position followed by arts, literature and language. Gives the central position to the child. Gives maximum freedom to children. Education is the natural development of the student’s power and abilities. Self Expression Self Preservation Redirection of Human Instincts Struggle for Existence Education according to Nature Perfect Development of Individuality Literary and aesthethic culture. Study of past experiences. Inductive Method Observer Stage Setter Emphasizes mental or spiritual aspect of the universe. Education is something which leads one to the highest moral conduct and deepest spiritual insight. Exaltation in Human Personality Universal Education Enrichment of cultural environment Cultivation of moral values Religious studies Spiritual Studies Literature History Fine Arts Questioning Discussion Imitation Lecture Method Role Model Midway between idealism and naturalism. Emphasizes the practicality of life. Education is based upon a close relationship between theory and practice of education. Harmonious development of individual Continuous reconstruction of experiences. Social efficiency. Personal and social adjustment should consist of such Child activities varieties of learning Integration and experiences which experimentation promote original thinking and freedom to develop social and purposeful attitudes. Pragmatic curriculum deals with the integration of subjects and activities. Proponent: Jean-Jacques Rousseau Idealism Proponent: Friedrich Froebel Pragmatism Proponent: John Dewey METHOD OF TEACHING Should change according to the requirement of the child. DEFINITION Prepares the children for the concrete duties of the actual life. ROLE OF THE TEACHER Facilitator/Guide