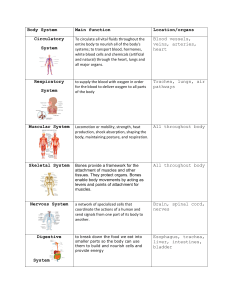
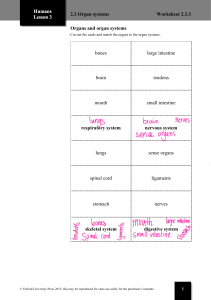
Summary of lesson: Types of Cells and Body Systems - Different levels of organization of the human body: Cells * Building blocks of life. * Basic unit of all living things. Ex: - Red blood cells → carry oxygen to organs and tissues. - Nerve cells → responsible for picking and sending information. Tissue * Group of cells share same function. Ex: - Epithelial tissue → barrier between the inside and outside our body. (heart – liver) - connective tissue → maintains the form of body organs and provides internal support. (blood) - muscle tissue → provides movement. - Nerve tissue → transmits electrical impulses. Organs * made of different types of tissues and cells that work together. Organ System * 2 or more organs working together. Ex: - Digestive System - Respiratory System - Circulatory System - Muscular System - Skeletal System - Urinary System - Nervous System - Reproductive System Organism * All organs work together to form an organism. Ex: - Multicellular organisms Organ System Digestive System Circulatory System Skeletal System Function Convert food into energy and basic nutrients. Transport material through the body. Transport oxygen and nutrients to body cells and carries away wastes. Main Organs Stomach, intestines, mouth, esophagus Heart, vessels, blood Provides our body with structure and protects our main organs. Bones Respiratory System Responsible for the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the blood and the external environment. Lungs Nervous System Controls the body vital functions like sleeping and breathing. Brain, spinal cord, nerves Muscular System Responsible for the movement of the body. Urinary System Filters the blood from wastes and excess water. Muscles Bladder, kidneys