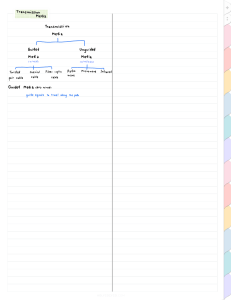
Class 1st Octet Class A Number of Hosts Subnet Mask Reserved Address 1 - 126 # of bits in network 8 16.7 million 255.0.0.0 10.0.0.0 - 10.255.255.255 Class B 128 - 191 16 65 thousand 255.255.0.0 172.16.0.0 – 172.31.255.255 Class C 192 - 223 24 254 255.255.255.0 192.168.0.0 – 192.168.255.255 Class D 224 - 239 28 Class E 240-255 Public IPS How to calculate Network ID? Compare the IP and Subnet Mask one octet at a time, wherever there is a 255 bring down the IP address, and if there is a 0 in the subnet mask bring that down into the Network ID, or NID. For Example: IP- 192.168.30.10 SM- 255.255.255.0 NID- 192.168.30.0 Example 2: IP- 192.168.40.32 SM- 255.255.255.0 NID- 192.168.40.0 Example 3: IP- 120.10.40.60 SM- 255.0.0.0 NID- 120.0.0.0 Two computers need to have the same NID’s in order to communicate on the same network. Example 4: Can these two computers communicate on the same network? Computer 1: IP- 180.16.32.100 Computer 2: IP- 180.17.19.100 SM- 255.255.0.0 SM- 255.255.0.0 NID- 180.16.0.0 NID- 180.17.0.0 Answer= No, these two computers cannot communicate. Class First Address Last Address Class A 10.0.0.0 10.255.255.255 Class B 172.16.0.0 172.31.255.255 Class C 192.168.0.0 192.168.255.255 Private IP addresses: CIDR: Classless Inter Domain Router. Notated by /8 /16 /24 representing the subnet mask for Class A, B and C IP addresses respectively. For example a Class C subnet mask of 255.255.255.0 will have 8 bits in each octet that has a 255 in it, so 8+8+8 = 24. A Class B subnet mask of 255.255.0.0 will have 8+8 = 16. Unicast: One to one communication. Public IP: Routable IP Addresses assigned by an ISP. Private IP: Non-routable IP Addresses. APIPA: Automatic private IP address self-assigned by a host when DHCP is not available. o IP address range: 169.254.0.0 – 169.254.255.255 *remember the 169.254 octets for APIPA. Example, if you ever see an IP address that says 169.254.x.x it means that is an APIPA address, meaning the computer tried to get an IP address from the DHCP server but failed to get one, meaning it won’t have internet or even lan access. *Possible problems could be: Switch is bad, DHCP server is down, NIC card is bad, maybe the cable is bad, etc. Multicast: One to many communication IP address range: 224.0.0.0 – 239.255.255.255 Broadcast (Layer 3): One to everyone communication IP Address: 192.168.30.255/24. Always the last IP in the range. Loopback (localhost): IP address that’s already assigned to your machine that represents you. used for a host to communicate with itself to test connectivity. IP address range 127.0.0.0 – 127.255.255.255 ARP (Address Resolution Protocol): Translates IP address to Mac address. Examples: 192.168.30.0/24 - Network ID (NID) 192.168.30.1-254 – Assignable IP (AIP) 192.168.30.255 – Broadcast IP (BIP), not assignable because it’s used by the computer to communicate with every computer on the network. 172.30.6.4/16 172.30.0.0 NID 172.30.255.255 BIP IPV6: Eight blocks, 16 bits each giving you 128 bits total, written in Hex which is 0-9 and A-F. Prefix: First 64 bits of an IPv6 address, assigned to an organization. The first 48 bits are known as a Global Routing Prefix, the last 16 bits are the Subnet-ID. Interface-ID: Last 64 bits of an IPv6 address and is used to identify a unique interface on a host. Global Unicast Addresses: Publicly routable addresses used to communicate outside of a local network. 2000::/3 represents the subnet; this was the originally defined address space. Unique Local Addresses: FC00::/7 non-publicly routable addresses used to communicate within a local network. Link Local addresses: FE80::/10 replacement for Automatic Private IP Addresses (APIPA), every IPv6 host will have a link local address. Multicast IPv6: FF00::/8 One to many, packet is sent to many interfaces. Loopback IPv6: ::1 Used for testing. Anycast: One to nearest, packet is sent to the nearest interface in terms of routing distance. Replaces broadcast from IPv4. Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP): is a client/server protocol that automatically provides an IP host with it’s IP address and other related configuration information such as the subnet mask and default gateway. Common DHCP Configurations: o Scope: is the range of addresses the server can assign o Exclusion range: The range of addresses the server can NOT assign. o Lease Time: defines how long an IP address is “owned” by a host before it can be assigned to another host. Available leases identify how many addresses are still available from the scope. o Reservations: allow you to bind a MAC address to a specific IP address. Allows DHCP to consistently assign the same IP address to a device without having to configure a static IP address. Domain Name Service (DNS): Provides name to IP address resolution for host. DNS servers can be in your LAN or out on the Internet. A host is normally assigned a DNS server via DHCP, but it can also be assigned manually. DNS Name Types o Host names: identify a specific device in a network. o Domain names identify a specific network o Domain name = companyx.lan o Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN): identify a specific device in a specific network. Domain Keys Identified Mail (DKIM): provides authentication of mail being sent and received to prevent spam. Canonical Name (CNAME): resolves an alias to a domain name. Mail Exchanger (MX): Resolves a name to a mail exchanger (email server) Virtual Private Network (VPN): Creates a secure tunnel to a private network over the internet. Required to access resources in a LAN over the internet. Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN): any network that is partitioned and isolated in a computer network at the data link layer or by switches. DSL: DSL is a broadband service that operates over the public switched telephone network (PSTN). Requirements: DSL modem, DSL Filter/Splitter must be used to prevent noise when connecting a telephone to a DSL line. Not widely used anymore but may be used in rural areas. Cable: Uses the DOCSIS (Data Over Cable Service Interface Specification) standard to deliver Internet over coax. Described as a FTTN (Fiber to the Node) service. Fiber: Fiber services like FIOS are FTTP (Fiber to the Premise) Requirements: ONT (Optical Network Transceiver) converts the fiber cable from the provider to twisted pair to connect to a router. Satellite: Widely available and might be the only option for those in rural areas. Requirements: Satellite dish connected to aa satellite receiver via coax, and a clear view into space. Satellite suffers from high latency which makes it unusable for the following services. VOIP, video streaming, online gaming. Cellular: cellular Internet has gained usage as coverage has grown quickly. WISP (Wireless Internet Service Provider): Provides internet to smaller municipalities where cable or fiber services aren’t available. Providers use wireless access points deployed and at customer sites. Requires user be within the limited coverage area. MAN (Metropolitan Area Network): Spread across a single city. Connections between the sites are often privately owned and managed by the organizations that use them. CAN (Campus Area Network) spread across a limited geographical distance like a college/corporate/military campus. It is privately owned and managed. PAN (Personal Area Network): small networks usually made up of two devices. These devices can be connected over wired connections (Ethernet or USB) or wireless connections (Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Infrared). WAN (Wide Area Network): When an organization needs to connect their office on one side of the world to the other, they connect through a WAN. The internet is a public WAN that anyone can get access to. Site-to-Site connections are used by large organizations to connect their different locations over private WAN links. SAN (Storage Area Network): Specifically built to store data. The network consists of high-speed fiber links and large storage servers. Crimper: Used to terminate RJ45 and RJ11 heads to twisted-pair cables. Cable Stripper: used to strip the jacket of a cable. Wireless Analyzer: Application for your desktop or mobile phone that can analyze the type and strengths of wireless networks. Useful to understand where to place access points. Toner Probe: Used to identify the other end of a twisted-pair cable. Tone generator sends a signal through the known end of the cable. The probe is used to locate the other end of the cable. Punch Down Tool: used to terminate twisted-pair to a 110 or 66 block. Cable Tester: a simple tool that is used to test twisted pair terminations. One end of the cable is plugged into the main unit and the other end to the remote. Lights should go off in sequence on both ends. Loopback Plug: used to test if a network port can communicate to itself. These are available for copper and fiber interfaces. Network Cables Transmission Speeds o Copper cables: achieve speeds of up to 40 Gigabits o Fiber cables: achieve speeds above 100 Gigabits Transmission Distance o Copper Cables: can reach distances of 1,100 meters (3,609 feet) o Fiber Cables: can reach distances of 40 kilometers (25 miles) Attenuation: is the loss of signal strength in networking cables or connections. Usually occurs due to using a cable that’s too long, usually copper cables. Fiber doesn’t suffer from it as much. Noise Immunity o EMI (Electro Magnetic Interference) is a condition when signals from a device or cable leak out and disrupt signals of another device or cable. o Copper cables are highly susceptible to interference. Use shielded cables to protect against EMI. o Fiber cables are NOT susceptible to EMI since it is not copper. Twisted Pair cables: Consist of eight wires that are twisted into four pairs. This is the most used networking cable in homes and offices. o Twisted Pair Types STP (Shielded Twisted Pair): Has shielding to protect against EMI. Direct-burial cable: a special type of electrical wiring or cable that is designed to be buried in a trench underground. UTP (Unshielded Twisted Pair): Does NOT have shielding to protect against EMI. Twisted Pair Categories Category Cat 5 Cat 5e Speed 100 Mbps 1,000 Mbps / 1 Gbps Distance 100 meters 100 meters Note Used in older networks More twist per foot allows it handle disturbances to achieve faster speeds. Cat 6 10,000 Mbps / 10 Gbps 1,000 Mbps / 1 Gbps 55 meters 100 meters Cat 6a 10,000 Mbps / 10Gbps 100 meters Includes a piece of plastic to separate the 4 wire pairs which minimizes crosstalk Thicker wires to carry a more powerful signal for longer distance. Coaxial Cable: is a round cable often used for cable and satellite television connections. It’s thick outer jacket makes it ideal for outdoor use. o RG-6 is the most common type of coax cable. o Advantages: Shielding protects against EMI Long transmission distance (1100 meters) More affordable than fiber optic cables o Disadvantages: More expensive than twisted pair cable Copper core can snap if mishandled. BNC Connector: Secure locking connector commonly used in the old bus and ring networks. F Connector: Twisting hand screw commonly found on cable modems Fiber Optic Cable: o Advantages: Not susceptible to EMI Longest transmission distance up to 40km Fastest speeds up to 255 Tbps o Disadvantages: Most expensive cable Most difficult to install. Difficult to troubleshoot issues. Expensive tools needed for installation and troubleshooting. Can’t easily repair cables in the field. o Fiber Connectors: (Just need to know that ST, LT SC and Dual LC are fiber connections) ST Connector: Straight Tip Connector BNC style connector from the late 1980s and 1990s Used in SMF (Single Mode Fiber) installations. LC Connector: LC (Little Connector) Snaps-in style connector Small form-factor connector Used in SMF and MMF (Multi Mode Fiber) installations. SC Connector: Standard Connector/Subscriber Connector/Square Connector Dual LC Connector: Dual LC, snaps-in style connector. Small Form Factor connector, used in SMF and MMF installations. Network Cable Specs SATA Versions SATA 1: 1.5 Gbps / 150 MB/s SATA 2: 3 Gbps / 300 MB/s SATA 3: 6 Gbps / 600 MB/s