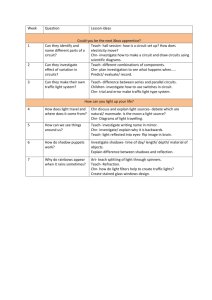
DMARDS Patients with RA – understand that the expectation is for these meds to slow joint degeneration & progression. Methotrexate: ● ● ● ● ● Therapeutic Effect/Uses; ○ immunomodulator med to slow joint degeneration and progression of RA Major Side Effects & Important Teaching points – ○ Drink 2-3 L of water on the day(s) you take the medication (worry about renal toxicity) ○ Hepatic fibrosis and toxicity ○ Bone marrow suppression ○ Ulcerative stomatitis/ other GI ulcerations ○ Fetal death/congenital abnormalities ○ *infections ○ Bruising- thrombocytopenia Contraindicated- liver failure, alcohol use disorder, blood dyscrasias Interactions- Salicylates, NSAIDS, penicillin, etc can cause toxicity. folic acid may reduce effectiveness, no alcohol therapeutic effect- 2-3 weeks to get started; 3-6 for full effect Hydroxychloroquine – ● ● Therapeutic Effect/Uses; ○ antimalarial agent ○ RA, lupus, malaria ○ reduces inflammation Major Side Effects & Important teaching points – ○ Have eyes evaluated every 6-12 months, wear sunglasses, avoid sun. could cause retinal damage (blindness) ○ Blurred vision Glucocorticoids Prednisone – ● ● ● Therapeutic Effect/Uses; ○ provide relief of inflammation and pain. can also delay disease progression ○ anybody with acute inflammatory response is put on prednisone ○ short term therapy until DMARDS take effect ○ Prevention of organ rejection (kidney, liver, heart) ○ Treats UC, IBS, crohns Major Side Effects & Important Teaching points. ○ Long term use- bone loss. monitor pt for compression fracture (take calcium/vit D) ○ hyperglycemia (counteracts effects of insulin and oral hypoglycemics) ○ risk for infection (fever/sore throat), osteoporosis, fluid retention, Gi discomfort, hypokalemia (don't take with diuretics/ digoxin), Adrenal suppression ○ Must taper med contraindicated- in systemic fungal infections and live virus vaccines NSAIDS ● These meds are mainly used for pain – do they slow disease progression? ○ Provide rapid, relief of inflammation and pain but do not slow disease progression To ease the potential effect on the GI system – what is an important tip for patient using these medications? ○ Take meds with food Aspirin – ● Therapeutic Effect/Uses; ○ salicylate ○ pain, inflammation, fever, do NOT slow disease progression ● Major Side Effects & Important Teaching points. Ex. ○ ASA is contraindicated in patients with peptic ulcer disease or bleeding disorders. ○ SE- salicylism (tinnitus, vomiting/diarrhea, resp. alk.) Ibuprofen – ● Therapeutic Effect/Uses; ○ Mild to mod pain, fever, inflammation. inhibits prostaglandin synthesis ● Major Side Effects & Important Teaching points ○ GI upset/bleed, renal toxicity, rash, headache ○ Contra- PUD/ bleeding disorders ○ avoid alc ○ Take med with food Naproxen ● Therapeutic Effect/Uses; ○ mild to mod pain for those with RA, OP, gout ● Major Side Effects & Important Teaching points ○ take with food and water. monitor for GI bleed/ulcer ○ No antacid ● Gout Treatment - Agents for Hyperuricemia Important teaching on preventing gout? ● Avoid alcohol & foods high in purine, drink alot of water, exercise regularly, maintain healthy BMI Nursing Administration – Monitor uric acid levels, CBC, urinalysis, liver & kidney function tests Colchicine ● Therapeutic Effect/Uses; ○ Antigout agent. Once considered drug of choice for acute gout, now usually reserved for clients who do not response to or cannot tolerate safer agents ○ only effective for inflammation caused by acute gout attacks ○ PO ● Major Side Effects & Important Teaching points ○ SE- mild GI distress- diarrhea (possible toxicity), thrombocytopenia, suppressed bone marrow, rhabdomyolysis ○ no grapefruit ○ take with food ● Contraindicated- severe renal, c.ardiac, hepatic, gi dysfunction ● Caution- older adults and those with blood disorders Allopurinol ● Therapeutic Effect/Uses; ○ inhibits uric acid production (hyperuricemia) due to chronic gout or secondary to cancer chemo ● Major Side Effects & Important Teaching points, ○ Ex. Drink plenty of fluids ○ Avoid alcohol ○ Comps- hypersensitivity reaction (fever, rash, kidney, liver damage), hepatitis, n/v, increase in gout attacks (first months) ● Interactions- Slows metabolism of warfarin within liver- pt at rx for bleeding ● contra- idiopathic hemochromatosis ● Nursing admin ○ Well diluted. Admin over 30-60 min Probenecid ● Therapeutic Effect/Uses; ○ Inhibits uric acid reabsorption by renal tubules ● Major Side Effects & Important Teaching points ○ comps- renal calculi, renal injury, GI, hypersensitivity (rash) ○ Can precipitate acute gout (avoid after recent attack) ○ Salicylates (ASA) can lessen effectiveness Medications for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) Belimumab ● Therapeutic Effect/Uses; ○ Monoclonal antibody medication ○ disrupts activation of B-lymphocytes through interference with BLyS, a protein needed for B-cell activation and survival ● Major Side Effects & Important Teaching points ○ Worry about infection when you're suppressing immune system ○ SE- GI, headache, depressed, insomnia, infusion reaction ● Contra- severe renal ● Nursing Admin ○ give slowly over 1 hr at room temp ○ dont give if recent vaccination ○ refrigerate no longer than 8 hr after reconstitution with sterile water Medications for Fibromyalgia Duloxetine – ● Serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors. ● Therapeutic Effect/Uses; ○ restores balance of neurotransmitters, serotonin and norepinephrine ○ used for fibromyalgia, depression & diabetic peripheral neuropathy. ● Major Side Effects & Important Teaching points ○ SE- drowsiness, dizzy, blurred vision, GI, insomnia, HTN, tachy, withdrawal syndrome, sexual dysfunction ○ taper over 2 wks ● ○ swallow capsule whole Contra○ hepatic/renal, those taking MAOI within 14 days ○ Caution- cardiac probs, DM, GI disorders, glaucoma (GABA) Pregabalin ● Therapeutic Effect/Uses; ○ treats fibromyalgia, seizures, and neuropathic pain ● Major Side Effects & Important Teaching points – ○ SE- drowsiness, increased app, wt gain, constipation, angioedema, rhabdomyolysis, erectile dysfunction ○ notify provider if suicidal ideation present ○ taper atleast 1 wk ● Caution ○ Cardiac probs, angioedema, DM, renal, mental illness, thrombocytopenia Antimycobacterials Isoniazid INH ● Therapeutic Effect/Uses; ○ inhibits growth of mycobacteria, prevents synthesis of mycolic acid ○ for active & latent ● Major Side Effects & Important Teaching points. ○ I- inhibits B6 absorption- give daily supplements to avoid ○ N- neuropathy-report new numbness ○ Hepatotoxicity- check liver function. no alc ○ Hyperglycemia- monitor BG ○ give with meals / full glass of water ○ Birth control may not work as well ● How do you evaluate the liver of a patient when they are taking a medication that is hepatoxic – you evaluate: Rifampin ● Therapeutic Effect/Uses; ○ effective for gram + & gram - bacteria ○ given with one other antituberculosis med to help prevent ab resistance ● Major Side Effects & Important Teaching points. ○ Key – reddish discoloration of secretions. ○ hepatotoxicity- monitor liver, avoid alc ○ pseudomembranous colitis- DC med if fever, diarrhea, abd pain or bloody stools ○ 1-2 hrs after meals or with full glass of water ○ use non-hormonal conraception Antiprotozoals Metronidazole ● Therapeutic Effect/Uses; ○ treats protozoal infections (ex- trichomoniasis) ○ prophylaxis for pts who have undergone surgical procedures and are at high rx for infection ● ● ○ treats ab induced C-diff, gardnerella vaginalis ○ used with other meds to treat H pylori Major Side Effects & Important Teaching points. ○ take with meals, dark urine is a harmless SE ○ dry mouth/ metallic taste ○ neurotoxicity or pseudomembranous colitis- stop med ○ avoid alc (disulfiram- like reaction) ○ Inhibits warfarin, pheytoin, lithium- monitor PTT, INR, drug levels ○ Use condoms (decreases effectiveness) ○ dont have sex if being used to treat STD ○ Ataxia- stop med contra- first trimester of pregnancy, active CNS disorders & blood dyscrasias Antifungals Watch for renal injury in patients using antifungals – monitor creatinine & decreased urine output (oliguria) Amphotericin B ● Therapeutic Effect/Uses; ○ polyene ab for systemic mycosis (candidiasis, aspergillosis, cryptococcosis, mucormycosis) ● Major Side Effects & Important Teaching points ○ highly toxic- use for severe life-threatening fungal infections ○ dont admin if precipitation ○ SE- thrombophlebitis (rotate sites), nephrotoxicity (monitor I&O), elec imb (K), bone marrow suppression (know baseline CBC and HCT), FEVER ● NI- The terror – Highly toxic medication reserved for life-threatening fungal infections. Slow IV infuse slowly over 2 hr (infuse sodium chloride first) Ketoconazole ● Therapeutic Effect/Uses; ○ azole for treating both superficial & systemic mycosis ● Major Side Effects & Important Teaching points. ○ comps- hepatotoxicity gynecomastia, irregular menstrual flow ● Ex. This medication is also hepatotoxic – monitor liver, S&S of issues with liver. Nystatin ● Therapeutic Effect/Uses; ● Major Side Effects & Important Teaching points ○ Store medication at room temperature ○ Do not need to take on empty stomach, swallow for highest effectiveness ○ Take entire dose Overview Concepts What is the purpose of the culture and sensitivity ● ● ● Identification of causative agent and sensitivity to an antimicrobial Tells you what it is and what will kill it. Helps choose which antibiotic to use **used before antimicrobial treatment SATA: teaching a patient important points about a new antibiotic Rx. ● ● ● ● ● ● Finish medications to prevent super infections Accidental pregnancy- cillins and cycline (think Cs- child) No alcohol- hard on liver Move The Food- Macrolides, Tetracycline, Fluoroquinolones Avoid Fun in the Sun- fluoroquinolones, tetracyclines, sulfa drugs (trimethrorim-sulfa/bactrim) SuperToxic- mycins ○ kidneys, ears What are some of the key Points about Antibiotic Administration: ● ● ● ● perform hand hygiene before and after encourage prevention with up to date immunizations finish prescription to prevent resistance and recurrence of infection prevention control techniques- aseptic, standard and transmission-based, careful assignment of rooms Nephrotoxicity Key Labs: ● ● ● Creatinine >1.3 is bad BUN 6-20 Urine Output <30mL is bad Ototoxicity – signs & symptoms of ototoxicity – teaching patient ● ● ● ● Ringing of the ears- tinnitus Balance problems Headache Trouble hearing certain things Peak and Trough – why do we do this? ● ● ● A peak is the highest level of the medication in the blood,while a trough level indicates the lowest concentration too high- kidney injury too low- bacteria growth Antibiotics that are hard on the body – lead to toxicity: ● mycins (Vancomycin/Neomycin/Gentamicin) Antibiotic Resistance: HealthCare acquired resistance. Some examples: MRSA, VREF, VRSA The use of prophylactic antibiotics (p.358 ATI) prosthetic heart valves, recurring UTIs ● Infections for clients undergoing GI, cardiac, peripheral vascular, orthopedic, or gynecological surgeries ● ● ● STIs following sexual exposure use in pt with prosthetic heart valves prior to dental or other procedures (danger of bacterial endocarditis) recurring UTIs Vancomycin – glycopeptide (p. 323 in McCuistion) ● ● ● Uses: treats serious infections due to MRSA; Treats ab associated pseudomembranous colitis due to C-diff Side effects: ○ Red Man Syndrome (related to rapid infusion)- rash, itching, flushing, tachycardia, hypotension ○ ototoxicity (esp with loop diuretics/ aminoglycoside abs) Teach- dilute med and rotate injection sites Penicillins ● ● ● ● ● Narrow spectrum SE- **hypersensitivity, anaphylaxis (monitor for 30 min following admin), superinfection, tongue discoloration, stomatitis, C-diff, interactions- decrease aminoglycoside effectiveness; probenecid delays excretion of penicillin Types○ basic- anthrax, tetanus, diphtheria, endocarditis, respiratory infections, syphilis ○ broad-spectrum- respiratory, skin, intraabdominal, urinary tract, gynecological infections, otitis media, sinusitis ○ penicillinase-resistant- endocarditis, meningitis, bacteremia, skin and resp infections ○ extended-spectrum- respiratory, intraabdominal, and skin infections ○ Provide prophylaxis against bacterial endocarditis in at rx pt prior to dental and other procedures teach- penicillin V, and amoxicillin with meal, all others with water 1-2 hrs after meals. Oral contraception ineffective (use additional contraception) Cephalosporins ● ● ● ● ● ● Drug- cephalexin (broad spectrum) Treats- respiratory, urinary, skin, bone, joint, and genital infections Side effects○ anaphylaxis, superinfection ○ headache, dysgeusia, C-diff, increased bleeding, seizures, pseudomembranous colitis, phlebitis Interactions- Alcohol (disulfiram like reaction), uricosurics- decrease excretion, probenecid delays renal excretion, calcium and ceftriaxone with med can cause precipitation and comps Contraindicated- bleeding disorders or taking anticoagulants (monitor PT) Teach- take with food, often those allergic to penicillin are also allergic to these, store oral suspension in fridge Carbapenems ● ● ● Drug- imipenem-cilastatin, metropenem Treat- broad spectrum; Useful for serious infections (pneumonia, peritonitis, UTIs) ○ should be reserved for clients who can't be tx with more narrow-spectrum SE○ resistance may occur if used alone to treat pseudomonas aeruginosa infections (use combo) ○ allergy, cross-sensitivity to peni/cephalos, superinfections ○ monitor for colitis ○ Use cautiously in renal impairment ● interactions- can reduce blood levels of valproic acid causing breakthrough seizures Macrolides ● ● ● ● ex- erythromycin (broad spectrum), azithromycin Use- used for those who have penicillin allergy. mild to mod respiratory, sinuses, skin, soft tissue, GI tract infections, diphtheria, impetigo, STIs, legionnaires’ disease, pertussis, chlamydial, pneumonia, strep infections SE○ anaphylaxis, superinfections, tinnitus, ototoxicity, dysgeusia, tooth discoloration, stevens-johnson, dysrhythmias ○ Monitor for tinnitus ○ Monitor liver function with erythromycin ○ drug interactions■ increase levels of warfarin, theophylline, carbamazepine, dig, antihistamines ■ Erythromycin levels increase with fluconazole, ketoconazole, verapamil, diltiazem, and clarithromycin ■ azithromycin levels may be reduced by antacids Teach- dont take with food, decreases BC Tetracyclines ● Drug- Doxycycline, minocycline, demeclocycline ● use- broad spectrum. treats acne, anthrax, gingivitis, lyme disease, STIs, skin, chlamydia and respiratory (pneumonia) infections ● SE- photosensitivity, diplopia, dizziness, lightheadedness, discoloration of permanent teeth (pregnant women taking this med can stain the teeth of their children (1st set/not adult teeth). Will stain the adult teeth of children if given to them ages 4 months to 8 years), pancytopenia, ototoxicity ● Drug-food interactions○ milk (calcium and iron supplements) & antacids- ingest 1 hr after or 2 hr before admin ○ oral contraception ○ penicillins, aminoglycosides ○ minocycline & doxycycline- increase rx of dig toxicity ● Teach- 1 hr before or 2 hr after meals, don’t take before lying down (ulcers) Aminoglycosides ● Drugs- Gentamicin, tobramycin, neomycin ● Treats- serious respiratory, skin, urinary, bone/joint, intra abdominal infections, plague, bacteremia, septicemia, endocarditis, meningitis, hepatic encephalopathy, bowel prep ● SE- photosensitivity, anemia, seizures, ototoxicity, neuromuscular blockage (resp depression/weakness) ● drug interactions- penicillins decrease effectiveness, increased action of oral anticoagulants, ethacrynic acid with aminoglycosides may cause ototoxicity ● teach- increase fluids Fluoroquinolones ● Ex. Ciprofloxacin ● ● ● Treat- anthrax (prevention- clients who have inhaled anthrax spores), skin, soft-tissue, bone/joint, gynecologic, intraabdominal, urinary, and respiratory tract infections SE- photosensitivity, phototoxicity (severe sunburn), eye damage, visual disturbances, tendinitis, tendon rupture, c-diff Teach- dont take with food, avoid the sun (wear sunglasses, sun block, protective clothing in the sun) Overview Concepts Cancer patient treated with opioids for pain mgmt.. – will they need increasing doses of the medications and if so – why? Ondansetron – Uses, Side effects & teaching. When do you administer antiemetics to patients receiving chemotherapy – before/during or after treatment? ● ● use- helps decrease nausea and vomiting. take before beginning chemo can be used in combo with dexamethasone, granisetron, metoclopramide Immunosuppression for those receiving Chemotherapy – Important teaching of patient & family concerning this – no plants/fresh fruits, avoid those who are sick/limit healthcare workers entering room, limit invasive procedures. ● ● ● ● ● ● ● Restricting visitors (esp w/ infection) No plants No fresh fruits/veggies Avoid contaminating with one’s own bacterial flora (no rectal temp/ IM) Private room they should stay in Dedicated equipment in room Administer colony stimulating factors (filgrastim) to stimulate WBC production Missed doses of ART therapy can lead to medication resistance. Patients being treated with HAART may also have additional medications to treat the adverse effects of those medications and/or prophylactic treatment of secondary infections. Cancer Finasteride – Uses, side effects & teaching ● ● ● Antiandrogen Treat- blocks conversion of testosterone to dihydrotestosterone SE- decreased libido, erectile dysfunction, orthostatic hypotension, gynecomastia Tamoxifen – Uses, side effects & teaching – p. 349 (ATI) ● ● Hormonal agents: Estrogen receptor blockers Use- treat/prevent breast cancer ● ● ● ● ● Comps- Thromboembolic events, hypercalcemia (bone pain), n/v, hot flashes, endometrial cancer, vaginal discharge/bleeding (get yearly gyno exam and pap smear) Contra- warfarin, hx of blood clots or PE Interactions- can increase anticoagulation or warfarin, SSRI depressants (paroxetine) decrease effectiveness of tamoxifen NI- assess dysrhythmias, breath sounds, fluid status, weights weekly (report wt gain), CBC, calcium levels Teach- Increase calcium/ vit D, weight bearing exercises, monitor weigh, prevent pregnancy Cisplatin – Uses, side effects & teaching - p. 344 (ATI) ● ● ● ● ● ● ● Platinum compounds Use- bladder, testicular, ovarian cancers SE- BMS, highly emetogenic (within 1 hour after dosing and can persist several days), renal toxicity (increase fluids, give diuretic), tinnitus contra- severe myelo, kidney, hearing loss Interactions- aminoglycosides can increase rx of renal toxicity, furosemide can increase hearing loss NI- assess hearing prior to admin Teach- good oral hygiene, birth control during treatment Transplant Cyclosporine – Uses, side effects & teaching p. 384 ● ● ● ● Calcineurin inhibitors. Use- prevent organ rejection in various autoimmune conditions. maintenance therapy SE- elevated BUN, creat, HTN, hirsutism, tremor, acne, hyperglycemia, hyperuricemia, DM, seizures, hyperkalemia Teach- avoid grapefruit, give with orange juice/apple to improve taste Adherence to the medication regimen for transplant recipients is key, list some important considerations related to adherence p 391 (M) . Nurses play a key role in promoting adherence. ● ● ● post transplant regimen- life long drug regimen, exercise, and health promotion factors that effect adherence- episodes of rejection, comorbid illness, side effects of tx, health care costs NI- incorporating education, motivational strategies, coping strategies HIV/AIDS NRTIs: Zidovudine – Uses, side effects & teaching – p 387 (ATI) Ex.. Teach patient to monitor for bleeding, monitor liver enzymes ● ● ● ● Use- Inhibits DNA synthesis & viral replication. First-line; short term care SE- BMS, lactic acidosis (hyperventilation, nausea, abdominal pain; pregnancy increases rx), n/v/d, hepatomegaly (monitor liver enzymes) Interactions○ probenecid, valproic acid, methadone increase zido ○ ganciclovir further suppress BM ○ clarithromycin reduce zido ○ phenytoin alters levels Teach- monitor for bleed, baseline CBC and platelets, notify if pregnancy is suspected, can take without food NNRTIs: Delavardine – Uses, side effects & teaching – p. 388 (ATI) Ex. Stevens- Johnson syndrome. Don’t use antacids. This drug interacts with many medications. ● ● ● ● act directly on reverse transcription to stop rep. often used in combo SE- rash (can lead to stevens johnson syndrome), flu-like symptoms, dizzy, insomnia, neuropathy, liver failure Interactions- (many meds. Know antacids) ○ antacids- decrease absorption ○ increase effectiveness of benzos, antihistamines, CCB, warfarin, etc ○ decrease BC ○ increase in sildenafil (monitor hypotension and vision) ○ Rifampin & phenytoin decrease levels teach- take drug at night on empty stomach Acyclovir (antiviral) – Uses, side effects & teaching p. 385 (ATI) Ex. Caution nephrotoxicity – increase IV & oral fluids, infuse slowly/over 1 hour. ● ● ● ● ● ● Use- herpes simplex & varicella zoster viruses SE- phlebitis and inflammation at IV site (rotate), nephrotoxicity, mild discomfort with PO (headache, n/d) Contra- renal impairment, dehydration, on nephrotoxic meds Interactions- probenecid decreases elimination, zidovudine combo may cause drowsiness NI- slow infusion over 1 hr or longer, use condoms after fully healed, increase fluids during and 2 hrs after infusion Teach- not a cure, use glove when using topical, wash affected area with soap 3-4x a day and dry after, refrain from sexual activity HAART – Highly active antiretroviral therapy – is used as an aggressive treatment method using 3 or more different medications to reduce virus and increase CD4 count. Antiretrovirals: Protease inhibitors: Ritonavir – Uses, side effects & teaching, P 389 ATI – many side effects: hyperglycemia, hyperlipidemia, osteoporosis. Dietary recommendations. ● ● ● ● ● Use- HIV-1 & 2; alter and inactivate virus. usually used in combo with 1+ transcriptase inhibitors or PIs to increase effect SE- bone loss/OP, DM/hyperglycemia, hypersensitivity, n/v, elevated blood lipids, altered fat distribution, hemolytic anemia Contra- liver disease, DM, pancreatitis, hypercholesterolemia, AV block Interactions○ can cause multiple meds (quinidine) to raise to toxic levels ○ can increase sildenafil, tadalafil, vardenafil ○ decreases ethinyl estradiol in BC ○ grapefruit juice Teach- increase calcium/ vit D, monitor blood sugar/ s/s of DM, may need to change diet based on SE, take with food SATA Question – Teaching a patient about ART therapy related to effectiveness/expectations of the medication regimen – Viral load? CD4 count? Regimen? Reporting Side effects or new symptoms ● ● ● Viral load- decrease or become undetectable CD4 count- increase Regimen- The correct dose of the current drug at the correct time with at least 95% drug adherence ● SE- protective precautions as necessary to decrease infection. report unmanageable se such as nausea or diarrhea ○ Patients may confuse drug side effects with new onset of symptoms. careful follow up assessment is important Chapter 17 – Stimulants Amphetamine drug used as an anorexiant – possible side effects, teaching Methylphenidate - uses? Assessments (side effects) Interventions (teaching/administration ) ● ● use- ADHD, narcolepsy, increase attn span SE- Tachycardia, palpitations, hypertension, dysrhythmias, Restlessness, tremors, irritability, Dizziness, headache, blurred vision, Euphoria, confusion, Anorexia, dry mouth, diarrhea, constipation, weight loss, Seizures, Erectile dysfunction ● interactions- caffeine (and caffeine containing foods), oral anticoags/barbiturates/anticonvulsants/tca/maoi- all can have increased effects, decreased effects of antihtn, may alter insulin effects monitor BS ● Teach- no caffeine, take before meals, irregular heart beat, record height weight and growth of children ● use sugarless gum, avoid foods containing caffeine (chocolate) , do not abruptly stop Modafinil - uses? Assessments (side effects) Interventions (teaching/administration) ● ● ● Use- correct hypersensitivity caused by ADHD, increase attn span and control narcolepsy; increase wakefulness in pts with sleep disorders like narcolepsy SE- anorexia, dry mouth, n/v, dizziness,insomnia, restless, irritable, confusion, depressed, hyperhidrosis, blurred vision, headache, abd pain, constipation, weight loss NI○ monitor vitals and report irregularities ○ evaluate height weight and growth ○ observe withdrawal symptoms ○ monitor for : insomnia, restlessness, nervousness, tremor, irritability, elevated bp, and tachycardia Medications used to treat narcolepsy and ADHD, compare ADHD and narcolepsy (assessment & interventions) Analeptics – Theophylline - Uses, side effects ● ● use- relax bronchioles; stimulate respirations in newborns; airway obstruction and bronchospasm prophylaxis SE- palpitations, tachycardia, dysrhythmias, insomnia, restless, tremors, seizures Chapter 18 (M) Depressants Ch 15 & 16 ATI Benzodiazepines – alprazolam: uses, side effects; teaching ● ● ● use- anxiety and panic disorder SE- lethargy, drowsy, dizziness, headache, constipation, amnesia, memory impairment, fatigue, agitation,ataxia, increased appetite, blurred vision, decreased and increased libido, dry mouth nausea edema, weight gain or loss Teach- take med as prescribed and do not abruptly stop can cause withdrawal symptoms; possible dependance during/after treatment and notify hcp is suspected Restoril - uses? Assessments (side effects) Interventions (teaching/administration) ● ● ● Temazepam- benzo Treat- insomnia SE- anterograde amnesia/ sleep related behaviors (sleep driving/eating) ● Teach- take 15-20 min before bedtime. limit continuous use to 7-10 days Benzodiazepines - uses? Assessments (side effects) Interventions (teaching/administration) – what are the instructions related to discontinuing the use of this drug. ● uses: anxiety, panic disorder, seizure disorder, insomnia, muscle spasm, alcohol withdrawal, induction of anesthesia/preop sedation ● SE○ lightheadedness, drowsy, incoordination ○ insomnia, euphoria, excitation, anxiety, rage ○ N/V/anorexia ○ respiratory depression ,physical dependance ○ acute toxicity: give gastric lavage ● NI○ ensure proper route of administration ○ taper dose when discontinuing over several weeks ○ admin with meals and swallow tablets do not chew ○ insomnia- take 15-20 mins prior to bed ● Teach ○ avoid alcohol and cns depressants ○ teach nonpharmacologic strategies to facilitate sleep ○ when discontinuing taper for several weeks; if abruptly stopped can cause withdrawal symptoms Versed – hypnotic medication given the night prior to surgery for what purpose? Side effects, teaching? ● ● ● Midazolam- benzo use- rapid induction of anesthesia/preoperative sedation (sedated and relaxed but responsive to commands). minor sx or procedures like intubation and mechanical ventilation NI- can cause conscious sedation and should be avoided if cardiopulmonary disorder Chapter 19 – Antiseizure Drugs - Ch 13 ATI Phenytoin - uses? Assessments (side effects) Interventions (teaching/administration) Reddish-brown color to the patient’s urine – explain if this is normal/abnormal. therapeutic level 10-20mcg/ml ● ● ● Use○ SE○ ○ ○ ○ NI○ ● stabilize nerve cell membranes, suppress abnormal electrical impulses in cerebral cortex CNS: nystagmus, sedation, ataxia, double vision, cog impaired Gingival hyperplasia: softening or overgrowth of gum/bleeding rash, dysrhythmias, hypotension endocrine: Monitor serum drug levels of the antiseizure drug to determine the therapeutic range. 10-20; dosage is age-related ○ Warn female patients taking oral contraceptives and antiseizure drugs to use an additional contraceptive method. ○ dont drive ○ risk for falls ○ determine adequate renal function prior to admin teaching ○ shake suspension thoroughly before taking ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ may cause drowsiness- no hazardous activities may have temporary teratogenic effects- have female contact provider monitor serum levels because seizures may occur no alcohol or cns depressants, no herbs med alert bracelet, preventive dental checkups do not abruptly stop URINE HARMLESS PINKRED/REDDISH BROWN Phenobarbital – Uses, CNS effects, nursing actions, teaching/client education. theraputic range 20-40mcg/ml 15-40 in tb ● use ○ used in tonic-clonic, partial myoclonic and status epilepticus; decreasing seizure activity by enhancing gaba ● SE- CNS: drowsiness, sedation, depression; elderly- irritability and hyperactivity; kids: irritability and hyperactivity ● NI- warfarin dosage might need to be increased; never give with primidone; monitor INR, calcium, vit d ● Teach- take additional form of BC; high doses can lead to respiratory depression and coma ● client education ○ discontinuing should be gradual to reduce the risk of seizures ○ take with food ○ monitor therapeutic levels, taking antiepileptic do not cure seizures just control ○ keep seizure diary- to monitor effectiveness of therapy ○ avoid activities that require alertness- driving ○ traveling- carry extra ○ do not take if in childbearing age or avoid pregnancy Carbamazepine – Uses, nursing actions, patient teaching ● ● ● uses: administered for bipolar/trigeminal/glossopharyngeal neuralgias ○ tonic clonic,partial seizures ○ psych disorders NI○ low doses and gradually increase; take at bedtime ○ baseline CBC, monitor bleeding gums, sore throat, fever, pallor and weakness ○ do not give to immunosuppressed or bleeding disorders ○ monitor blood Na frequently; monitor edema, decreased output and htn ○ treat mild skin reactions: anti inflammatory ○ discontinue med if severe skin rash teaching ○ no grapefruit Patient with epilepsy – use of anticonvulsant medications, important teaching points for the patient on use of the medication. Obtaining drug levels to assess for toxicity. Chapter 20 (M) – Parkinsonism & Alzheimers Drugs - Ch 13 ATI Carbidopa-levodopa (Sinemet) - uses? Assessments (side effects) Interventions (teaching/administration) . For patients with Parkinsons ● use ○ ○ most effective PD treatment but the beneficial effects diminish by year 5 wearing off effect may occur at the end of dosing interval, meds= subtherapeutic ○ ● ● ● “on-off”phenomena can occur during dosing interval, lasting minutes to hours and becoming more intense over time side effects ○ N/V ○ Dyskinesias (head bobbing, tics, grimacing, tremors) ■ if occurs decrease dose and give amantadine ○ orthostatic hypotension ○ tachy, palpitations, irregular beats ○ psychosis: visual hallucinations, nightmares, paranoid ideation ○ discoloration of sweat and urine NORMAL teaching ○ take with food but not high protein foods ○ if eating protein eat small protein meals ○ do not eat pyridoxine foods (wheat germ, green veggies, bananas, whole grain cereals, liver legumes) ○ monitor Bp, increase intake of salt and water ○ postural hypotension (lightheaded, dizzy) avoid fast position changes administration ○ monitor ECG, vitals, caution in cardiovascular disorders ○ clozapine decreases psychotic effects ○ avoid with haloperidol, and MAOIs Compare the side effects/adverse effects of acetylcholinesterase inhibitors used to treat Alzheimer disease. Uses, patient teaching ● ● ● ● Reversible inhibitors- therapeutic effects last 2-4 hrs Donepezil SE- excessive muscarinic stimulation (increased GI motility/ secretions, diaphoresis, salivation, bradycardia, urinary urgency), cholinergic crisis (excessive muscarinic stim, resp depression) NI- admin atropine for SE Alzheimers disease medications – will they cure the disease? What can you tell the family/patient ● No cure; goal is to receive appropriate assistance for care needs Chapter 46 (M) – Pituitary, Thyroid, Parathyroid & Adrenal Disorders ATI Ch 40 Growth Hormone – Somatropin Uses, Side effects & adverse effects, Routes, Patient teaching ● ● ● ● use- Ant. Pit hormones/growth hormones used to treat growth deficiencies, turners, prader-willi syndrome, chronic renal insufficiency, cachexia, and short bowel syndrome ○ AIDS wasting syndrome, pediatric growth failure assoc, with chronic renal insuff, cachexia and short bowel syndrome Route: IM or SQ (preferred) SE○ hypercalciuria and renal calculi ○ hyperglycemia (polyphagia, polydipsia, polyuria), monitor BG ○ inactivation: antibodies binding to render inactive NI○ baseline height and weight and monitor growth patterns monthly ● ○ reconstitute do not shake, rotate injection sites abd/thigh (SQ) Teach○ monitor flank pain, fever, dysuria and report ○ monitor blood glucose and manifestations of hyperglycemia Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH) – Vasopressin, Desmopressin Uses, side effects & adverse effects, Routes, Patient teaching ● ● ● ● ● Use○ ○ ○ Route○ ○ SE○ ○ treat DI (desmopressin is drug of choice), vasopressin is used during cpr to decrease blood flow to periphery and increase flow to heart/brain desmopressin can be used to decrease production of urine at night, and promote clotting factors Desmopressin: oral, intranasal, SubQ, IV Vasopressin: SubQ, IM, IV water intoxication (retaining water) - sleepiness, pounding headache myocardial ischemia (vasopressin)- excessive vasoconstrict ■ angina pectoris, coronary insufficiency, and MI NI○ ○ ○ ○ Teach○ ○ monitor ECG and BP monitor I and O, specific gravity, labs, BP daily weight and hr Monitor headache, drowsiness, confusion intranasal: bedtime- I&O if for nocturia 2x daily reduce fluid intake to prevent retaining notify HCP is chest pain/tightness and diaphoresis Thyroid hormone – levothyroxine sodium Uses, side effects & adverse effects, Routes, Patient teaching ● Use (MCG dosage)○ thyroid hormone replacement for hypothyroidism, emergency treatment of myxedema coma(IV), maintenance of thyroid levels after surgery/radiation ● NI○ baseline vitals weight and height before admin ○ monitor angina cp palpitation and dysrhythmias, check apical pulse ○ start low and go slow ○ monitor t4 and tsh ● SE○ overmedication ■ can cause toxicosis: anx, tachy, cp, nervous, tremors, palp, abd cramp, heat intol, fever, disphoresis, weight loss ○ chronic overtreatment ■ can cause atrial fib and increased risk of fractures ● Teach○ take med daily 30-60 minutes before breakfast (USUALLY 6AM) ○ lifelong replacement is important after improvement do not d/c Antithyroid Drugs (thionamides - Methimazole) Uses, side effects & adverse effects, routes, patient teaching ● use(1st line therapy) ○ ● ● ● treatment of graves, produces euthyroid state prior to removal, used in adjunct of irradiation of thyroid gland, emergency treatment of thyrotoxicosis side effects ○ hypothyroidism: drowsy, depression, weight gain, edema, bradycardia, anorexia, cold intolerance, dry skin, menorrhagia ○ agranulocytosis: (watch sore throat/fever, monitor CBC) ■ give Filgrastim if occurs NI○ monitor vitals, i&o baseline and periodically ○ monitor thyroid levels before during and after ○ may be given “lol” to decrease tremors/tachy ○ monitor hypothyroidism symptoms ○ monitor CBC for leukopenia and thrombocytopenia Teach○ report fever chills headache malaise, and weakness ○ therapeutic effect can take up to 2 weeks with full benefit up to 12 weeks ○ take at same time each day either with or without food ○ do not abruptly dc ○ no shellfish or anything containing iodine Glucocorticoids – short acting (cortisone); intermediate acting (methylprednisolone); long acting (dexamethasone) Uses, side effects & adverse effects, routes, patient teaching ● ● ● ● use○ ○ SE○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ NI○ ○ Teach○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ acute/chronic replacement of adrenocortical insufficiency (addisons/adrenal crisis) Nonendocrine disorders: cancer, inflammation, and allergic reactions glucose intolerance: can increase plasma glucose: hypergly/glycosuria F&E imbalance: can cause Na and K loss: leads Htn, edema, dysrhythmias Osteoporosis adrenal suppression: increase doses with stress do not DC peptic ulcer/GI discomfort infection : watch signs of infection cushings: will occur with lg doses and long term glucocorticoids monitor weight BP and electrolytes, monitor BG in DM give with food to decrease gastric distress, DO NOT STOP MED take calcium, vit d, and bisphosphonate and regular exercise no NSAIDS, no loop diuretics, no vaccines or toxoids notify HCP: fatigue, muscle weakness, weight loss, nausea, vomiting, confusion and hypotension) increases doses during large amts of stress notify HCP: coffee ground emesis, bloody/tarry stool/ abdominal pain avoid contact with disease notify hcp: muscle weakness, moon face, buffalo hump, cutaneous striations Chapter 34 ATI Bone Disorders Calcium Supplements - Calcium Carbonate: Uses, Side Effects/precautions/ Administration/ Patient Teaching ● ● ● ● ● ● ● use- clients who have hypocalcemia, deficiencies of parathyroid hormone, vit D or dietary calcium SE○ Hypocalcemia ■ tachycardia, elevated bp then leads brady and hypotension ■ muscle weakness, hypotonia, constipation, nausea, vomiting, abd pain, lethargy, confusion contraindicated- hypercalcemia, renal calculi, hypophosphatemia, digoxin tox and v fib caution- kidney disease and decreased gi function interactions ○ decreased tetra/gluco/thyroid ○ use with thiazide diuretics= increased risk hypercalcemia ○ no rhubarb, beets, bran, whole gains ○ no digoxin can lead severe bradycardia (PARENERAL) administration ○ chew tab to increase bioavailability ○ instruct client to read instructions ○ warm infusions to body temp Teach○ take calcium 1 hr apart from glucocorticoids/tetracyclines and 4 hrs apart from thyroid hormone ○ take oral with 8oz h2o Biphosphonates – Alendronate: Uses, Side Effects/Precautions; Administration/Patient Teaching ● ● ● ● ● ● ● use- prophylaxis in postmenopausal osteoporosis, males who have osteoporosis, propholayxis in chronic glucocortoid use, pagets disease SE & NI○ esophagitis- sit up/ambulate for 30 min after taking med, tabs with 8 oz of water/ liquid form with 2 oz, d/c call HCP with difficulty swallowing/heartburn ○ musculoskeletal pain- mild analgesic and notify HCP ○ visual disturbances- d/c call HCP ○ osteonecrosis of jaw- dentist prior to beginning tx/ avoid dental work during admin ○ kidney toxicity- monitor kidney function/ hydration status Contra- dysphagia, esophageal stricture/disorders, serious kidney impairment, hypocalcemia Caution- lactation, upper GI disorders, infection, liver impairment interactions- absorption decreases with calcium, iron, mag supps, antacids, orange juice, caffeine (take med 2 hours before) NI- monitor bone density (BDS q. 12-18 months), monitor blood calcium (norm- 9-10.5) Teach- empty stomach with 8 oz of water, in morning, wt-bearing exercise (walk 30-40 min/day), if dose skipped, wait till next day. increase calcium and vit D intake Calcitonin – Calcitonin-salmon: Uses, Side Effects/Precautions; Administration/Patient Teaching ● ● ● ● ● use- treats BUT DOES NOT PREVENT postmenopausal osteoporosis, moderate paget’s, hypercalcemia caused by hyperparathyroidism and cancer side effects- Nausea; nasal dry/irritation (alternate) contraindication- hyeprsensitivity of med and fish (do skin allergy test prior) caution- kids, lactating and kidney disease ○ intranasal is only approved for postmenopausal administration ● ○ salmon (IM/ subq, intranasal) intranasal- osteoporosis ○ keep container upright ○ check chvostek/trosseau (hypocalcemia) ○ monitor bone density patient teaching ○ diet high calcium and vitamin d ○ subq sites need to be rotated to prevent inflammation ○ admin intranasal in different nostril each day Chapter 55 – Emergency Medications Aspirin – uses, side effects – complications: ex. GI bleeding ● ● ● ● ● ● ● class- NSAID (salicylate) treat- First line emergency drug used to decrease platelet aggregation in management of acute coronary syndromes and MI. Best admin on onset of CP (dose- 160-325 mg) therapeutic range- 15 to 30 mg/dL SE- n/v/d/a, abdominal pain, melena, hematoma, epistaxis, dehydration; hypersensitivity- tinnitus, vertigo, bronchospasm Contraindication- allergy, presence of cerebral hemorrhage on CT scan, recent GI bleed, children with flu symptoms (reye syndrome), last trimester of pregnancy NI- have pt chew tab to speed absorption; take with water, milk, or food (GI) teach- dont take with warfarin, inform dentist Nitroglycerin – uses, side effects – protocol for administration (how often can it be repeated) . Consider effects on BP. P. 723 – Key point to know about using this medication: “If pain persists despite 3 doses of the sublingual or aerosol forms, further interventions are necessary in an emergency or critical care setting.” ● ● ● ● ● treat○ Dilates coronary arteries and improves blood flow to ischemic myocardium. treatment of choice for angina pectoris and MI ○ first line for acute cardiogenic pulmonary edema because it decreases both preload (blood in ventricle after diastole) and afterload (PVR) SE- hypotension (especially first time), HA, tachycardia, bradycardia Contra- viagra within 48 hrs (hypotension), CCB, BB, alcohol enhance hypotension NI- monitor heart rate and BP closely. must have SBP >90; taper over several weeks Teach○ sit or lie down during admin and moisten 1 tab with saliva then place under tongue ○ if CP not relieved repeat at 5 min intervals until 3 have been taken ○ Ointment or patch- remove at bedtime for 12 hr free Morphine – uses, side effects especially related to effects on heart p. 743 & p. 733 Evaluate effect on preload/BP/chest pain. ● ● ● class- narcotic analgesic treat○ CP associated with STEMI, unstable angina, acute cardiogenic pulmonary edema ○ relieves pain, dilates venous vessels, decreases pulmonary venous congestion, reduces workload on heart (decreases preload- amount of blood returning to right ventricle) dose- IV 1-5 mg q. 5-30 min ● ● ● SE- respiratory depression (but can relieve dyspnea), hypotension NI- admin slowly and titrate, monitor closely reversal- naloxone Atropine – used for the treatment of hemodynamically significant bradycardia…also used for:__________Important to maintain which monitoring when administering this medication? ● ● class- parasympatholytic treats○ hemodynamically significant bradycardia and some types of heart block (AV at the nodal level), asystole, as an emergency drug to reverse toxic effects of organophosphate pesticide and nerve agent exposure (bradycardia and excessive secretions) ○ increases heart rate by inhibiting action of the vagus nerve (parasympatholytic effect) ○ treat toxicity from cholinesterase inhibitors (increased muscarinic stimulation and respiratory depression) ● ● ● SE- dysrhythmias, tachycardia, MI, restlessness, anxiety, mydriasis, thirst, urinary retention, xerostomia NI- dose should never be less than 0.5 mg (may produce paradoxical bradycardia), 3 mg max, monitor cardiac and BP, dilute, given IV or IO teach- avoid hot environments, do not drive, oral hygiene Adenosine – Paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia - >150 beats/min. Consider half-life of this medication & what that means for administration. (IV Site/speec of administration) ● ● ● ● ● treat- paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (PVST) (>150 beats/min) half life- less than 5 seconds (admin fast via PIV site in port most proximal to patient as a 6 mg bolus over 1-3 seconds followed by 20 mL saline flush, followed by 12 mg in 1-2 min if needed); max 12 mg/dose SE- transie ectopy, bradycardia, flushing, CP, dyspnea, short period of asystole (up to 15 seconds after admin), HA, dizzy, paresthesia Contra- poison or drug related tachycardia, 2nd and 3rd degree heart block, sick sinus syndrome NI- continuous cardiac monitoring and VS, inhibited by caffeine, theophylline (higher dose may be needed) Amiodarone – used for the treatment of life-threatening ventricular dysrhythmias and cardiac arrest. Understand the process of administering this medication & maintenance. Side Effects and how you would respond. ● ● ● ● treat-first- line in life-threatening ventricular dysrhythmias and cardiac arrest (pulseless Vtach and Vfib, hemodynamically stable Vtach, PSVT refractory to adenosine, ventricular rate control in afib, afib) ○ esp good in pt with impaired heart function who have atrial/ventricular dysrhythmias SE- hypotension, bradycardia, Admin○ pulse- 150 mg over 10 min, then 1 mg/min for 6 hrs, then 0.5 mg/min for 18 hrs ○ cardiac arrest- 300 mg diluted in 20-30 mL D5W rapidly, then ^ NI- slow infusion, prepared to admin fluids, vasopressors, agents to increase HR, or temp pacemaker. long-half life. don’t give with drugs that prolong QT interval (such as procainamide) Albuterol – uses, side effects (tremor, nervousness…) ● ● ● ● class- beta2-adrenergic BD usually given by nebulizer treat- reverse bronchoconstriction in anaphylactic shock; asthma, inflammation, and narrowing of airways caused by enhanced responsiveness of tracheobronchial system to variety of stimuli; and COPD SE- tachycardia, tremor, nervousness, dysrhythmias, HTN, hypokalemia contra- milk protein hypersensitivity ● ● NI- assess breath sounds before and after admin (evidence of effectiveness- relief of bronchospasm), subjective respiratory distress before and after Teach- how to use MDI, keep track of doses Epinephrine – Uses, side effects Be clear on pediatric dose v adult dose (related to concentration). Constant cardiac & hemodynamic monitoring. AND understand use for anaphylactic shock. ● ● ● ● ● ● ● treat- profound bradycardia, hypotension, asystole, pulseless Vtach, vfib, anaphylaxis improves perfusion of heart and brain in cardiac arrest states by constricting peripheral blood vessels SE- myocardial ischemia, dysrhythmias, n/v, restless, tremor, oliguria, hypo/hyperglycemia, weak, dyspnea, HTN, pulm edema contra- never in same site as alkaline soln such as sodium bicarb (inactivate), met/resp acidosis decreases effectiveness, dysrhythmias, glaucoma, HTN, h yperthyroidism, DM, renal dysfunction dosing○ 1:1000- continuous infusion or IM ○ 1:10,000- single IV/IO dose; anaphylaxis ○ 0.1 mg/kg (1:10,000 soln) given ever 3-5 min IV/IO for cardiac arrest in pediatrics NI- constant cardiac and hemodynamic monitoring FOR ANAPHYLAXIS ○ s/s- severe bronchoconstriction and hypotension from cardiovascular collapse ○ bronchodilation, enhanced cardiac performance, vasoconstriction to increased BP ○ SE- tachycardia, dysrhythmias, HTN, angina, excitability, anxiety, fear, restlessness ○ NI- those on IV must be on cardiac monitoring with resuscitation equipment immediately available; given with antihistamine and steroid Naloxone – uses, side effects. Most important – Important to know – most opiate drugs have a longer duration of action than naloxone – what does this mean related to care of a patient who has overdosed? ● ● ● ● ● ● class- opiate antagonist (morphine, hydromorphone, fentanyl, codeine, propoxyphene, heroin) treat- OD, resp/cardiovascular depression or arrest from therapeutic doses, coma/ cardiac arrest arrest on unknown etiology dose- 0.4-2 mg IV q. 2 min contra- hypersensitivity, resp depression SE- n/v, sweating, tachy, HTN, can precipitate withdrawal symptoms in pt addicted to opiates, anaphylaxis, pulmonary edema in OD of morphine NI- opiate drugs have longer duration of action so monitor pt closely for s/s of recurrent opiate effects (resp depression, hypotension) --> repeat injection or continuous IV; monitor for combative behavior after OD Glucagon – uses, side effects - Compare the use of glucagon in severe hypoglycemia to Dextrose 50% . How do they work differently? Which one is faster? ● ● ● ● class- pancreas-produced hormone that elevates blood glucose by stimulating glycogen breakdown (glycogenolysis) tx- severe hypoglycemia, such as that which results from insulin shock; reverse effects of calcium channel blocker/ beta blocker OD; dilates esophagus ○ when dextrose 50% not available or cannot be admined IV, glucagon SE- n/v, hypersensitivity (bronchospasm/ resp distress), tachycardia, hypoglycemia Teach- effects within 10-15 min, fam members should be taught how to admin Flumazenil – Uses/Side Effects. Antidote for alprazolam toxicity ● ● ● reversal agent for resp depressants and sedative effects of benzos (diazepam, midazolam, chlorodiazepam, alprazolam) SE- drowsy, dizzy, blurred vision, ataxia, seizures,hyperacusis, palpitations, vomiting, dry mouth NI- resp rate and effort, BP, mental status. if reversed too rapidly, pt may have emergence reactions (agitated, confused, perceptual distortions), seizure precautions; max 3 mg Describe the process of preparing and safely administering 50% dextrose solution IV to a child with hypoglycemia. ● ● dextrose 25% or less (dilute at least 1:1 in sterile water to reduce osmolarity and prevent peripheral sclerosis of peripheral veins) standard dose is 0.5-1 g/kg IV or IO Activated Charcoal – Uses, Side Effects, Teaching/administration. “This med is ineffective and should not be given to patients who have ingested some forms of pesticides, hydrocarbons, alcohol, acids or alkalis, lithium, solvents , and iron supplements” p. 738 Use of cathartic – to speed elimination of the charcoal-toxin from the body – bowel movement. ● ● ● ● ● treat- prevent absorption of toxins into body if ingested substance is known to be effected by charcoal in GI tract SE- vomiting contra- milk products, ingestion of pesticides, hydrocarbons, alcohol, acids, alkalis, lithium, solvents, iron supps NI- those with impaired gag-reflex or impaired mental status are at high for risk for aspiration; pt may need to be intubated for airway protection after admin via gastric tube Teach- cathartic may be given to speed elimination, black stools, poison control center should be contacted as soon as possible for guidance Dopamine – Uses, Side Effects – Important consideration in stopping the infusion/interrupting an infusion. Also – concern over extravasation & interventions. ● ● ● ● treat○ sympathomimetic agent often used to treat hypotension in shock states, increase heart rate in bradycardic rhythms when atropine has not been effective ○ enhances cardiac output by increasing myocardial contractility and increasing heart rate, elevates BP through VC SE- tachycardia, dysrhythmias, myocardial ischemia, n/v contra- sodium bicarb inactivates NI- lowest effective dose, wean gradually (severe hypotension), dilute, use infusion pump, continuous heart and BP monitoring, document VS, cardiac rhythms, I&O; assess IV hourly for s/s of infiltration/ extravasation ○ if extravasation- inject phentolamine in multiple areas to prevent tissue damage Dobutamine – Uses, Side Effects. Medication must be tapered – can’t abruptly discontinue. ● ● ● ● class- sympathomimetic drug with beta-adrenergic activities tx- shock states when improvement in cardiac output and performance is desired SE- myocardial ischemia, tachycardia, dysrhythmias, headache, nausea, tremors NI- admin via infusion pump, taper gradually to prevent clinical deterioration, continuous cardiac and BP monitoring, monitor I&O, assess for s/s of myocardial ischemia (CP, dysrhythmias) Diphenhydramine Hydrochloride – Uses, Side Effects, Important information about administration (liquid/pill/IV/IM) How would you choose which route – based on patient presentation? ● ● antihistamine, administered with epinephrine, to treat anaphylactic shock Admin- ● ● ○ 25-50 mg IV or deep IM- preferred in emergencies ○ oral pill or liquid- for home emergency self-amin SE- drowsy, sedation, confusion, vertigo, excitability, hypotension, tachycardia, GI disturbances, dry mouth Teach- liquid is easier to swallow than pill, esp in presence of tissue edema in mouth/throat Nitroprusside Sodium – Uses, Side Effects, Important nursing considerations p. 742 ● ● treat- reduce arterial BP in hypertensive emergencies (vasodilation) ○ effects end when d/c NI○ continuous, accurate BP monitoring ○ rapidly inactivated by light (wrap with aluminum foil or opaque material) ○ blue or brown discoloration indicates degradation and necessitates soln be discarded (faint brown color is normal) ○ when therapy is prolonged or when it's infused at max dose for more than 10 minutes, pt at risk for toxicity resulting from elevated serum thiocyanate or cyanide levels ■ s/s- met acidosis, hypotension, dyspnea, dizziness, vomiting ■ serum thiocyanate levels should be monitored q. 24-72 hrs for pt receiving prolonged infusions of more than 2 mcg/kg/min ■ pt with renal insufficiency or failure are at higher risk because metabolites are excreted in urine ○ place on oral antihypertensive asap so NS can be tapered slowly Furosemide – Uses, side effects, Important nursing considerations – how quickly do you expect results? How do you evaluate your results (I & O) lung sounds, work of breathing….related to the “main indications for the use of furosemide as an emergency drug: acute pulmonary edema from left ventricular dysfunction & hypertensive crisis.” ● ● ● ● ● ● ● class- loop diuretic- promotes renal excretion of water, sodium, chloride, magnesium, hydrogen, and calcium, and depletes potassium Treats○ acute pulmonary edema from left ventricular dysfunction and HTN crisis ○ peripheral and renal vasodilator effects that can lower BP SE- hypovolemia, dehydration, electrolyte disturbance (everything low), n/d/a, dizzy, tinnitus, cramps, weak, HA contra- anuria interactions- Increased risk for dig toxicity because of hypokalemia, ginseng, licorice (decreases K+) NI- assess electrolytes, BUN, creat before and after admin, auscultate breath sounds for rales, strict surveillance of I&O Teach- diuresis should begin within 10 minutes of drug admin and may continue for approximately 6 hrs, indwelling urinary catheter may be necessary