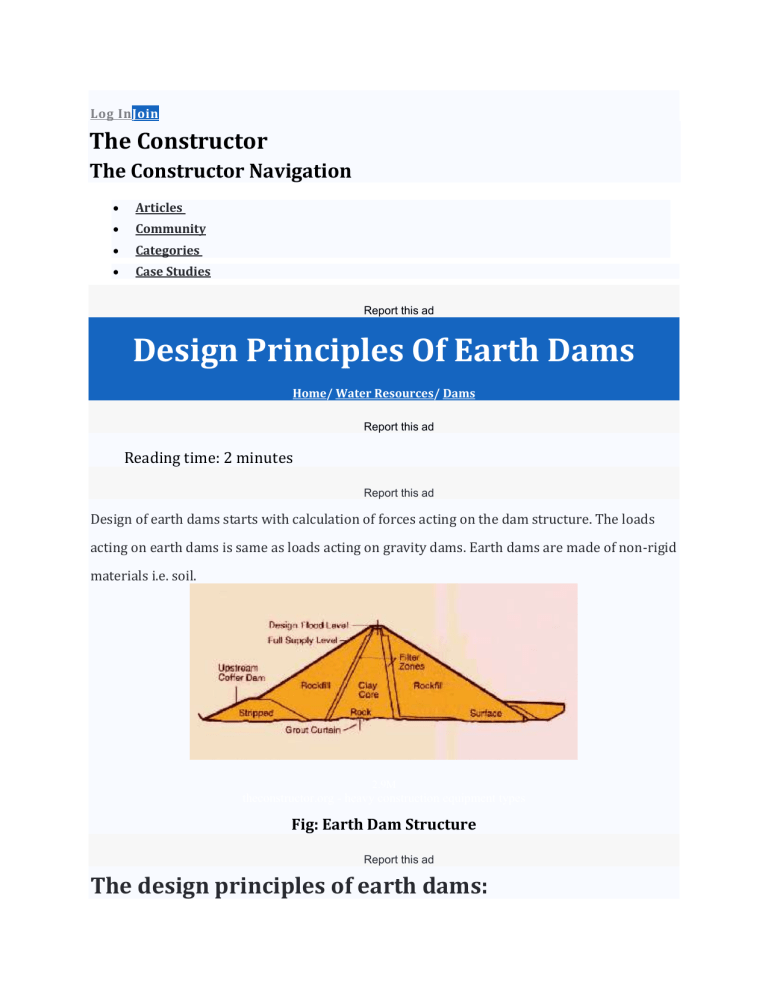
Log InJoin The Constructor The Constructor Navigation Articles Community Categories Case Studies Report this ad Design Principles Of Earth Dams Home/ Water Resources/ Dams Report this ad Reading time: 2 minutes Report this ad Design of earth dams starts with calculation of forces acting on the dam structure. The loads acting on earth dams is same as loads acting on gravity dams. Earth dams are made of non-rigid materials i.e. soil. 2.9M theconstructor.org - heavy construction equipment types Fig: Earth Dam Structure Report this ad The design principles of earth dams: 1. The filling material to be used for earth dams should be sufficiently less permeable. 2. The earth dams should be constructed by utilizing available materials in local area to serve the intended purpose with low cost. In order to reduce the leads for carrying excavated earth, the borrow pits should be as close to the dam site as possible. 3. Sufficient outlets and spillways should be provided to avoid the possibility overtopping during design floods. 4. For frost action, wave action and earthquake motions, sufficient freeboard must be provided. 5. If the stability of foundations and embankments is not impaired by piping, sloughing etc., there should be little harm in seepage through a flood control dam. But a conservation dam should be as water-tight as possible. 6. To avoid sloughing of face of earth dam, the phreatic line i.e. seepage line should be within the downstream face of the dam. 7. The downstream face must be protected properly against rain, waves, up to tail water and the upstream face against wave action. To reduce erosion due to flow of rain water horizontal berms may be provided at suitable intervals in the downstream face. Ripraps may be provided on the entire upstream slope and on the downstream slope near the toe so as to prevent erosion. 8. By providing suitable horizontal filler drain or chimney drain or toe drain, the portion of the dam and downstream of the impervious core should be properly drained. 9. There must be no possibility of free flow of water from upstream to downstream face. 10. The upstream and downstream slopes should be designed so as to be stable under worst conditions of loading. Such critical conditions occur for the upstream slope during sudden downstream of the reservoir and for the downstream slope during steady seepage under full reservoir. 11. The upstream slope and downstream slope must be flat enough to provide sufficient base width at the foundation level, such that the maximum shear stress developed remains well below the corresponding maximum shear strength of the soil so as to provide suitable factor of safety. 12. Due to development of excessive pore pressure and consequent reduction in shear strength of soil, the stability of the embankment and foundations is very critical during construction or even after the construction during the period of consolidation. So under this critical condition the embankment slopes must remain safe.







