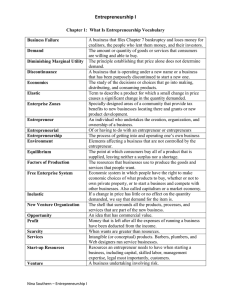
DAILY LESSON LOG School Dasmariñas Integrated High School Teacher Victoria M. Flores Teaching Dates and Time Week 1 (June 4-8, 2018) Session 1-3 Session 1 Session 2 Grade Level 12 Learning Area Entrepreneurship Quarter First Session 3 I. OBJECTIVES A. Content Standards B. Performance Standards C. Learning Competencies/ Objectives II. CONTENT The learner demonstrates understanding of key concepts, underlying principles and core competencies in Entrepreneurship. The learner demonstrates understanding of key concepts, underlying principles and core competencies in Entrepreneurship. The learner demonstrates understanding of key concepts, underlying principles and core competencies in Entrepreneurship. The learner independently creates/provides a quality and marketable product and/or service in Entrepreneurship as prescribed in the TESDA Training Regulation The learner independently creates/provides a quality and marketable product and/or service in Entrepreneurship as prescribed in the TESDA Training Regulation The learner independently creates/provides a quality and marketable product and/or service in Entrepreneurship as prescribed in the TESDA Training Regulation At the end of the lesson, the learners should be able to: a. Define entrepreneur and entrepreneurship b. Describe the salient features of entrepreneurship c. Discuss the different theories on entrepreneurship d. Distinguish between entrepreneurial venture and ordinary small business activity At the end of the lesson, the learners should be able to: a. Define entrepreneur and entrepreneurship b. Describe the salient features of entrepreneurship c. Discuss the different theories on entrepreneurship d. Distinguish between entrepreneurial venture and ordinary small business activity At the end of the lesson, the learners should be able to: a. Define entrepreneur and entrepreneurship b. Describe the salient features of entrepreneurship c. Discuss the different theories on entrepreneurship d. Distinguish between entrepreneurial venture and ordinary small business activity Defining Key Terms/Salient Features of Entrepreneurship Theories of Entrepreneurship Entrepreneurship and Ordinary Small Business Activity III. LEARNING RESOURCES A. References 1. Teacher’s Guide pages 2. Learner’s Material pages 3. Textbook pages Nick L. Aduana (2016). Entrepreneurship in Philippine Nick L. Aduana (2016). Entrepreneurship in Philippine Nick L. Aduana (2016). Entrepreneurship in Philippine Setting, C and E Publishing Inc. Setting, C and E Publishing Inc. Setting, C and E Publishing Inc. 4. Additional Materials from Learning Resource portal 1 B. Other Learning Resources Session 1 Session 2 Session 3 IV. PROCEDURES 1. Teacher welcomes the class and introduces himself/herself. A. Reviewing previous lesson or presenting a new lesson B. Establishing a purpose for the lesson C. Presenting examples/instances of the new lesson Teacher reviews activities from the last session. Class reviews presentations from the last session. Class discusses what they have learned from the presentation. Teacher presents the different theories of entrepreneurship and gives a brief explanation for each. Ask: What does this statement mean? Entrepreneurship is different from the activities of ordinary small businesses. The distinction lies in the descriptive word “ordinary”. Theories of Entrepreneurship 1. Innovation Theory – was contributed by Joseph Schumpeter, an Austrian economist and political scientist. He wrote about it in his book, The theory of Economic Development. The Innovation Theory regards economic development as the product of structural change or innovation. It becomes the primary role of the entrepreneur to introduce innovation in any of the following forms: a. new product b. new production method c. new market d. new supplier c. new industry structure 2. Keynesian Theory – was developed by John Maynard Keynes, a British economist. The General Theory of Employment, Interest and Money, which was published during the Great Depression in 1936. Entrepreneurship and Ordinary Small Business Activity Entrepreneurship is different form the activities of ordinary small businesses. This does not mean, however, that entrepreneurship does not connote small business. It does because entrepreneurship covers small and medium scale businesses. The distinction lies in the descriptive word “ordinary”. Entrepreneurship and the activities of ordinary small businesses differ in the following areas: 1. Motive in opening a business – an entrepreneur starts a business venture based on entrepreneurial concepts and principles and the aspiration to become successful. He/She is constantly on the lookout for new and fresh ideas, which can be found in the business environment. Owner of an ordinary small business opens a business with the primary goal of making it his/her source of livelihood. The business becomes a major provider of the family for their financial requirements. The owner of an ordinary small 2. Motivation Activity: Unscramble the Word The learners will be grouped into four and will be tasked to unscramble the word to be given by the teacher. Three rambled words will be given and learners will have to unscramble each word for one (1) minute. After arranging the letters the group leader or representative will go in front to write their answers on the board. 1 point will be given to the group who will be able to give the correct answer. The group with the highest score will be declared the winner. Suggested Words: 1. Business 2. Entrepreneur 3. Venture Ask: What does this statement mean? “Entrepreneurship is living a few years of your life like most people won’t. So that you can spend the rest of your life like most people can’t.” 1. Before the discussion remind the class to take down notes. 2. Discuss entrepreneur and entrepreneurship. 3. Provide a definition and examples of entrepreneur and entrepreneurship. 4. Discuss the difference of small and ordinary small business. 5. End the discussion by asking a number of learners to summarize what they have learned. 2 The theory put so much emphasis on the role of the government in entrepreneurial and economic development, most especially when the economy was experiencing depression. It suggests that entrepreneurial activities may not be favorable in the future unless the short-term problem of economic disequilibrium is finally resolved through the active participation of the government. 3. Alfred Marshal Theory - Alfred Marshall an English economist strongly asserted that there are four factors in the production (land, labor, capital and organization) of goods and services in the economy, he considered organization as the coordinating element. Without the active participation of organization, the other factors of production will remain inactive in their role for economic development. 4. Risk and Uncertainty-Bearing Theory – Frank Hyneman Knight, an American economist, conceptualized the risk and uncertainty bearing theory of entrepreneurship in his book, Risk, Uncertainty and Profit. By adopting some concepts of the early economist, Knight viewed an entrepreneur as an agent of the production process where he/she connects the producers and the consumers. Knight, however, added risk-taking as an important dimension that will differentiate an entrepreneur from a worker. Knight considered uncertainty an important factor in the production of goods and services. He believed that the entrepreneur must anticipate possible random events to happen while shouldering the risk at the same time. The entrepreneur would be eventually rewarded with high profits. business operates with a basic motive of earning profit. However, the level of profitability is sometimes neglected. The profitability aspect and the level of profitability are two distinct important issues. 2. Perception of risk in the business – The entrepreneur takes and faces the business risk squarely. He/She considers it inherent in the business venture, prepares the business for it, and finds ways to minimize its effects. The owner of an ordinary small business, on the other hand, believes that the business risk is a deterrent to the operation of the business and must be avoided. 3. Reactions to changes in the environment – The entrepreneur reacts positively to the changes in the environment. Changes in the business environment bring new ideas for entrepreneurial opportunities. The entrepreneur considers changes in the environment a creative mechanism for development and growth in the entrepreneurial activities. They become a new source of possible entrepreneurial venture. 4. View on competition – For the entrepreneur the presence of competition is a sign of a healthy economic environment. The environment where the venture operates can be considered neutral of free-trade because of healthy competition. Competition will undoubtedly force entrepreneurs to continuously improve their present products or services. It will be one of the factors that will make them creative in their endeavor. The owner of an ordinary small business, however, views competition as an unhealthy element in the business environment and tries to avoid it. He/She is very uncomfortable working in a competitive environment and strongly discourages competition in the business community. 5. Vision for development and growth – The entrepreneur usually outlines the course of his/her entrepreneurial venture in terms of short-term, medium-term and long-term plans of action. He/She makes sure that the vision and mission of his/her business is clear. The entrepreneur aligns the daily business activities toward the attainment of the plans. He/She properly manages the venture in such a way that the operations will provide development and growth to the venture. The owner of an ordinary small business, on the other hand, relies upon chance or luck in maintaining the status quo of his/her business. He/She is not so much concerned about its development and growth as long as he/she is satisfied with its earnings. 6. Horizon of business operation – An entrepreneur thinks globally but acts locally. His/Her sight is always focused on the 3 stars above, while his/her feet are firmly anchored on the ground. He/She is primarily concerned with the major economic events not only in the local environment but also in the global business market. The entrepreneur has a strong notion that the business venture will be going out of the local market and will soon face healthy competition in the international market. The entrepreneur has both local and global perspectives. 7. Sources of business funds – When the entrepreneur finds that the proposed business endeavor is a wealth-creating venture, he/she explores ways to generate the much-needed funds from both internal and external resources. He/She strongly believes that the wealth that the venture may create is external resources. He/She strongly believes that the wealth that the venture may create is more than enough to compensate for the sourced funds. On the contrary, the owner of an ordinary small business tends to limit the funding of his/her business enterprise to personal resources. Loans from external resources can be a risky undertaking for him/her. He/She fears that financial institutions will not be willing to extend financial assistance to the business. In other words, he/she is already fully convinced that he/she is pursuing the unprogressive type of business endeavor. 1. Teacher will discuss the different salient features of entrepreneurship. D. Discussing new concepts and practicing new skills #1 2. Discuss entrepreneurship as an art of correct practices. Ask: Is creativity present in the operation of ordinary small business along the streets and highways and in your neighborhood? Why do you say so? 3. Discuss entrepreneurship as a wealth-creating venture. 4. Discuss how entrepreneurship provides valuable goods and services. 5. Discuss how entrepreneurship entails opening and managing the self-owned enterprise. 6. Discuss entrepreneurship as a risk taking venture. Ask: Do you know someone who owns a small business? Does he/she personally manage his/her own business? Do you think he/she is an entrepreneur or an ordinary small businessperson? Why? Other Theories on Entrepreneurship 1. Weber’s Sociological Theory – In sociological theory, Max Weber stressed that social cultures are the primary driving elements of entrepreneurship. The entrepreneur is expected to perform the role of a good constituent by executing his/her entrepreneurial activities in line with good customs and traditions, religious beliefs and morals. 2. Kaldor’s Technological Theory – The technological theory was developed by Nicholas Kaldor who considered modern technology as an essential factor in production. In the absence of modern technology application in entrepreneurship, economic development would be slow and growth might not be expected. The entrepreneur is expected to keep abreast with modern technology and find ways to apply the same in the entrepreneurial endeavor. Proper application of modern technology will promote efficiency in the production of goods and services. 3. Leibenstein’s Gap-Filling Theory - In this theory on entrepreneurship, Henry Leibenstein proposed that the primary role of entrepreneurship in any economic activity is to fill the existing gap. Entrepreneurship is responsible for recognizing trends in the market. The entrepreneur is expected to possess abilities that will connect the different 4 markets. He/She must extend assistance to entrepreneurial ventures experiencing failures and deficiencies. 4. Kirzner’s Learning-Alertness Theory – Israel Kirzner was the main proponent of this theory. He pointed out spontaneous learning and alertness as the two major attributes of entrepreneurship in any given economy. The entrepreneur must be alert in recognizing entrepreneurial opportunities and the ignorance of consumers as well. He/She must immediately find appropriate remedy to correct the error or wrong perception. E. Developing mastery (Leads to Formative Assessment) Learners shall be able to orally answer the questions to be given by the teacher. Ask the class to discuss the features and significance of the theories on entrepreneurship. Learners shall be able to differentiate an entrepreneur from an owner of an ordinary small business in the following areas: 1. Motive in opening a business. 2. Perception of risk in the business. 3. Vision for development and growth. Discuss: A theory is a generalization that explains a set of facts or phenomena. It is not an absolute truth. It can be supported by another observation or proven to be otherwise. Regardless of definition of success, there are a great number of common characteristics that are shared by successful entrepreneurs, although they think and process information differently. Entrepreneurial process shows that creative thinking is the must have skill of an entrepreneur for the creation of new ideas. Choose one small business in your neighborhood. Conduct a guided interview of its owner. Elicit the primary reason why he/she opened the business. Determine if he/she manages the business as an entrepreneur or as an owner of an ordinary small business. Explain the career opportunities open to graduates of entrepreneurship 1. In your own words, what is entrepreneur? Entrepreneurship? and Small Business? 2. Differentiate wealth-creating venture from an incomegenerating venture 3. What is your view about competition? F. Finding practical applications of concepts and skills in daily living G. Making generalizations and abstractions about the lesson H. Evaluating learning I. Additional activities for application or remediation Move around in your barangay. Record 5 either micro, small or medium enterprises that have been established there for at least five years. Find out the effects of their presence in your community. Form groups of six members each, preferably with members from the same community. Observe the activities of the entrepreneur in your local community. Report your observation in class. Look for a woman entrepreneur in your community. Ask her about the reasons for her engaging in entrepreneurship. Report in class what you have gathered. Mae your own theory on entrepreneurship for the businesses that you observed, give your theory a name and explain how it applies to the said business. V. REMARKS VI. REFLECTION 5 A. No. of learners who earned 80% on the formative assessment B. No. of learners who require additional activities for remediation C. Did the remedial lessons work? No. of students who caught up with the lesson D. No. of learners who continue to require remediation E. Which of my teaching strategies work well? Why did these work? F. What difficulties did I encounter which my principal or supervisor help me solve? G. What innovation or localized materials did I use/discover which I wish to share with other teachers? Prepared by: Checked by: VICTORIA M. FLORES Subject Teacher JAYZEL V. ALAM Subject Coordinator 6