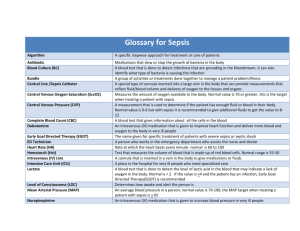
Chapter 23 THE CARDIOVASCULAR AND LYMPHATIC SYSTEMS The cardiovascular system: The heart, blood and blood vessels The lymphatic system: The lymph, lymph vessels, lymph nodes and the lymphoid organs Function: - Distribution of nutrients and oxygen to body tissues and carry away waste products - Defense mechanism BACTERIAL DISEASES OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR AND LYMPHATIC SYSTEMS SEPSIS AND SEPTIC SHOCK Gram negative sepsis Gram positive sepsis Puerperal sepsis SEPSIS AND SEPTIC SHOCK Questions: Is blood sterile? Can a microorganism enter blood without causing harm? How? When can the microorganism cause a disease? Answers: Yes Yes, if moderate numbers In hospital conditions as invasive procedures, such as insertion of catheters and IV feeding tubes If defense mechanisms fail and microbes can proliferate in blood SEPSIS AND SEPTIC SHOCK – CONT’D Septicemia: persistence of pathogenic organisms and their toxins in blood Sepsis: systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) - At least two of a set of defined conditions: fever, rapid heart or respiratory rates, and a high count of WBCs Lymphangitis inflamed lymph vessels visible as red streaks under the skin Lymphangitis SEPSIS AND SEPTIC SHOCK – CONT’D Sever sepsis: a drop in blood pressure and dysfunction of at least one organ Septic shock: the final stage, low blood pressure can no longer be controlled by addition of fluids GRAM NEGATIVE SEPSIS Septic shock is most likely to be caused by Gram negative bacteria (Why?) Septic shock is called endotoxic shock (Why?) Treatment: - Is antibiotic use of value? GRAM POSITIVE SEPSIS Gram positive bacteria are the most common cause of sepsis in hospitals…why? Predisposing factors? Virulence factors ? Staphylococus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes :TSS Enterococcus spp: :infections of wounds, UTI and others Group B streptococcus (S.agalactiae), the most common cause of life threatening neonatal sepsis - CDC, recommends that pregnant women be tested for vaginal GBS….Why? Treatment: vancomycin PUERPERAL SEPSIS Puerperal fever or childbirth fever: Infection of the uterus as a result of childbirth or abortion Causative bacteria: GAS Local infection of the uterus----- peritonitis and sepsis Mode of transmission? Treatment: - Penicillin - Modern hygienic practices BACTERIAL INFECTIONS OF THE HEART “ENDOCARDITIS” The heart: endocardium, myocardium and pericardium Endocardium: it is the inner layer lines the heart muscles and covers the valves Endocarditis? Subacute bacterial endocarditis: It develops slowly over a period of weeks or months Characterized by: fever, general weakness and heart murmur Causative bacteria: Streptococcus viridans (oral streptococci). E.g. S.mutans and S.sangius Predisposing factors? BACTERIAL INFECTIONS OF THE HEART “ENDOCARDITIS”-CONT’D Pathogenesis: After tooth extraction bacteria enter the blood, and find their way to the heart The body’s defense mechanisms? Abnormal heart valves, the bacteria lodge in the preexisting lesion The bacteria multiply and become entrapped in blood clots that protect them from phagocytes and antibodies Pieces of the clot break off and can block blood vessels or lodge in the kidneys The function of the heart valve is impaired SBE is fatal within few months Subacute – Bacterial Endocarditis ACUTE BACTERIAL ENDOCARDITIS Causative organism: Staph.aureus - From the initial site of infection to normal or abnormal heart valves - Fatal within a few days or weeks if untreated Pericarditis: inflammation of the sac around the heart (pericardium). Streptococcus pyogenes can cause it (GAS) RHEUMATIC FEVER Causative organism: Streptococcus pyogenes (GAS) Post streptococcal squeal in 4-18 years, following streptococcal sore throat Complain: short periods of arthritis and fever, then subcutaneous nodules at joints accompany this stage Pathogenesis: misdirected immune reaction against streptococcal M protein, damages the heart valves?? - Reinfection with streptococci renews the immune attack - Damage of the heart valves may be serious enough to result in eventual failure and death Treatment: long acting penicillin (monthly injection) THEORIES OF OCCURRENCE OF RHEUMATIC FEVER Direct toxicity:? Antigenic cross reactivity:? A nodule causes by rheumatic fever BRUCELLOSIS (UNDULANT FEVER) Causative bacteria: Brucella, small aerobic gram negative coccoid bacilli zoonosis? Brucella abortus: in cattle and camels Brucella suis: in swine, and can infect cattle when kept in contact with swine Brucella meletensis: in goats and sheep Virulence factor?? Mode of transmission: - Occupational disease: farmers, shepherds, butchers and veterinaries. - Oral route, skin abrasions, droplet infection through mucous membranes - Person to person transmission is very rare. BRUCELLOSIS (UNDULANT FEVER)-CONT’D IP: 1-3 weeks or longer Symptoms: - Fever (often rising and falling= undulant fever), malaise, night sweats and muscle aches - Physical examination: splenomegaly may be the only finding Complications: arthritis and meningitis Diagnosis: - Serological tests - Isolation of organism from blood or tissues - It needs incubation for a long period…Why? Treatment: combination of at least 2 antibiotics as tetracycline and streptomycin for at least 6 weeks Control?? GANGRENE – CLOSTRIDIAL MYONECROSIS Causative bacteria: Clostridium perfringenes - It is widely found in ……….. Virulence factors: -Toxin: lecithinase. -Enzymes (spreading factors??) Pathogenesis: - Trauma (wound) will lead to interrupted blood supply (ISCHEMIA) and the wound becomes anaerobic - Ischemia leads to necrosis (death of the tissues) - The death of soft tissue results from the loss of blood supply is called gas gangrene, especially in muscle tissues (myonecrosis) Trauma Ischemia Necrosis Anaerobic GANGRENE – CONT’D Pathogenesis “ continue”: - Cl.perfringenes ferment carbohydrates in the tissues and produce gasses (carbon dioxide and hydrogen) that swell the tissues - The bacteria produce toxins that move along muscle bundles, killing cells and produce necrotic tissues - The toxins and bacteria then enter the blood stream - Production of enzymes degrade collagen leading to spread of the disease Symptoms: - IP 1-3 days after injury, pain in the affected area, crepitation of SC tissues, foul smelling - Skin color changes and finally becomes black - Death occurs rapidly in untreated cases GANGRENE – CONT’D - Treatment: - Surgical - Hyperbaric chamber -High dose of Penicillin or clindamycin or metronidazole The toes of a patient with gangrene REVIEW QUESTIONS True or false: Septicemia refers to the presence of bacteria in blood Gram positive sepsis can lead to endotoxic shock Endotoxic shock occurs due to the presence of teichoic acid in bacterial cell wall Antibiotic intake causes immediate improvement of a patient with endotoxic shock It is recommended to test pregnant females for vaginal colonization with Staph.aureus The commonest organism causing puerperal sepsis is Strept.viridans