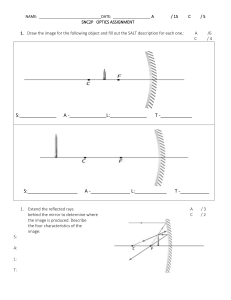
Reflection Notes - 10 d56209cc-3417-4c65-8bcb-76afb65c8af6
advertisement
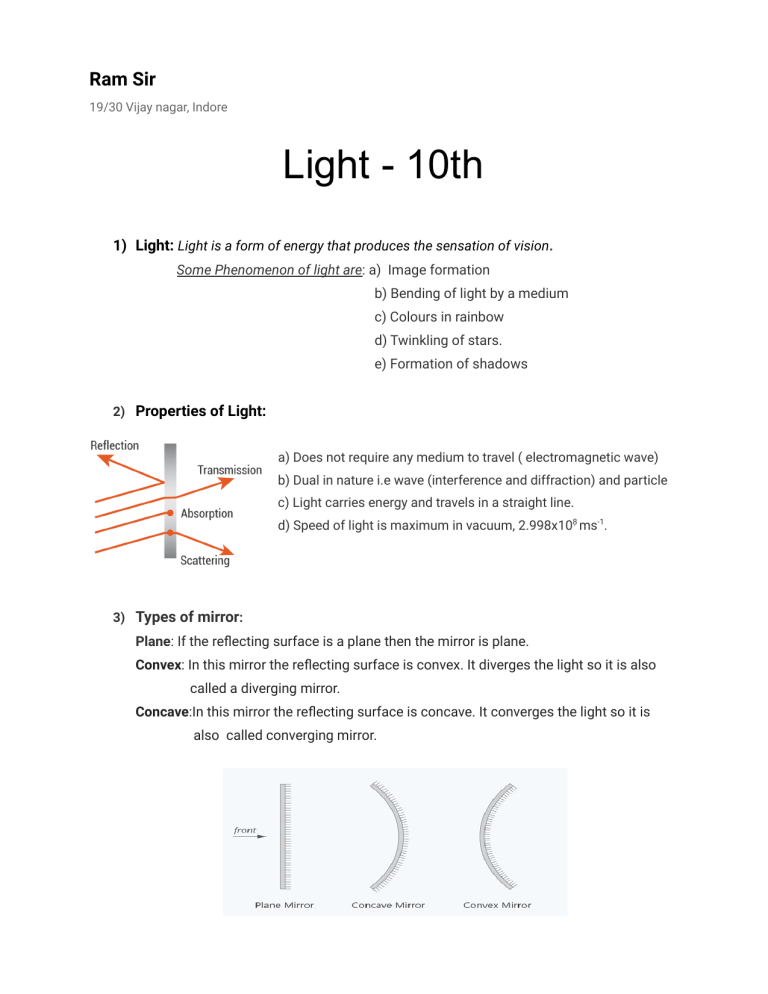
Ram Sir 19/30 Vijay nagar, Indore Light - 10th 1) Light: Light is a form of energy that produces the sensation of vision. Some Phenomenon of light are: a) Image formation b) Bending of light by a medium c) Colours in rainbow d) Twinkling of stars. e) Formation of shadows 2) Properties of Light: a) Does not require any medium to travel ( electromagnetic wave) b) Dual in nature i.e wave (interference and diffraction) and particle c) Light carries energy and travels in a straight line. d) Speed of light is maximum in vacuum, 2.998x108̣ ms-1. 3) Types of mirror: Plane: If the reflecting surface is a plane then the mirror is plane. Convex: In this mirror the reflecting surface is convex. It diverges the light so it is also called a diverging mirror. Concave:In this mirror the reflecting surface is concave. It converges the light so it is also called converging mirror. Ram Sir 2 Reflection: Bouncing back of light when it hits/strikes to a polished surface Laws of Reflection: 1) The incident ray, reflected ray and the normal all lie in the same plane 2) Angle of incidence = Angle of reflection i.e ∠θi=∠θr Virtual and Real Image: Virtual Image Real Image Formed when lights appear to meet Formed when lights actually meet Can’t be obtained on screen Can be obtained on screen Erect Inverted Eg: plane mirror convex mirror Eg: concave mirror (cinema screen) Image formed by Plane mirror: 1) Virtual and erect 2) Size of image = size of object 3) Laterally inverted Eg: AMBULANCE Spherical Mirror: A spherical mirror is formed by cutting out a piece of a sphere and silvering either the inside or outside surface Ram Sir 3 Anatomy of curved mirror: ● Center of Curvature(C):The centre of hollow sphere of which mirror is a part. ● The radius of curvature(R): The radius of the hollow sphere of which mirror is a part. ● Pole: The centre of the mirror (middle point) is pole. ● Principal axis: The line joining the pole and center of curvature ● Aperture: Size of mirror is called the aperture of mirror. ● Principal Focus: The point on the principal axis, where all the incident rays parallel to the principal axis converge or diverge after reflection through mirror. ● Focal Length(F): The distance between pole and focus point is focal length. F = R/2 Sign Convention: 1) Object is placed at the left of mirror 2) Distance measured along incident ray is positive (+) 3) Distance measured against the incident ray is negative (-). 4) Distance measured perpendicular and above the principal axis is positive (+). 5) Distance measured perpendicular and below the principal axis is negative(-). Ram Sir 4 Ray diagrams formed by concave mirror at different positions: - Position Of Object Position Of Image Size Nature of Image a) At infinity At F Point size (Diminished) Real, inverted b) Beyond C Between C & F Diminished Real, inverted c) At C At C Same SIze Real, inverted d) Between C & F Beyond C Enlarged Real, inverted e) At F At Infinity HIghly Enlarged Real, inverted f) After F Behind the mirror Enlarged Virtual, Erect Uses of Concave Mirror: It is used as a makeup mirror, the reflector in torches, in headlights of cars and searchlights, doctor’s head-mirrors, solar furnace, etc Ram Sir 5 Ray diagrams formed by concave mirror at different positions: - Uses of Convex Mirror: Convex mirror used as rear view mirror in vehicles, as shop security mirrors, etc. Mirror Formula and Magnification: v: Image distance, u: object distance, f: focal length Magnification (m) = height of image/ height of object: m = hi/ho -> if ‘m’ is negative, image is real -> if ‘m’ is positive, image is virtual Ram Sir 6 Questions: 1) Focal length of plane mirror is a.) At infinite b) Zero c.) Negative d.) None of these 2) Image formed by plane mirror is a. Real and erect b. Real and inverted c. Virtual and erect d. Virtual and inverted 3) A concave mirror gives real, inverted and same size image if the object is placed a.) At F b.) At infinity c.) At C d). Beyond C 4) Power of the lens is -40, its focal length is a.) 4m b.) -40m c.) -0.25m d.) -25m 5)A concave mirror gives virtual, refract and enlarged image of the object but image of smaller size than the size of the object is a.) At infinity b.) Between F and C c). Between P and F d.) At E 6) A ray of light that strikes a plane mirror PQ at an angle of incidence of 30o, is reflected from the plane mirror and then strikes a second plane mirror QR placed at right angles to the first mirror. The angle of reflection at the second mirror is: (a) 30o (b) 45o (c) 60o (d) 90o 7) A concave mirror produces a magnification of +4. The object is placed: (a) At the focus (b) Between focus and centre of curvature (c) Between focus and pole (d) Beyond the centre of curvature Ram Sir Answers: 1) A 2) C 3) C 4) C 5) C 6) C 7) C 7