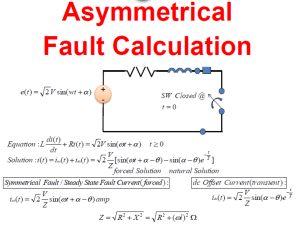
A STUDY ON CONSUMERS BUYING BEHAVIOUR TOWARDS INSTANT FOOD
advertisement

A STUDY ON CONSUMERS BUYING BEHAVIOUR TOWARDS INSTANT FOOD PRODUCTS Research Project Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of B.COM HONOURS By BHAVYA SAXENA To The DEPARTMENT OF COMMERCE THE BHOPAL SCHOOL OF SOCIAL SCIENCES April,2021 Under the Guidance o f Dr. SWAPNA PILLAI ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR DEPARTMENT OF COMMERCE CERTIFICATE It is certified that the work contained in the project report titled “A STUDY ON CONSUMERS BUYING BEHAVIOUR TOWARDS INSTANT FOOD PRODUCTS”, by “BHAVYA SAXENA”, has been carried out under my/our supervision and that this work has not been submitted elsewhere for a degree. Signature Of Supervisor: ……………………. Name: Dr. Swapna Pillai, Associate Professor Department: Commerce The Bhopal School of Social Sciences April 2021 DECLARATION I hereby declare that this project report entitled “A STUDY ON CONSUMERS BUYING BEHAVIOUR TOWARDS INSTANT FOOD PRODUCTS” was carried out by me for the degree of B.COM HONOURS under the guidance and supervision of Dr. Swapna Pillai, Associate Professor of Department Of Commerce, BSSS College. The interpretations put forth are based on my reading and understanding of the original texts and they are not published anywhere in any form. The other books, articles and websites, which I have made use of are acknowledged at the respective place in the text. This research report is not submitted for any other degree or diploma in any other university. Place: Bhopal Name of The Student: Bhavya Saxena Class & Section: B.com Honours final year 3A Date: 15th April,2021 ACKNOWLEDGEMENT I would like to thank our Principal Dr. Fr. John P.J. and Vice Principal Dr. Sr. Sonia Kurien for their immense support and blessings. I thank our HOD Dr. Amit Kumar Nag for his support. I would like to express my special thanks of gratitude to my research guide Dr. Swapna Pillai, Associate Professor of Department of Commerce for her valuable suggestions and guidance and for giving me the golden opportunity to do this wonderful research project on the topic: CONSUMER BUYING BEHAVIOUR TOWARDS INSTANT FOOD PRODUCTS. Without her help it would have been difficult for me to have reached this state of completion of my project report. Also, I would like to thanks my parents and friends who helped me a lot in the preparation of this project. I wish to acknowledge the help of those who have provided me information, guidance and other help during my research period. TABLE OF CONTENTS CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION OF THE TOPIC 1.1 Rationale of the Study 1.2 Introduction to the Industry 1.3 Introduction to the Company 1.4 Justification of the Topic CHAPTER 2: REVIEW OF LITERATURE 2.1 International Reviews 2.2 National Reviews CHAPTER 3: RESEARCH METHADOLOGY 3.1 Objectives of the Study 3.2 Research Hypothesis 3.3 Scope of the Study 3.4 Data Collection CHAPTER 4: DATA REPRESENTATION & ANALYSIS 4.1 Data Representation & Interpretation 4.2 Hypothesis Testing CHAPTER 5: RESULTS & DISCUSSIONS 5.1 Major Findings 5.2 Discussions & Suggestions 5.2.1 Discussions 5.2.2 Suggestions 5.3 Conclusions REFERENCES ANNEXURE CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION TO THE TOPIC 1.1 RATIONALE OF THE STUDY The study has been conducted to understand the consumer buying behavior towards instant food products. With globalization and modernization, the modern competitive business is based on understanding the best products and services that consumer wants. Instant food products occupy a legitimate shelf space in stores and super markets in India. New and high quality of instant food products have changed the life style of people and led to more number of Indian companies enter the market with varities of instant food products. The present research highlights the study of consumer behavior regarding instant food products among the consumers. an attempt has been made to analyse the consumer purchasing frequency for the instant food products. Further efforts have also been made to know the consumer awareness towards products and to analyse factors influencing the instant food products. The word 'food' refers to the chemical substances consumed by individuals in order to keep their body in a healthy and active condition. The human body requires food for growth, repair and replacement of its worn-out tissues. Hence, food has to provide the required raw material, energy and other substances, like vitamins and for the smooth functioning of the body, besides meeting the calorific requirements like carbohydrates, proteins, fats, etc., India is the world’s second largest producer of food next to China and deemed to be potential of being biggest industry with food and agricultural sector contributing 32 per cent to Indian GDP. 1.2 INTRODUCTION TO THE INDUSTRY The food industry is a complex, global network of diverse businesses that supplies most of the food consumed by the world's population. The term food industries covers a series of industrial activities directed at the production, distribution, processing, conversion, preparation, preservation, transport, certification and packaging of foodstuffs. The food industry today has become highly diversified, with manufacturing ranging from small, traditional, family-run activities that are highly labor-intensive, to large, capital-intensive and highly mechanized industrial processes. Many food industries depend almost entirely on local agriculture, produce, or fishing. Food is an essential part of our lives. The food industry is the basic and important to every nation. It is one of the seventeen national critical sectors of US economy. It plays a crucial role in public health, food safety, food security, social development, and nutrition. Product quality, health, and sanitation issues are major concerns in the food industry. In India, the food sector has emerged as a high-growth and high-profit sector due to its immense potential for value addition, particularly within the food processing industry. It is challenging to find an inclusive way to cover all aspects of food production and sale. The UK Food Standards Agency describes it as "the whole food industry – from farming and food production, packaging and distribution, to retail and catering”. The Economic Research Service of the USDA uses the term food system to describe the same thing, stating: "The U.S. food system is a complex network of farmers and the industries that link to them. Those links include makers of farm equipment and chemicals as well as firms that provide services to agribusinesses, such as providers of transportation and financial services. The system also includes the food marketing industries that link farms to consumers, and which include food and fiber processors, wholesalers, retailers, and foodservice establishments." Most food produced for the food industry comes from commodity crops using conventional agricultural practices. Agriculture is the process of producing food, feeding products, fiber and other desired products by the cultivation of certain plants and the raising of domesticated animals. The food industry has a large influence on consumerism. Organizations, such as The American Academy of Family Physicians (AAFP), have been criticized for accepting monetary donations from companies within the food industry, such as Coca-Cola. These donations have been criticized for creating a conflict of interest and favoring an interest such as financial gains. The Indian food processing industry accounts for 32 per cent of the country’s total food market, one of the largest industries in India and is ranked fifth in terms of production, consumption, export and expected growth. It contributes around 8.80 and 8.39 per cent of Gross Value Added (GVA) in Manufacturing and Agriculture respectively, 13 per cent of India’s exports and six per cent of total industrial investment. Instant food products play a vital role in every human in his day–to-day life. The present study gives an insight into important factors creating awareness and purchasing frequency of the product. The online food ordering business in India is in its nascent stage, but witnessing exponential growth. With online food delivery players like FoodPanda, Zomato, TinyOwl and Swiggy building scale through partnerships, the organised food business has a huge potential and a promising future. The online food delivery industry grew at 150 per cent year-on-year with an estimated Gross Merchandise Value (GMV) of US$ 300 million in 2016. The food industry is the largest industry in the world, which are the complex, collective of so many businesses that contribute the supply of the food energy for world population. 1.4 INTRODUCTION TO THE COMPANY With liberalization, privatization, globalization and modernization, the modern competitive business is based on understanding the best products and services that he wants. Considering the truth that the consumer is the king , every organization wants to increase market share and profit . the competitors are also following the same strategy. It involves the psychological processes that consumers got through in recognizing needs, finding ways to solve these needs, making purchase decisions , interpret information ,make plans and implement those plans by engaging in comparision shopping or actually purchasing a product . consumer behavior is one of the stimulating and challenging areas in marketing studies being a human activity focused on the products and services . understanding the behavior of the consumers is a great challenge. Instant food usually refers to precooked food that requires very little preparation prior to eating it. This often tends to include foods that are dehydrated and just require the addition of water to prepare. The marketing concept behind the idea of instant food is that people in fastpaced, mobile societies no longer have the time to cook and prepare food in the traditional manner, yet they still want meals that are nutritious and taste good. Convenience food labeled as instant food is an attempt to satisfy this need, while being palatable enough so that consumers will choose them over foods that require the use of recipes and cooking. Ready-made food sometimes has the reputation of being expensive and loaded with preservatives, additives, and other potentially harmful fillers, food colors, and so on, which can give it a negative image in the mind of the consumer when shopping for groceries. Among the easiest category of instant food to produce and package are grain-related products, such as noodles, flavored oatmeal, breakfast cereals, and more. This is because these foods are naturally stored in airtight, dry conditions to preserve their quality, and usually require nothing more than the addition of hot water or milk to quickly prepare. Dehydrated potatoes are another widely popular instant food that just require the addition of hot water, and they are often served in institutional settings for public school lunches, and in nursing or retirement homes where preparing potatoes in the traditional manner can be time consuming and impractical. Other types of common instant food products include drink mixes, such as instant coffee, tea and nutrition supplements for milk that add both flavor and vitamins. Instant coffee requires no preparation in a standard coffeemaker, and can be ready to drink in less than a minute with water heated for it in a microwave, as can tea and other hot drinks, such as cocoa or powdered fruit-flavored drink mixes resembling orange and other juices. One other broad category of instant foods is that of the TV dinner, a prepackaged dinner usually containing all the standard elements of a traditional dinner such as meat, vegetables, and some sort of dessert, pasta, or grain product. Unlike olden days where man used to have his food lavishly and slowly, the present trend changed the food habits for those which are simple and easy to digest. Hence, the existence of these food fulfilled the needs of modern human being. Canned food, convenience food, fast food, frozen food, instant products, dried food, preserved food, all comes under instant food. The standard of living is also changing due to rise in income level, influence of western countries, more global trade and traveling. Hence, people are changing their taste to instant food as compared to the old traditionally prepared food. Instant foods are convenience foods which require minimal preparation, typically just adding water or milk. Some authors define "instant" food as requiring less than five minutes of preparation and "ultra-instant food" as requiring less than one minute. Instant foods are often dehydrated, freeze-dried, or condensed. In India, majority of food consumption is still at home. Homemade food products get special attention from customers. Nevertheless, outof-home food consumption is increasing due to increase in urbanization, breaking up of the traditional joint family system, desire for quality, time which translates into an increased need for convenience, increasing number of working women, rise in per capita income, changing lifestyles and increasing level of affluence in the middle income group had brought about changes in food habits. The Instant food products, which originated in Japan with Instant noodles had its beginning in India in 80’s, are found today in the kitchen shelves of every Indian household. The advancement of science and technology offered the people new foods processing vessels, equipment and tools but still people are in search of new techniques to speed up the cooking process in order to cope up with mechanical life, as they do not have sufficient time to cook food in the conventional methods. In the ever changing socio-domestic scenario, both men and women have to necessarily go for employment to augment the household income and cooking food in traditional methods is really an ordeal for women. Capitalizing this situation, business houses ranging from small time manufactures to multinational corporation shave started innovating and commercializing “easy to cook food items” like noodles, vermicelli, gulab jamun, instant idli, vada, dosa mix, etc., that are otherwise called instant. The instant food products are not only easy to cook but also have a significant role and place in the celebration of the family functions and religious functions of the people. 1.4 JUSTIFICATION OF THE TOPIC In the modern days, where the life is at fast pace with the time very valuable to every person, "Instant Foods" play an important role in everyone's day-to-day life. The very term 'instant food' means simple, fast and convenient food, which is easy and fast to prepare besides being hygienic, free from microbial contamination and also convenient to eat. Unlike olden days where man used to have his food lavishly and slowly, the present trend changed the habits to foods, which are simple and easy to digest. Hence, the existence of these foods fulfilled all the needs of modern human being. Preparing food with instant mixes has become a way life and no doubt they are going to be an integral part of food habit in future. Canned foods, convenience foods, fast foods, frozen foods, instant products, dried foods, preserved foods, etc. all come under instant foods or ready-to-eat foods. The food habits in India have changed due to the Western influence and the usage of these foods is also on the rise. These foods are widely used in catering industries as well as at homes. There are varieties of instant/ready-to-eat foods available in the market to choose from and they have become apart of every day life. It is a food revolution that's been a long time coming. As double-income nuclear families become the norm in urban India, everyone who is anyone in the food business has been eyeing the readyto-eat food sector with considerable hunger. Among the processed food segment, instant food products occupied a considerable shelf space in stores and super markets in India. Food companies through instant food products had provided high quality food choices, which would have been inconceivable to ancestors. Instant food mixes formed a range of convenience food for households, being easy to use without terminal processing and women found it very convenient to use. It helped them to save time and effort and relieved them of the tedious jobs of collecting various ingredients, cleaning and sorting them and preparing food. Modern homes also do not offer the facilities necessary for traditional processing and hence these products gained instant acceptance. These instant mixes can be used for preparations of various snack foods, sweets and preparations with rice. The instant mix market in India was approximately Rs.150 crore during the year 2003 and at the end of 2004, it was around Rs.350 crore. And by March2007 the size of the Indian Ready to eat market was approximately Rs.600700million(Indian television.com. March 10, 2007). Generally, food is prepared depending on the habits, tastes, social status, economic factor, availability, traditions, habitats, etc., of the people of that region. The most sought after in the present age are the instant/ready-to-eat foods. They are very popular in the Western region of the world. Even India is being influenced by these instant foods. CHAPTER 2 REVIEW OF LITERATURE 2.1 INTERNATIONAL REVIEW Jorin (1987) examined changes in spending power and buying habits of Swiss consumers since the beginning of the 20th century and in the more recent past. Current trends include greater emphasis on health and safety of foodstuffs and less attention to prices increased demand for low calorie light products and increased demand for organically grown foods. For young people, more concern with enjoyment and less for health, with more meals eaten away from home, and generally an increased demand for convenience foods. The prospects for high quality branded products are seen to be good. Sabeson (1992) in his study stated that, high quality, price and taste of the product were the major criteria based on which the consumers selected a brand of processed fruits and vegetable products. Rees (1992), in his study revealed that factors influencing the consumer’s choice of food are flavour, texture appearance, advertising a reduction in traditional cooking, fragmentation of family means and an increase in ‘snacking’. etc. Demographic and household role changes and the introduction of microwave ovens have produced changes in eating habits. Vigorous sale of chilled and other prepared foods is related to the large numbers of working wives and single people, who require and value convenience. Development in retailing with concentration of 80% of food sales in supermarkets is also considered to be important. Consumers are responding to messages about safety and health eating. They are concerned about the way in which food is produced and want safe, ‘natural’, high quality food at an appropriate price. Mergos and Donatos (1989) applied the “Almost Ideal Demand System” model for annual food expenditure in Greece for the period from 1950-1986. The empirical results showed that milk had an income elasticity of 0.76, which was the highest. The demand for milk, dairy products and eggs was high and had a rather stable food budget share. Meat had acquired a dominant position as indicated by its fourfold increase in quantity, but had low price elasticity. Gluckman (1986) studied the factors influencing consumption and preference for wine. The explicit factors identified were, the familiarity with brand name, the price of wine, quality or the mouth feel of the liquid, taste with regards to its sweetness or dryness and the suitability for all tastes. Some of the implicit factors identified through extensive questioning were, colour and appearance. Most consumers seemed to prefer white wine to red. Packaging, appearance, colour, ornateness, use of foreign language and graphics were taken as important clues for quality and price. Consumers preferred French or German made wines to Spanish or Yugoslavian wines. Yee and Young (2001), aimed to create awareness of high fat content of pies, studied consumer and producer awareness about nutrition labeling on packaging. For this, seven leading pie brands were analyzed for fat content and are ranged from 7.1 to 19.2% fat. Potato topped or cottage pies had the lowest fat content (7.19.2% fat). Most pies did not display nutritional labeling on packaging. Over half of the consumers (52%) who responded to the survey (42% response rate) were aware of the campaign. The study was successful at raising consumer awareness about the high fat content of pies and influencing the food environment with a greater availability of lower fat pies. It is possible to produce acceptable lower fat pies and food companies should be encouraged to make small changes to the fat content of food products like pies. Potato topped pies are lower in fat and are widely available. Regular pie eaters could be encouraged to select these as a lower fat option. Prell et al.(2002) conducted a study to examine the factors influencing adolescents' fish consumption in school. Fish consumption was assessed by observation on 4 occasions. Attitudes towards the fish, friends' behaviour and perceived control were important predictors of the intention to eat fish and barriers for fish consumption were a negative attitude towards both smell and accompaniments and fear of finding bones. But the eaters of fish were more satisfied with the taste, texture and appearance of the fish and rated safety significantly higher than those who resisted. They also thought to a greater extent that the fish was healthy and prepared with care. The results suggested that, it is important to alter dishes so that they appeal to children and to pay attention to the whole meal, accompaniments included. Finally it was recommended to convey the pupils that the fish served would be healthy and prepared with care. White (2001) examined the factors motivating US specialty food and beverage buyers to make purchases via the Internet. More than half (55.6%) of the respondents who purchased items available locally and 39% of the respondents who purchased items that were not available locally cited convenience as a motivator. Nearly one-third of all respondents indicated that their purchase was motivated by product-related factors, such as, brand loyalty, previous experience with a retailer, product selection, perceived quality and/ product experimentation. Price was of relatively little importance to respondents, with 22% citing it as a purchase motivator. Kamenidou (2002) presented the findings on the purchasing and consumption behaviour of Greek households towards three processed peach products: canned peaches in syrup, juice and peach jam. The results revealed that 47.5% of the households purchased canned peaches in syrup, 67.4% purchased peach juice and 42.6% purchased peach jam. Reasons for such purchase were satisfactory taste and qualities and households' perception that they are healthy products. The results also indicated that the consumption quantities were considered low, while households usually purchased the same brand name, meaning that there is a tendency for brand loyalty. 2.2 NATIONAL REVIEWS Indumathi et al.(2007) in their study have revealed that occupation of the women, income of the family and saving time while cooking are the most influencing factors of spicy products. The authors say that most of the consumers have purchase 200 gm pack of powders and masala, while small number of consumers prefer 100 gm packets. Kamalareni and nirmala (1996) in their study, have portrayed that most of the instant food products. Most of the consumers regularly purchase at least three varieties of food items and they suggest that the door to door distribution of free sample is used as a main tool of sales promotion by the instant food product manufactures. Kumar et al(1987) examined various factors influencing the purchasing decision making of different food products. Origin and brand of the products were cross-tabulated against age, gender and income. Results revealed that age, education and income were the singnificant factors influencing in buying decision. Consumers were attracted by the brand image than the origin of the product. Ramasamy et al (2005) have concentrated on the buying behaviour that is vastly influenced by awareness and brand image towards the product. Television advertisement is the most important source of information followed by display in retail outlets. Based on the opinion of consumers accept, quality and price of the product as an important factor to purchase. Ranjith kumar (2007) concluded that the advertisement influences product purchase for a non-durable product like masala powder, the main factor is the quality. Consumers get more awareness and influence from the advertisements. As there is an option for home made preparation of masala powder, the marketers should be highly competitive without sacrificing the quality of the product. Saritha Bahl (2012) has develope a model to understand the determinants of consumer behaviour regarding buying decision. The frequency of consumer’s shopping for food products has been analysed among different occupations. Efforts have been taken to know the attitude of the consumers towards food product labels and their perception about food safety which has also analysed. Ragavan (1994) reported that, quality, regular availability, price, accuracy in weighing and billing, range of vegetables and accessibility as the factors in the order of importance which had influenced purchase of vegetables by respondents from modern retail outlet. The study undertaken by Sheeja (1998) in Coimbatore district considered the quality aspects like aroma, taste, freshness and purity as the major factors deciding the preference for a particular brand of processed spices. Amitha (1998) studied the factors influencing the consumption of selected dairy products in Bangalore city. The results of the study revealed that, income and price significantly influenced the consumption of table butter. Price had a negative impact and income a positive impact on consumption. Banumathy and Hemameena, M (2006) discussed in their study on brand preference of soft drinks in rural Tamil Nadu that using Garrets ranking technique, to rank factors influencing the soft drinks preferred by rural consumer. They found that, the product quality was ranked as first, followed by retail price. Good quality and availability were the main factors, which influenced the rural consumers of a particular brand of a product. Srinivasan (2000) reported that, consumer with higher educational level was found to consume more processed products. The quantities of processed fruit and vegetable products were consumed more in high-income group. The tolerate limit of price increase identified was less than 5%, any price change above this limit, would result in discontinuance of the use processed product. Consumers preferred processed products because of convenience of ready to eat form. Kamalaveni and Nirmala (2000) reported that, there is complete agreement betweenranking given by the housewives and working women regarding the reasons promoting themto buy Instant food products. Age, occupation, education, family size and annual income hadmuch influence on the per capita expenditure of the Instant food products. CHAPTER 3 RESEARCH HYPOTHESIS 3.1 OBJECTIVE OF STUDY The researcher has observed and evaluated consumer opinion and the growing demand for instant food products. The basic objectives of the systematic research are given below: To study the awareness about instant food products. To analyze the consumer purchasing frequency of instant food products. To know the media for selecting the instant food products. To find out the influencing factors on instant food products. To analyze brand loyalty for Instant Food Products. To estimate demand potential for Instant Food Products. 3.2 RESEARCH HYPOTHESIS A research hypothesis is an assumption that demonstrates the interpreted relationships among various possible factors. The hypothesized correlation coefficients are based on existing writings. Many such inferential statistics or methodologies can be used to confirm all such relationships. Based on the success of regression techniques, these hypothesis may or may not be embraced. The following hypothesis was developed for testing in accordance with the study’s objectives: H1 Product related dimension is positively correlated with pre purchase evaluation H2 Regulatory dimension is positively correlated to the pre purchase evaluation H3 Lifestyle is positively correlated to the pre purchase evaluation H4 Consumer’s attitude towards instant food products is directly and positively correlated to the pre purchase evaluation H5 Pre purchase evaluation is directly and positively correlated to actual purchase behaviour. 3.3 SCOPE OF THE STUDY “Nothing is stable except change” in the modern days, life is changing fast time is very valuable to every person. Instant food products play a vital role in every human in his day –to-day life. The present study gives an insight into important factors creating awareness and purchasing frequency of the instant food products. The number of respondents has been limited to 50 as during the coronavirus pandemic, it was difficult to approach people physically owing to physical mobility constraints. Therefore, in order to collect responses from respondents, an online questionnaire was formulated and was circulated among respondents based in Bhopal. It was circulated to people who consume instant food products either on a regular basis or occasional and also to the people who don’t consume instant food -products. The time period selected for this survey and circulation of questionnaire was April,2021 during which the country was facing pandemic. Therefore, owing to lack of available resources, the scope of the study is limited in nature. 3.4 DATA COLLECTION GEOGRAPHICAL AREA: BHOPAL DURATION OF STUDY: 15 DAYS SAMPLE SIZE: 50 PEOPLE (DIFFERENT AGE GROUPS) SAMPLING TECHNIQUE: RANDOM SAMPLING TECHNIQUE POPULATION: It is the predefined set of potential elements or respondents in a geographical area. It is the aggregate of all the elements sharing some common set of characteristics that compromise the universe for the purpose of addressing the research problem. In this study, the universe for the present study shall constitute consumer who purchase instant foods products from different stores. SAMPLE: Sample is a subgroup of population selected for the participation of the study. In this study, a sub group of adults and millennial are taken into considerations. SAMPLE SIZE: It specifies the number of samples chosen from a target population. The sample size has been selected as 50 in order to include some more elements of the population. SAMPLING METHOD: The sample size of 50 respondents from Bhopal has been estimated by using random sampling technique. 3.4 LIMITATIONS OF THE STUDY Despite all sincere efforts to collect relevant information and data regarding this topic, there are some limitations to this study. Although the study is explanatory in nature, sample for the study is restricted to respondents in certain cities of India and the heterogeneous population could act as a limitation owing to demographic, sociographic and psychographic factors. The respondents were aged 15-80 years, as this age group wherein people have literacy regarding the food products they consume is good for health or not. The respondents cognitive biases, prejudices and preferences along with the respondent fatigue may have affected their decisions while filling out the questionnaire, which could have affected the quality of the study. Since there’s a large food market in India containing many sectors, all of the sectors could not be covered. So as to facilitate easy explanation and understanding of this study, the sector for research is limited to instant food products. This may also be viewed as a limitation to this study. The study area was limited to Bhopal district and the findings may not be applicable to other markets, as vast differences exist among the consumers with regard to demographic and psychographics characteristics. Further owing to the lockdown due to coronavirus pandemic, the number of respondents that could be approached was 50 as physical questionnaire could not be handed out. Time and money based restrictions also served as a limitation. CHAPTER 4 DATA REPRESENTATION AND ANALYSIS 4.1 DATA REPRESENTATION AND INTERPRETATION To evaluate the objectives of the study, required data were collected from primary sources. The data required for the study were collected from the selected respondents by circulating an online questionnaire. General information from the individual respondents on their social and demographic characteristics like age, educational status, occupation. 4.2 HYPOTHESIS TESTING The two major types of hypothesis are null and alternative. Null hypothesis states that there is no significant relationship between the two variables being studied and the results are due to chance and are not significant in terms of supporting the idea being investigated. Alternative hypothesis states that there is relationship between the two variables studied and that the results are not due to chance and that they are significant in terms of supporting the theory being investigated. Null Hypothesis (H0): There is no significant relationship between consumer perception of instant food products and their awareness regarding it. Alternative Hypothesis(H1): There is significant relationship between consumer perception of instant food products and their awareness regarding it. CHAPTER 5 RESULTS & DISCUSSIONS 5.1 MAJOR FINDINGS The research based on a primary survey of 50 people in Bhopal aimed at studying the consumers buying behavior and their perception and awareness towards instant food products. The findings from the research are: Among 50 respondents 58% were females and 42% are males. Among 50 respondents 34% belongs to (0-20) age group, 34% belongs to (21-40) age group, 22% belongs to (41-60) age group and 10% belongs to (61-80) age group. Among 50 respondents 54% were students, 20% were professionals and the rest 26% were house makers. Among 50 respondents 98% were aware about instant food products and 2% of respondents were not aware. Among 50 respondents 96% use to purchase instant food products and the rest 4% dosen’t purchase. Among 50 respondents 76% of people came to know about instant food products from the source of television whereas, 18% from neighbours and the rest of 6% came to know about it from other sources. Among 50 respondents, the quality factor was important to 96% of the people whereas to 4% it was not important. Among 50 respondents, 48% use to consume Maggie, 12% pickle, 16% gulabjamun and the rest 24% idlee. Among 50 respondents, 58% of people used to buy instant food products from supermarket, 22% from wholesale shop and the rest 20% from retail shop. 5.2 DISCUSSIONS & SUGGESTIONS (5.2.1) DISCUSSIONS An attempt has been made to analyse the consumer purchasing frequency for the instant food products. Most of the people like to eat foods which are easy to prepare. Due to the development of Retail sector many ready to eat foods are Noodles, vermicelli etc., India is one of the most Instant Food production in the World. In next ten years total food production in India will likely to double the total production. Demand for Instant Food products will increase due to the changes in urbanization, food habits, and traditions. After compiling data it is been disclosed that awareness about the complete range of instant food product available in the market mostly attracts the teenagers and housemakers. Most of the instant food products are sold in supermarkets. Retail and wholesale shops are not keeping instant food products. Television is the major source of advertisement of instant food products as it can be clearly seen in the above data. (5.2.2) SUGGESTIONS Distribution of free sample would increase the sales promotion of instant food products. It can be seen that the price of the instant food products is very high and if the products are reasonably priced, sales would shoot up. Television advertisments significantly influence the consumers of instant food products. Hence, more and more TV advertisments will lead to an increase in the sales of products. The marketer need to take necessary steps to increase quality and taste so as to bring trust of consumers towards instant food products. The study revealed that in majority of the households women made the buying decisions of instant food products. Sales promotion should target this group. It was found that retailers and wholesalers are not keeping much products of instant food, so they should be given training and incentives to promote sales. There is a general perception among the consumers that Instant Food Products areexpensive than home made products, efforts must be made to overcome thisperception by propaganda and publicity. 5.3 CONCLUSIONS Consumer behavior is a stimulating sphere consisting of the consumers themselves. Consumption of increase of instant food products is due to increase in urbanization, breaking up of the traditional joint family system, time, convenience, changing lifestyles and increasing level of affluence in the middle income group. Noodles are found today in the kitchen shelves of every Indian household. all the respondents are aware of various instant food products. The ready availability, and saving of the time are the reasons for consuming instant food products. Food zones and supermarkets are the major source of purchase of instant food products. The consumer’s relationship with food and other everyday goods has changed dramatically, not only in the way products are purchased, but also in the way they are consumed. In India, majority of food consumption is still at home. Nevertheless, out-of-home food consumption is increasing due to increase in urbanization, breaking up of the traditional joint family system, desire for quality, time which translates into an increased need for convenience, increasing number of working women, rise in per capita income, changing lifestyles and increasing level of affluence in the middle income group had brought about changes in food habits. Hence, Instant Food Products came into light, which originated in Japan with Instant noodles and had its beginning in India in 80’s, are found today in the kitchen shelves of every Indian household. The advancement of science and technology offered the people new foods processing vessels, equipment and tools but still people were in search of new techniques to speed up the cooking process in order to cope up with mechanical life, as they do not have sufficient time to cook food in the conventional methods. Capitalizing this situation, business houses ranging from small time manufactures to multinational corporations have started innovating and commercializing “easy to cook food items” like noodles, vermicelli, gulabjamun, instant idli, vada, dosa mix etc… that are otherwise called instant. The instant food products are not only easy to cook but also have a significant role and place in the celebration of the family functions and religious functions of the people. “Instant food products which are prepared and packaged often in powdered form are required only the addition of a liquid as water or milk for final preparation” [Oxford Advanced Learners Dictionary]. Unlike olden days where man used to have his food lavishly and slowly, the present trend changed the habits to foods, which are simple and easy to digest. Hence, the existence of these foods fulfilled all the needs of modern human being. Canned foods, convenience foods, fast foods, frozen foods, instant products, dried foods, preserved foods, etc. all comes under instant foods or ready-to-eat foods. The food habitats in India have changed due to the Western influence and the usage of these foods is also on the rise. The instant mix market in India was approximately Rs.150 crore during the year 2003 and at the end of 2004, it was around Rs.350 crore and in March 2007 the size of the Indian ready to eat market is approximately Rs.600-700million (Indiantelevision.com. March 10, 2007). Since, with the rising income levels of the consumers and their changing tastes and preferences, the demand for instant food products is undergoing a change both in qualitative and quantitative terms. Though there are so many instant foods available in the market, their popularity is increasing in a slow pace especially in the rural markets due to lack of awareness compared to larger cities where they are widely available and are also more popular. Hence, in the present investigation, an attempt was made to examine the buying behavior, consumption pattern, factors influencing the buying behavior, brand loyalty, brand composition and also estimated demand potential for instant food products. REFERENCES Jorin, R., 1987, Consumer behavior is changing and offering new opportunities. Berater- Information. 26 (9) : 8-14 Sabeson, R., 1992, Consumer preference towards processed fruits and vegetable products- a case study in Coimbatore city. MSc (Agri) Thesis (unpublished) Tamil Nadu Agril Univ, Coimbatore. Rees, A. M., 1992, Factors influencing consumer choice. J. Society of Dairy Technology 45 (4): pp. 112-116. Mergos, G.J. and Donatos, G.S., 1989, Demand for food in Greece: An almost ideal demand system analysis. J. Agril Econ. 40 (2) : 178-184. Yee, J. and Young, L., 2001, A Public health approach to reducing the fat content of meat pies in Auckland. J. New-Zealand Dietetic Association. 55 (1) : 22-27. Prell, H., Berg, C. and Jonsson, L., 2002, Why don’t adolescents eat fish? Factors influencing fish consumption in school. Scandinavian. J. Nutrition. 4(4) : 184-191. White, G.K. and Manning, B.J., 2001, Convenience, price, product: motivators for online specialty food consumers. J. Food Products Marketing .7 (1/2) : 53-65 Kamenidou, L., Zimitra-kalogianni, L., Zotos, Y. and Mattas, K., 2002, Household purchasing and consumption behavior towards processed peach products. New-Medit . 1 (1) : 45-49 Indumathi. V.M S. D. Sivakumar, N. Raveendaran, P. Balaji- consumer buying behavior of process sed spice products- Indian journal of marketing august(2007).PP 52-55. Kamalaveni, D. and Nirmala., 2000, Consumer behavior in instant food products. Ind. J.Marketing . 30 (5-7) : 12-18 Kumar, K., Ambarish, Jordan, B.B. and Barker Tansu, A., 1987, Made in India, what it means to Indian consumers? Ind. J. marketing . 17 (9) : 26-34. Ramasamy, K., Kalaivanan, G., and Sukumar, S., 2005, Consumer behavior towards instant food products. Ind. J. marketing. 35 (6) : 2425. R.Renjith Kumar, An evaluation of television advertisements of masala powder in Pollachi (tamil nadu). Indian journal of marketing. April , 2007. PP 13-99. Dr.Sarita Bahl. Consumer behavio r towards food retailing system a journal of economics and managements vol.1 issue 4,July 2012. Ragavan, R., 1994, A study on the consumer response towards franchise vegetable outlets-A case of Just picked, (Unpublished.). M.Sc. (Agri) Thesis, Tamil Nadu Agril. Univ, Coimbatore. Sheeja, A., (1998). An Analysis of Consumer buying behavio r towards processed spices. M.sc(Agri) Thesis. Tamil Nadu Agril. Univ. Coimbatore. Amitha, K., 1998, A study of household consumption pattern of selected dairy products in Bangalore city. MSc (Agri) Thesis, (unpublished). Univ. Agric. Sci. Bangalore. Banumathy, S. and Hemameena, M., 2006, Analysis of brand preference of soft drinks in the global environment. Ind. J. Marketing, 36(6) : 12-16. Srinivasan, N. and Elangovan, D., 2000, Consumer perception towards processed fruits and vegetable products. Ind. J. Marketing. 30 (11-12) : 22-25. D.Kamalaveni and M.Nirmala (1996), consumer behavior in instant food products. Indian journal of marketing. PP 12-8. https://www.academia.edu/6533488/A_STUDY_ON_BUYING_BEH AVIOUR_OF_CONSUMERS_TOWARDS_INSTANT_FOOD_PRO DUCTS_IN_KOLAR_DISTRICT_Thesis_submitted_to_the_Univers ity_of_Agricultural_Sciences_Dharwad_in_partial_fulfillment_of_the _requirement_for_the_Degree_of_MASTER_OF_BUSINESS_ADMI NISTRATION_In_AGRIBUSINESS_MANAGEMENT https://www.indianjournals.com/ijor.aspx?target=ijor:jims8m&volum e=18&issue=4&article=004 http://iosrjournals.org/iosr-jbm/papers/Vol16-issue11/Version3/C0161131721.pdf ANNEXURE Gender Male Female Age 0-20 21-40 41-60 61-80 Occupation Student Professional House maker Are you aware of instant food products ? Yes No Do you p Purchase instant food products? Yes No From where you came to know about instant food products? Television Neighbors Others Is quality is an important factor to buy instant food products? Yes No Which instant food product do you buy the most? Maggie Pickle Gulab jamun Idli From where do you buy the instant food products? Supermarket Retail shop Wholesale shop