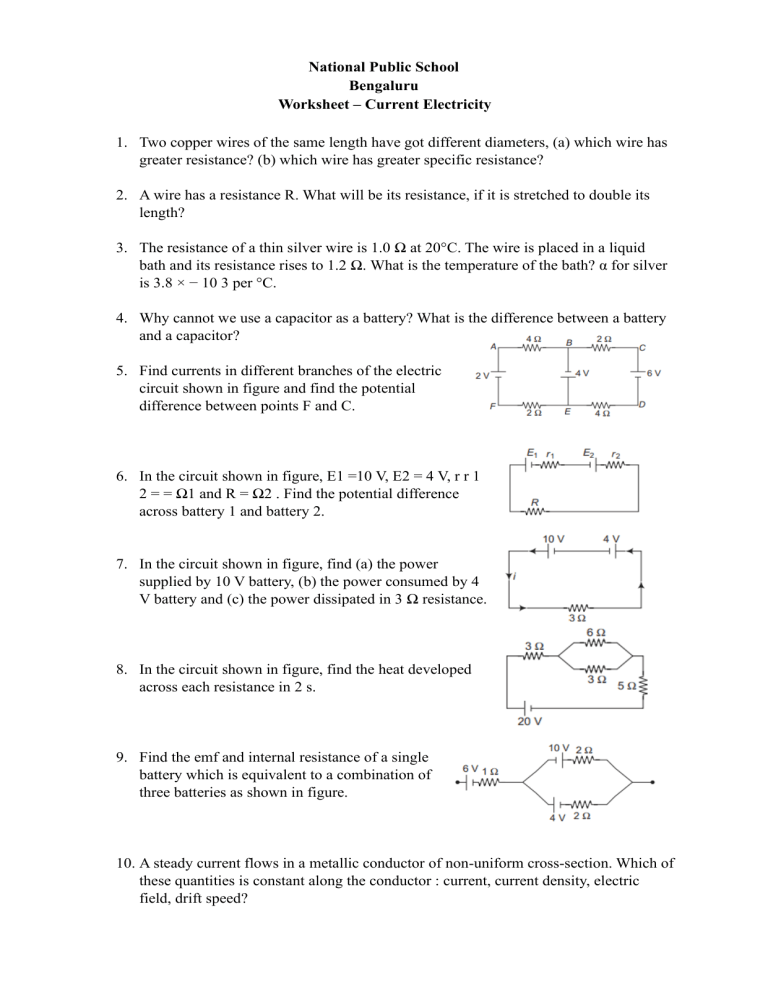
National Public School Bengaluru Worksheet – Current Electricity 1. Two copper wires of the same length have got different diameters, (a) which wire has greater resistance? (b) which wire has greater specific resistance? 2. A wire has a resistance R. What will be its resistance, if it is stretched to double its length? 3. The resistance of a thin silver wire is 1.0 Ω at 20°C. The wire is placed in a liquid bath and its resistance rises to 1.2 Ω. What is the temperature of the bath? α for silver is 3.8 × − 10 3 per °C. 4. Why cannot we use a capacitor as a battery? What is the difference between a battery and a capacitor? 5. Find currents in different branches of the electric circuit shown in figure and find the potential difference between points F and C. 6. In the circuit shown in figure, E1 =10 V, E2 = 4 V, r r 1 2 = = Ω1 and R = Ω2 . Find the potential difference across battery 1 and battery 2. 7. In the circuit shown in figure, find (a) the power supplied by 10 V battery, (b) the power consumed by 4 V battery and (c) the power dissipated in 3 Ω resistance. 8. In the circuit shown in figure, find the heat developed across each resistance in 2 s. 9. Find the emf and internal resistance of a single battery which is equivalent to a combination of three batteries as shown in figure. 10. A steady current flows in a metallic conductor of non-uniform cross-section. Which of these quantities is constant along the conductor : current, current density, electric field, drift speed? 11. Is Ohm's law universally applicable for all conducting elements? If not give examples of elements which do not obey Ohm's law? 12. Choose the correct alternative. (a) Alloys of metals usually have (greater/less) resistivity than that of their constituent metals. (b) Alloys usually have much (lower/higher) temperature coefficients of resistance than pure metals. (c) The resistivity of the alloy manganin is (nearly independent of/increases rapidly) with increase of temperature. (d) The resistivity of a typical insulator (e.g. Amber) is greater than that of a metal by a factor of the order of (1022 / 103) 13. A battery of emf E and internal resistance r is connected with an external resistance R. Draw (a) the current versus external resistance graph ( i - R graph ) (b) the current versus potential difference across the terminals of the battery graph (i – V) graph. 14. When a motor car is started then its head light becomes slightly dim. Explain why? 15. Distinguish between kilowatt and kilowatt-hour. 16. What is/are the material (s) used in (i) electric heater and (ii) fuse wire? 17. We have two bulbs one of 60W and other of 100W. (a) Which bulb has more resistance? (b) Which bulb will consume more power, if they are connected in parallel? (c) Which bulb will consume more power, if they are connected in series? 18. What is potential gradient? State its SI units. 19. Which one of the two, an ammeter or a milliammeter, has a higher resistance and why? 20. What would happen, if we connect an ammeter in parallel and a voltmeter in series in a circuit? 21. In the Bohr model of hydrogen atom, the electron is pictured to rotate in a circular orbit of radius 5 x 10-11 m , at a speed 2.2 ×106 m/s . What is the current associated with electron motion? 22. Copper has one conduction electron per atom. Its density is 8.89g cm/ 3 and its atomic mass is 63.54 g mol / . If a copper wire of diameter 1.0 mm carries a current of 2.0 A, what is the drift speed of the electrons in the wire? 23. In household wiring, copper wire 2.05 mm in diameter is often used. Find the resistance of a 35.0 m long wire. Specific resistance of copper is 1.72 × 10-8 Ω m. 24. An aluminium wire carrying a current has diameter 0.84 mm, the electric field in the wire is 0.49V m/ . What is, (a) the current carried by the wire? (b) the potential difference between two points in the wire12.0 m apart? (c) the resistance of a 12.0 m length of this wire? Specific resistance of aluminium is2.75 - × − 10 8 Ω m. 25. Find the current through 2 Ω and 4 Ω resistance. 26. In the circuit shown in figure, find the potentials of A, B, C and D and the current through 1Ω and 2 Ω resistance. 27. For what value of E, the potential of A is equal to the potential of B? 28. In the circuit shown in figure, a 12 V power supply with unknown internal resistance r is connected to a battery with unknown emf E and internal resistance 1Ω and to a resistance of 3 Ω carrying a current of 2 A. The current through the rechargeable battery is 1A in the direction shown in figure. Find the unknown current i, internal resistance r and the emf E. 29. The full scale deflection current of a galvanometer of resistance 1Ω is 5 mA. How will you convert it into a voltmeter of range 5V? 30. A micrometer has a resistance of 100 Ω and full scale deflection current of 50µA. How can it be made to work as an ammeter of range 5 mA? *************************************