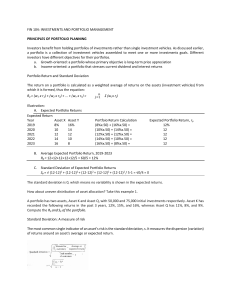
FINS2624: Final Exam FORMULA SHEET • The price of a bond, P is given by: 𝑃= 𝑐 1 𝐹𝑉 + [1 − ] 𝑦 (1 + 𝑦)𝑇 (1 + 𝑦)𝑇 Where c is the dollar coupon, y is the yield-to-maturity, T is the time to maturity and FV is the face value. • If X and Y are two random variables, 𝑎 and 𝑏 are constants o o o o o o o o o o • 𝐸(𝑎𝑋 + 𝑏) = 𝑎𝐸(𝑋) + 𝑏 𝐸(𝑋 + 𝑌) = 𝐸(𝑋) + 𝐸(𝑌) 𝑉𝑎𝑟(𝑋) = 𝐸[𝑋 − 𝐸(𝑋)]2 𝑉𝑎𝑟(𝑎𝑋 + 𝑏) = 𝑎2 𝑉𝑎𝑟(𝑋) 𝑉𝑎𝑟(𝑋 + 𝑌) = 𝑉𝑎𝑟(𝑋) + 𝑉𝑎𝑟(𝑌) + 2𝐶𝑜𝑣(𝑋, 𝑌) 𝐶𝑜𝑣(𝑋, 𝑌) = 𝐸(𝑋𝑌) − 𝐸(𝑋)𝐸(𝑌) 𝐶𝑜𝑣(𝑋, 𝑋) = 𝑉𝑎𝑟(𝑋) 𝐶𝑜𝑣(𝑎𝑋 + 𝑏, 𝑐𝑌 + 𝑑) = 𝑎𝑐𝐶𝑜𝑣(𝑋, 𝑌) 𝐶𝑜𝑣(𝑋 + 𝑌, 𝑃 + 𝑄) = 𝐶𝑜𝑣(𝑋, 𝑃) + 𝐶𝑜𝑣(𝑋, 𝑄) + 𝐶𝑜𝑣(𝑌, 𝑃) + 𝐶𝑜𝑣(𝑌, 𝑄) 𝐶𝑜𝑣(𝑋, 𝑌) = 𝜌𝑋,𝑌 𝜎𝑋 𝜎𝑌 Variance of portfolio returns: o 𝜎𝑃2 = 𝑉𝑎𝑟(𝑟𝑃 ) = 𝐶𝑜𝑣(𝑤𝐴 𝑟𝐴 , 𝑤𝐴 𝑟𝐴 ) + 𝐶𝑜𝑣(𝑤𝐵 𝑟𝐵 , 𝑤𝐴 𝑟𝐴 ) + 𝐶𝑜𝑣(𝑤𝐴 𝑟𝐴 , 𝑤𝐵 𝑟𝐵 ) + 𝐶𝑜𝑣(𝑤𝐵 𝑟𝐵 , 𝑤𝐵 𝑟𝐵 ) o 𝜎𝑃2 = 𝑤𝐴2 𝜎𝐴2 + 𝑤𝐵2 𝜎𝐵2 + 2𝑤𝐴 𝑤𝐵 𝜌𝜎𝐴 𝜎𝐵 • Optimal weight on risky portfolio: • 𝐸(𝑟𝑃∗ ) − 𝑟𝑓 1 𝐸(𝑟𝑃∗ ) − 𝑟𝑓 = ⋅ 2 2 𝐴 𝐴𝜎𝑃∗ 𝜎𝑃∗ Asset weights in optimal risky portfolio - two risky asset case: 𝑦∗ = 𝐸(𝑅1 )𝜎22 −𝐸(𝑅2 )𝐶𝑜𝑣(𝑅1 ,𝑅2 ) 2 2 1 )𝜎2 +𝐸(𝑅2 )𝜎1 −(𝐸(𝑅1 )+𝐸(𝑅2 ))𝐶𝑜𝑣(𝑅1 ,𝑅2 ) 𝑊1 = 𝐸(𝑅 • The Optimal weight, 𝑤𝐴∗ of the active portfolio A is: 𝑤0 where, 𝑤𝐴0 = 𝐴 𝑤𝐴∗ = 1+𝑤0 (1−𝛽 𝐴 • 𝑤ℎ𝑒𝑟𝑒 𝐸(𝑅𝑖 ) = 𝐸(𝑟𝑖 ) − 𝑟𝑓 𝐴) The optimal weight of an individual asset i in the active portfolio is: 𝑤𝐴,𝑖 = 2 𝛼𝑖 ⁄𝜎𝜖,𝑖 2 ∑𝑁 𝑗=1 𝛼𝑗 ⁄𝜎𝜖,𝑗 2 𝛼𝐴 ⁄𝜎𝜖,𝐴 2 [𝐸(𝑟𝑀 )−𝑟𝑓 ]⁄𝜎𝑀 • Black-Scholes pricing formula for European Call Options 𝑐𝑡 = 𝑆𝑡 𝑁(𝑑1 ) − 𝑋𝑒 −𝑟(𝑇−𝑡) 𝑁(𝑑2 ) where N() is the standard normal cumulative probability 𝑑1 = 𝑆 𝜎2 ln ( 𝑋𝑡 ) + (𝑟 + 2 )(𝑇 − 𝑡) 𝜎√(𝑇 − 𝑡) 𝑑2 = 𝑑1 − 𝜎√(𝑇 − 𝑡) Where, t refers to the current time point, T refers to the expiration; 𝑆𝑡 is the current price of the underlying asset; X is exercise price; r is continuously compounded risk-free rate; σ is return volatility of the underlying asset. NORMAL DISTRIBUTION TABLE