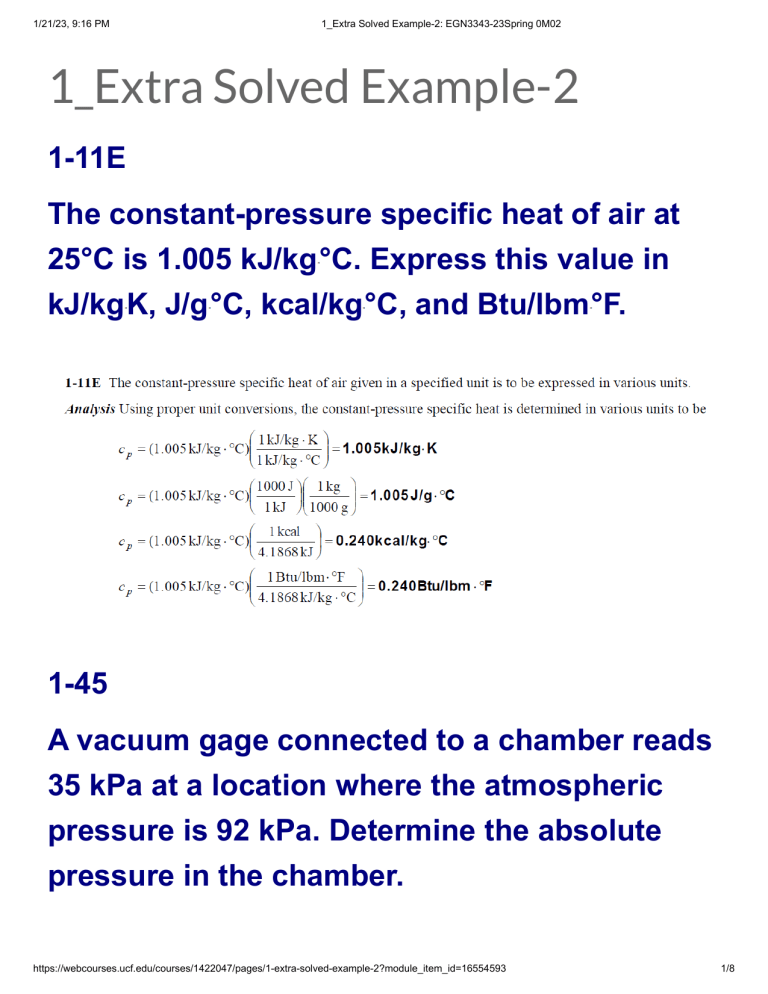
1/21/23, 9:16 PM 1_Extra Solved Example-2: EGN3343-23Spring 0M02 1_Extra Solved Example-2 1-11E The constant-pressure specific heat of air at 25°C is 1.005 kJ/kg°C. Express this value in kJ/kgK, J/g°C, kcal/kg°C, and Btu/lbm°F. 1-45 A vacuum gage connected to a chamber reads 35 kPa at a location where the atmospheric pressure is 92 kPa. Determine the absolute pressure in the chamber. https://webcourses.ucf.edu/courses/1422047/pages/1-extra-solved-example-2?module_item_id=16554593 1/8 1/21/23, 9:16 PM 1_Extra Solved Example-2: EGN3343-23Spring 0M02 1-46 The pressure in a compressed air storage tank is 1200 kPa. What is the tank's pressure in (a) kN and m units; (b) kg, m, and s units; and (c) kg, km, and s units? 1-49E A manometer is used to measure the air pressure in a tank. The fluid used has a specific gravity of 1.25, and the differential https://webcourses.ucf.edu/courses/1422047/pages/1-extra-solved-example-2?module_item_id=16554593 2/8 1/21/23, 9:16 PM 1_Extra Solved Example-2: EGN3343-23Spring 0M02 height between the two arms of the manometer is 28 in. If the local atmospheric pressure is 12.7 psia, determine the absolute pressure in the tank for the cases of the manometer arm with the (a) higher and (b) lower fluid level being attached to the tank. 1-73 Determine the pressure exerted on a diver at 45 m below the free surface of the sea. https://webcourses.ucf.edu/courses/1422047/pages/1-extra-solved-example-2?module_item_id=16554593 3/8 1/21/23, 9:16 PM 1_Extra Solved Example-2: EGN3343-23Spring 0M02 Assume a barometric pressure of 101 kPa and a specific gravity of 1.03 for seawater. Answer: 556 kPa 1-74 Consider a U-tube whose arms are open to the atmosphere. Now water is poured into the U-tube from one arm, and light oil (ρ = 790 kg/m3) from the other. One arm contains 70cm-high water, while the other arm contains both fluids with an oil-to-water height ratio of 4. Determine the height of each fluid in that arm. https://webcourses.ucf.edu/courses/1422047/pages/1-extra-solved-example-2?module_item_id=16554593 4/8 1/21/23, 9:16 PM 1_Extra Solved Example-2: EGN3343-23Spring 0M02 Figure P1-74 1-81 Consider the system shown in Fig. P1-81. If a change of 0.7 kPa in the pressure of air causes the brine–mercury interface in the right column to drop by 5 mm in the brine level in the right column while the pressure in the https://webcourses.ucf.edu/courses/1422047/pages/1-extra-solved-example-2?module_item_id=16554593 5/8 1/21/23, 9:16 PM 1_Extra Solved Example-2: EGN3343-23Spring 0M02 brine pipe remains constant, determine the ratio of A2/A1. Figure P1-81 https://webcourses.ucf.edu/courses/1422047/pages/1-extra-solved-example-2?module_item_id=16554593 6/8 1/21/23, 9:16 PM 1_Extra Solved Example-2: EGN3343-23Spring 0M02 1-90E https://webcourses.ucf.edu/courses/1422047/pages/1-extra-solved-example-2?module_item_id=16554593 7/8 1/21/23, 9:16 PM 1_Extra Solved Example-2: EGN3343-23Spring 0M02 What is the weight of a 1-kg substance in N, kN, kgm/s2, kgf, lbmft/s2, and lbf? Copyrights Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display. https://webcourses.ucf.edu/courses/1422047/pages/1-extra-solved-example-2?module_item_id=16554593 8/8




