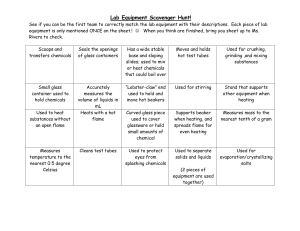
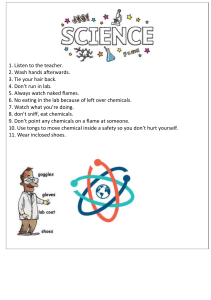
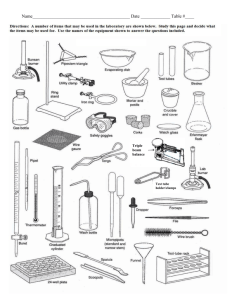
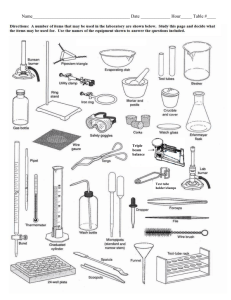
Laboratory Equipments Lab rules Do not eat food, drink beverages, or chew gum in the laboratory. 2. Safety goggles and lab coat must be worn whenever you work in the lab. Gloves should be worn whenever you use chemicals that cause skin irritations or when you need to handle hot equipment. 3. Know the locations and operating procedures of all safety equipment including the first aid kit, eyewash station, safety shower, spill kit, fire extinguisher, and fire blanket. Know where the fire alarm and the exits are located. 4. Notify the instructor immediately of any unsafe conditions you observe. 5. Dispose all chemical waste properly. Solid chemicals, metals, matches, filter paper, and all other insoluble materials are to be disposed of in the proper waste containers. 1. 7. Labels and equipment instructions must be read carefully before use. 8. Keep hands away from your face, eyes, mouth, and body while using chemicals. 9. Wash your hands with soap and water after performing all experiments. 10. If you spill acid or any other corrosive chemical on you skin or clothes, immediately wash the area with large amounts of water (remember that small amounts of water may be worse than no water at all). Test Tubes • -used for mixing, heating, and storing small quantities of chemicals. • – many different sizes Test Tube Rack • Racks made of wood, metal, or plastic - used for holding test tubes upright when they contain chemicals - also to hold test tubes upside down to dry. Test Tube Holder • Tongs used to hold and transport hot test tubes – Made of stainless steel or brass Beaker • used for mixing and heating chemicals DO NOT USE FOR MEASURING EXACT VOLUME. Conical Flask • used for mixing, heating and storing chemicals • Shape allows contents to be swirled without spilling and slows the rate at which contents cool. • DO NOT USE FOR MEASURING EXACT VOLUMES. Electronic Balance • Digital balance used to measure the mass of substances • very accurate and precise. Thermometer • Sealed glass tube containing a colored alcohol solution that is used to measure the temperature of a substance. Graduated Measuring Cylinder • Glass cylinders with many markings that are used to measure liquid volumes accurately. • Always use the smallest volume that can hold the volume you want to measure so that the measurement will be most accurate Burette • is used to measure and dispense liquid volumes accurately with decimal places. Volumetric Pipette • Glass tubes are used to measure small liquid volumes very accurately .– Some are straight tubes, while others have a bulb-shaped reservoir in the middle Volumetric Flask • used for preparing solutions and diluting chemicals • tear-drop shaped with a long cylindrical neck Dropper / graduated Pipette • A glass or plastic device consisting of a bulb and a stem that is used for transferring and dispensing small volumes of liquids. Bunsen Burner •Device used for heating chemicals and equipment Parts of burner • Barrel • Air holes • Collar • Gas jet • Gas tap • Base Two types of flame in Burner Luminous Flame Air holes are closed Non luminous Flame Air holes are opened Flame colour • Yellow flame • Blue flame Hotness • Not very hot • Very hot Visiblity • Visible • Invisible Use • For lighting • For heating Problem • Smoke is produced • No smoke is produced Hot Plate • used to heat chemicals instead of Bunsen burners when open flames are not appropriate in the laboratory (why?) Mortar and Pestle • Used to grind solid chemicals into smaller pieces so that they may dissolve or react with other chemicals more quickly. Forceps • Forceps (not "tweezers") are made of stainless steel and are used to handle small pieces of solid material. Evaporating Dish • thin-walled ceramic dish used to evaporate the liquid away from a small volume of solution – This is done to collect the solute that is dissolved in a solution. Scoop style spatula • Used to scoop (solid) chemicals and transfer them, and to scrape chemicals from containers, much like a spatula is used to scrape food from a bowl. Stirring Rod • Narrow glass rod used to stir mixtures and facilitate the pouring of liquids. – Glass is best because of its resistance to chemical reactivity. Retort Stand - is used to provide support for other lab equipment and a way of raising equipment above the work surface. Wire Gauze • A metal mesh screen with a ceramic fiber circle in the center that is used for supporting beakers and flasks when they are being heated with a Bunsen Burner Iron Ring • When attached to a ring stand, this device is used to support laboratory equipment above the work surface Crucible • Small ceramic dish (with a lid that is used to heat chemicals (usually solids) to high temperatures .– This may be necessary to dry a solid completely, or to initiate a reaction outside of solution. Clay Triangle • Used to support crucibles when heating them. • The triangle is set on top of an iron ring, and the crucible sits down in the center of the triangle. Clamp • A clamp used to provide stability and support for other equipment by attaching the equipment to a ring stand Funnel • Used for transferring liquids(sometimes powders) to containers with small openings, in order to prevent spills. Can also be used with filter paper in the process of filtration Crucible Tongs • Tongs are made of stainless steel or brass that are used for handling crucibles, evaporating dishes, and other hot objects. Wash Bottle • Most commonly used to store and dispense distilled water – Wash bottle can be used to dispense distilled water whenever it is needed in an experimental procedure, as well as to provide a final rinse when glassware is washed at the end of an experiment. Hazardous signs