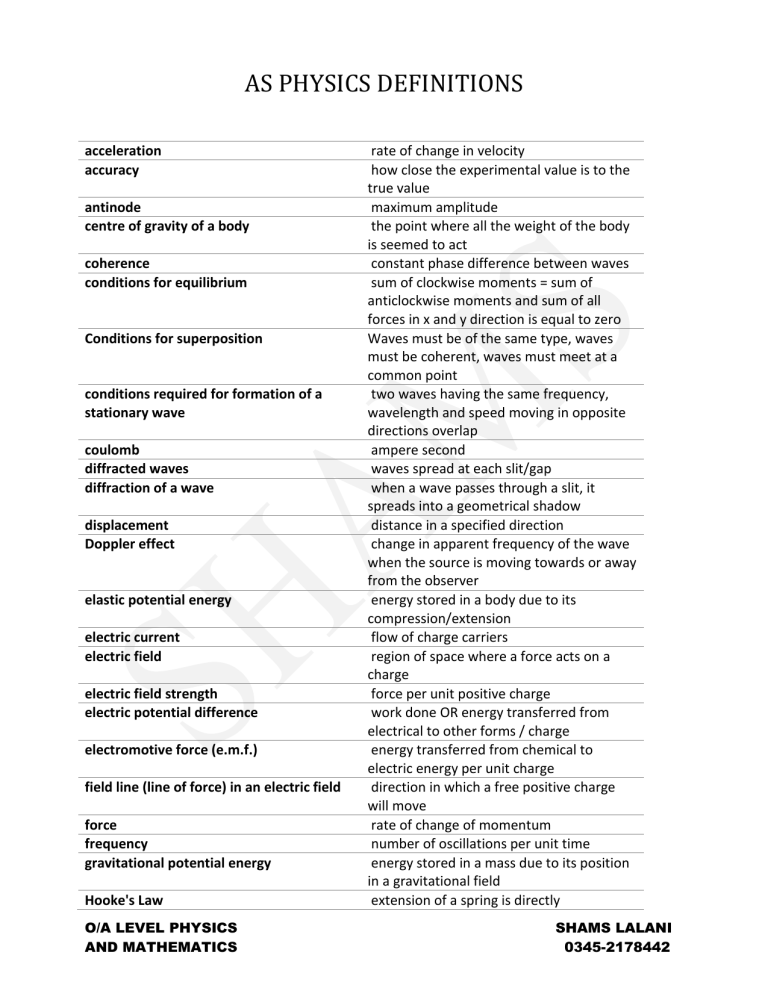
AS PHYSICS DEFINITIONS acceleration accuracy antinode centre of gravity of a body coherence conditions for equilibrium Conditions for superposition conditions required for formation of a stationary wave coulomb diffracted waves diffraction of a wave displacement Doppler effect elastic potential energy electric current electric field electric field strength electric potential difference electromotive force (e.m.f.) field line (line of force) in an electric field force frequency gravitational potential energy Hooke's Law O/A LEVEL PHYSICS AND MATHEMATICS rate of change in velocity how close the experimental value is to the true value maximum amplitude the point where all the weight of the body is seemed to act constant phase difference between waves sum of clockwise moments = sum of anticlockwise moments and sum of all forces in x and y direction is equal to zero Waves must be of the same type, waves must be coherent, waves must meet at a common point two waves having the same frequency, wavelength and speed moving in opposite directions overlap ampere second waves spread at each slit/gap when a wave passes through a slit, it spreads into a geometrical shadow distance in a specified direction change in apparent frequency of the wave when the source is moving towards or away from the observer energy stored in a body due to its compression/extension flow of charge carriers region of space where a force acts on a charge force per unit positive charge work done OR energy transferred from electrical to other forms / charge energy transferred from chemical to electric energy per unit charge direction in which a free positive charge will move rate of change of momentum number of oscillations per unit time energy stored in a mass due to its position in a gravitational field extension of a spring is directly SHAMS LALANI 0345-2178442 Intensity interference kinetic energy Kirchhoff's first law Kirchhoff's second law Law of conservation of energy linear momentum longitudinal wave mass moment of a force Moment of a couple Newton's first law of motion Newton's second law of motion Newton's third law of motion node ohm period power precision pressure principle of conservation of momentum principle of moments principle of superposition O/A LEVEL PHYSICS AND MATHEMATICS proportional to the force applied to it, provided that the limit of proportionality has not been reached Power per unit area sum of displacements of waves when they meet energy stored in a body due to its motion the sum of current flowing into a junction = sum of current flowing out of a junction (charge) sum of e.m.f. = sum of p.d. around a closed circuit (energy) Energy can neither be created nor destroyed, it can only be transformed from one form to another mass x velocity direction of propagation of energy is parallel to the direction of wave travel quantity of matter in a body force x perpendicular distance between the pivot and the line of force Two equal, anti-parallel forces acting at different parts produces a rotation an object stays at rest or at constant speed unless an external force acts on it force is proportional to rate of change in momentum force on body A is equal in magnitude and opposite in direction to the force on body B zero amplitude volt/ampere time taken for one complete oscillation work done per unit time the difference in the experimental values (range) force per unit area total momentum is constant, sum of momentum before = sum of momentum after in an isolated system for a body in equilibrium, the sum of clockwise moments is equal to the sum of anticlockwise moments when two or more waves meet at a point, resultant displacement is the sum of the individual displacements SHAMS LALANI 0345-2178442 quantised resistance scalar spontaneous strain stress transverse wave upthrust vector velocity Viscous drag volt wavelength work done young modulus O/A LEVEL PHYSICS AND MATHEMATICS charge only exists in discrete amounts voltage per unit current a quantity with a unit and magnitude rate of decay is not affected by external factors extension / original length force per unit area vibrations are perpendicular to the direction of propagation of energy Upward force caused by the pressure difference between top and bottom surfaces (always directed upwards) a quantity with unit, magnitude and direction change in displacement per unit time Resistance experienced by the object when it moves in the liquid (opposite to direction of motion) joule per coloumb distance between two successive in phase points OR minimum distance b/w two wavefronts force x distance moved in the direction of the force stress/strain SHAMS LALANI 0345-2178442





