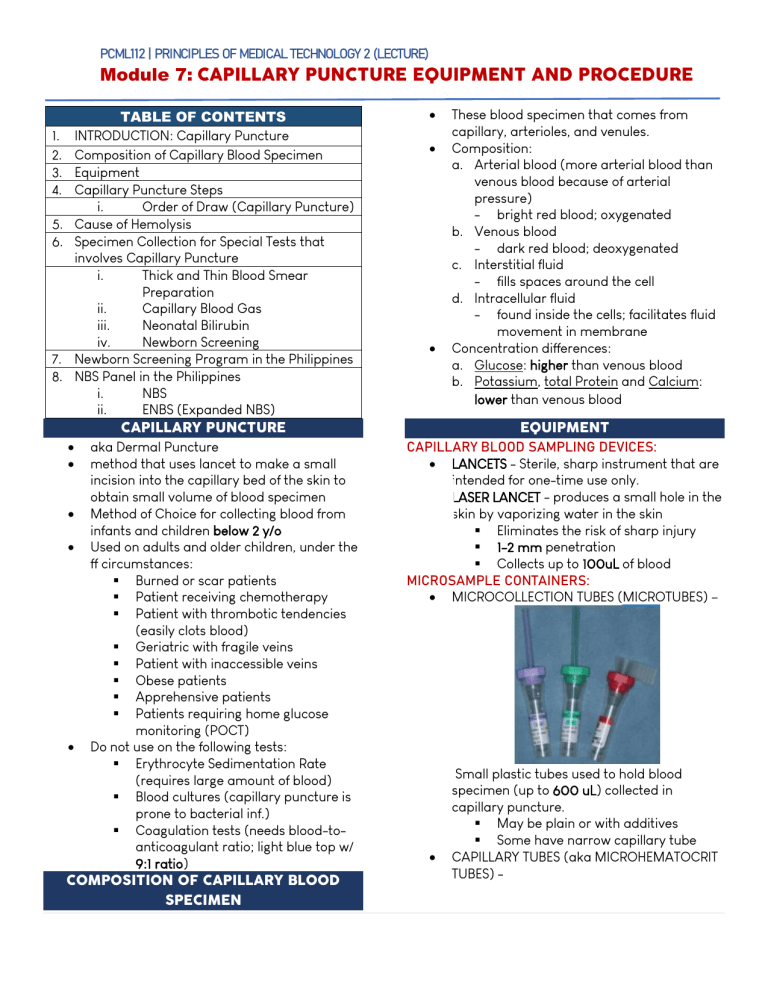
lOMoARcPSD|24136438 PCML112 | PRINCIPLES OF MEDICAL TECHNOLOGY 2 (LECTURE) Module 7: CAPILLARY PUNCTURE EQUIPMENT AND PROCEDURE TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. INTRODUCTION: Capillary Puncture 2. Composition of Capillary Blood Specimen 3. Equipment 4. Capillary Puncture Steps i. Order of Draw (Capillary Puncture) 5. Cause of Hemolysis 6. Specimen Collection for Special Tests that involves Capillary Puncture i. Thick and Thin Blood Smear Preparation ii. Capillary Blood Gas iii. Neonatal Bilirubin iv. Newborn Screening 7. Newborn Screening Program in the Philippines 8. NBS Panel in the Philippines i. NBS ii. ENBS (Expanded NBS) CAPILLARY PUNCTURE aka Dermal Puncture method that uses lancet to make a small incision into the capillary bed of the skin to obtain small volume of blood specimen Method of Choice for collecting blood from infants and children below 2 y/o Used on adults and older children, under the ff circumstances: Burned or scar patients Patient receiving chemotherapy Patient with thrombotic tendencies (easily clots blood) Geriatric with fragile veins Patient with inaccessible veins Obese patients Apprehensive patients Patients requiring home glucose monitoring (POCT) Do not use on the following tests: Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (requires large amount of blood) Blood cultures (capillary puncture is prone to bacterial inf.) Coagulation tests (needs blood-toanticoagulant ratio; light blue top w/ 9:1 ratio) COMPOSITION OF CAPILLARY BLOOD SPECIMEN These blood specimen that comes from capillary, arterioles, and venules. Composition: a. Arterial blood (more arterial blood than venous blood because of arterial pressure) - bright red blood; oxygenated b. Venous blood - dark red blood; deoxygenated c. Interstitial fluid - fills spaces around the cell d. Intracellular fluid - found inside the cells; facilitates fluid movement in membrane Concentration differences: a. Glucose: higher than venous blood b. Potassium, total Protein and Calcium: lower than venous blood EQUIPMENT CAPILLARY BLOOD SAMPLING DEVICES: LANCETS - Sterile, sharp instrument that are intended for one-time use only. LASER LANCET - produces a small hole in the skin by vaporizing water in the skin Eliminates the risk of sharp injury 1-2 mm penetration Collects up to 100uL of blood MICROSAMPLE CONTAINERS: MICROCOLLECTION TUBES (MICROTUBES) – Small plastic tubes used to hold blood specimen (up to 600 uL) collected in capillary puncture. May be plain or with additives Some have narrow capillary tube CAPILLARY TUBES (aka MICROHEMATOCRIT TUBES) - 1|ELANIE LADY A. MALABANA Downloaded by Roiselle Gamut (roisellegamut28@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|24136438 PCML112 | PRINCIPLES OF MEDICAL TECHNOLOGY 2 (LECTURE) Module 7: CAPILLARY PUNCTURE EQUIPMENT AND PROCEDURE - Small glass tubes used to collect capillary blood for the purpose of microhematocrit test (approx. 50-75 uL). Ends are sealed with clay sealant or plastic plug 2 Types (color-coded): a. Plain (blue band) - used when test is performed on blood from pre-collected EDTA blood. b. Heparinized (red band) - used when test is performed on blood collected from dermal puncture ; w/ Heparin which is an anticoagulant ADDITIONAL SUPPLIES: 1. MICROSCOPE SLIDES - used for blood films/smear for hematology/parasitology determinations 2. WARMING DEVICES - used to warm the puncture site to increase blood flow by 7folds HEEL WARMER - disposable packets containing sodium thiosulfate and glycerin that produce heat when mixed together by gentle squeezing. Warm washcloths/towel 3. CAPILLARY BLOOD GAS EQUIPMENT 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Special equipment used for collecting capillary blood gas specimens - Contains: collection tubes, stirrers, magnet, and plastic caps CAPILLARY PUNCTURE STEPS STEP 1-5 Review and check accession test request Approach, Identify and Prepare the patient Verify diet restriction and latex sensitivity Sanitize hands and put on gloves Position the patient: Patients arm should be placed on firm surface Arms extended, palm facing up Heel puncture - patient in supine position and foot in not lower than torso STEP 6: SELECT PUNCTURE SITE General criterion: site should be pink, normal in color, and warm. Heel Puncture Site Used on infants (≤ 1y/o) (not yet walking) For infants: incision site should be less than 2.0 mm deep 2|ELANIE LADY A. MALABANA Downloaded by Roiselle Gamut (roisellegamut28@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|24136438 PCML112 | PRINCIPLES OF MEDICAL TECHNOLOGY 2 (LECTURE) Module 7: CAPILLARY PUNCTURE EQUIPMENT AND PROCEDURE Acceptable Area: Lateral or Medial Plantar area - Distance between skin and calcaneus is the greatest Finger Puncture Site Used on adults and children (≥ 1y/o) Acceptable area: Central palmar area of third or fourth finger of nondominant hand STEP 7: WARMING THE SITE Dilates blood vessels and increase arterial blood flow for up to seven-folds. Warm washcloth/towel (42 C) for 3-5 mins Heel warmer - mix the packet to activate and place on the puncture site for 3-5 minutes Warming should not exceed 10 minutes ² may alter test results. - increases arterial blood flow hence, altering capillary blood composition that may affect the results STEP 8: Clean and air-dry the site Use antiseptics (ex. 70% isopropanol) STEP 9: Prepare equipment STEP 10: PUNCTURE THE SITE (quick and deep) Incision depth: 2 - 2.5 mm HEEL PUNCTURE: Hold heel between thumb (at bottom) and index finger (near the arch) Lancet is positioned in median/lateral plantar surface of heel FINGER PUNCTURE: Finger is held between the nondominant thumb and index finger, with the palmar surface facing up and the finger pointing downward to increase blood flow. Lancet placed flat against central fleshy part of site STEP 11: Wipe the first drop of blood Contaminated with tissue fluids (can dilute the blood and may alter the results) STEP 12: FILL AND MIX TUBES ORDER OF DRAW (Capillary puncture) Important as platelet has tendency to accumulate at the site of wound ORDER OF DRAW ADDITIVES INVERSION/MI XING Capillary Blood Gas Heparin Rotate between palms Blood Smears N/A (placed N/A in glass slides) Lavender top EDTA 10 Heparinized Lithium 10 Heparin No Inversion if Green top microhemato Microhemat crit tube ocrit tube w/ red band Plasma Separator Lithium 10 Tubes heparin with gel separator Oxalate/Fluoride Sodium 10 Tubes fluoride with Potassium oxalate Serum tube with Clot 5 additives activator Serum tube without N/A 0 additive Newborn Screening Use 0 spot/filter cards STEP 13: Place gauze and apply pressure ‡ Keep incision site elevated (so that the blood flow diminishes) 3|ELANIE LADY A. MALABANA Downloaded by Roiselle Gamut (roisellegamut28@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|24136438 PCML112 | PRINCIPLES OF MEDICAL TECHNOLOGY 2 (LECTURE) Module 7: CAPILLARY PUNCTURE EQUIPMENT AND PROCEDURE STEP 14: Label specimen and observe proper handling STEP 15: Check the site and apply bandage STEP 16: Disposal of used and contaminated materials STEP 17: Transport specimen to the Laboratory CAUSE OF HEMOLYSIS Hemolysis is more frequently encountered in capillary puncture than in venipuncture. Milking - excessive squeezing of puncture site. Newborn have increased RBC and increased RBC fragility Residual alcohol at the puncture site Vigorous mixing of microcollection tubes after collection SPECIMEN COLLECTION FOR SPECIAL TESTS THICK AND THIN BLOOD SMEAR PREPARATION Thin blood smear preparation is used to appearance of blood cells for diagnostic purposes: Blood cell abnormalities Identification and differential quantification of WBC (manually counting of eosinophils, neutrophils etc.) Platelet estimate count Malaria parasite identification Procedure: 1. Place one drop of blood near one end of a glass slide 2. Use another slide to spread the drop of blood into thin smear 3. Air dry then stain. Thick blood smear preparation is used for quantitative malaria determination (counting of the parasite) Procedure: 1. Place one drop of blood on the center of the slide 2. Place a drop of water and mix 3. Allow to air dry then stain CAPILLARY BLOOD GAS Arterial blood - preferred sample for blood gas analysis and pH determination Capillary blood is only used among newborns and infants. Arterialize capillary blood by warming the site prior to collection (40-42 C) for 5minutes Microcollection tube: Heparinized Sample are place in ice slurry and transported to the laboratory immediately. - ice slurry – prevents changes in pH and deterioration of blood gases NEONATAL BILIRUBIN to determine any liver disorder in infants. Collected with a heel stick. BILIRUBIN a light sensitive analyte that imparts dark yellow discoloration in the blood, skin and eyes. decreases concentration w/ presence of light Commonly performed among newborn Bilirubin is critical for infant survival and mental health - can easily accumulate in the brain since newborns’ brain barrier are still underdeveloped HYPERBILIRUBINEMIA (newborn) – Jaundice Hemolytic disease of the newborn Underdeveloped liver of premature newborns Microcollection tubes: a. Amber-colored tubes 4|ELANIE LADY A. MALABANA Downloaded by Roiselle Gamut (roisellegamut28@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|24136438 PCML112 | PRINCIPLES OF MEDICAL TECHNOLOGY 2 (LECTURE) Module 7: CAPILLARY PUNCTURE EQUIPMENT AND PROCEDURE b. Covering tubes with carbon paper. NEWBORN SCREENING part of routine check for infants to determine inborn disorders such as phenylketonuria, hypothyroidism, galactosemia, cystic fibrosis. Testing of newborns for: a. genetic b. metabolic c. hormonal, and d. functional disorders that may cause physical disabilities, mental retardation, or even death, if not detected early (24 to 48 hours after birth) Presently, up to 50 inherited disorders can be detected but only common disorders are usually performed Blood is collected by heel prick and placed on a special filter paper. NBS should be done immediately after 24 hours of birth Types of NBS in the Philippines NBS EXPANDED NBS (ENBS) Panels 6 disorders ≥ 28 disorders Standardized P550 to 600 P1750 to 1800 price Philhealth Until May 2019 May 2019 to coverage present Availability Hospitals, lying-in, rural health units, health centers Specimen Medical Technologist, Physician, Collector Nurse, trained Midwife Parents who refuse to perform NBS on their newborn must fill-up a Refusal form. Manner of reporting: a. Negative screen - no disorder b. Positive screen - must perform confirmatory test on the panel. NBS PANEL IN THE PHILIPPINES NBS - screening of 6 inherited disorders DISORDER DESCRIPTION COMPLICATI ON Phenylketonuria Lack of Mental enzyme that retardation metabolizes (irreversible) Congenital Hypothyroidism hormone deficiency Galactosemia Lack of enzyme that converts galactose to glucose Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia Lack of enzymes needed to make specific Importance: Newborn may appear normal at birth Metabolic disorders may be detected before clinical symptoms manifest. To start treatment immediately NEWBORN SCREENING PROGRAM IN THE PHILIPPINES phenylalanine Thyroid adrenal Delays in growth and brain development Mental Retardation Liver disease, renal failure, cataracts, blindness, mental retardation, death Genital ambiguity Genital and nipple pigmentation Hormones 5|ELANIE LADY A. MALABANA Downloaded by Roiselle Gamut (roisellegamut28@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|24136438 PCML112 | PRINCIPLES OF MEDICAL TECHNOLOGY 2 (LECTURE) Module 7: CAPILLARY PUNCTURE EQUIPMENT AND PROCEDURE G6PD deficiency (Glucose-6phosphate dehydrogenase) Lack of enzymes that protect cells from oxidative Damage MSUD (Maple Syrup Urine Disease) Lack of enzyme needed to breakdown Leucine, Isoleucine and Exposure to triggering factors may cause hemolytic anemia Neurologic damage Valine ENBS PANEL IN THE PHILIPPINES Expanded NBS (ENBS) - screening of more than 28 inherited disorders Divided into 7 groups: 1. Endocrine disorders (2) 2. Amino acid disorders (5) 3. Fatty acids disorders (8) 4. Organic acid disorders (7) 5. Urea cycle defect (2) 6. Hemoglobinopathies (1 with 7 subtypes) 7. Others (4) 6|ELANIE LADY A. MALABANA Downloaded by Roiselle Gamut (roisellegamut28@gmail.com)