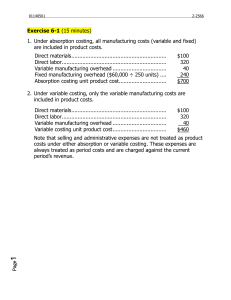
ABSORPTION AND VARIABLE COSTING BSA-2 I. Joy Sexy, Inc. uses standard costing system for a product it manufactures. For the year 2019, it established the following standards based on normal production of 1,000 units: Direct Materials 3 pcs. @ P15/pc. P 45 Direct Labor 4 hrs. @ P35/hr. 140 Variable overhead 4 hrs. @ P15/hr. 60 Fixed overhead 4 hrs. @ P10/hr. 40 Product Cost per unit P285 During 2019, the company produced 1,100 units and sold 1,050 units at P500/unit. Other data regarding the actual results for 2019 operations are as follows: Direct Materials used (3,250 pcs @ P16/pc) P 52,000 Direct Labor (4,300 hrs @ P35.50/hr) 152,650 Variable Overhead (4,300 hrs @ P16/hr) 68,800 Fixed overhead 42,000 Variable selling and administrative expenses 11,000 Fixed selling and administrative expenses 15,000 Required: 1. Variance for each product cost element. 2. Net Income under absorption and variable costing. II. Information taken from Grille Corporation’s May accounting records are as follows: Direct Materials used Direct Labor Variable Manufacturing overhead Fixed Manufacturing overhead Variable Selling and Administrative Expenses Fixed Selling and Administrative Expenses Sales Revenues 150,000 80,000 30,000 100,000 51,000 60,000 625,000 Required: 1. Compute the inventoriable costs for the month under absorption and variable costing. 2. Assume that anticipated and actual production totalled 20,000 units, and that 18,000 units were sold during May. Determine the amount of fixed manufacturing overhead and fixed selling and administrative costs that would be expensed for the month under (a) variable costing and (b) absorption costing. 3. Using the same date in no. 2, compute the contribution margin that would be reported on a variable-costing income statement.