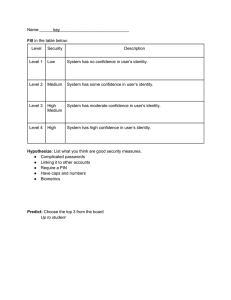
Sure, here's an updated cheat sheet with the additional information: 1. Top 5 Challenges of Cybersecurity: Lack of skilled professionals, Complexity of IT environment, Advanced persistent threats, Insider threats, Increasing number of endpoints. 2. Definition of Cybersecurity: Practice of defending computers, servers, mobile devices, etc from malicious attacks. 3. 5 Layers of Security: Data security, app security, endpoint security, web security, network security. 4. Business Impact after Attack: Reputation damage, financial loss, litigation. 5. Cybersecurity includes: Operational security, information security, network security, application security. 6. CIA Triangle: Confidentiality, integrity, availability. 7. 2 approaches: Top-Down approach (CEO and C-Suite dictate policy) and Bottom-Up approach (lower level workers dictate policy due to technical expertise). 8. CCPA - California Consumer Privacy Act. 9. OSI Model - Types of Attacks: phishing (presentation layer), session hijacking (session layer), spoofing (data link layer). 10. Good Cybersecurity includes: New technologies, organizational policies and procedures, industry standards and government laws. 11. 6 dimensions of e-commerce security: Integrity, nonrepudiation, authenticity, confidentiality, availability, privacy. 12. 3 key points of vulnerabilities: Client, Server, Pipeline. 13. Most common security threats: Malicious code, potentially unwanted programs, and phishing. 14. Spoofing is when an attacker disguises themselves as someone else to gain access to sensitive information. 15. DoS (Denial of Service) vs DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service). 16. Vishing (voice), smishing (SMS), madware (mobile adware) are types of social engineering attacks. 17. Sniffing is a type of cyber attack where an attacker intercepts network traffic to gain access to sensitive information. 18. Firewall - Packet filter and Application gateways are types of firewalls. 19. IDS - Intrusion Detection System (detection) and IPS - Intrusion Prevention System (prevention) are types of security systems. 20. Firewall vs Proxy: Firewall reads and filters, proxy is a go-between for traffic. 21. 5 Phases Security Plan - Risk Assessment, Develop Policy, Develop Implementation, Training, Maintenance. 22. Ugly Chart/Beautiful Chart 5 things: Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, Recover. 23. Small Business Cybersecurity Plan with 13 points - Multifactor authentication, Firewall, Lockdown end stations, Regularly backup data, Keep software updated, Secure Wi-Fi networks, Limit access to sensitive information, Establish clear security policies, Provide employee training, Monitor activity and network traffic, Use encryption, Set up incident response plan, Work with a cybersecurity expert. 24. Security Protocols: SSL/TLS, IPSec, SSH ● SSL/TLS: Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) and its successor, Transport Layer Security (TLS), are protocols that provide secure communication between two machines over a network. They are commonly used to encrypt communication between a web server and a web browser, ensuring that sensitive information such as passwords and credit card numbers are transmitted securely. ● IPSec: Internet Protocol Security (IPSec) is a protocol suite used to secure communication between two devices over the internet. It provides authentication, integrity, and confidentiality by encrypting data at the IP layer. ● SSH: Secure Shell (SSH) is a protocol used to provide secure remote access to a device over a network. It provides encryption, authentication, and confidentiality for remote connections. 25. Common Network Threats: Man-in-the-Middle (MitM), Denial of Service (DoS), Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS), Spoofing, Sniffing, and Social Engineering ● Man-in-the-Middle (MitM): A type of attack where an attacker intercepts communication between two devices in order to eavesdrop, steal information, or manipulate the data being transmitted. ● Denial of Service (DoS): An attack where an attacker floods a network or server with traffic in order to overwhelm it and make it unavailable to legitimate users. ● Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS): A type of DoS attack where multiple computers or devices are used to flood a network or server with traffic, making it much more difficult to mitigate. ● Spoofing: A type of attack where an attacker impersonates a legitimate device or user in order to gain access to restricted resources or steal sensitive information. ● Sniffing: A type of attack where an attacker intercepts and reads network traffic in order to steal sensitive information such as passwords or credit card numbers. ● Social Engineering: A type of attack where an attacker uses psychological manipulation to trick users into giving up sensitive information or taking actions that compromise security. 26. Access Control: Authorization, Authentication, and Identification ● Authorization: The process of granting or denying access to a resource based on a user's identity and permissions. ● Authentication: The process of verifying the identity of a user, device, or application before granting access to a resource. ● Identification: The process of uniquely identifying a user, device, or application before authentication can take place. 27. Network Topologies: Star, Bus, Ring, Mesh, Hybrid ● Star: A topology where each device is connected to a central hub or switch. ● Bus: A topology where devices are connected to a central backbone or "bus" using a shared communication medium. ● Ring: A topology where devices are connected in a circular loop, with data being transmitted around the loop in one direction. ● Mesh: A topology where devices are connected in a network of interconnecting paths, allowing data to take multiple routes between devices. ● Hybrid: A topology that combines elements of multiple topologies, such as a star-bus hybrid. 28. Types of Network Attacks: Phishing, Spear-Phishing, Smishing, Vishing, Baiting, Pretexting, Watering Hole, and Trojan ● Phishing: A type of attack where an attacker sends a fraudulent email or message in order to trick the recipient into revealing sensitive information or downloading malware. ● Spear-Phishing: A targeted version of phishing where the attacker has researched the victim and uses personalized information to increase the likelihood of success. ● Smishing: A type of attack where an attacker sends a fraudulent SMS message in order to trick the recipient into revealing sensitive information or downloading malware. ● Vishing: A type of attack