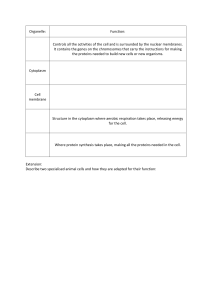
Cell Structure and Function Cheat Sheet by Morghay123 via cheatography.com/53154/cs/14396/ Functions of Cells Osmotic Solutions (cont) Basic unit of life H2O moves H2O moves Cell remains Cell metabolism and energy release into cell out intact LYSIS (burst) Crenation (shrinks) Synthesis of molecules Communication Cell Structures (cont) Cell Structures Reproduction and inheritance Cytoplasm - Location Whole Cell Activity A cells characteristics are determined by the type of proteins it produces Proteins' function is determined by genetics Information in DNA provides the cell with a cade for its cellular processes Osmosis - reticulum (RER) or free-floating in ic - - Function Give cell shape and hold Function organelles in place RER (Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum) - - Location Center of cell Location - All cells contain nucleus at some - Membranes with ribosomes Characterist point Characte attached Houses DNA - - Function membrane Nuclear Envelope Solutions Solutions - lower higher Equal concentration concentration concentrati of solutes of solutes ons of outside cell outside cell Higher Produce proteins Nucleus (not part of the cytoplasm) movement of water across cell Solutions cytoplasm Characterist Pressure Isotonic transported to the cytoplasm Jelly-like fluid the force required to prevent Hypertonic produce ribosomes that are then Function attached to rough endoplasmic Osmotic Hypotonic - Location membrane Osmotic Solutions Location - it? membrane in nucleus Inside cell Diffusion of water across a cell osmosis across a selectively permeable - Ribosome What is A measure of the tendency of water to move by Nucleolus ics - Location: edge of nucleus Nuclear Pores ristic SER (Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum) - - Function Where materials pass in and out Characte of nucleus ristic - Inside nucleus - Made of DNA and proteins - solutes Location higher Water - Function concentration concentration doesn't of H2O outside of H2O inside move Chromatin cell cell Inside nucleus - Loosely coiled chromosomes Characterist ic Site of lipid synthesis Golgi Apparatus ic - Location membranes with no ribosomes Function Characterist Part of genetic makeup Cytoplasm Location Surface of nucleus - Location Site of protein synthesis Function - Location Chromosome Cytoplasm Cytoplasm - Closely, packed stacks of Characte membranes ristic - Collect, sort, package, and Function distribute proteins and lipids Secretory Vesicle - Cytoplasm Location - Distributes materials out of cell Function By Morghay123 Published 20th January, 2018. Sponsored by Readability-Score.com cheatography.com/morghay123/ Last updated 20th January, 2018. Measure your website readability! Page 1 of 4. https://readability-score.com Cell Structure and Function Cheat Sheet by Morghay123 via cheatography.com/53154/cs/14396/ Cell Structures (cont) Movement through the Cell Membrane Endocytosis Lysosome - Cell membrane - Enzymes, glycogen, What is Process that brings materials into selectively and potassium are it? cell using vesicles determines what can found in higher pass in and out of the concentrations INSIDE 1. Cell eating (solid particles) cell the cell - Sodium, calcium, - Nutrients must be and chloride are able to enter the cell found in higher and waste products concentrations must be able to exit OUTSIDE the cell the cell 1. Directly through O2 and CO2 (small diffusion (passive): molecules) 2. Facilitated - proteins that extend diffusion (passive) from one side of the through membrane cell membrane to other - Location Cytoplasm - Function Enzymes that digest foreign material Mitochondria - Location Cytoplasm - Contains folds (cristae) Characteristic s - Function Produces ATP Main Components of a cell Plasma or cell membrane Organelles channels: Cytoplasm Phagocyto sis 2. Cell drinking (liquid particles) Pinocytosi s 3. Receptor mediated endocytosis Cytoskeleton What is is? - Made of proteins Functions - enable cell to change charge (+/-) determine - Ex. Na+ passes 1. Separate the inside from the outside of the cell 2. Enable the immune system to recognize the cell as self or non-self --> marker glycoproteins or glycolipids through Na+ channels 3. Carrier - bind to molecules, molecules: transport them across, shape Types of Cytoskeleton Microtubules - Can transport a variety of materials 3. Attach cells together or to the extracellular - Fuse with cell matrix --> adhesion proteins membrane - Largest diamete - Provide structural support and drop them off 4. Vesicles: - Provide support - Hold organelles in place - Size, shape and what can go through Jobs of the Cell Membrane - Cells framework - Form cilia and flagella Intermediate - Medium diameter filaments - maintain cell shape Microfilaments - Smallest diameter - Involved in cell 4. Receive signals from outside the cell and movement transmit the signals to inside the cell --> receptor proteins Cell Division 5. Selectively transport substances from inside - Formation of 2 daughter cells from a single to outside the cell, or outside to inside the cell parent cell via transport mechanisms - Uses mitosis and meiosis - each cell (except sperm and egg) contains 46 chromosomes (diploid) By Morghay123 Published 20th January, 2018. Sponsored by Readability-Score.com cheatography.com/morghay123/ Last updated 20th January, 2018. Measure your website readability! Page 2 of 4. https://readability-score.com Cell Structure and Function Cheat Sheet by Morghay123 via cheatography.com/53154/cs/14396/ Cell Division (cont) Cell Membrane (cont) - Sperm and egg contain 23 chromosomes Nonpolar Regions (haploid) Mitosis - Cell division that occurs in all cells except sex cells - Forms 2 daughter cells 1. Interphase: 46 chromosomes 2. Prophase: Chromosomes doubled to 92 3. Prometaphase: Nucleus dissolves and microtubules attach to centromeres 4. Metaphase: Chromosomes align at middle of cell 5. Anaphase: Separated chromosomes pulled apart 6. Telophase: Microtubules disappear cell division begins 7. Cytokinesis: Two daughter cells formed each with 46 chromosomes - "tails" Counter - a diffusing substance moves in - hydrophobic porter direction opposite to that of - away from H2O protein transported substance cell membrane consists of phospholipids, cholesterol (for strength and flexibility), and proteins Diffusion - Selective barrier -Encloses cytoplasm Microtubules of the Cytoskeleton Centriole - Composed of 9 microtubules Centrosome - 2 centrioles oriented perpendicular to one another. What is movement of molecules from areas it? of high to low concentration Solution solid, liquid, or gas that contains one or more solutes Solute Substance added to solvent that dissolves Solvent Substance such as H2O that solute is being added to Is energy no required? Mediated Transport Mechanisms Cell Membrane Funtions: Mediated Transport Mechanisms (cont) Facilitat - diffusion with aid of a carrier ed molecule diffusio - requires no ATP Plays a role in mitosis Flagella - Location Cell surface - 1 per cell Characterist ic - Function move cell, Eg. Sperm Cilia - Location Cell Surface - Many per cell Characterist ic - Function Move materials across cell's surface Extracellular Material outside of cell n - passive transport Microvilli Intracellular Material inside cell Active - moves substance from low to high - Location Cell Surface transpor concentration - required ATP - Shorter than cilia t membrane Fluid Mosaic a 2D liquid in which Model phospoholipids and proteins Ex. Sodium-potassium pump diffuse easily Cotrans - a diffusing substance moves in Made of phospholipids form a double port same direction as a transported phospholipids layer or bilayer substance and proteins Polar Region Characterist ic - Function Increase surface area DNA Double helix - "heads" - hydrophilic Deoxyribose-phosphate backbone - exposed to H2O Nucleotide base pairs Backbone = sugar (ribose-phosphate) By Morghay123 Published 20th January, 2018. Sponsored by Readability-Score.com cheatography.com/morghay123/ Last updated 20th January, 2018. Measure your website readability! Page 3 of 4. https://readability-score.com Cell Structure and Function Cheat Sheet by Morghay123 via cheatography.com/53154/cs/14396/ DNA (cont) Gene Expression - information in DNA directs protein synthesis - nucleotide sequence of a gene determines amino acid sequence of specific protein - Enzymes regulate chemical reactions - Uses transcription and translation Flow of Genetic Information Central Dogma DNA - transcribe - RNA - translate - Protein Transcription - Process by which DNA is read - Occurs in the nucleus - Produces mRNA - mRNA contains codons - Codons: set of 3 nucleotide bases that code for a particular amino acid Translation - Process by mRNA is converted into - Produces proteins amino acids (polypeptides) - Codons pair with anticodons - anticodons: 3 nucleotide bases carried by tRNA By Morghay123 Published 20th January, 2018. Sponsored by Readability-Score.com cheatography.com/morghay123/ Last updated 20th January, 2018. Measure your website readability! Page 4 of 4. https://readability-score.com