RICCARDO SAMBATARO - Earth's Orbit Learning Opportunity
advertisement

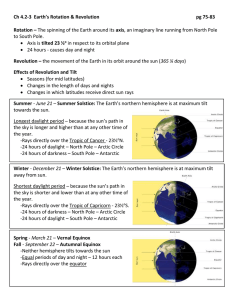
NAME: Riccardo Sambataro Earth’s Orbit Learning Opportunity Directions: Today’s learning opportunity is to answer the two questions below with complete answers. The learning opportunity will be graded based on the rubric below. Please type your answers below each question. Learning Outcome: Explain complex phenomena, such as tides, variations in day length, solar insolation, apparent motion of the planets, and annual traverse of the constellations NY Attempts to identify or explain how or why complex phenomena occur. 1. S Partially identifies or explains how or why complex phenomena occur and/or attempts to provide evidence supporting explanations. MS Identifies or explains how or why complex phenomena occur and provides sufficient evidence supporting explanations. ES Identifies or explains how or why complex phenomena occur and completely supports explanations with all relevant specific evidence. How does the revolution of the Earth around the Sun affect the orbital velocity of the Earth? ANSWER: The revolution of the Earth around the Sun affects the orbital velocity of the Earth by how close or far the Earth is to the sun because of Kepler’s second law. This law, known also as law of equal area, describes that the areas through which an object, which revolves in an elliptical orbit, sweeps in each period are equal. This law defines how the speed of objects change when they travel along their elliptical orbit. If we draw a line that connects from the center of the sun to the center of an object around the sun while the object is orbiting around the sun and then separate it with equal areas, we can see two things. Firstly, when the object is close to the sun, the line is short. However, since the object moves quickly when it is near the Sun, the line sweeps through a short, wide, pie-shaped sector. Also, when the object is far away from the sun, the line is long. However, the object moves slowly while it is far away from the Earth so the line sweeps through a long, thin, pie-shaped vector in the same period as the previous example. Gravity is the force that holds the planets and other objects in the solar system in their orbits due to gravity pulling stars and planets to the materials they are made of. The force of gravity depends on two factors, The mass of each object and the distance between them. So, if you increase the mass of one of the objects the gravitational pull becomes higher due to the gravity’s formula. However, if you increase the distance between two objects, then the gravitational pull is less. Due to orbits not being completely circular, the distance between the Earth and the Sun are not always the same and will change while the earth is revolving around the sun. This also causes the speed of the revolution to change as well. So, when the Earth is the closest to the sun, the Earth moves the fastest, while Earth is at its farthest from the sun, it will move at its slowest. However, this speed change is so slow and small that we will not notice it while we are at Earth. 2. How does the revolution of the Earth around the Sun affect the season and the amount of daylight New York receives? ANSWER: The revolution of the Earth around the sun affects the season and the amount of daylight New York receives due to the 23½° tilt of Earth’s axis. While earth is revolving around the sun, its spin axis is always pointing in the same direction in space, however it causes the North Pole to tilt alternatively toward and away from the sun. During the summer, the northern hemisphere is pointing directly towards the sun, which gives us all of this heat and warmth while the southern hemisphere is experiencing winter. While the earth is revolving, the north pole slowly titles to the center causing the autumnal equinox. Then, during winter the north pole and the northern hemisphere is pointing away from the sun, which gives us all of this cold air and snow while the southern hemisphere is experiencing winter. Finally, the north pole titles to the center again, causing the vernal equinox. After that, the whole process repeats again causing our seasons to change yearly. Also, the earth’s tilt causes the amount of daylight New York receives to change due to the north pole tilt. During the summer solstice, the northern hemisphere is directly facing the sun due to the north pole tilt, which causes the sun to be in the sky for a longer period of time and causes the noon sun to be higher in the sky which causes more daytime. During the equinox, the north pole tilt is lined up in the center, causing the sun to give us exactly 12 hours of sunlight and 12 hours of night time on the northern hemisphere. This also causes the noon sun to be in the center between the noon sun during the summer solstice and the noon sun during the winter solstice. During the winter solstice, the north pole is lined up away from the sun, which causes the sun to be in the sky for the lowest amount of time and causes the noon sun to be lower in the sky which also causes less daylight. Then, the equinox happens again causing the north pole titl to be centered again, and causing the northern hemisphere to receive 12 hours of daytime and 12 hours of night time again. Finally, the whole process repeats again which sets up our yearly sun cycle in New York.