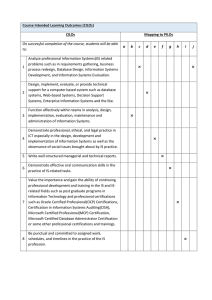
Overview of CISA & CISM Certifications Objectives Certification overview Benefits of certifications How to obtain the CISA and CISM certifications Personal side of certifications Applying certifications to real-world scenarios Explanation of the technical audit process 2 Certifications Generally voluntary Require passing a written exam Can take years to obtain experience Employers may view as benchmark of knowledge Opinions are divided on value of certification Worker may have “studied only to pass the exam” Some certifications substantially improve workers’ salaries and career prospects Throughout this presentation, think of certifications that apply to your profession 3 Top Technical Certification Source: Indeed Career Guide Project Management Professional (PMP) Certified Scrum Master (CSM) AWS Certified Solutions Architect – Associate AWS Certified Developer – Associate Certified Information Security Manager (CISM) Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH) Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP) Certified in Risk and Information Systems Control (CRISC) Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA) Google Certified Professional Cloud Architect 4 Top Finance Certification Source: Indeed Career Guide Certified Financial Planner (CFP) Certified Management Accountant (CMA) Certified Investment Management Analyst (CIMA) Certified Public Accountant (CPA) Chartered Financial Consultant (ChFC) Personal Financial Specialist (PFS) Certified Treasury Professional (CTP) Certified Government Financial Manager (CGFM) Certified Healthcare Financial Professional (CHFP) Certified International Investment Analyst (CIIA) Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA) 5 What are the CISA and CISM Certifications? Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA) Standard for those who audit, control, monitor and assess an organization’s information technology and business systems Certified Information Security Manager (CISM) Standard for those who design, build and manage enterprise information security programs Generally more managerial and operational than technical CISA & CISM certifications are offered through ISACA (Information Systems Audit and Control Association) www.isaca.org 6 Certifications Salary and Market Competiveness CISA & CISM holders can earn a pay premium increase of 10% to 15% of base salary (Source: IT Skills and Certifications Pay Index (ITSCPI) report from Foote Partners) Simple search on Indeed, CareerBuilder, Dice, and other job sites reveal hundreds of job opportunities for those that hold a CISA, CISM, and other credentials IT Auditor Security Architect IT Risk and Security Analyst Compliance Manager 7 Benefits of Earning CISA or CISM Certification Quantifies and markets your expertise Demonstrates that you have knowledge necessary to evaluate information technology system controls Is globally recognized as an IS audit professional Provides you with credibility in the marketplace Increases your value to the organization Gives you a competitive advantage over peers when seeking job opportunity and growth 8 Why do employers hire someone with a CISA or CISM credential? Certification holders are good indicators of proficiency in their profession Provide the enterprise with a certification for IT assurance that is recognized by multinational clients, lending credibility to the enterprise A certification simply shows the individual goes the extra mile! 9 CISA Certification Process Successfully pass five areas of the CISA certification exam: The process of Auditing Information Systems Governance and Management of IT Information Systems Acquisition, Development, and Implementation Information Systems Operations, Maintenance, and Support Protection of Information Assets A minimum of 3-5 years of IS auditing, control, or security work experience depending on level of formal education Adhere to Continuing Professional Education (CPE) program Adhere to Code of Professional Ethics 10 CISM Certification Process Successfully pass four areas of the CISM exam: Information Security Governance Information Risk Management and Compliance Information Security Development and Management Information Security Incident Management Minimum of five years of information security work experience Various experience substitutions apply such as: CISA, CISSP and several other certification holders Post-graduate degree in information security or related field Adhere to Continuing Professional Education (CPE) program Adhere to Code of Professional Ethics 11 How Certifications Helped Me in My Own Career Living in a small (big) town – Tulsa, Oklahoma About to lose job through layoffs Working as a manager in telecommunications industry that was reducing massive number of jobs 12 How Certifications Helped Me in My Own Career Knew that I needed to differentiate myself from other candidates in the job market. My differentiators include: Formal education (college degree) Interpersonal skills and appearance Aptitude and attitude 13 How Certifications Helped Me in My Own Career Found a new job but vowed to become more marketable going forward Studied for the CISA Failed the first time; passed the second Passed CISM on first try My career – Part II Owned and operated a successful IT consulting business from 2006 to 2016 I’m convinced that CISA & CISM credentials made a difference with earning credibility and ultimately – the consulting project! Speaking at public events 14 Next few slides focus on applying the CISA & CISM certifications to real-world situations 15 Recent Security Breaches – Could They Have Been Prevented? Equifax – 143 million American consumers affected Ashley Madison – 35 million identities JP Morgan Chase – 76 million households affected Home Depot – 56 million credit cards due to malware Target – 40 million credit cards and personal customer records due to malware Veteran Affairs – 26 million records exposed that were stored on a stolen laptop Facebook – 6 million records shared due to software bug The list is endless! 16 How does a company reduce the risk of a security breach? Answer: Start with a Technical Audit or Risk Assessment 17 Developing an Audit Plan Research the business environment from a technical perspective Identify areas that should be audited Perform a risk assessment of auditable areas Perform independent risk assessment annually Be flexible with the audit universe and adjust audits as necessary Pinpoint the audits based on: Level of risk Senior management and operation management requests General observations 18 Developing an Audit Plan Mandated Risk Assessed H Risk Impact High Total Audit Universe Consider alternative audit approach Low L Risk Likelihood H Key Considerations Perform risk assessment on all audit subjects Select audits from the high, medium and low quadrants with the bulk of the audits going to the high-risk areas Consider the Control Self Assessment approach to the low-risk areas 19 Information Technology Audit Example IT General Controls IT General Controls Review Meet with management Determine what they consider the most vulnerable risk in their organization Design the IT audit to cover the following areas: Logical and Physical Security Controls 1. Logical Access Security Administration a. Login ID and Password Controls b. Privileged User Account Administration c. Employee Access Authorization and Termination Processes d. Security Awareness and Training 2. Antivirus Protection 3. E-mail Security Controls (i.e., spam, data protection, etc) 4. Preliminary Vulnerability and Port Scan Assessment 5. Computer Physical Access Controls 6. Data Center Controls a. UPS/Emergency Power Backup b. Fire suppression, detectors, alarms 7. Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity Review 1441 South Carson Avenue Tulsa, OK 74103 P (918) 582-1873 F (918) 582-4716 magnir.com 20 Information Security Audit Example Cloud Risk Assessment Information Security Risk Assessment Process Example Send risk assessment questionnaire to application cloud provider Ask that the questionnaire be completed by the department most knowledgeable and responsible for application security controls Ask that the questionnaire be completed as thoroughly as possible Ask that the questionnaire be returned by a certain date Receive the questionnaire from provider Evaluate the questionnaire responses. The Information Security Risk Assessment reviews sixteen specific areas of security pertaining to the application. These areas include: Description of Services to Be Provided Data Management and Protection Data Classification Information Lifecycle Cryptographic Services Customer Authentication, Access Control, and Audit Restricting Unauthorized Access, and Audit Supplier-Employee Authentication, Access Control, Audit, and Backup Security Devices and Procedures Used for Virus Detection and Cleansing Process for System Hardening (i.e. Fine Tuning the Security Controls) Change Management Process Documented Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery Plans Security Training and Certifications Third-Party Contracts Third Party Audits Procedures for Computer Incident Response Team Capability Devices and Procedures for Intrusion Detection Administrative Process for Applying Patches and Upgrades Security Policy After reviewing the security controls, a report is provided to management and is typically used as 1) part of the selection process and 2) documentation that controls were reviewed. 1632 South Denver Avenue Tulsa, OK 74103 P (918) 582-1873 F (918) 582-4716 magnir.com 21 Audit Report Example Example eDiscovery Audit Report Example eDiscovery Readiness Assessment Report Outline Title Page Table of Content Executive Summary Introduction Review Objectives Findings and Recommendations Estimated Cost of eDiscovery Preparedness Conclusion ~~~~~ Findings and Recommendations The items listed below were identified during the review as strengths, opportunities and areas of improvement….. Strengths S.1 The personnel assigned to xyz department appear professional, knowledgeable, and detail oriented in performing duties involving records management. S.2 Documentation of existing processes…. Weaknesses Note: All identified risks are listed from highest risk to lowest risk. 22 Testimonials The benefit—the main benefit of the CISA certification in my case—has been to be recognized, not only locally in my country, but at an international level, as a professional with knowledge and skills, able to give an opinion and to audit all the areas related to IT. Ana Virginia Escalante, CISA, CGEIT, Vice President, SIIAS, SA The value of CISA is its instant recognition that you are a professional IS auditor. There's no need for an auditor or someone who doesn't know you to question your credentials—you have a CISA, so your credentials are understood! Michael A. Howard, CISA I decided to pursue the CISA certification because I found that an undergrad degree typically is not enough and the CISA designation allows me to set myself apart from other IT auditors. From what I’ve seen in the workforce, the CISA is the gold standard for IT audit professionals. John Pouey, CISA, CISA Once I became certified, I immediately noticed a difference in [the credibility I receive] from the business community— the CISA is proof that I passed a rigorous examination of IT auditing and controls. Vincent Chan, CISA, CGEIT 23 1441 South Carson Avenue., Suite 101, Tulsa, OK 74119 24