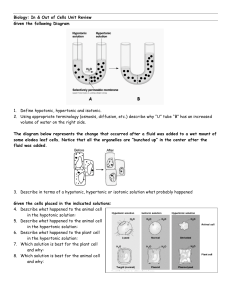
Describe the difference Name of student Course Code: Course Title Instructor Date of Submission One of the most common symptoms of hypokalemia is an abnormally low concentration of phosphate in the blood. The body's cells communicate electrically, and potassium assists in this process. Specifically, cardiac muscle cells rely on it for neuronal function. Unusually low sodium content in the blood is known as hyponatremia. You require salt to maintain fluid balance, regulate blood pressure, and maintain neuron and muscle function. There should be between 135 and 145 milligrams per liter of sodium in the blood. Hyponatremia occurs when your blood sodium levels fall below 135 mEq/L. (Yang et al.,2022, p.299). Hypertonic solutions cause cells to shrink when they are dissolved in them. Because an isotonic environment has no net water flow, the cell size remains constant. When a cell is inserted in a hypotonic surrounding, water enters the cell, causing it to expand. Red blood cells thrive in isotonic conditions, which your body maintains through homeostatic (stability-maintaining) mechanisms. Placing red blood cell is a hypotonic solution causes it swell and explode, but if it is placed in a hypertonic solution, the cytoplasm will get concentrated, and the cell may die. Plant cells, on the other hand, require a hypotonic extracellular fluid. As the cell wall is too rigid to allow any further expansion of the plasma membrane, a cell's membrane cannot rupture or lyse. A cell's internal turgor pressure will limit the amount of water that may enter the cell (Yang et al.,2022, p.299). For the plant's health, it is essential to maintain this equilibrium between water and dissolved solutes. A plant's extracellular fluid becomes isotonic or hypertonic if it isn't watered, causing water to leak out of the cells. Turgor pressure drops, and you may have observed this as wilting. A condition known as plasmolysis develops when the cellular membranes disengage from the cell wall and tighten the cytoplasm under osmotic pressure situations. References Yang, H., Yoon, S., Kim, E. J., Seo, J. W., Koo, J. R., Oh, Y. K., ... & Baek, S. H. (2022). Risk factors for overcorrection of severe hyponatremia: a post hoc analysis of the SALSA trial. Kidney Res Clin Pract.