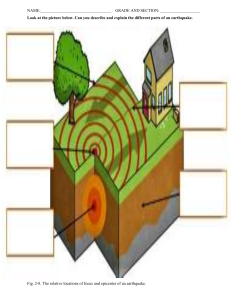
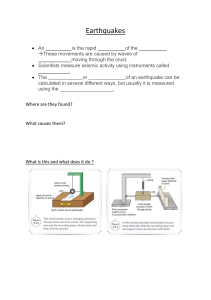
How Earthquakes are Measured Name: _____________________________________ Date: __________________ Directions: Read the passage and answer the questions. An earthquake is a sudden release of energy caused by moving rock. Most earthquakes happen at the boundary of two tectonic plates. When the plates move, energy builds up until the rocks break. A crack where rock breaks is called a fault. The ground shakes in an earthquake. After a big earthquake, the ground may shake for days or weeks! These extra shakes are called aftershocks. When the rock along the fault completely stops moving, the aftershocks stop. Scientists use a special tool called a seismograph to record the shaking caused by earthquakes. Seismographs measure the strength of an earthquake and how long the earthquake lasts. The strength of an earthquake is called its magnitude. The strength, or magnitude, of an earthquake is identified by a number between 1 and 10. This is called the Richter scale. The higher the number, the stronger the earthquake. Each number is ten times stronger than the number before it, so a magnitude 5 earthquake is ten times stronger than a magnitude 4 earthquake. That also means that a magnitude 6 earthquake is one hundred times stronger than a magnitude 4 earthquake! Seismograph machines create a diagram of the earthquake called a seismogram. A seismogram shows each type of wave made by the earthquake. It also shows when the waves were made. This helps scientists measure the strength and duration of an earthquake. How Earthquakes are Measured Name: _____________________________________ Date: __________________ Directions: Answer the questions with the information in the reading. 1. What is an earthquake? An ______________________________ is a sudden release of ___________________ caused by moving __________________. 2. What is a fault? A ________________________ is a _______________________ where rocks break. 3. When will aftershocks stop? ______________________________ stop when rock along the ___________________ completely _______________________ moving. 4. What tool is used to record the shaking of an earthquake? A ________________________________ is a tool used to ______________________ the ________________________ caused by an earthquake. 5. What is “magnitude”? The ____________________________ is the ___________________ of an earthquake. 6. What is the name of the scale that measures the magnitude of an earthquake? The _______________________ ________________ 7. How many times stronger is a magnitude 5 earthquake than a magnitude 4 earthquake? _________ times stronger 8. What is a “seismogram”? A _________________________ is a diagram that shows each type of _____________ made by the earthquake and _________________ the waves were made.