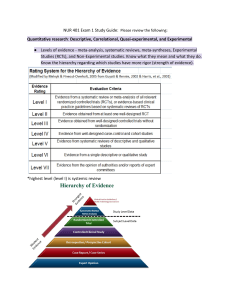
Inquiries, Investigations and Immersion Week 1 Research - a careful study that is done to find and report new knowledge about something - an investigation or experimentation aimed at the discovery and interpretation of facts, revision of accepted theories or laws in the light of new facts, or practical application of such new or revised theories or laws - the practice of collecting information about a particular subject The following are the things that may be considered before starting the research activity: 1. A problem that is most interesting to you. 2. Existing problems in the classroom/school/campus/university which one may want to solve. 3. Existing needs of the community or society 4. Area of interest, specialization or event from related fields 5. Offshoots of friendly conversations The following are the things that may be considered before starting the research activity: 6. Observations, intuitions or a combination of both 7. The type of data you need 8. The participants and sources 9. The location and timescale of the research 10. Prevailing theories and philosophy Criteria in Choosing a Research Topic: 1. It should be something new or different from what has already been written about. 2. It must be original. 3. It should be significant to the field of study or discipline. 4. It must necessarily arouse intellectual curiosity. 5. It should be of researcher’s interest and researcher must be___ with the topic. 6. It should be a modest one for a beginner to be carried out within a limited period of time. Criteria in Choosing a Research Topic: 7. It should be clear, not ambiguous. 8. It should be specific, not general. 9. It should consider the training and personal qualifications of the researcher. 10. It should consider the availability of data involved in the study and the methods and techniques to be employed in gathering them. 11. It should consider the availability of effective instruments for gathering the data and their treatment. 12. It should consider the financial capacity of the researcher to support the project. 13. It should consider the time factor involved in the undertaking. Directions: Identify the statements if it is QUALITATIVE or QUANTITATIVE. 1. Research is scientific explanation. 2. Respondents are called to the target people in this research. 3. Presents frequency and magnitude. 4. Uses observations as an instrument. 5. It controls hypothesis. 6. The design is evolving and emergent. 7. Presents cause and effect relationship. 8. Focus on the meaning and experience of target people. 9. Participants are called to the target people in this research. 10. Reality is subjective. A. DIRECTIONS: Write TRUE if the statement is true and FALSE if it is not. 1. Research may start from a simple situation, an observation, a hypothesis, or an existing problem. 2. Research is the process of finding the answers to an inquiry. 3. To successfully start a research, ask any question regardless of the SHS strand. 4. When thinking about research project, there are five W questions to ask. 5. My research project should be about something ambitious and big. B. DIRECTIONS: Write QNT if the statement describes quantitative research, QLT if it describes qualitative research 1. Focuses on the experiences of the participants. 2. Wanted to prove the hypothesis made. 3. Shows cause and effect relationship. 4. Research is structured and pre-determined. 5. Researcher as instrument. 11-15. Differentiate Qualitative and Quantitative Research