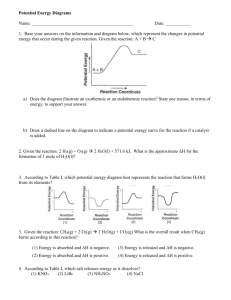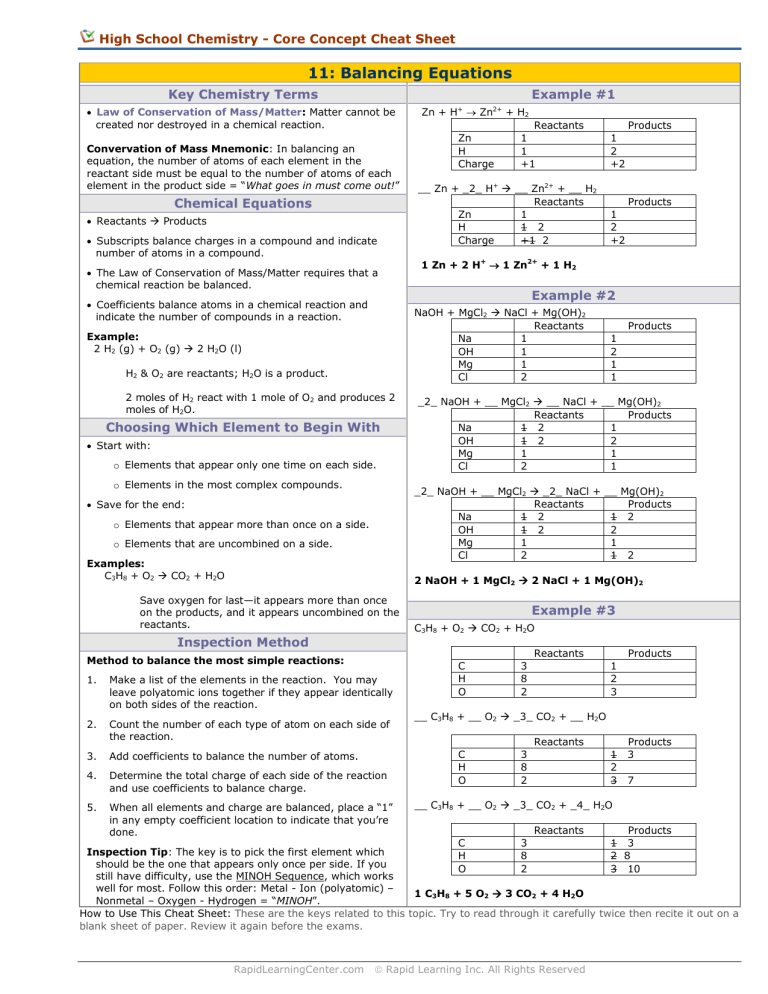
High School Chemistry - Core Concept Cheat Sheet 11: Balancing Equations Key Chemistry Terms Example #1 Law of Conservation of Mass/Matter: Matter cannot be created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction. Convervation of Mass Mnemonic: In balancing an equation, the number of atoms of each element in the reactant side must be equal to the number of atoms of each element in the product side = “What goes in must come out!” Chemical Equations Reactants Products Subscripts balance charges in a compound and indicate number of atoms in a compound. The Law of Conservation of Mass/Matter requires that a chemical reaction be balanced. Coefficients balance atoms in a chemical reaction and indicate the number of compounds in a reaction. + 2+ Zn + H Zn Zn H Charge + H2 Reactants 1 1 +1 __ Zn + _2_ H+ __ Zn2+ + __ H2 Reactants Zn 1 H 1 2 Charge +1 2 H2 & O2 are reactants; H2O is a product. 2 moles of H2 react with 1 mole of O2 and produces 2 moles of H2O. Choosing Which Element to Begin With Start with: o Elements that appear only one time on each side. o Elements in the most complex compounds. Products 1 2 +2 1 Zn + 2 H+ 1 Zn2+ + 1 H2 Example #2 NaOH + MgCl2 NaCl + Mg(OH)2 Reactants Na 1 OH 1 Mg 1 Cl 2 Example: 2 H2 (g) + O2 (g) 2 H2O (l) Products 1 2 +2 Products 1 2 1 1 _2_ NaOH + __ MgCl2 __ NaCl + __ Mg(OH)2 Reactants Products Na 1 2 1 OH 1 2 2 Mg 1 1 Cl 2 1 _2_ NaOH + __ MgCl2 _2_ NaCl + __ Mg(OH)2 Reactants Products Na 1 2 1 2 OH 1 2 2 Mg 1 1 Cl 2 1 2 Save for the end: o Elements that appear more than once on a side. o Elements that are uncombined on a side. Examples: C3H8 + O2 CO2 + H2O 2 NaOH + 1 MgCl2 2 NaCl + 1 Mg(OH)2 Save oxygen for last—it appears more than once on the products, and it appears uncombined on the reactants. Example #3 C3H8 + O2 CO2 + H2O Inspection Method Reactants Method to balance the most simple reactions: 1. Make a list of the elements in the reaction. You may leave polyatomic ions together if they appear identically on both sides of the reaction. 2. Count the number of each type of atom on each side of the reaction. 3. Add coefficients to balance the number of atoms. 4. Determine the total charge of each side of the reaction and use coefficients to balance charge. 5. When all elements and charge are balanced, place a “1” in any empty coefficient location to indicate that you’re done. C H O 3 8 2 Products 1 2 3 __ C3H8 + __ O2 _3_ CO2 + __ H2O Reactants C H O 3 8 2 1 2 3 Products 3 7 __ C3H8 + __ O2 _3_ CO2 + _4_ H2O Reactants C H O 3 8 2 Products 1 3 2 8 3 10 Inspection Tip: The key is to pick the first element which should be the one that appears only once per side. If you still have difficulty, use the MINOH Sequence, which works well for most. Follow this order: Metal - Ion (polyatomic) – 1 C3H8 + 5 O2 3 CO2 + 4 H2O Nonmetal – Oxygen - Hydrogen = “MINOH”. How to Use This Cheat Sheet: These are the keys related to this topic. Try to read through it carefully twice then recite it out on a blank sheet of paper. Review it again before the exams. RapidLearningCenter.com Rapid Learning Inc. All Rights Reserved