The Test Bank for Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition) by Amy Karch
advertisement
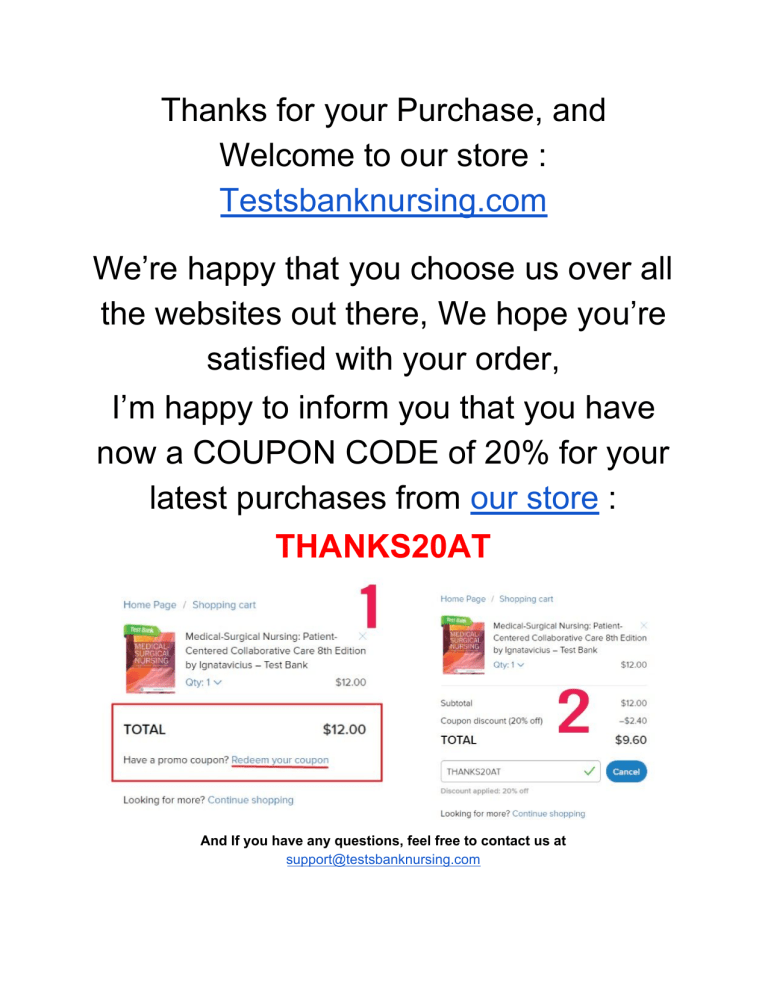
Thanks for your Purchase, and Welcome to our store : Testsbanknursing.com We’re happy that you choose us over all the websites out there, We hope you’re satisfied with your order, I’m happy to inform you that you have now a COUPON CODE of 20% for your latest purchases from our store : THANKS20AT And If you have any questions, feel free to contact us at support@testsbanknursing.com Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 1 Table of Contents Table of Contents Chapter 01 - Introduction to Drugs Chapter 02 - Drugs and the Body Chapter 03 - Toxic Effects of Drugs Chapter 04 - The Nursing Process in Drug Therapy and Patient Safety Chapter 05 - Dosage Calculations Chapter 06 - Challenges to Effective Drug Therapy Chapter 07 - Introduction to Cell Physiology Chapter 08 - Antiinfective Agents Chapter 09 - Antibiotics Chapter 10 - Antiviral Agents Chapter 11 - Antifungal Agents Chapter 12 - Antiprotozoal Agents Chapter 13 - Anthelmintic Agents Chapter 14 - Antineoplastic Agents Chapter 15 - Introduction to the Immune Response and Inflammation Chapter 16 - Antiinflammatory, Antiarthritis, and Related Agents Chapter 17 - Immune Modulators Chapter 18 - Vaccines and Sera Chapter 19 - Introduction to Nerves and the Nervous System Chapter 20 - Anxiolytic and Hypnotic Agents Chapter 21 - Antidepressant Agents Chapter 22 - Psychotherapeutic Agents Chapter 23 - Antiseizure Agents Chapter 24 - Antiparkinsonism Agents Chapter 25 - Muscle Relaxants Chapter 26 - Narcotics, Narcotic Antagonists, and Antimigraine Agents Chapter 27 - General and Local Anesthetic Agents Chapter 28 - Neuromuscular Junction Blocking Agents Chapter 29 - Introduction to the Autonomic Nervous System Chapter 30 - Adrenergic Agonists Chapter 31 - Adrenergic Antagonists Chapter 32 - Cholinergic Agonists Chapter 33 - Anticholinergic Agents Chapter 34 - Introduction to the Endocrine System Chapter 35 - Hypothalamic and Pituitary Agents Chapter 36 - Adrenocortical Agents Chapter 37 - Thyroid and Parathyroid Agents Chapter 38 - Agents to Control Blood Glucose Levels Chapter 39 - Introduction to the Reproductive System Chapter 40 - Drugs Affecting the Female Reproductive System Chapter 41 - Drugs Affecting the Male Reproductive System Chapter 42 - Introduction to the Cardiovascular System Chapter 43 - Drugs Affecting Blood Pressure Chapter 44 - Agents for Treating Heart Failure Chapter 45 - Antiarrhythmic Agents Chapter 46 - Antianginal Agents Chapter 47 - Lipid-Lowering Agents Chapter 48 - Drugs Affecting Blood Coagulation Chapter 49 - Drugs Used to Treat Anemias Chapter 50 - Introduction to the Renal System 1 3 20 37 54 71 86 103 120 138 155 172 188 204 220 237 254 270 287 304 320 337 354 371 388 404 420 436 453 470 487 503 520 536 553 569 585 602 619 636 653 669 685 702 719 735 752 768 785 801 817 Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) Chapter 51 - Diuretic Agents Chapter 52 - Drugs Affecting the Urinary Tract and the Bladder Chapter 53 - Introduction to the Respiratory System Chapter 54 - Drugs Acting on the Upper Respiratory Tract Chapter 55 - Drugs Acting on the Lower Respiratory Tract Chapter 56 - Introduction to the Gastrointestinal System Chapter 57 - Drugs Affecting Gastrointestinal Secretions Chapter 58 - Drugs Affecting Gastrointestinal Motility Chapter 59 - Antiemetic Agents 2 833 849 866 883 900 917 933 949 965 Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 3 Chapter 01 - Introduction to Drugs 1. A nurse working in radiology administers iodine to a patient who is having a computed tomography (CT) scan. The nurse working on the oncology unit administers chemotherapy to patients who have cancer. At the Public Health Department, a nurse administers a measles-mumps-rubella (MMR) vaccine to a 14-month-old child as a routine immunization. Which branch of pharmacology best describes the actions of all three nurses? A) Pharmacoeconomics B) Pharmacotherapeutics C) Pharmacodynamics D) Pharmacokinetics Ans: B Feedback: Pharmacology is the study of the biologic effects of chemicals. Nurses are involved with clinical pharmacology or pharmacotherapeutics, which is a branch of pharmacology that deals with the uses of drugs to treat, prevent, and diagnose disease. The radiology nurse is administering a drug to help diagnose a disease. The oncology nurse is administering a drug to help treat a disease. Pharmacoeconomics includes any costs involved in drug therapy. Pharmacodynamics involves how a drug affects the body and pharmacokinetics is how the body acts on the body. 2. A physician has ordered intramuscular (IM) injections of morphine, a narcotic, every 4 hours as needed for pain in a motor vehicle accident victim. The nurse is aware this drug has a high abuse potential. Under what category would morphine be classified? A) Schedule I B) Schedule II C) Schedule III D) Schedule IV Ans: B Feedback: Narcotics with a high abuse potential are classified as Schedule II drugs because of severe dependence Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 4 liability. Schedule I drugs have high abuse potential and no accepted medical use. Schedule III drugs have a lesser abuse potential than II and an accepted medical use. Schedule IV drugs have low abuse potential and limited dependence liability. 3. When involved in phase III drug evaluation studies, what responsibilities would the nurse have? A) Working with animals who are given experimental drugs B) Choosing appropriate patients to be involved in the drug study C) Monitoring and observing patients closely for adverse effects D) Conducting research to determine effectiveness of the drug Ans: C Feedback: Phase III studies involve use of a drug in a vast clinical population in which patients are asked to record any symptoms they experience while taking the drugs. Nurses may be responsible for helping collect and analyze the information to be shared with the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) but would not conduct research independently because nurses do not prescribe medications. Use of animals in drug testing is done in the preclinical trials. Select patients who are involved in phase II studies to participate in studies where the participants have the disease the drug is intended to treat. These patients are monitored closely for drug action and adverse effects. Phase I studies involve healthy human volunteers who are usually paid for their participation. Nurses may observe for adverse effects and toxicity. 4. What concept is considered when generic drugs are substituted for brand name drugs? A) Bioavailability B) Critical concentration C) Distribution D) Half-life Ans: A Feedback: Bioavailability is the portion of a dose of a drug that reaches the systemic circulation and is available to act on body cells. Binders used in a generic drug may not be the same as those used in the brand name drug. Therefore, the way the body breaks down and uses the drug may differ, which may eliminate a generic drug substitution. Critical concentration is the amount of a drug that is needed to cause a therapeutic effect and should not differ between generic and brand name medications. Distribution is the phase of pharmacokinetics, which involves the movement of a drug to the body’s tissues and is the Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 5 same in generic and brand name drugs. A drug’s half-life is the time it takes for the amount of drug to decrease to half the peak level, which should not change when substituting a generic medication. 5. A nurse is assessing the patient’s home medication use. After listening to the patient list current medications, the nurse asks what priority question? A) Do you take any generic medications? B) Are any of these medications orphan drugs? C) Are these medications safe to take during pregnancy? D) Do you take any over-the-counter medications? Ans: D Feedback: It is important for the nurse to specifically question use of over-the-counter medications because patients may not consider them important. The patient is unlikely to know the meaning of orphan drugs unless they too are health care providers. Safety during pregnancy, use of a generic medication, or classification of orphan drugs are things the patient would be unable to answer but could be found in reference books if the nurse wishes to research them. 6. After completing a course on pharmacology for nurses, what will the nurse know? A) Everything necessary for safe and effective medication administration B) Current pharmacologic therapy; the nurse will not require ongoing education for 5 years. C) General drug information; the nurse can consult a drug guide for specific drug information. D) The drug actions that are associated with each classification of medication Ans: C Feedback: After completing a pharmacology course nurses will have general drug information needed for safe and effective medication administration but will need to consult a drug guide for specific drug information before administering any medication. Pharmacology is constantly changing, with new drugs entering the market and new uses for existing drugs identified. Continuing education in pharmacology is essential to safe practice. Nurses tend to become familiar with the medications they administer most often, but there will always be a need to research new drugs and also those the nurse is not familiar with because no nurse knows all medications. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 7. 6 A nurse is instructing a pregnant patient concerning the potential risk to her fetus from a Pregnancy Category B drug. What would the nurse inform the patient? A) Adequate studies in pregnant women have demonstrated there is no risk to the fetus. B) Animal studies have not demonstrated a risk to the fetus, but there have been no adequate studies in pregnant women. C) Animal studies have shown an adverse effect on the fetus, but there are no adequate studies in pregnant women. D) There is evidence of human fetal risk, but the potential benefits from use of the drug may be acceptable despite potential risks. Ans: B Feedback: Category B indicates that animal studies have not demonstrated a risk to the fetus. However, there have not been adequate studies in pregnant women to demonstrate risk to a fetus during the first trimester of pregnancy and no evidence of risk in later trimesters. Category A indicates that adequate studies in pregnant women have not demonstrated a risk to the fetus in the first trimester or in later trimesters. Category C indicates that animal studies have shown an adverse effect on the fetus, but no adequate studies in humans. Category D reveals evidence of human fetal risk, but the potential benefits from the use of the drugs in pregnant women may outweigh potential risks. 8. Discharge planning for patients leaving the hospital should include instructions on the use of over-thecounter (OTC) drugs. Which comment by the patient would demonstrate a good understanding of OTC drugs? A) OTC drugs are safe and do not cause adverse effects if taken properly. B) OTC drugs have been around for years and have not been tested by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). C) OTC drugs are different from any drugs available by prescription and cost less. D) OTC drugs could cause serious harm if not taken according to directions. Ans: D Feedback: It is important to follow package directions because OTCs are medications that can cause serious harm if not taken properly. OTCs are drugs that have been determined to be safe when taken as directed; however, all drugs can produce adverse effects even when taken properly. They may have originally been prescription drugs that were tested by the FDA or they may have been grandfathered in when the Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 7 FDA laws changed. OTC education should always be included as a part of the hospital discharge instructions. 9. What would be the best source of drug information for a nurse? A) Drug Facts and Comparisons B) A nurse’s drug guide C) A drug package insert D) The Physicians’ Drug Reference (PDR) Ans: B Feedback: A nurse’s drug guide provides nursing implications and patient teaching points that are most useful to nurses in addition to need-to-know drug information in a very user friendly organizational style.Lippincott’s Nursing Drug Guide (LNDG) has drug monographs organized alphabetically and includes nursing implications and patient teaching points. Numerous other drug handbooks are also on the market and readily available for nurses to use. Although other drug reference books such as Drug Facts and Comparisons, PDR, and drug package inserts can all provide essential drug information, they will not contain nursing implications and teaching points and can be more difficult to use than nurse’s drug guides. 10. The nurse is preparing to administer a medication from a multidose bottle. The label is torn and soiled but the name of the medication is still readable. What is the nurse’s priority action? A) Discard the entire bottle and contents and obtain a new bottle. B) Find the drug information and create a new label for the bottle. C) Ask another nurse to verify the contents of the bottle. D) Administer the medication if the name of the drug can be clearly read. Ans: A Feedback: When the drug label is soiled obscuring some information the safest action by the nurse is to discard the bottle and contents because drug labels contain a great deal of important information, far more than just the name of the drug. Concentration of the drug, expiration date, administration directions, and precautions may be missing from the label and so put the patient at risk. Looking up drug information in a drug handbook or consulting with another nurse will not supply the expiration date or concentration of medication. Be safe and discard the bottle and its contents. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 11. What aspect of pharmacology does a nurse study? (Select all that apply.) A) Chemical pharmacology B) Molecular pharmacology C) Impact of drugs on the body D) The body’s response to a drug E) Adverse and anticipated drug effects Ans: C, D, E Feedback: Nurses study pharmacology from a pharmacotherapeutic level, which includes the effect of drugs on the body, the body’s response to drugs, and both expected and unexpected drug effects. Chemical and molecular pharmacology (Options A and B) are not included in nursing pharmacology courses. 12. The nurse, providing patient teaching about home medication use to an older adult, explains that even when drugs are taken properly they can produce negative or unexpected effects. What are these negative or unexpected effects called? A) Teratogenic effects B) Toxic effects C) Adverse effects D) Therapeutic effects Ans: C Feedback: Negative or unexpected effects are known as adverse or side effects. Teratogenic effects are adverse effects on the fetus and not a likely concern for an older adult. Toxic effects occur when medication is taken in larger than recommended dosages caused by an increase in serum drug levels. Therapeutic effects are the desired actions for which the medication is prescribed. 13. After administering a medication, for what would the nurse assess the patient? 8 Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) A) Drug effects B) Allergies C) Pregnancy D) Preexisting conditions Ans: A 9 Feedback: After the medication is administered, the nurse assesses the patient for drug affects, both therapeutic and adverse. The nurse would assess the patient for allergies, preexisting conditions, and pregnancy before administering a medication. 14. The nurse receives an order to administer an unfamiliar medication and obtains a nurse’s drug guide published four years earlier. What is the nurse’s most prudent action? A) Find a more recent reference source. B) Use the guide if the drug is listed. C) Ask another nurse for drug information. D) Verify the information in the guide with the pharmacist. Ans: A Feedback: The nurse is responsible for all medications administered and must find a recent reference source to ensure the information learned about the medication is correct and current. Using an older drug guide could be dangerous because it would not contain the most up-to-date information. Asking another nurse or the pharmacist does not guarantee accurate information will be obtained and could harm the patient if the information is wrong. 15. What would the nurse provide when preparing a patient for discharge and home medication selfadministration? A) Personal contact information to use if the patient has questions B) Thorough medication teaching about drugs and the drug regimen C) Over-the-counter medications to use to treat potential adverse effects Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) D) A sample size package of medication to take home until prescription is filled Ans: B 10 Feedback: The nurse is responsible for providing thorough medication teaching about drugs and the drug regimen to ensure the patient knows how to take the medication and when to notify the provider. The nurse never provides personal contact information to a patient. If adverse effects arise, the patient is taught to call the health care provider and should not self-medicate with over-the-counter drugs, which could mask serious symptoms. The nurse never dispenses medication because it must be properly labeled for home use; this is done by the pharmacy. 16. In response to the patient’s question about how to know whether drugs are safe, the nurse explains that all medications undergo rigorous scientific testing controlled by what organization? A) Food and Drug Administration (FDA) B) Drug Enforcement Agency (DEA) C) Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) D) Joint Commission on Accreditation of Healthcare Organizations (JCAHO) Ans: A Feedback: The FDA is responsible for controlling and regulating the development and sale of drugs in the United States, allowing new drugs to enter the market only after being subjected to rigorous scientific testing. The DEA regulates and controls the use of controlled substances. The CDC monitors and responds to infectious diseases. The JCAHO is an accrediting body that inspects acute care facilities to ensure minimum standards are met. 17. The nurse, assisting with Phase I drug studies, is talking with a woman who asks, Why can’t I participate in this study? What would be the nurse’s best response? A) Drugs pose a greater risk to women of reproductive age. B) Drugs are only tested on men because they are stronger. C) Women are more prone to adverse effects from medications. D) Drugs affect women differently than they affect women. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) Ans: 11 A Feedback: Phase I drug trials usually involve healthy male volunteers because chemicals may exert an unknown and harmful effect on ova in women which could result in fetal damage when the woman becomes pregnant. Drugs are tested on both men and women, but women must be fully informed of risks and sign a consent stating they understand the potential for birth defects. Women are not more prone to adverse effects of medications. Although some drugs may affect women differently than men, this is a rationale for why drugs need to be tested on women, not an explanation of why women are not included in a phase I study. 18. The patient tells the nurse about a new drug being tested to treat the disease she was diagnosed with and asks the nurse whether the doctor can prescribe a medication still in the preclinical phase of testing. What is the nurse’s best response? A) The doctor would have to complete a great deal of paperwork to get approval to prescribe that drug. B) Sometimes pharmaceutical companies are looking for volunteers to test a new drug and the doctor could give them your name. C) Drugs in the preclinical phase of testing are only tested on animals and so would not be available to you. D) Drugs in the preclinical phase of testing are given only to healthy young men and so would not be available to you. Ans: C Feedback: During the preclinical phase of testing drugs are tested on animals and are not available to patients. In phase I, the drug is tested on volunteers who are usually healthy young men. It is only in phase III studies that the drug is made available to prescribers who agree to closely monitor patients getting the medication. 19. The nurse is caring for a patient who had a severe, acute, previously unseen adverse effect of a drug in Phase III testing. The patient asks, After all the testing done on this drug, didn’t they know this adverse effect could occur? What is the nurse’s best response? (Select all that apply.) A) Pharmaceutical companies sometimes underreport problems to make more money. B) Your response to this medication will be reported to the drug company and the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). C) When a drug begins to be used by a large clinical market, new adverse effects may be found. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 12 D) The pharmaceutical company weighs the benefits of the drug with the severity of adverse effects. E) After a drug reaches phase III testing it is considered an accepted drug and will not be recalled. Ans: B, C Feedback: When a new and unexpected adverse effect occurs, especially one of a serious nature, it is reported to the drug company who reports it to the FDA immediately. When a large number of people begin using the drug in phase III studies, it is not unusual to identify adverse effects not previously noted. It would be both unprofessional and inaccurate to imply that pharmaceutical companies put profit ahead of patient concern because lawsuits would remove any potential profit if a drug proves harmful. The FDA is responsible for weighing risk versus benefit in deciding whether to allow the drug to move to the next phase of testing. Drugs found to have serious adverse effects can be removed from the market at any time. 20. The telephone triage nurse receives a call from a patient asking for a prescription for a narcotic to manage his surgical pain. The nurse explains that narcotic prescriptions must be written and cannot be called in to the pharmacy. The patient says, Why are narcotics so difficult to get a prescription for? What is the nurse’s best response? A) The Drug Enforcement Agency (DEA) determines the risk for addiction and the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) enforces their control. B) The increase in the number of drug addicts has made the rules stronger. C) The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) regulates use of controlled substances to reduce the risk of injury. D) Controlled substances like narcotics are controlled by the FDA and the DEA. Ans: D Feedback: Controlled substances are controlled by the FDA and the DEA: the DEA enforces control while the FDA determines abuse potential. Regulations related to controlled substances have remained strict and specific and have not been significantly impacted by substance abusers. The CDC is not involved in control of narcotics and other controlled substances. 21. A) The nurse explains the Drug Enforcement Agency’s (DEA’s) schedule of controlled substances to the nursing assistant who asks, Do you ever get a prescription for Schedule I medications? What is the nurse’s best response? Schedule I medications have no medical use so they are not prescribed. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) B) Schedule I medications have the lowest risk for abuse and do not require a prescription. C) Schedule I medications are only prescribed in monitored units for patient safety. D) Schedule I medications are found in antitussives and antidiarrheals sold over the counter. Ans: A 13 Feedback: Schedule I medications have no medical use and are never prescribed. Schedule V medications have the lowest risk for abuse and are found mostly in antitussives and antidiarrheals but they are not sold over the counter. 22. The nurse, working on the maternity unit, receives a call from a pregnant woman asking how she can know whether a medication is safe to take while pregnant. What is the nurse’s best response? A) You can take any drug indicated as a Category A. B) No medications should be taken during pregnancy. C) Never take medication until you receive approval from your health care provider. D) Most medications are safe but you need to weigh benefit against risk. Ans: C Feedback: The best response to a pregnant woman asking about medication usage is to talk with her obstetric practitioner because the best advice will come from someone who knows their health and pregnancy history. While Category A drugs have no known risk, they may be contraindicated by the woman’s health condition or pregnancy issues and many pregnant women would not know what it means to be a Category A drug. Medications can be helpful during pregnancy if taken safely and appropriately. Although risk benefit needs to be weighed, it should occur with advice from the obstetric practitioner. 23. A patient asks the nurse, What is a Drug Enforcement Agency (DEA) number? What is the nurse’s best response? A) DEA Numbers are given to physicians and pharmacists when they register with the DEA to prescribe and dispense controlled substances. B) Physicians must have a DEA number in order to prescribe any type of medication for patients. C) DEA numbers are case numbers given when someone breaks the law involving a controlled substance. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) D) DEA numbers are contact numbers to talk with someone at the DEA when questions arise about controlled substances. Ans: A 14 Feedback: All pharmacists and physicians must register with the DEA. They are given numbers that are required before they can dispense or prescribe controlled substances. DEA numbers are only needed when prescribing controlled substances. A DEA number is neither a case number nor a phone number. 24. When moving to another state, what is the nurse responsible for becoming familiar with? A) Local policies and procedures for controlled substance administration B) Local provider’s Drug Enforcement Agency (DEA) number for prescribing controlled substances C) The agency monitoring controlled substances in the new state D) Board of Nursing regulations of controlled substances in the new state Ans: A Feedback: The nurse needs to learn local policies and procedures for controlled substance administration because they can vary with some local governments more rigorous than others. Nurses do not memorize a provider’s DEA numbers. The DEA is a federal agency that monitors controlled substances in all states. State boards of nursing do not regulate controlled substances but may regulate how controlled substances are administered by nurses. 25. The patient looks at the prescription provided by the doctor and asks the nurse whether he can request a generic substitution. The nurse answers No when noting what on the prescription? A) No refills B) DAW C) Brand name used on prescription D) Patient older than 65 years of age Ans: B Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 15 Feedback: DAW stands for dispense as written and means that the doctor does not want a generic substituted for the prescribed medication. Requesting no refills does not preclude the substitution of a generic medication. Even when the brand name is ordered, the pharmacist can substitute a generic equivalent so long as the prescriber does not write DAW. Generic substitutions are not impacted by the patient’s age. 26. The patient asks the nurse why generic drugs would be used and voices concerns that only the brand name product will be safe. What is the nurse’s best response? A) Generic drugs are often less expensive. B) Some quality control problems have been found with generic drugs. C) Most generic drugs are very safe and can be cost effective as well. D) Although initial cost is higher for a brand name it may cost less in the long run. Ans: C Feedback: Most generic medications are completely safe and may be identical to the brand name drug except generic medications are often less expensive, but this does not address the patient’s concern about safety. Although some quality control issues have occurred in the past, this does not address the patient’s concerns regarding safety or explain why generic drugs are prescribed and used. Although some doctors believe initial cost is higher but will cost less over time, this response also does not address the patient’s concerns. 27. While studying for the test, the nursing student encounters the following drug: papaverine (Pavabid). What does the nursing student identify the name Pavabid as? A) The generic name B) The chemical name C) The brand name D) The chemical and generic name Ans: C Feedback: Several clues indicate the brand name including capitalization of the first letter in the name and in parentheses. Generic names are not capitalized; chemical names are descriptions of the chemistry of the Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 16 medication resulting in complicated names. 28. The patient is prescribed a medication that was just placed in Phase IV study. The patient tells the nurse, This medication is too expensive. Could the doctor order a generic form of this medication? What is the nurse’s most accurate response? A) Medications are not produced in generic form until the patent expires, which normally takes several years. B) You can request the generic form but the binder used may make the drug less effective for this medication. C) The generic form of the medication would not be any less expensive because this is a relatively new medication. D) Generic medications are lower quality drugs and that would mean you would not be getting the best treatment available. Ans: A Feedback: When a new drug enters the market, it is given a time-limited patent; generic forms of the medication cannot be produced until the patent expires. Because no generic version of this drug will exist because it is so new, it is impossible to predict what binder will be used or what the cost would be. 29. The nurse learns that a drug needed by the patient is classified as an orphan drug and recognizes what as a reason for this classification? (Select all that apply.) A) The drug is rarely prescribed. B) The drug has dangerous adverse effects. C) The drug treats a rare disease. D) The patent on the medication is still effective. E) Production by a company that only manufactures drugs. Ans: A, B, C Feedback: Drugs are classified as orphan drugs when they are not financially viable for a drug company to produce either because of risk for lawsuits about adverse effects or because the drug is not prescribed, which is often seen in rare diagnoses. Generic drugs are not produced until the patent expires, but this Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 17 has no impact on classifying a particular drug as an orphan drug. Generic drugs are often produced by companies that only manufacture drugs without conducting research, but this has no bearing on the classification of orphan drugs. 30. While collecting a medication history, the patient admits to doubling the recommended dosage of an over-the-counter (OTC) medication, saying It’s harmless or they would require a prescription. What is the nurse’s best response? A) OTC drugs are serious medications and carry serious risks if not taken as directed. B) Taking medications like that is careless and you could kill yourself doing it. C) Sometimes you need to take more than the package directs to treat the symptoms. D) Did you notify your doctor of the increased dosage you were taking? Ans: A Feedback: OTC drugs are no less a medication than prescription drugs and carry the same types of risks for overdosage and toxicity if directions are not followed. Although increasing the dosage is careless and dangerous, it is important to use the information as a teaching opportunity rather than scolding the patient. Agreeing with the patient or asking her if she talked to the doctor misses the teaching opportunity, which could be harmful for the patient. 31. The patient asks the nurse, Is it safe to take over-the-counter (OTC) medications with prescription medications? What is the nurse’s best response? (Select all that apply.) A) OTC medications can interact with prescription medications. B) It is important to tell your doctor all medications you take, including OTC. C) OTC medications could mask or hide signs and symptoms of a disease. D) You should avoid taking any OTC medication when taking prescription drugs. E) Taking OTC medications can make your prescription medication more effective. Ans: A, B, C Feedback: OTC medications can interact with prescription medications or other OTC so it is always important to consult your pharmacist and provider for advice. To provide the most accurate instruction, the health care provider must know all medications taken including dietary supplements, OTC, and prescription. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 18 OTC medications could mask or hide symptoms of a disease so it is always important to consult a physician if symptoms persist. OTC medications are not prohibited when taking prescription drugs as long as no drug interaction occurs. How an OTC will impact a prescription medication varies depending on the medications involved, so it is incorrect to say it will make the prescription drug more effective. 32. Before administering a prescription medication, what information does the nurse find on the drug label? (Select all that apply.) A) Brand name B) Generic name C) Drug concentration D) Expiration date E) Adverse effects Ans: A, B, C, D Feedback: Prescription drug labels will contain the brand name, generic name, drug concentration, and expiration date. Adverse effects will not be listed on drug labels. 33. The nurse is preparing a medication that is new to the market and cannot be found in the nurse’s drug guide. Where can the nurse get the most reliable information about this medication? A) Package insert B) Another nurse C) Drug manufacturer D) Physician Ans: A Feedback: The most reliable information about the drug can be found on the package insert supplied by the manufacturer because it was prepared according to strict Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulations. Asking another nurse or the physician is not reliable and cannot be verified as accurate. It would not be realistic to call the drug manufacturer for information. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 34. 19 The nurse explains that what drug resource book is compiled from package inserts? A) Nurses Drug Guide B) Physicias’s Desk Reference (PDR) C) Drug Facts and Comparisons D) AMA Drug Evaluations Ans: B Feedback: The PDR is a compilation of information found on package inserts. The Nurses Drug Guide uses more easily understood language and incorporates nursing considerations and patient teaching points. Drug Facts and Comparisons includes cost comparison, often not found in other drug resource guides. The AMA Drug Evaluations is far less biased than the PDR and includes drugs still in the research stage of development. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 20 Chapter 02 - Drugs and the Body 1. Drugs do not metabolize the same way in all people. For what patient would a nurse expect to assess for an alteration in drug metabolism? A) A 35-year-old woman with cervical cancer B) A 41-year-old man with kidney stones C) A 50-year-old man with cirrhosis of the liver D) A 62-year-old woman in acute renal failure Ans: C Feedback: The liver is the most important site of drug metabolism. If the liver is not functioning effectively, as in patients with cirrhosis, drugs will not metabolize normally so that toxic levels could develop unless dosage is reduced. A patient with cervical cancer or kidney stones would not be expected to have altered ability to metabolize drugs so long as no liver damage existed. The patient with renal failure would have altered excretion of the drugs through the renal system but metabolism would not be impacted. 2. A patient presents to the emergency department with a drug level of 50 units/mL. The half-life of this drug is 1 hour. With this drug, concentrations above 25 units/mL are considered toxic and no more drug is given. How long will it take for the blood level to reach the non-toxic range? A) 30 minutes B) 1 hour C) 2 hours D) 3 hours Ans: B Feedback: Half-life is the time required for the serum concentration of a drug to decrease by 50%. After 1 hour, the serum concentration would be 25 units/mL (50/2) if the body can properly metabolize and excrete the drug. After 2 hours, the serum concentration would be 12.5 units/mL (25/2) and reach the nontoxic range. In 30 minutes the drug level would be 37.5 units/mL, whereas in 3 hours the drug level would be Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 21 6.25. 3. A patient has recently moved from Vermont to Southern Florida. The patient presents to the clinic complaining of dizzy spells and weakness. While conducting the admission assessment, the patient tells the nurse that he have been on the same antihypertensive drug for 6 years and had stable blood pressures and no adverse effects. Since his move, he has been having problems and he feels that the drug is no longer effective. The clinic nurse knows that one possible reason for the change in the effectiveness of the drug could be what? A) The impact of the placebo effect on the patient’s response. B) The accumulative effect of the drug if it has been taken for many years. C) The impact of the warmer environment on the patient’s physical status. D) Problems with patient compliance with the drug regimen while on vacation. Ans: C Feedback: Antihypertensive drugs work to decrease the blood pressure. When a patient goes to a climate that is much warmer than usual, blood vessels dilate and the blood pressure falls. If a patient is taking an antihypertensive drug and moves to a warmer climate, there is a chance that the patient’s blood pressure will drop too low, resulting in dizziness and feelings of weakness. Even mild dehydration could exacerbate these effects. Most antihypertensives are metabolized and excreted and do not accumulate in the body. Patients must be very compliant with their drug regimen on vacation. After several years on an antihypertensive drug, the effects of that drug are known; therefore, the placebo effect should not be an issue. 4. An important concept taught by the nurse when providing medication teaching is the need to provide a complete list of medications taken to health care providers to avoid what? A) Spending large amounts of money on medications B) Allergic reactions to medications C) Drugdrug interactions D) Critical concentrations of medications in the body Ans: C Feedback: It is important that all health care providers have a complete list of the patient’s medications to avoid drugdrug interactions caused by one provider ordering a medication, unaware of another medication the Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 22 patient is taking that could interact with the new prescription. Using the same pharmacist for all prescriptions will also help to prevent this from happening. Informing the provider of all medications taken will not reduce costs of medications, which is best accomplished by requesting generic medications. Allergies should be disclosed to all health care providers as well, but this is not why it is important to provide a complete list of medications taken. Critical concentrations are desirable because that is the amount of drug needed to cause a therapeutic effect, or, in other words, to have the effect the drug is prescribed for. 5. A pharmacology student asks the instructor what an accurate description of a drug agonist is. What is the instructor’s best response? A) A drug that reacts with a receptor site on a cell preventing a reaction with another chemical on a different receptor site B) A drug that interferes with the enzyme systems that act as catalyst for different chemical reactions C) A drug that interacts directly with receptor sites to cause the same activity that a natural chemical would cause at that site D) A drug that reacts with receptor sites to block normal stimulation, producing no effect Ans: C Feedback: Agonists are drugs that produce effects similar to those produced by naturally occurring neurotransmitters, hormones, or other substances found in the body. Noncompetitive antagonists are drugs that react with some receptor sites preventing the reaction of another chemical with a different receptor site. Drugenzyme interactions interfere with the enzyme systems that stimulate various chemical reactions. 6. A nurse is caring for a patient who has been receiving a drug by the intramuscular route but will receive the drug orally after discharge. How does the nurse explain the increased dosage prescribed for the oral dose? A) Passive diffusion B) Active transport C) Glomerular filtration D) First-pass effect Ans: D Feedback: Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 23 The first-pass effect involves drugs that are absorbed from the small intestine directly into the portal venous system, which delivers the drug molecules to the liver. After reaching the liver, enzymes break the drug into metabolites, which may become active or may be deactivated and readily excreted from the body. A large percentage of the oral dose is usually destroyed and never reaches tissues. Oral dosages account for the phenomenon to ensure an appropriate amount of the drug in the body to produce a therapeutic action. Passive diffusion is the major process through which drugs are absorbed into the body. Active transport is a process that uses energy to actively move a molecule across a cell membrane and is often involved in drug excretion in the kidney. Glomerular filtration is the passage of water and water-soluble components from the plasma into the renal tubule. 7. A nurse is working as a member of a research team involved in exploring the unique response to drugs each individual displays based on genetic make-up. What is this area of study is called? A) Pharmacotherapeutics B) Pharmacodynamics C) Pharmacoeconomics D) Pharmacogenomics Ans: D Feedback: Pharmacogenomics is the area of study that includes mapping of the human genome. In the future, medical care and drug regimens may be personally designed based on a patient’s unique genetic makeup. Pharmacotherapeutics is the branch of pharmacology that deals with the uses of drugs to treat, prevent, and diagnose disease. Pharmacodynamics involves how a drug affects the body. Pharmacoeconomics includes the costs involved in drug therapy. 8. The nurse uses what term to describe the drug level required to have a therapeutic effect? A) Critical concentration B) Dynamic equilibrium C) Selective toxicity D) Active transport Ans: A Feedback: A critical concentration of a drug must be present before a reaction occurs within the cells to bring about the desired therapeutic effect. A dynamic equilibrium is obtained from absorption of a drug from Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 24 the site of drug entry, distribution to the active site, metabolism in the liver, and excretion from the body to have a critical concentration. Selective toxicity is the ability of a drug to attach only to those systems found in foreign cells. Active transport is the process that uses energy to actively move a molecule across a cell membrane and is often involved in drug excretion in the kidney. 9. A nurse is caring for a patient who is supposed to receive two drugs at the same time. What is the nurse’s priority action? A) Wash her hands before handling the medications. B) Consult a drug guide for compatibility. C) Question the patient concerning drug allergies. D) Identify the patient by checking the armband and asking the patient to state his name. Ans: B Feedback: A nurse should first consult a drug guide for compatibility when two or more drugs are being given at the same time. After compatibility is determined the medication can be administered. The nurse will perform hand hygiene, check for patient allergies, and ensure the right patient receives the medication by using two identifiers. 10. The nurse is talking with a group of nursing students who are doing clinical hours on the unit. A student asks if all intramuscular (IM) drugs are absorbed the same. What factor would the floor nurse tell the students to affect absorption of the IM administration of drugs? A) Perfusion of blood to the subcutaneous tissue B) Integrity of the mucous membranes C) Environmental temperature D) Blood flow to the gastrointestinal tract Ans: C Feedback: A cold environmental temperature can cause blood vessels to vasoconstrict and decreases absorption or in a hot environment vasodilate and increase absorption of IM medications. Blood flow to the subcutaneous tissues interferes with subcutaneous injection and blood flow to the gastrointestinal (GI) tract causes alterations in absorption for oral medications. The condition of mucous membranes can interfere with sublingual (under the tongue) and buccal (in the cheek) administration of drugs. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 11. 25 The patient is taking a drug that affects the body by increasing cellular activity. Where does this drug work on the cell? A) Receptor sites B) Cell membrane C) Golgi body D) Endoplasmic reticulum Ans: A Feedback: Many drugs are thought to act at specific areas on cell membranes called receptor sites. After the receptor site is activated, this in turn activates the enzyme systems to produce certain effects, such as increased or decreased cellular activity, changes in cell membrane permeability, or alterations in cellular metabolism. Receptor sites are generally located on the outside of cells and allow the drug to bypass the cell membrane. The Golgi body and endoplasmic reticulum are not involved in this process. 12. Several processes enable a drug to reach a specific concentration in the body. Together they are called dynamic equilibrium. What are these processes? (Select all that apply.) A) Distribution to the active site B) Biotransformation C) Absorption from the muscle D) Excretion E) Interaction with other drugs Ans: A, B, D Feedback: The actual concentration that a drug reaches in the body results from a dynamic equilibrium involving several processes: Absorption from the site of entry (can be from the muscle, the gastrointestinal (GI) tract if taken orally, of the subcutaneous tissue if given by that route); Distribution to the active site; biotransformation (metabolism) in the liver; excretion from the body. Interaction with other drugs is not part of the dynamic equilibrium. 13. A nurse is administering digoxin to a patient. To administer medications so that the drug is as effective Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 26 as possible, the nurse needs to consider what? A) Pharmacotherapeutics B) Pharmacokinetics C) Pharmacoeconomics D) Pharmacogenomics Ans: B Feedback: When administering a drug, the nurse needs to consider the phases of pharmacokinetics so that the drug regimen can be made as effective as possible. Pharmacogenomics is the area of study that includes mapping of the human genome. Pharmacotherapeutics is the branch of pharmacology that deals with the uses of drugs to treat, prevent, and diagnose disease. Pharmacoeconomics includes all costs involved in drug therapy. 14. The nurse is explaining how medications work to a group of peers and explains that disruption of a single step in any enzyme system disrupts what? A) Cell life B) Cell membrane C) Cell receptor sites D) Cell function Ans: D Feedback: If a single step in one of the many enzyme systems is blocked, normal cell function is disrupted. Cell life and cell membrane may be impacted by disruption of some enzymes but not all enzymes. Receptor sites would not be disrupted by disruption in a single step in the enzyme system. 15. The processes involved in dynamic equilibrium are key elements in the nurse’s ability to determine what? A) Dosage scheduling B) Amount of solution for mixing parenteral drugs Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) C) Timing of other drugs the patient is taking D) How long the patient has to take the drug Ans: A 27 Feedback: These processes are key elements in determining the amount of drug (dose) and the frequency of dose repetition (scheduling) required to achieve the critical concentration for the desired length of time. The processes in dynamic equilibrium are not key elements in determining the amount of diluents for intramuscular (IM) drugs; they do not aid in the timing of the other drugs the patient is taking or how long the patient has to take the drug. 16. What factor influences drug absorption? A) Kidney function B) Route of administration C) Liver function D) Cardiovascular function Ans: B Feedback: Drug absorption is influenced by the route of administration. IV administration is the fastest method; drug absorption is slower when given orally. Kidney function impacts excretion, liver function impacts metabolism, and cardiovascular function impacts distribution. 17. What does the lipid solubility of the drug influence? A) Absorption of the drug B) Metabolism of the drug C) Excretion of the drug D) Distribution of the drug Ans: D Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 28 Feedback: Factors that can affect distribution include the drug’s lipid solubility and ionization and the perfusion of the reactive tissue. The lipid solubility of a drug does not influence absorption, metabolism, or excretion. 18. The nursing students are learning about the half-life of drugs. A student asks the instructor to explain half-life. What is the instructor’s best response? A) Half-life of a drug is the time it takes for the amount of drug in the body to decrease to half of the peak level it previously achieved. B) Half-life is the amount of time it takes for the drug to be metabolized by the body. C) Half-life is the amount of time it takes for half of the drug to reach peak level in the body. D) Half-life of a drug is the time it takes for the drug to reach half its potential peak level in the body. Ans: A Feedback: The half-life of a drug is the time it takes for the amount of drug in the body to decrease to half the peak level it previously achieved. Therefore Options B, C, and D are not correct. 19. The patient is taking a 2-mg dose of ropinerol XR. The drug has a half-life of 12 hours. How long will it be before only 0.25 mg of this drug remains in the patient’s system? A) 24 hours B) 36 hours C) 48 hours D) 60 hours Ans: B Feedback: The half-life of a drug is the time it takes for the amount of drug in the body to decrease to half of the peak level it previously achieved. At 12 hours there will be 1 mg of the drug available to the body. At 24 hours there will be 0.5 mg; at 36 hours there will be 0.25 mg; at 48 hours there will be 0.125 mg, and at 60 hours there will be 0.0625 mg. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 20. 29 The patient has a diagnosis of multiple sclerosis and is taking the drug interferon beta-1a (Rebif). The patient takes this drug by subcutaneous injection three times a week. The dosage is 44 mcg per injection. If the patient takes an injection on Monday, how much of the drug would still be in the patient’s system when she takes her next injection on Wednesday, assuming the half-life of the drug is 24 hours? A) 22 mcg B) 16.5 mcg C) 11 mcg D) 5.5 mcg Ans: C Feedback: The half-life of a drug is the time it takes for the amount of drug in the body to decrease to 1 half the peak level it previously achieved. On Tuesday, there would be 22 mcg remaining in the body, so option A is incorrect. On Wednesday 11 mcg would remain, so option C is the correct answer. At 12 hours before taking the next dose on Wednesday, there would be 16.5 mcg remaining. If the injection were not taken on Wednesday, 12 hours after the dose was due, there would be 5.5 mcg remaining. 21. The patient is a 6-year-old child who is taking 125 mg of amoxicillin every 6 hours. Assuming that the half-life of Amoxicillin is 3 hours, how much Amoxicillin would be in the child’s body at the time of the next administration of the drug? A) 62.5 mg B) 46.875 mg C) 31.25 mg D) 15.625 mg Ans: C Feedback: The half-life of a drug is the time it takes for the amount of drug in the body to decrease to 1 half the peak level it previously achieved. Option A would occur at 3 hours after the original dose of amoxicillin. Option B would occur 4 1/2 hours after the original dose. Option C would occur at 6 hours after the original dose. Option D would occur at 7 1/2 hours after the original dose. 22. A drug with a half-life of 4 hours is administered at a dosage of 100 mg. How much of the drug will be in the patient’s system 8 hours after administration? Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) A) 75 mg B) 50 mg C) 37.5 mg D) 25 mg Ans: D 30 Feedback: The half-life of a drug is the time it takes for the amount of drug in the body to decrease to 1 half the peak level it previously achieved. Option A would occur 2 hours after administration of the drug. Option B would occur at 4 hours. Option C would occur at 6 hours. Option D would occur at 8 hours after the original administration of the drug. 23. The nurse administers amoxicillin 500 mg. The half-life of this drug is approximately 1 hour. At what point would the drug level in the body be 62.5 mg if the drug was not administered again? A) 1 hours after the original dose B) 2 hours after the original dose C) 3 hours after the original dose D) 4 hours after the original dose Ans: C Feedback: The half-life of a drug is the time it takes for the amount of drug in the body to decrease to one-half of the peak level it previously achieved. At a dose of 500 mg the drug level would be 250 mg in 1 hour, 125 mg in 2 hours, 62.5 mg in 3 hours, and 31.25 mg in 4 hours so the correct answer is 3 hours. 24. The nurse is caring for a patient who is receiving gentamicin, 250 mg and fluconazole (Diflucan), 500 mg at the same time. The nurse knows that if these two drugs competed with each other for proteinbinding sites, what would this do? A) Make the patient gentamicin deficient B) Make the patient fluconazole deficient Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) C) Counteract any positive benefit the drugs would have D) Alter the effectiveness of both drugs Ans: D 31 Feedback: Some drugs compete with each other for protein-binding sites, altering effectiveness or causing toxicity when the two drugs are given together. Nothing in the scenario would indicate that the patient would be either Gentamicin or Diflucan deficient, nor does it indicate that these drugs cannot be given together because they would counteract each other. 25. The student nurse asks the instructor why a patient with a central nervous system infection is receiving antibiotics that will not cross the bloodbrain barrier. What is the instructor’s most correct response? A) A severe infection alters the bloodbrain barrier to allow the drug to cross. B) A medication that is water soluble is more likely to cross the blood-brain barrier. C) Antibiotics are the exception to the bloodbrain barrier and cross easily. D) An infection that spreads outside the central nervous system helps drugs cross the barrier. Ans: A Feedback: Effective antibiotic treatment can occur only when the infection is severe enough to alter the bloodbrain barrier and allow antibiotics to cross. Lipid-soluble, not water-soluble, medications cross the bloodbrain barrier more easily and most antibiotics are lipid soluble, so they are not the exception. No matter where the infection originates, drugs must cross the bloodbrain barrier to treat central nervous system infections. 26. The patient is taking low dose aspirin daily for his heart. The nurse knows only a portion of the medication taken actually reaches the tissue due to what process? A) Distribution B) First-pass effect C) Reduced absorption D) Gastrointestinal circulation Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) Ans: 32 B Feedback: Drugs that are taken orally are usually absorbed from the small intestine directly into the portal venous system and then delivers these absorbed molecules into the liver, which immediately break the drug into metabolites, some of which are active and cause effects in the body, and some of which are deactivated and can be readily excreted from the body. As a result, a large percentage of the oral dose is destroyed at this point and never reaches the tissues. This process is not caused by distribution, absorption, or gastrointestinal circulation. 27. What needs to happen to the proteindrug complex for the drugs to reach the cells where the drug can act? A) The proteindrug complex must break itself into smaller pieces to enter the capillaries. B) The binding site on the protein picks up a chemical to make it soluble in the serum. C) The drug must break away from the protein-binding site and float freely. D) The drug must be dissolved in the plasma so it can enter the capillaries and then the tissues. Ans: C Feedback: Most drugs are bound, to some extent, to proteins in the blood to be carried into circulation. The proteindrug complex is relatively large and cannot enter into capillaries and then into tissues to react. The drug must be freed from the protein’s binding site at the tissues. This occurs without the introduction of another chemical or by dissolving in it plasma. 28. The nurse is reviewing the results of the patient’s laboratory tests. What must the nurse keep in mind when reviewing these results related to medication administration? A) The patient’s emotional response to the disease process B) The timing of the last dose of medication relative to when blood was drawn C) The possibility of a druglaboratory test interaction D) A change in the body’s responses or actions related to the drug Ans: C Feedback: Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 33 The body works through a series of chemical reactions. Because of this, administration of a particular drug may alter results of tests that are done on various chemical levels or reactions as part of a diagnostic study. This druglaboratory test interaction is caused by the drug being given and not necessarily by a change in the body’s responses or actions. The patient’s emotional response or timing of the last dose is not important in drug-laboratory interactions. 29. A patient has come to the clinic and been diagnosed with Lyme disease. The physician has ordered oral tetracycline. What is important for the nurse to include in the teaching plan about tetracycline? (Select all that apply.) A) Do not take the drug with anything high in sodium content to keep from producing a state of hypernatremia in the body. B) Do not take the drug with foods or other drugs that contain calcium. C) Do not take the drug at the same time you take an iron supplement or with foods that are high in iron content. D) Avoid exposure to the sun when taking this drug as it can turn your skin purple. E) Avoid eating bananas at the same time you take this drug as the potassium content of the tetracycline can produce hyperkalemia in the body. Ans: B, C Feedback: The antibiotic tetracycline is not absorbed from the gastrointestinal (GI) tract if calcium or calcium products (e.g., milk) are present in the stomach. It cannot be taken with iron products because a chemical reaction occurs preventing absorption. Although tetracycline can increase sun sensitivity, it does not turn the skin purple. Patients who take tetracycline do not need to avoid eating bananas or foods that are high in potassium. 30. A nurse is caring for a patient taking multiple drugs and is concerned about a possible drugdrug interaction. What is the nurse’s first and best means of avoiding this problem? A) Consult a drug guide. B) Call the pharmacist. C) Contact the provider. D) Ask another nurse. Ans: A Feedback: Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 34 Whenever two or more drugs are being given together, first consult a drug guide for a listing of clinically significant drugdrug interactions. Sometimes problems can be avoided by staggering the administration of the drugs or adjusting their dosages. Consulting the pharmacist is not wrong, but it would not be the first action to take. The nurse holds responsibility for his or her own practice so asking a health care provider or another nurse is based on the assumption that that professional is knowledgeable about all drugdrug interactions, which is likely not the case. 31. The nurse promotes optimal drug effectiveness by doing what? (Select all that apply.) A) Incorporate basic history and physical assessment factors into the plan of care. B) Evaluate the effectiveness of drugs after they have been administered. C) Modify the drug regimen to modify adverse or intolerable effects. D) Minimize the number of medications administered to patients. E) Examine factors known to influence specific drugs if they are to be effective. Ans: A, B, C, E Feedback: Incorporate basic history and physical assessment factors into any plan of care so that obvious problems can be identified and handled promptly. If a drug simply does not do what it is expected to do, further examine the factors that are known to influence drug effects. Frequently, the drug regimen can be modified to deal with that influence. Minimizing the number of medications administered is usually not an option because each drug is ordered for a reason of necessity for the patient. 32. The nurse administers a specific medication to an older adult patient every 4 hours. The patient has a history of chronic renal failure. Why would this patient be at risk for toxic drug levels? A) Cumulative effect B) First-pass effect C) Drug interactions D) Cross-tolerance effect Ans: A Feedback: Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 35 If a drug is taken in successive doses at intervals that are shorter than recommended, or if the body is unable to eliminate a drug properly, the drug can accumulate in the body, leading to toxic levels and adverse effects. This is a cumulative effect. First-pass effect addresses the reduction of available drug when taken orally due to metabolism in the liver before the drug reaches the bloodstream. Drug interactions occur when taken with other drugs, food, or complementary alternative therapies. Crosstolerance is resistance to drugs within the same class. 33. The patient, diagnosed with cancer, is receiving morphine sulfate (a potent narcotic pain reliever) to relieve cancer pain. Approximately every 7 days the medication is no longer effective in controlling the patient’s pain and a larger dose is needed to have the same effect. How might the nurse explain why this is happening? A) Tolerance B) Cumulation C) Interactions D) Addiction Ans: A Feedback: The body may develop a tolerance to some drugs over time. Tolerance may arise because of increased biotransformation of the drug, increased resistance to its effects, or other pharmacokinetic factors. When tolerance occurs, the amount of the drug no longer causes the same reaction. Therefore, increasingly larger doses are needed to achieve a therapeutic effect. Cumulative effect occurs when the drug is not properly eliminated and more of the drug is administered, resulting in toxic levels accumulating. Interactions occur when the drug reacts badly with another substance such as food, another drug, or an alternative or complementary therapy. Addiction is the psychological need for a substance. 34. While administering a medication that the nurse has researched and found to have limited effectiveness, the patient tells the nurse, I have read all about this drug and it is such a wonder drug. I’m so lucky my doctor prescribed it because I just know it will treat my problem. The nurse suspects this drug will be more effective than usual for this patient because of what effect? A) Cumulative effect B) First-pass effect C) Placebo effect D) Cross-tolerance effect Ans: C Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 36 Feedback: A drug is more likely to be effective if the patient thinks it will work than if the patient believes it will not work. This is called the placebo effect. If a drug is taken in successive doses at intervals that are shorter than recommended, or if the body is unable to eliminate a drug properly, the drug can accumulate in the body, leading to toxic levels and adverse effects. This is a cumulative effect. Firstpass effect addresses the reduction of available drug when taken orally due to metabolism in the liver before the drug reaches the bloodstream. Cross-tolerance is resistance to drugs within the same class. 35. The nurse administers an intravenous medication with a half-life of 24 hours but recognizes what factors in this patient could extend the drug’s half-life? (Select all that apply.) A) Gastrointestinal disease B) Kidney disease C) Liver disease D) Cardiovascular disease E) Route of administration Ans: B, C, D Feedback: Kidney disease could slow excretion and extend the drug’s half-life. Liver disease could slow metabolism resulting in an extended half-life. Cardiovascular disease could slow distribution resulting in a longer half-life. Gastrointestinal disease would not impact half-life because the medication was injected directly into the bloodstream. Route of administration would not extend half-life because IV injection eliminates the absorption step in the process. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 37 Chapter 03 - Toxic Effects of Drugs 1. A nurse is planning patient teaching about a newly prescribed drug. What is a priority teaching point included by the nurse to improve compliance and safety? A) List of pharmacies where the drug can be obtained B) Measures to alleviate any discomfort associated with adverse effects C) The cost of the brand name drug compared with the generic form D) Statistics related to Phase III testing for the prescribed drug Ans: B Feedback: If a patient is aware of certain adverse effects and how to alleviate or decrease the discomfort, he or she is more likely to continue taking the medication. A list of pharmacies can be useful information but will not improve safety or compliance. Knowing the cost of the brand name versus the generic form could also be helpful to the patient. However, a substitution may not be allowable and the cost of a drug does not improve patient safety. Most patients are not concerned with the statistics related to drug testing and it would not improve compliance or safety even if the patient was interested in the information. 2. A patient presents at the clinic complaining of vaginal itching and a clear discharge. The patient reports to the nurse that she has been taking an oral antibiotic for 10 days. The nurse is aware that the patient is experiencing what? A) An adverse reaction from the antibiotic B) A drug toxicity effect of the antibiotic C) An overdose of the drug that is damaging to more than one body system D) A superinfection caused by the antibiotic, which has destroyed normal flora Ans: D Feedback: Superinfections often occur with antibiotic use because the drug kills normal bacterial flora. This is not a result of toxic levels of the antibiotic, but rather an effect of the medication that has killed normal flora, which it is designed to do. Vaginal itching and a clear discharge are not considered adverse effects of an antibiotic. An overdose of a drug that damages more than one body systems is considered Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 38 drug poisoning. 3. A 42-year-old male patient is brought to the emergency department by ambulance. The patient is in distress. The nurse suspects an anaphylactic reaction resulting from taking oral penicillin. What assessment findings are important in making this diagnosis? A) Blood pressure (BP): 186/100, difficulty breathing B) Hematocrit (Hct): 32%, decreased urine output C) Temperature: 102º, swollen joints D) Profuse sweating, Blood Pressure: 92/58 Ans: A Feedback: An anaphylactic reaction is an immune reaction that causes a massive release of histamine, which results in edema and swelling that can lead to respiratory distress and increased blood pressure. A decreased hematocrit and decreased urine output suggests a cytotoxic reaction. An increased temperature and swollen joints could suggest serum sickness. Profuse sweating and decreased blood pressure may indicate cardiac-related issues. 4. A patient with seasonal allergies is taking an antihistamine to relieve itchy, watery eyes, and a runny nose. When planning teaching for this patient, the nurse would include what teaching point? A) Advise the patient to limit fluid intake to dry out mucous membranes. B) Advise the patient to avoid driving or operating machinery. C) Advise the patient to report strange dreams or nightmares. D) Advise the patient to decrease dietary fat. Ans: B Feedback: An adverse effect of antihistamines is drowsiness, so that injury to the patient or others can occur if driving or operating machinery. An increase in fluids would be indicated to help keep nasal membranes moist. It is common for dreams to occur when taking medication and it is not necessary to report them. Dietary fat should not interfere with the drug metabolism of antihistamines. 5. A nurse is providing teaching to a group of patients who are beginning drug therapy for acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). What should be included in her instructions to the group? Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) A) Take your medications as directed. Poisoning occurs with overdosage causing damage to more than one body system. B) Renal injury results from first-pass effect when the drug is excreted from the system. C) A blood dyscrasia due to drug therapy can be serious. Call us if your skin looks yellowish or you experience itching. D) Most drugs are metabolized in the liver and the first indication of damage is dark red papules, which should be reported immediately. Ans: A 39 Feedback: Poisoning resulting from overdosage can lead to the potential for fatal reactions when more than one body system is affected. Liver, not kidney, injury can be caused by the first-pass effect and can cause the skin to have a yellow appearance. Most drugs are metabolized in the liver but liver damage causes jaundice, manifested as a yellow tinge to the skin and sclera. Dark red papules appearing on limbs are characteristic of Stevens-Johnson syndrome, a potentially fatal erythema multiforme exudativum, which should be reported but is not due to liver damage. 6. The pharmacology instructor is talking to the nursing students about potassium-sparing diuretics and how they can lead to hyperkalemia, indicated by what assessment finding? A) Urine output of 1,500 mL/24 hours B) Blood pressure of 98/60 C) Potassium level of 5.9 mEq/L D) Calcium level of 11.4 mg/dL Ans: C Feedback: The normal range of serum potassium for an adult is 3.5 to 5.0 mEq/L. A level higher than 5.0 mEq/L can indicate hyperkalemia. Normal urinary output is between 1,500 and 2,000 cc per day. Urinary output below 1,000 mL per day would include oliguria and would indicate hyperkalemia. A decrease in blood pressure and pulse can indicate hypokalemia. Hyperkalemia refers to an elevated potassium level and not an elevated calcium level. 7. An 80-year-old patient presents at the clinic for a follow-up appointment. She is taking a macrolide antibiotic and is experiencing tinnitus. The nurse is talking with family members about home care for the patient. What should the nurse include in her instructions regarding home care? Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) A) Keep the patient in a prone position when in bed. B) Eliminate salt from the patient’s diet. C) Provide protective measures to prevent falling or injury. D) Monitor exposure to sunlight. Ans: C 40 Feedback: Macrolide antibiotics can cause severe auditory nerve damage, which can cause dizziness, ringing in the ears (tinnitus), and loss of balance and hearing. The patient would be at high risk for injury due to falls. Usually a person who is dizzy is unable to lie flat and needs to recline with the head elevated. Salt and sunlight are not a component of this patient’s presenting complaint. 8. Oral antidiabetic drugs can cause alterations in glucose metabolism. Patients who are taking these drugs would need to be observed for what? A) Increased urination B) Deep Kussmaul’s respirations C) Thirst and hot or flushed skin D) Confusion and lack of coordination Ans: D Feedback: Antidiabetic medications decrease blood glucose levels. If levels fall too low, symptoms of hypoglycemia would include confusion and lack of coordination. Elevated blood glucose levels can occur when the patient does not take the medications. With inadequate dosage, hyperglycemia can occur, resulting in increased urination in an attempt to eliminate serum glucose, deep Kussmaul’s respirations to reduce blood pH by eliminating carbon dioxide, thirst, and hot or flushed skin. 9. A patient is taking chloroquine (Aralen) for rheumatoid arthritis. What problem reported by the patient would the nurse suspect may be an adverse reaction of the medication? A) I have to urinate all the time. B) Sometimes I have blurred vision. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) C) I have tingling in my arms and legs. D) Sometimes I feel like I am off balance. Ans: B 41 Feedback: Chloroquine (Aralen) can cause ocular toxicity with blurring of vision, color vision changes, corneal damage, and blindness. Increased urination, tingling, and numbness are signs of hyperkalemia and hypokalemia. Loss of balance can be caused by auditory damage due to drug toxicity. 10. A 68-year-old patient who must take antihistamines for severe allergies is planning a vacation to Mexico. The nurse will encourage the patient to do what? A) Avoid sightseeing during the hottest part of the day. B) Discontinue the antihistamines if he becomes extremely restless. C) Decrease the dosage of the drugs if he experiences excessive thirst. D) Continue taking the antihistamines even if he begins to hallucinate. Ans: A Feedback: Antihistamines can cause anticholinergic effects, which would result in decreased sweating and place the patient at high risk for heat stroke. Avoiding the hottest part of the day will help prevent dehydration and heat prostration. Extreme restlessness could indicate Parkinson-like syndrome not usually associated with antihistamines. Excessive thirst is characteristic of hyperglycemia. Hallucinations are associated with drugs that affect neurologic functioning. Further, nurses should never tell patients to decrease or discontinue a drug unless the prescriber has instructed them to do so. 11. A 77-year-old man is brought to the clinic by his daughter for a routine follow-up appointment. The daughter tells the nurse that her father is only taking half the prescribed dosage of several of his medications. What effect would the nurse explain could result from this behavior? A) Increased risk of primary actions B) Dermatologic reaction C) Superinfection D) Reduced therapeutic effect Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) Ans: 42 D Feedback: Taking too little of the medication would mean that therapeutic levels are not being reached and the drugs will be less effective at lower dosages. Primary actions are the result of overdose, which is not the case in this patient who is taking too little of the drug. Dermatologic reactions are not likely if the patient is taking too little of the drug unless the drug is treating a dermatologic problem, which is not indicated by the question. Superinfection would only result if the patient was taking an antibiotic, which is not indicated by the question. 12. A patient with Parkinson’s disease is taking an anticholinergic drug to decrease the tremors and drooling caused by the disease process. The patient complains that he is having trouble voiding. The nurse would explain that this is what? A) A hypersensitive action of the drug B) A primary action of the drug C) An allergic action of the drug D) A secondary action of the drug Ans: D Feedback: Sometimes the drug dosage can be adjusted so that the desired effect is achieved without producing undesired secondary reactions. But sometimes this is not possible, and the adverse effects are almost inevitable. In such cases, the patient needs to be informed that these effects may occur and counseled about ways to cope with the undesired effects. The situation described is not a hypersensitivity reaction that would indicate an allergic reaction, a primary reaction that would be excessive therapeutic response, or an allergic reaction to the drug. 13. The nurse is assessing a patient new to the clinic. The patient says she is allergic to penicillin. What would be the nurse’s appropriate next action? A) Ascertain the exact nature of the patient’s response to the drug. B) Document the patient is allergic to penicillin. C) Mark the patient’s chart in red that she has a penicillin allergy. D) Continue to assess the patient for other allergies. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) Ans: 43 A Feedback: Ask additional questions of patients who state that they have a drug allergy to ascertain the exact nature of the response and whether it is a true drug allergy. Patients may confuse secondary actions of the drug with an allergy. Only after it was determined the action was truly an allergy would the nurse document the allergy, mark the patient’s chart, and continue to assess for other allergies. 14. The pharmacology instructor is discussing the adrenergic drug ephedrine with the nursing students and lists an adverse reaction of this drug as what? A) Bronchoconstriction B) Hyperglycemia C) Cardiac arrhythmias D) Severe constipation Ans: B Feedback: Ephedrine (generic), a drug used as a bronchodilator to treat asthma and relieve nasal congestion, can break down stored glycogen and cause an elevation of blood glucose by its effects on the sympathetic nervous system. Ephedrine does not cause bronchoconstriction, cardiac arrhythmias, or severe constipation. 15. The nurse needs to consider teratogenic effects of medications when caring for what population of patients? A) Older adults B) Patients with a history of cancer C) Children D) Young adult women Ans: D Feedback: A teratogen is a drug that can harm the fetus or embryo so the nurse would consider the teratogenic Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 44 properties of medications when caring for woman of child-bearing age including adolescents and young adult women. Teratogens have no impact on older adults or children. Carcinogens are chemicals that cause cancer. 16. The nurse is caring for a patient receiving an antineoplastic medication who reports fever, chills, sore throat, weakness, and back pain. What type of adverse effect does the nurse suspect this patient is experiencing? A) Dermatologic reaction B) Blood dyscrasia C) Electrolyte imbalance D) Superinfection Ans: B Feedback: Symptoms of blood dyscrasias include fever, chills, sore throat, weakness, back pain, dark urine, decreased hematocrit (anemia), low platelet count (thrombocytopenia), low white blood cell count (leukopenia), and a reduction of all cellular elements of the complete blood count (pancytopenia). Dermatologic reactions would be reflected in skin alterations, electrolyte imbalances would result in differing symptoms depending on the electrolyte involved but would not cause chills and fever, and a superinfection could cause a fever but would not cause a sore throat, weakness, or back pain unless the infection involved those body parts. 17. The pharmacology instructor explains to students that adverse effects can be extensions of what? A) Primary action of a drug B) Anaphylaxis C) Secondary action of a drug D) Anticholinergic responses to the drug Ans: A Feedback: Primary action adverse effects are extensions of the therapeutic action and are usually the result of overdosage, essentially too much of the therapeutic effect. Anaphylaxis is not an extension of the therapeutic action of the drug but a histamine reaction to an allergen. Secondary actions of a drug are negative effects of the drug that occur even when the drug is in the therapeutic range. Anticholinergic responses occur in response to drugs that block the parasympathetic nervous system. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 18. 45 A student nurse asks her study group how to define a drug allergy. What would be the peer group’s best response? A) A second effect of the body to a specific drug B) The formation of antibodies to a drug protein causing an immune response when the person is next exposed to that drug. C) A serum sickness caused by a reaction to a drug D) Immediate systemic reaction to the drug when exposed to the drug the first time. Ans: B Feedback: A drug allergy is the formation of antibodies to a drug or drug protein; causes an immune response when the person is next exposed to that drug. A drug allergy does not occur at the first exposure to a drug. A second action of a specific drug is an adverse response that the drug causes in addition to the therapeutic effect. Serum sickness is one type of allergic reaction but does not define allergic reaction. An immediate systemic reaction to a drug, usually not on first exposure, is an anaphylactic reaction. 19. The home health nurse is caring for an elderly patient with benign prostatic hypertrophy. An anticholinergic drug has been prescribed. What would be the nurse’s priority teaching point for this patient? A) Urinary incontinence may develop. B) Bladder hypertonia may develop. C) An increased dosage may be required. D) Empty the bladder before taking the drug. Ans: D Feedback: A patient with an enlarged prostate who takes an anticholinergic drug may develop urinary retention or even bladder paralysis when the drug’s effects block the urinary sphincters, so anticholinergic drugs are avoided whenever possible. However, if the medication is needed, the patient must be taught to empty the bladder before taking the drug. A reduced dosage also may be required to avoid potentially serious effects on the urinary system but this would not be a teaching point for the patient because the provider will make that decision. Hypotonia, not hypertonia, is more likely to occur. Urinary incontinence is not a likely effect in this case. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 20. 46 The Kardex record of a male patient who is prescribed antihistamines for treating an allergy reads as follows: Age: 32; Profession: Carpenter; Lifestyle & diet: Lives alone, average smoker, nonalcoholic, no food preferences, practices yoga; Medical history: Suffers from hay fever, recent urinary tract infection that has been treated successfully. What information from the Kardex is likely to have the greatest implication in educating the patient about antihistamine administration? A) The patient’s age B) The patient’s smoking habit C) The patient’s profession D) The patient’s medical history Ans: C Feedback: Most antihistamines cause drowsiness, so the nurse should advise the patient not to operate machinery or perform tasks that require alertness when taking antihistamines (e.g., climbing ladders, working on rooftops, standing on iron supports at the top of a building). Because the patient is not an older adult, his age has no implications on the therapy. Although encouraging the patient to make better lifestyle choices is an important part of the patient’s plan of care, this information is not related to administration of antihistamines. There is nothing in the documented medical history that is significant to antihistamine use. 21. The nurse is caring for a patient who experienced a severe headache. When the prescribed number of over-the-counter pain relievers did not work the patient said she took double the dosage an hour later. The nurse recognizes this patient is at greatest risk for what? A) An allergic reaction B) Anaphylactic reaction C) Poisoning D) Sedative effects Ans: C Feedback: This patient has taken an overdosage of the medication. Poisoning occurs when an overdose of a drug damages multiple body systems, leading to the potential for fatal reactions. Allergic and anaphylactic reactions can occur with any drug administration but this is not the patient’s greatest risk. More Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 47 information about the exact type of medication would be needed to determine whether sedative effects are likely. 22. What classification of drug allergy would be described as an immune system reaction to injected proteins used to treat immune conditions? A) A cytotoxic reaction B) Serum sickness C) A delayed reaction D) An anaphylactic reaction Ans: B Feedback: Serum sickness is an immune system reaction to certain medications, injected proteins used to treat immune conditions, or antiserum, the liquid part of blood that contains antibodies that help protect against infectious or poisonous substances. An allergic reaction can occur with any drug, not just those containing protein. Anaphylaxis is an acute, systemic, life-threatening allergic reaction. A cytotoxic reaction is one in which antibodies circulate and attack antigens on cell sites, causing death of that cell. 23. Why does the nurse need to be alert for any indication of an allergic reaction in patients? A) To obtain early warning of noncompliance in drug therapy B) To increase the effectiveness of a specific medication C) To maintain the patient’s safety during drug therapy D) To reduce the risk of adverse effects during drug therapy Ans: C Feedback: Being alert to adverse effectswhat to assess and how to intervene appropriatelycan increase the effectiveness of a drug regimen, provide for patient safety, and improve patient compliance. Indications of allergic reactions would not indicate noncompliance or improve effectiveness of a specific medication. Indications of allergic reaction would indicate an adverse effect and would not reduce the risk. 24. The nurse administers erythromycin, a drug that is known to irritate mucosa in the stomach lining. When the patient reports abdominal discomfort after taking the medication, the nurse would classify Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 48 this discomfort as what type of adverse effect? A) Primary action B) Secondary action C) Hypersensitivity reaction D) Allergic reaction Ans: D Feedback: Secondary actions are those actions that occur as a result of taking a medication but do not fall under the category of therapeutic action and are often negative. This patient is experiencing a secondary action of erythromycin. Primary actions would be extensions of therapeutic action. Hypersensitivity reaction would be an excessive response to either the primary or secondary effects of a drug. An allergic reaction would be an immune response to the drug. 25. The nurse administers antipsychotic medications to the patient who has taken these same drugs for many years. What signs and symptoms would the nurse attribute to secondary actions of the drug? (Select all that apply.) A) Muscular tremors B) Drooling C) Changes in gait D) Yellow discoloration of skin and sclera E) Fine red rash on the trunk Ans: A, B, D Feedback: Drugs that affect the dopamine levels in the brain (e.g., antipsychotic drugs), cause a syndrome that resembles Parkinson’s disease including lack of activity, akinesia, muscular tremors, drooling, changes in gait, rigidity, extreme restlessness or jitters (akathisia), or spasms (dyskinesia). Yellow discoloration of the skin and sclera indicate jaundice and would suggest liver damage. A fine red rash on the trunk would be a dermatologic reaction unrelated to an antipsychotic agent’s secondary effects. 26. The nurse is acting as the triage nurse in the emergency department when a 16-year-old boy is brought in by his friends. The patient is in respiratory distress, he is vomiting, and blood is noted in the vomitus. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 49 He is somnolent and his electrocardiogram shows an arrhythmia. The boy’s friends tell you he was taking a bunch of little green pills he got from the cupboard at his grandparent’s house. The nurse suspects what? A) Overdose of sleeping pills B) Poisoning C) Anaphylactic shock D) Allergic reaction to Dyazide Ans: B Feedback: Poisoning occurs when an overdose of a drug damages multiple body systems, leading to the potential for fatal reactions. The situation described does not indicate what was contained in the little green pills so it is not possible to say whether the drugs were sedatives or triamterene and hydrochlorothiazide (Dyazide). The symptoms do not indicate an anaphylactic reaction, which would not normally include bloody vomitus. 27. The patient with diabetes is also taking ephedrine to treat asthma that causes her blood sugar to increase. The patient asks the nurse, Why does this medication make my blood sugar go up? What is the nurse’s best response? A) The active ingredient in ephedrine is mixed with sugar. B) Ephedrine is a placebo containing only sugar. C) Stored glycogen is broken down by ephedrine, which is causing higher blood sugar levels. D) Insulin is inactivated by ephedrine so it cannot work to control sugar levels. Ans: C Feedback: Ephedrine breaks down stored glycogen, which then enters the bloodstream as glucose and causes an increase in serum blood glucose, or blood sugar, levels. Ephedrine is not mixed with sugar and is not a placebo. Ephedrine has no effect on insulin. 28. The nurse is writing a plan of care for a patient who is exhibiting Parkinson-like syndrome. What would be an appropriate intervention if, on assessing the patient, the nurse finds the patient is having difficulty swallowing? Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) A) Thicken all liquids. B) Keep the patient NPO (not taking anything orally). C) Give only soft or pureed foods. D) Provide small, frequent meals. Ans: D 50 Feedback: Provide small, frequent meals if swallowing becomes difficult. Keeping the patient NPO would be inappropriate because these effects often result from medications that will be taken throughout the patient’s life. Soft or pureed foods are often more difficult to swallow than more rigid foods. Thickening liquids would only be necessary if the dysphagia, or difficulty swallowing, continued to progress. 29. The post-anesthesia care unit nurse is serving a patient after a right knee arthroscopy. As the patient begins to wake up from anesthesia, the nurse assesses rigidity, involuntary movements, hyperthermia, and tachycardia. What would the nurse suspect is causing these effects? A) Neuroleptic malignant syndrome B) Parkinson-like syndrome C) Malignant tachycardia D) Anaphylactic shock Ans: A Feedback: Neuroleptic malignant syndrome is a generalized syndrome that includes extrapyramidal symptoms such as slowed reflexes, rigidity, involuntary movements; hyperthermia; autonomic disturbances (e.g., hypertension, fast heart rate); fever may be noted as well. This is most often seen after administering general anesthesia or drugs with central nervous system (CNS) effects. This syndrome was once known as malignant hyperthermia. These symptoms are not consistent with Parkinson-like syndrome or anaphylactic shock. Malignant tachycardia is a distracter. 30. A) A patient is admitted to the intensive care unit with hyperkalemia. The nurse caring for the patient knows that the most severe adverse effect of hyperkalemia is what? Renal failure Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) B) Cardiac emergency C) Liver failure D) Respiratory distress Ans: B 51 Feedback: Monitor for cardiac irregularities because potassium is an important electrolyte in the action potential, needed for cell membrane stability. When potassium levels are too high, the cells of the heart become very irritable and rhythm disturbances can occur. Be prepared for a possible cardiac emergency. Hyperkalemia is often found in the patient with renal failure. Liver failure and respiratory distress are not generally caused by hyperkalemia. 31. The nurse administers an anticholinergic medication to the patient. When assessing this patient, what finding will the nurse consider a secondary effect of the drug? A) Nasal congestion B) Tachycardia C) Hyperthermia D) Profuse sweating Ans: A Feedback: Anticholinergic secondary effects include dry mouth, altered taste perception, dysphagia, heartburn, constipation, bloating, paralytic ileus, urinary hesitancy and retention, impotence, blurred vision, cycloplegia, photophobia, headache, mental confusion, nasal congestion, palpitations, decreased sweating, and dry skin. Tachycardia, hyperthermia, and profuse sweating would not be expected findings or consistent with anticholinergic effects and would require further assessment. 32. Before administering a macrolide antibiotic the nurse would question the order for what patient? A) An 82-year-old woman with hypertension B) A 12-year-old boy with hearing loss C) A 30-year-old pregnant patient Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) D) A 51-year-old man after myocardial infarction Ans: B 52 Feedback: Macrolide antibiotics can cause severe auditory nerve damage so the nurse would question administration of this drug to the child with hearing loss because another antibiotic may be indicated to preserve remaining hearing. This drug is not contraindicated in older adults, although a lower dosage may be indicated. It may safely be given in pregnancy and after myocardial infarction. 33. What cardiac effect would the nurse be prepared to see in the patient with an extremely high potassium level? A) Arrhythmia B) Tachycardia C) Sudden death D) Bradycardia Ans: A Feedback: Elevated potassium levels irritate cardiac cells and increase the likelihood of a cardiac arrhythmia. Tachycardia, sudden death, and bradycardia would be the result of an arrhythmia if they were to occur. 34. The nurse administers a loop diuretic to the patient. In addition to sodium and water, what other electrolyte would the nurse expect to be excreted in significant amounts? A) Calcium B) Magnesium C) Potassium D) Zinc Ans: C Feedback: Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 53 Loop diuretics increase excretion of sodium, water, and potassium most significantly. Although other electrolytes may be excreted, loss of magnesium, calcium, and zinc are usually not significant. 35. The nurse administers a medication to the patient that induces the secondary action of hypoglycemia. What organ will be most acutely impacted by inadequate circulating glucose? A) Brain B) Heart C) Lungs D) Skin Ans: A Feedback: While all cells require glucose to function, the brain uses the greatest amount. As a result, hypoglycemia has the greatest impact on the brain, which explains why hypoglycemia has so many neurological signs and symptoms including fatigue, drowsiness, anxiety, headache, shaking, lack of coordination, numbness and tingling of the mouth, tongue, and /or lips; confusion, and in severe cases, seizures or coma may occur because the brain cannot function without adequate supplies of glucose. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 54 Chapter 04 - The Nursing Process in Drug Therapy and Patient Safety 1. A 70-year-old patient has just received a drug that can cause sedation. What would be the priority nursing diagnosis for this patient? A) Noncompliance: Cost of the drug B) Deficient knowledge: Unfamiliar with drug therapy C) Risk for injury: Related to adverse effects of the drug D) Ineffective health maintenance: Need for medication Ans: C Feedback: Because of the patient’s age and that the medication causes sedation, the highest priority nursing diagnosis is related to maintaining the patient’s safety. Safety for the patient is the nurse’s number one concern. There is nothing indicated related to the cost of the drug or the risk of noncompliance for this patient. Deficient knowledge will need to be addressed but it is not the priority when compared with patient safety. There is no indication the patient’s need for this medication is related to an ineffective health maintenance issue. 2. What is the responsibility of the nurse related to the patient’s drug therapy? (Select all that apply.) A) Teaching the patient how to cope with therapy to ensure the best outcome B) Providing therapy as well as medications C) Evaluating the effectiveness of therapy D) Altering the drug regimen to optimize outcome E) Recommending appropriate over-the-counter medications to treat adverse effects of prescription drug therapy Ans: A, B, C Feedback: A nurse is, therefore, a key health care provider who is in a position to assess the whole patient, to administer therapy as well as medications, to teach the patient how best to cope with the therapy to ensure the most favorable outcome, and to evaluate the effectiveness of the therapy. Nurses do not alter Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 55 drug therapy or recommend over-the-counter medications because prescribing is outside the nurse’s scope of practice. 3. The nurse is gathering assessment data from a medication history of a 38-year-old man with four children. What assessment information would be most important in providing care for this patient? A) The medication history of the patient’s mother and/or father B) The name of the patient’s pharmacy C) Insurance, financial support, and stability for the patient and his family D) The last time the patient was hospitalized Ans: C Feedback: In this situation, insurance, financial support, and stability would be the most important data and may determine compliance with future drug therapy. The medication history of the patient’s parents could indicate a pattern of overall attitude about drug therapy but is not the priority concern. The last time the patient was hospitalized could indicate whether the patient seeks medical care when appropriate or if he self-medicates, contributing to the nurse’s knowledge of this individual but this is not the priority concern. The name of the pharmacy would be unnecessary unless the nurse anticipates having to call a prescription in to the pharmacy for the prescriber. 4. During what phase of the nursing process would the nurse be required to consider the efficacy of nursing interventions related to drug therapy? A) Assessment B) Nursing diagnosis C) Interventions D) Evaluation Ans: D Feedback: Evaluation allows the nurse to review what has changed since intervening to determine whether the nursing care has had a positive, therapeutic effect moving the patient toward a more healthful life. If outcomes have not improved, the nurse begins again at the assessment phase of the nursing process with the goal of changing the plan of care to improve outcomes. The patient’s response to the drug and occurrence of adverse drug effects indicate the effectiveness of the nursing interventions related to drug therapy. Assessment involves a systematic, organized collection of data concerning a patient. A nursing Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 56 diagnosis indicates actual or potential alterations in patient function based on the assessment of the clinical situation. Interventions are actions taken to meet the patient’s needs, such as administration of drugs. 5. When the nurse reads in the drug handbook the section related to recommended dosage, it is important to remember that this suggested dosage is based on what? A) A 40-year-old man B) An average-sized adult C) A 150-pound adult male D) A healthy young adult Ans: C Feedback: Drug studies base the therapeutic dosage, or that dose needed to reach a critical concentration, on the physiology of a 150-pound healthy adult male. Testing is not routinely done in women because of the potential for unknown effects on the ova. Testing would not be done on an obese adult or older adult because of the potential for underlying disease, altered metabolism, or reactions to the drug. Children and adolescents are never used for testing due to ethical concerns. 6. A nurse is caring for a child on the pediatric unit. A drug is ordered for the child, but no pediatric dose is listed for the drug. To make sure that the right dose has been ordered, what will the nurse use to calculate the correct dose? A) Surface area B) Height C) Birth date D) Adult dosage Ans: A Feedback: The surface area of a child is calculated using height and weight. It is the most accurate way to determine an appropriate dosage for that child. Age does not take into consideration variations in growth. Height alone does not take into account the mass of the child. Gestational age is simply a distracter. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 7. 57 You are evaluating the discharge teaching you have done with your patient concerning drug therapy. What statement from the patient would indicate that teaching had been effective? A) I have to take three pills each day and I can take them at the time that fits my schedule. B) I should take the white pill in the morning because the doctor wants me to take it. C) I will add the names and dosages of these new drugs to my medication list in my wallet. D) I have prescriptions at different pharmacies. I shop around for the best price for each drug. Ans: C Feedback: The patient needs to recognize the importance of keeping an updated list of all current medications and the need to share this list with all health care providers to avoid drug-drug interactions. The patient should understand exactly when to take medications, why that medication is being taken, and how to take it safely. Patients should be encouraged to use a single pharmacy because this will add another layer of safety because the pharmacy will know all drugs being prescribed to this patient. 8. The nurse would expect to see an adjusted dosage in what patients? (Select all that apply.) A) Young adult women B) Middle-aged men C) Infants D) Neonates E) Older adults Ans: C, D, E Feedback: Patients at the extremes of the age spectrumchildren and older adultsoften require dosage adjustments based on the functional level of the liver and kidneys and the responsiveness of other organs. The child’s age and developmental level will also alert the nurse to possible problems with drug delivery, such as an inability to swallow pills or follow directions related to other delivery methods. The adult, whether male or female, would not require altered dosage unless a secondary condition such as renal or hepatic alterations existed. 9. When taking a medication history on a patient why should the nurse ask about the use of complementary or alternative therapies? Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) A) Patients starting on new drugs are usually not compliant with medical regimens. B) Many drug-alternative therapy interactions can cause serious problems. C) Natural products may be more effective and the prescribed drug may not be needed. D) The cost of the drug and the alternative therapy may be too expensive for the patient to handle. Ans: B 58 Feedback: Alternative therapies often involve the use of herbal products, which contain natural chemicals that affect the body. Many drug-alternative therapy interactions have been reported that could cause serious adverse effects, but patients often don’t think to mention these therapies when asked about the medications they are taking. The health care provider needs to be alert to these possible interactions and to adjust treatment appropriately. Cost and effectiveness may be factors, but the balancing of these therapies in the drug regimen to prevent interactions is the main concern of the nurse. 10. The nurse is reviewing the patient’s medication orders and finds an order stating amoxicillin 250 mg every 8 hours. What would the nurse question regarding this order? A) Dose B) Route C) Frequency of administration D) Allowance for generic substitution Ans: B Feedback: For the nurse to administer a medication, all essential components of a medication order must be written by the prescriber including drug name, dosage, route, frequency, and patient name. This order is missing the route and the drug could be given IV, IM, or PO. The nurse should call the ordering health care provider and clarify what route the medication is to be administered. 11. A) The home health nurse is caring for a 77-year-old patient with congestive heart failure. What would the nurse consider a priority to assess to develop the most effective plan of care related to medication administration? Description of the patient’s living environment Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) B) Required lifestyle changes C) Family members in the community D) Compliance with therapy to reduce risk of skin breakdown Ans: B 59 Feedback: Nurses must consider how a person responds to disease and its treatment, including the changes in lifestyle that may be required. By recognizing required lifestyles during the home visit the nurse can teach the patient how to make healthy choices and support the process of changing to new choices. Although the environment would impact the physical plan of care, it would not be a factor in the administration of medications. Assessment of family members in the community would not be a necessary part of the assessment in relation to the patient’s drug therapy. Nothing suggests the patient is at risk for skin breakdown so this would not factor into the medication regimen. 12. Student nurses are learning to weigh patients and do vital signs. How does a correct weight impact administering medication? A) Proper dosage calculation B) Assessing changes in fluid balance C) Assessing changes in nutritional status D) Caloric needs Ans: A Feedback: Dosage of medication is often calculated based on the patient’s weight, so getting patients’ weight wrong could cause a medication error. The patient’s weight gives information into fluid balance, nutritional status, and caloric needs but this is not associated with drug therapy. However, a patient’s weight is most important in determining the appropriateness of drug dosage. 13. Teaching the patient/caregiver about her or his medications is an important step in reducing the risk of medication errors. What is an important teaching point about medications? (Select all that apply.) A) Speak up and ask questions. B) Store medications in a warm humid place. C) Adjust your medication according to how you feel. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) D) Keep a list of your prescribed medications. E) Take all medications together in the morning. Ans: A, D 60 Feedback: Appropriate patient teaching will reduce the risk of medication errors and complications. Nurses teach patients to speak up, ask questions, and act as his or her own advocate when medications are being prescribed. He should keep a complete list of medications and have a copy available at all times in case of accident. Store drugs in a dry, cool place away from children and pets that could be harmed. Take medications as they have been prescribed and do not adjust dosage without authorization from the prescriber. Take medications at the time they are prescribed to be taken, always being aware that some drugs cannot be taken together. 14. A 73-year-old male patient is being discharged home today. The discharge order reads: Take 10 mL of guaifenesin (Robitussin) PO q4h. This over-the-counter pharmaceutical comes in bottles with plastic measuring caps. How much should the nurse teach the patient to take at home? A) 1/2 tsp B) 1 tsp C) 2 tsp D) 1 tbsp Ans: C Feedback: The nurse is responsible for teaching the patient the correct drug dosage. You should teach the patient that 5 mL = 1 tsp, so 10 mL (5 × 2) = 2 tsp; therefore Options A, B, and D are incorrect. It is important that patients be taught how to take their medication using measurement systems they are familiar with and know how to use. 15. It is important for the nurse to evaluate the efficacy of what parameter when evaluating the drug therapy of a patient? A) Appropriateness of drug dosages B) Compliance C) Caregivers’ knowledge level Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) D) Nursing interventions Ans: D 61 Feedback: During the evaluation phase of care, nurses evaluate how effective care has been in meeting outcome goals. Appropriateness of drug dosages should be determined before administering the medication and not when evaluating their effects. Often, compliance cannot be evaluated until the nurse evaluates the effectiveness of therapy and finds the drug is not performing as expected, at which time the nurse may question the patient about whether medications are being taken as ordered. Caregivers’ knowledge level is an assessment providing data that will determine the teaching plan. 16. The nurse is conducting an admission assessment on a patient. When collecting data related to medications the nurse asks What medications are you currently taking? After collecting this information, what other questions should the nurse ask? (Select all that apply.) A) Do you take any medications? B) What over-the-counter (OTC) medications do you take? C) Do you take an herbs, vitamins, or supplements? D) Do you take medications safely when you take them? E) Why do you take this medication? Ans: B, C Feedback: Patients often neglect to mention OTC drugs or alternative therapies (e.g., herbals) because they do not consider them to be actual drugs or they may be unwilling to admit their use to the health care provider. Ask patients specifically about OTC drug and alternative therapy use. The question What medications are you taking? has already been asked so there is no need to ask if they take any medications. Often, patients may take medications unsafely, so do not ask whether the patient takes drugs safely but instead assess exactly how they take medications to determine whether they are being taken safely. Patients should always know why they are taking each medication to understand whether they are getting the desired effect. 17. A) A 27-year-old man is admitted to the emergency department (ED) after a serious motorcycle accident. The patient has a head injury, abrasions covering the left side of his body, a broken left femur, and internal injuries that are not fully assessed at this time. He is transferred from the ED to the intensive care unit (ICU). The nurse who is going to care for this patient in the ICU knows that a priority responsibility in regard to drug therapy is what? Support vital functions Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) B) Continue curative treatment C) Institute life-saving treatment D) Monitor patient’s response Ans: D 62 Feedback: Because the nurse has the greatest direct and continued contact with the patient, the nurse is in the best position to detect minute changes that ultimately determine the course of drug therapytherapeutic success or discontinuation because of adverse or unacceptable responses. The nurse would support vital functions, continue curative treatment, and institute life-saving treatment, but these actions occur regardless of drug therapy. 18. When assessing a patient before starting a drug regimen, why would the nurse consider it important to assess baseline kidney function? A) To anticipate adverse effects of drugs B) To determine patient’s baseline electrolyte levels C) To determine patient’s ability to excrete the drug D) To determine patient’s ability to metabolize the drug Ans: C Feedback: Patients with kidney or liver disease require very cautious medication administration, often needing dosages to be decreased and contraindicating some drugs altogether. The patient’s renal status will indicate the ability to excrete the drug. Liver function is needed to assess metabolism. Electrolyte levels would be indicated by serum blood test results, not by studies of kidney function. The nurse’s goal is to prevent or minimize adverse effects of drugs, not to anticipate them. 19. A nurse is caring for a 77-year-old patient. The nurse plans care for this patient based on the knowledge that the aging process impacts drug therapy in what important way? A) Blood volume decreases B) Subcutaneous tissue increases Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) C) Total body water increases D) Muscle mass increases Ans: A 63 Feedback: As patients age, the body undergoes many normal changes that can affect drug therapy, such as a decreased blood volume, decreased gastrointestinal (GI) absorption, reduced blood flow to muscles or skin, and changes in receptor site responsiveness. As a person ages, subcutaneous tissue decreases, total body water decreases, and muscle mass decreases. 20. The nurse is caring for a patient who takes several drugs. What patient would the nurse monitor most closely because of an increased risk for adverse effects of medications? A) The school-aged child B) The obese middle-aged man C) The adolescent D) The newborn infant Ans: D Feedback: Patients most likely to have adverse drug reactions include the very young or very old due to physiologic characteristics peculiar to these age groups. Therefore, the newborn infant would be at greater risk than the school-aged child who is at greater risk than the adolescent or middle-aged man. 21. Which statement best describes drug efficacy/toxicity in pediatric patients? A) Drug requirements for infants have been extensively studied. B) Drug dosage is altered by age and weight in children. C) Children always need smaller doses of medication than adults. D) Infants and children are not at risk for drug toxicity if the dosage is correct. Ans: B Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 64 Feedback: All aspects of pediatric drug therapy must be guided by the child’s age, weight, and level of growth and development. Drugs are generally studied using healthy young men and are never studied in infants because they are not old enough to give consent for themselves. Drug dosages are very specific and a big child may weigh more than an adult and require a larger dose. Even when medications are given accurately, adverse effects can occur. 22. A 7-year-old boy fell off a wood pile while playing. He has been admitted to the intensive care unit with multiple broken bones and internal bleeding. What should the nurse know about drug therapy in this type of patient? A) Adverse effects may be decreased. B) Therapeutic effects may be increased. C) Pharmacodynamics may be altered. D) Pharmacokinetics remain the same. Ans: C Feedback: The child’s developmental age will influence pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics; the immature liver may not metabolize drugs in the same way and the kidneys may not work as efficiently as those of an adult. Adverse effects might be increased and therapeutic effects may be decreased. 23. After admitting a patient to the unit, the nurse is organizing times to administer ordered medications. What important consideration will guide the nurse’s timing of each medication? A) Comfort B) Ethnicity of patient C) Gender D) Age Ans: A Feedback: Organizing the day and the drug regimen to make it the least intrusive on a patient’s comfort can help to prevent errors and improve compliance. Ethnicity, gender, and age should be a consideration when ordering the drug, but after the drug is chosen it should be administered in a way that will maintain the Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 65 patient’s quality-of-life. 24. The nursing instructor is discussing drug therapy in the older adult. What would the instructor tell the students about what could affect therapeutic dosing in an older adult? A) Changes in the gastrointestinal (GI) system can reduce drug absorption. B) In older adults, drugs enter into circulation more quickly. C) In older adults, drugs are distributed to a smaller portion of the tissues. D) In older adults, drugs have an increased action. Ans: A Feedback: As patients age, the body undergoes many normal changes that can affect drug therapy, such as a decreased blood volume, decreased GI absorption, reduced blood flow to muscles or skin, and changes in receptor site responsiveness. They are not released more quickly into circulation; distributed to a smaller portion of tissue; nor do they have an increased action. 25. In today’s health care environment there is often more contact between the patient and the nurse than between the patient and the physician. How does this increased patient contact impact drug therapy? A) Choosing the best medication to treat the patient’s condition B) Assessing the patient’s preferred communication strategies C) Assessing the therapeutic success of the drug therapy D) Reducing dosage quickly when adverse effects arise Ans: C Feedback: Because the nurse has the greatest direct and continued contact with the patient, the nurse is in the best position to detect minute changes that ultimately determine the course of drug therapytherapeutic success or discontinuation because of adverse or unacceptable responses. The nurse does not choose the medication or reduce dosage because it is outside the scope of practice of the nurse. Communication strategies used by patients are not related to drug therapy. 26. The nurse admits a patient to the unit and learns the patient has recently been diagnosed with chronic renal failure but has not informed the primary care provider of this diagnosis. What is the nurse’s first priority? Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) A) Administer medications ordered immediately. B) Maintain the patient’s confidentiality. C) Call the admitting physician immediately. D) Provide teaching about chronic renal failure. Ans: C 66 Feedback: Knowledge of the patient’s diagnosed renal failure is essential to proper medication ordering because some dosages will need to be decreased whereas other medications may be contraindicated in this patient. The nurse does not breach confidentiality when sharing information that impacts needed care to the primary care provider. Teaching about renal failure may be provided at some point but it is not the priority in this situation. Medications should not be administered until they are appropriately adjusted by a health care provider who is aware of the renal failure diagnosis. 27. It is often necessary to obtain baseline data prior to initiating many forms of drug therapy. These baseline data include what? (Select all that apply.) A) Education level B) Allergies C) Drug use D) Number of members in family E) Father’s occupation Ans: A, B, C Feedback: Assessing educational level allows the nurse to plan an effective teaching plan. Allergies must be fully assessed before administering any medication to prevent allergic responses. Understanding the patient’s current drug use informs the nurse about drugs that may interact or be impacted. Knowing the number of family members and father’s occupation would not promote safer drug administration. 28. A 32-year-old woman is admitted to the unit with a diagnosis of hypovolemia. The nurse is developing a care plan for this patient. What is an appropriate nursing diagnosis to help prevent medication errors? Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) A) Dysfunctional gastrointestinal motility B) Ineffective self-health maintenance C) Risk for injury D) Deficient fluid volume Ans: D 67 Feedback: Hypovolemia is condition involving fluid volume in the body that is less than required. This would affect drug therapy for this patient and would be an important inclusion in the plan of care. The situation described does not indicate dysfunctional GI motility or ineffective self-health maintenance. A patient who is severely fluid volume deficient might be at risk for falls and injury but more information would be needed to make this determination. 29. The nurse applies the nursing process in medication therapy to ensure what? A) That medications are given at the right time B) That care is efficient and effective C) That the right dose of the drug is given to the patient D) That the right drug is given to the right patient at the right time Ans: B Feedback: Nurses use the nursing process as a decision-making, problem-solving process to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of care. Options A, C, and D are incorrect and do not describe why the nursing process is important as much as they explain how to give medications safely. 30. A 35-year-old male patient is admitted to the hospital with pneumonia. He was originally being treated at home, but became worse when he quit taking his antibiotic prematurely. What is an appropriate nursing diagnosis for this patient? A) Deficient knowledge: monitoring temperature B) Noncompliance C) Risk for injury related to hypoxia Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) D) Non-adherence: overuse Ans: B 68 Feedback: This patient did not take his antibiotic as directed. He quit taking his medication too soon, probably when he began to feel better so he was noncompliant with care. Why he quit taking the medication is unknown; it could have been a knowledge deficit or inability to pay for the full prescription. This will require further assessment to determine. Further data would need to be collected to determine whether the patient is experiencing hypoxia. He did not overuse his medication so option D is inaccurate. 31. The nurse is reviewing the patient’s admission medication orders. What order would the nurse to question? A) Digoxin .5 mg orally nowgive one dose only B) Lasix 20 mg. IV every 4 hours times 3 C) Gentamicin 80 mg IV to infuse over 1 hour every 12 hours D) Acetaminophen 650 mg PO every 4 hours as needed for pain Ans: A Feedback: The nurse should question the order for Digoxin.5 mg to make sure 0.5 mg is meant versus 5 mg, or what should have been ordered which is 0.05 mg. There should always be a 0 before a decimal point if no other number is present to make sure the decimal point is seen. The remaining orders could be administered as written. 32. The nursing instructor observes several nursing students administer medications to their assigned patients. The instructor would stop what student from administering the medication until the error was corrected? A) The student checks the label on the medication against the administration record three times. B) The student enters the patient’s room and asks the patient Are you Mr. Jones? C) The student checks the drug’s brand name and generic name before taking it to the patient. D) The student documents the medication upon exiting the patient’s room. Ans: B Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 69 Feedback: When the student asks the patient, Are you Mr. Jones the patient may nod in agreement, even if that is not his name. Perhaps he misheard, or maybe he wasn’t paying attention to the name, or he may just want to be agreeable but this manner of ensuring the right patient receives a medication often results in errors. The student is correct to check the medication name against the medication administration record (MAR) three times to ensure the right drug is administered. The student who checks brand name and generic name is accurate in making sure the correct drug is prepared. Medication should be documented as soon as they are given so this student is also correct. 33. The nurse is caring for a patient scheduled for surgery this morning who is not to be given anything orally. The nurse reviews the medication administration record and finds the patient has an important medication due but it is supposed to be given orally. What is the nurse’s best action? A) Give the medication with a small sip of water. B) Give the medication via a different route. C) Hold the medication and put a note on the front of the chart for the surgeon. D) Call the ordering health care provider and clarify administration. Ans: D Feedback: The nurse would consult with the ordering provider to determine whether the medication should be held, given by another route, or taken with a sip of water. Administering the medication with a small sip of water could cause the cancellation of the procedure, either because of the sip of water or because the medication may interfere with anesthesia. The nurse cannot change the route of administration without an order. Holding the medication would constitute a drug error because the medication was not given on time. 34. The nurse admits an older adult patient to the emergency room with reports of shortness of breath on exertion and a productive cough. The nurse reviews the patient’s current medications and the patient says, I take one pink pill every morning. The nurse asks the name of the drug and the patient says she doesn’t know. The patient cannot supply the name of the drug or the purpose in taking it either. This happens with four other medications the patient says she takes. What is an appropriate nursing diagnosis for this patient? A) Acute confusion B) Risk-prone health behavior C) Ineffective health maintenance Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) D) Noncompliance Ans: C 70 Feedback: This patient is demonstrating ineffective health maintenance because knowledge of what medications are being taken and why they are being taken is essential to her health. Patients should be instructed to carry an up-to-date list of current medications to share with all health care providers. She is taking her medication as ordered according to what she said so that would eliminate risk-prone health behaviors and noncompliance. There is no indication the patient is confused. 35. What action does the nurse take during the intervention state of the nursing process related to drug therapy? (Select all that apply.) A) Administer the medication. B) Determine medication effectiveness. C) Document the medication. D) Analyze the data collected. E) Collect a nursing history. Ans: A, C Feedback: During the implementation phase, the nurse administers and documents the medication. Effectiveness of the medication is determined during the evaluation phase. Analyzing data occurs when assigning appropriate nursing diagnoses. Collecting a nursing history is part of the assessment stage of the nursing process. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 71 Chapter 05 - Dosage Calculations 1. The nurse is calculating a drug dosage and converting from milligrams to grams. What measurement system is the nurse using? A) Metric system B) Apothecary system C) Household system D) Avoirdupois system Ans: A Feedback: The metric system is the most widely used system of measurement in the world; it is based on the decimal system. The gram is the basic unit of solid measure, and the liter unit of liquid measure. The apothecary system uses the grain as the basic unit of solid measure. The household system uses the pound as the basic unit of measure. The avoirdupois system uses ounces and grains, but it is mostly used by drug manufacturers for bulk medications. 2. The nurse teaches a young mother the importance of administering appropriate dosages of acetaminophen (Tylenol) and determines further teaching is needed when the mother makes what statement? A) The children’s dosage will change with time as they grow. B) My baby’s dose of Tylenol is about 1 half an adult dose. C) It is important to give the right dose to prevent toxic effects of the medication. D) My children’s dose of Tylenol should be based on their weight or age. Ans: B Feedback: A child’s dose is never based on an adult’s dose. A child’s dosage is based on weight and age and will change with age as they grow. Larger than directed dosages can result in toxic effects of this medication. 3. A nurse calculates the pediatric patient’s medication dosage using Clark’s rule and uses what formula? Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) A) Infant’s age in months/150 months times the average adult dose B) Child’s age in years/child’s age in years plus 12 times the average adult dose C) Weight of child in pounds/150 pounds times the average adult dose D) Surface area in square meters/1.73 times the average adult dose Ans: C 72 Feedback: Clark’s rule uses the child’s weight to calculate the dose and assumes the adult dose is based on a 150pound person. Fried’s rule applies to a child younger than 1 year of age and assumes that an adult dose would be appropriate for a child who is 12.5 years (150 months) old. Young’s rule applies to children 1 to 12 years of age. Surface area calculation of a child’s dose is determined with the use of a nomogram including the child’s height and weight. 4. Ans: The nurse receives a new medication order for a patient to administer 240 mg of medication per day in equally divided doses every 6 hours. How many mg of the drug should the nurse administer for each dose? 60 mg Feedback: Because there are 24 hours in a day, giving a drug every 6 hours would mean giving the drug 4 times a day. Because the total daily dose is 240 mg, dividing that dose by 4 would mean each dose should be 60 mg. 5. A physician orders 500 mL of IV solution be administered over 8 hours. If the IV infusion set delivers 15 drops per mL, how many drops per minute should the nurse administer to the patient? A) 15 drops/min B) 20 drops/min C) 32 drops/min D) 64 drops/min Ans: A Feedback: Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 73 If a patient was to receive 500 mL in 8 hours, dividing 500 by 8 would mean that the patient would receive 62.5 mL in 1 hour, or 60 min. Setting up the equation, 15 drops/mL/X equals 62.5 mL/60 min; cross-multiplying, the answer will be 15 drops/min. 6. The nurse is teaching a diabetic patient to self-administer Humulin insulin, supplied in a vial labeled 100 units/mL. The provider has ordered 32 units of Humulin insulin to be taken each morning. How many mL of insulin would the patient prepare for one dose? A) 0.032 mL B) 0.32 mL C) 3.2 mL D) 0.64 mL Ans: B Feedback: There are 100 units in each mL. Divide that amount by 32 units for the answer (0.32 mL). 7. Ans: The provider orders a maintenance dose of oral aminophylline, 3 mg/kg every 6 hour. The patient weighs 50 kg. How many mg should the nurse administer to the patient in a 24-hour period? 600 milligram Feedback: The patient’s weight times the number of milligram/kilogram will provide daily dosage of medication: 50 kg × 3 mg/kg = 150 mg per dose. The patient is to receive a dose every 6 hours. The number of hours in a day divided by the number of hours separating each dose supplies the number of dosages the patient receives per day: 24 hours ÷ 6 hours between doses = 4 doses per day. If each dose is 150 mg and the patient receives 4 of these doses a day, the total amount of medication received is 150 mg × 4 daily doses = 600 mg. 8. The physician writes an order for oxazepam for a 6-year-old child. The nurse verifies that there is no established dosage for children 6 to 12 years of age for oxazepam. The nurse knows that the usual adult dose is 10 mg tid. What would the nurse calculate the appropriate dose to be? A) 0.03 mg tid B) 0.3 mg tid C) 1.8 mg tid Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) D) 3.3 mg tid Ans: D 74 Feedback: Because the nurse knows only the child’s age, the nurse would need to use Young’s rule to determine the appropriate dosage. The formula for Young’s rule is: Child’s dose = child’s age in years ÷ (child’s age + 12) × average adult dose. Using the information provided in the question: Dose = 6 ÷ (6 + 12) × 10 mg = 6 ÷ 18 × 10 = 0.33 × 10 = 3.3. 9. A newly admitted patient has orders to receive 1,000 mL of normal saline IV over 8 hours. If the IV infusion set is a microdrip set that delivers 60 drops per mL, how many drops per minute should the nurse administer to the patient? A) 60 drops/min B) 125 drops/min C) 240 drops/min D) 480 drops/min Ans: B Feedback: If a patient was to receive 1,000 mL in 8 hours, dividing 1000 by 8 would mean that the patient would receive 125 mL in 1 hour, or 60 minutes. Setting up the equation, 60 drops/mL ÷ X = 125 mL/60 minutes; cross-multiplying, the answer is 125 drops/min. 10. The nurse is preparing to administer cefadroxil 1 g PO. The medication is supplied in 500-mg tablets. How many tablets will the nurse administer? A) 0.5 tablet B) 1 tablet C) 2 tablets D) 3 tablets Ans: C Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 75 Feedback: Convert 1 g to mg by multiplying 1 g times 1,000 mg. There are 500-mg in each tablet. Dividing the 1000 mg prescribed dosage by 500-mg available dosage, the answer is two tablets. 11. The nurse begins administering 500 mL of 5% dextrose and water solution at 01:00 to run over 4 hours. At 02:00, the nurse administers 80 mg gentamicin in 50 cc normal saline to infuse over 30 minutes. How many mL of fluid will the nurse administer to the patient between 02:00 and 03:00? A) 175 mL B) 150 mL C) 125 mL D) 100 mL Ans: A Feedback: The patient is receiving 500 mL over 4 hours. To determine how much fluid is infusing per hour = 500 mL ÷ 4 = 125. In addition to the 125 mL of IV solution, the patient also receives 50 mL of gentamicin during the 02:00 to 03:00 hour. 125 mL + 50 mL = 175 total mL of fluid received during this hour. 12. Ans: An adult patient with renal cancer, weighing 95 kg, is to receive vincristine 25 mcg/kg/day IV. What is the dosage of vincristine that the nurse should administer to the patient daily in mg? __________ 2.375 mg Feedback: This order requires 25 mcg of medication for every 1 kg of body weight. The patient weighs 95 kg. To determine total dosage multiply weight times mcg of medication: 25 × 95 = 2,375 mcg. Convert mcg to mg by moving the decimal three places to the left, or you can divide 2,375 by 1,000 because there are 1,000 mcg per mg. 13. Ans: The nurse is preparing medication for a 30-month-old child with otitis media in the right ear. The child weighs 33 pounds. The physician has ordered Keflex, 50 mg/kg/d in equally divided doses every 8 hours. The medication concentration is 250 mg/5 mL. How many milliliters should the nurse give the toddler for each dose? 5 mL Feedback: Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 76 To calculate the correct dosage, the nurse first converts the child’s weight from pounds to kilograms by dividing weight in pounds by 2.2 (2.2 lb = 1 kg). 33 pounds ÷ 2.2 pounds/kg = 15 kg. The child is to receive 50 mg for every kilogram. To determine this child’s dosage multiply weight times daily dose (15 kg × 50 mg/kg = 750 mg). Thus, 750 mg is to be administered in equally divided dosages every 8 hours, or 3 times a day. 750 mg ÷ 3 = 250 mg/dose. There is 250 mg in 5 mL of medication so the patient would be given 5 mL. 14. An adolescent is admitted to the intensive care unit with diabetic ketoacidosis. The nurse prepares a continuous insulin infusion of 100 units (U) regular insulin in 500 milligram normal saline. When documenting this medication, how many units of regular insulin will this patient receive per milligram of IV solution? A) 0.175 U/milligram B) 0.2 U/milligram C) 0.25 U/milligram D) 0.5 U/milligram Ans: B Feedback: The problem tells us there is 100 U/500 milligram. To determine how many units are in each milligram, divide both numbers by 500: 100 U ÷ 500/500 milligram÷ 500 = 0.2 U/1 milligram. 15. The patient drinks 18 ounces of fluid at lunchtime. How many milliliters of intake will the nurse document? A) 1.7 mL B) 0.6 mL C) 540 mL D) 54 mL Ans: C Feedback: 1 ounce = 30 mL. Using the ratio-and-proportion method: 1 oz/30 mL = 18 oz/X. Cross-multiply to determine the patient drank 540 mL of fluid. 16. The pediatric nurse is caring for a child who weighs 44 pounds. The physician has ordered Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) methylprednisolone sodium succinate (Solu-Medrol), 0.03 mg/kg/d IV in normal saline. How many milligrams of medication will the nurse prepare? A) 6.5 B) 6 C) 0.65 D) 0.6 Ans: D Feedback: First convert the child’s weight to kilograms by dividing 44 pounds by 2.2 kg/1 pound = 20 kg. Multiply the dosage times the child’s weight: 20 kg × 0.03 mg/kg/d = 0.6 mg/d 17. The nurse is to infuse 100 mL of 5% dextrose and water solution containing an IV antibiotic over 30 minutes. The infusion set delivers 10 gtt/mL. How many drops per minute will the nurse administer? A) 33 gtt/min B) 30.3 gtt/min C) 30 gtt/min D) 3 gtt/min Ans: A Feedback: Use the following ratio to determine how many drops of fluid to administer per minute: Using the information from this problem: Because it is not possible to deliver 0.3 drops, round 33.3 to 33 gtt/min. 18. A) An 80-year-old patient with internal bleeding is admitted through the emergency room after a motor vehicle accident. The physician has ordered 2 units of packed red blood cells (1 unit is 250 mL) to infuse over 1 hour each. The drip rate on the blood administration set is10 gtt/mL. The nurse administers how many drops per minute to infuse the blood as ordered? 47 77 Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) B) 42 C) 37 D) 32 Ans: B 78 Feedback: Use the following ratio to determine how many drops of fluid to administer per minute: Using the information from this problem: Because it is not possible to deliver 0.7 of a drop, round 41.7 to 42 minutes 19. The physician prescribes 250 mg of a drug. The information on the drug vial says the concentration is 500 mg/mL. How much of the drug will the nurse prepare? A) 0.25 mL B) 0.33 mL C) 0.5 mL D) 0.75 mL Ans: C Feedback: To determine amount to prepare: 500 mg/1 mL = 250 mg/X. Cross-multiply to determine the nurse will prepare 0.5 mL. 20. An 81-year-old patient with congestive heart failure has been sent to a cardiologist who prescribes digoxin (Lanoxin) 0.125 mg PO every morning. The pharmacy dispenses pills that contain 0.25 mg of Lanoxin. How many pills should the nurse teach the patient to take every morning? A) 2 B) 1.5 C) 1 D) 0.5 Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) Ans: 79 D Feedback: 0.25 mg/1 tablet = 0.125 mg dose/X. Cross-multiply to determine 0.5 or 1/2 of a tablet is to be taken daily. The nurse may request the pharmacy dispense a different concentration to prevent the patient from having to cut the tablet in half. 21. A patient with diabetic ketoacidosis is to receive a continuous infusion of regular insulin. The physician orders 1 L of 5% dextrose and water solution to run at 150 mL/h once the patient’s blood glucose has reached 250 mg/dL. The drip factor of the tubing is 15 gtt/mL. How many drops per minute will the nurse deliver? A) 0.25 gtt/min B) 62 gtt/min C) 37 gtt/min D) 250 gtt/min Ans: C Feedback: Using the information from this problem: 37.5 can be rounded to 37 or 38 gtt/min. 22. A patient has orders to receive 2 L of IV fluid over a 24-hour period with ½ this amount to be infused in the first 10 hours of treatment. How many milliliters per hour will the nurse administer during the first 10 hours of the infusion? A) 50 mL/h B) 100 mL/h C) 83 mL/h D) 200 mL/h Ans: B Feedback: Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 80 ½ of the 2 liters is to infuse in the first 10 hours. ½ of 2 = 1 L; 1 L = 1,000 mL to infuse over 10 hours = 100 mL/L. 23. A patient is going to have bowel surgery in the morning. The physician orders 500 mL of GoLytely PO to be administered at 5 PM this evening. How many liters will the nurse administer? A) 1 B) ¾ C) ½ D) ¼ Ans: C Feedback: Cross-multiply to learn 500 mL = ½ or 0.5 L. 24. The patient returns from the postanesthesia care unit (PACU) with the following order: morphine 3 mg IV every 2 hours as needed for relief of pain. The vial reads morphine, 4 mg/mL. How many milliliters of morphine will the nurse administer? A) 1 mL B) 0.75 mL C) 0.5 mL D) 0.25 mL Ans: B Feedback: Using the figures from this problem: 4 mg/1 mL = 3 mg/X. Cross-multiply yielding 0.75 mL. 25. A) A patient is admitted with a deep vein thrombosis in his or her left calf. The physician orders Heparin, 7,500 units subcutaneously every 12 hours. The medication vial reads Heparin, 10,000 units/mL. How many milliliters does the nurse administer? 0.5 mL Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) B) 0.75 mL C) 1 mL D) 1.25 mL Ans: A 81 Feedback: Using the information supplied by the problem: 10,000 units/1 mL = 7,500/X. Cross-multiplying yields X = 0.75 mL for each dose. 26. A patient with an acute myocardial infarction is admitted to the coronary care unit. The physician has ordered heparin 25,000 units in 250 mL normal saline to infuse at a rate of 600 units/h. The nurse sets the infusion pump to deliver how many milliliters in an hour? A) 8 B) 7 C) 6 D) 5 Ans: C Feedback: First determine the number of units per mL = 25,000 units/250 mL = 100 units/1 mL. Next use the ratio and proportion method to determine the number of milliliters needed to supply 600 units/h. 100 units/1 mL = 600 units/X. Cross-multiplying yields 6 mL needed every hour to supply the required dose. 27. The physician has ordered 30 mg of Demerol IM for relief of a severe migraine headache. The package insert reads meperidine hydrochloride (Demerol) 50 mg/mL. How many milliliters would the nurse administer? A) 1.6 B) 1 C) 0.6 D) 0.5 Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) Ans: 82 C Feedback: Filling in the information from the problem: 50 mg/1 mL = 30 mg/X mL. Cross-multiply yielding 0.6 mL required to administer a 30-mg dosage. 28. A patient is experiencing pain, so the physician orders codeine ½ grain every 4 hours. How many milligrams of codeine would the nurse administer? A) 15 mg B) 30 mg C) 60 mg D) 120 mg Ans: B Feedback: The simplest way to convert measurements from one system to another is to set up a ratio and proportion equation. The ratio containing two known equivalent amounts is placed on one side of an equation, and the ratio containing the amount you wish to convert and its unknown equivalent is placed on the other side. 60 mg/1 grain = flexion range of motion. Cross-multiplying yields 30 mg. 29. A 79-year-old female patient presents at the clinic complaining of constipation for 1 week. The nurse practitioner prescribes Milk of Magnesia 2 teaspoons by mouth as needed for relief of constipation. How many milliliter will the nurse administer? A) 30 mL B) 7.5 mL C) 10 mL D) 15 mL Ans: C Feedback: Use the ratio and proportion method to convert from household system to metric system. 5 mL/1 tsp = Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 83 X mL/2 tsp. Cross-multiplying yields 10 mL = 2 tsp. 30. A patient has orders to receive 3,000 mL of IV fluid at a rate of 150 mL/h. If the infusion starts at 08:00, when would it be finished? A) 20:00 B) 23:00 C) 01:00 D) 04:00 Ans: D Feedback: Amount of fluid to infuse = 3,000 mL; rate of infusion = 150 mL. 3,000 ÷ 150 mL = 20 hours to infuse. There are 24 hours in a day 20 hours = 4 hours. The infusion will complete in 4 hours before 08:00 (08:00 04:00 = 04:00 hour) so the infusion completes at 04:00. 31. The nurse recognizes that what system is being used when seeing a medication ordered in minims? A) Apothecary B) Metric C) Household D) Avoirdupois Ans: A Feedback: The apothecary system used minims as the basic measure of liquid and is rarely used today. The metric system uses liters as the basic unit of measurement for fluid, while the household system uses ounces and the avoirdupois system uses ounces with a different conversion amount. 32. A) The nurse is calculating the patient’s intake and output record and converts ounces to milliliters. What systems is this nurse converting from and to? From household to metric Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) B) From metric to household C) From household to apothecary D) From apothecary to Avoirdupois Ans: A 84 Feedback: Ounces can be either household or Avoirdupois, although they are not equal measurements and milliliters is a metric measurement. Since Avoirdupois to metric is not an available choice, the correct answer is household to metric. 33. What is the most accurate method for the nurse to use when determining a pediatric dosage? A) A nomogram using body surface area B) Young’s rule C) Fried’s rule D) Clark’s rule Ans: A Feedback: The most accurate means of determining a pediatric drug dosage is a nomogram using body surface area because the weight and body surface area of two children who are of the same age can be significantly different. Young’s rule, Fried’s rule, and Clark’s rule are based on the child’s age and the usual adult dosage and are rarely used today unless no other method will suffice for a specific drug. 34. The nurse determines a child’s body surface area is 0.4 m2 and the average adult dosage of the medication is 500 mg. The medication is supplied in liquid form with 500mg/5 mL. How many milliliter will the nurse administer? A) 3.46 mL B) 1.73 mL C) 0.5 mL D) 12 mL Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) Ans: 85 A Feedback: The formula for calculating the child’s dose using body surface area is surface area in m2 divided by 1.73 and then multiplied by adult dosage. Using the information supplied in this problem (0.4 ÷ 1.73) × 500 mg = 346 mg. Using the ratio and proportion method, 500 mg/5 mL = 346 mg/X mL; crossmultiplying yields 3.46 mL for the nurse to administer. 35. The physician orders acetaminophen (Tylenol) 15 mg/kg q4 hours PRN (as needed) for pain. The drug is supplied with 160 mg/5 mL. The infant weighs 12 pounds. How many milliliter of medication will the nurse administer? A) 2.5 mL B) 5.6 mL C) 12.4 mL D) 10.7 mL Ans: A Feedback: Begin by converting the infant’s weight to kilograms (12 pounds ÷ 2.2 pounds/kg = 5.45 kg). The order says to give 15 mg/kg. To determine this child’s dosage multiply weight and 15 mg/kg (5.45 kg × 15 mg/kg = 81.75 mg/dose). Finally, use the ratio and proportion method to calculate how to prepare the medication: 160 mg/5 mL = 81.75 mg/X mL; cross-multiplying yields 2.5 mL. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 86 Chapter 06 - Challenges to Effective Drug Therapy 1. A nurse is preparing a drug for administration to a patient. The drug does not have an indicated use for the patient’s medical diagnosis. What should the nurse do? A) Administer the drug as ordered. B) Question the prescriber concerning the ordered drug. C) Ask a coworker his or her thoughts about the ordered drug for the patient. D) Ask the patient why the drug has been prescribed for him or her. Ans: B Feedback: If the nurse is not sure about giving a drug, the order should be questioned. The nurse should never give a medication that is not clear. Mistakes do happen and the drug ordered, if not approved for the condition that the patient has, could be an error on someone’s part. The person who wrote the order should be questioned, not a co worker, who probably does not know why an off-label drug is being used. It would be unprofessional and inappropriate to ask the patient about the drug. 2. According to Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommendations, what is the role of the nurse in preparing for the possibility of bioterrorism? A) Post updated information on signs and symptoms of infections caused by biological agents B) Provide guidelines for treating patients exposed to, or potentially exposed to, biological agents C) Remain current on recognition and treatment of infections caused by biological weapons D) Advocate for increased funding for research involving bioterrorism and patient treatment Ans: C Feedback: Nurses need to remain current about recognition of and treatment for those exposed to biological weapons because nurses are often called upon to answer questions, reassure the public, offer educational programs, and serve on emergency preparedness committees. The CDC posts updated information on signs and symptoms of infections caused by biological agents that nurses would read. The CDC also provides guidelines for how to treat patients exposed to biological agents and the nurse must remain current on this information. Although nurses could advocate for funding, this is not usually Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 87 the role of the nurse. 3. How can the nurse find the most up-to-date information about emergency preparedness related to bioterrorism agents? A) Read textbooks devoted to the topic. B) Ask coworkers to explain current events. C) Read journal articles about bioterrorism agents. D) Visit the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Web site. Ans: D Feedback: The most current information will be found on the CDC Web site because new information can be posted immediately whereas textbooks and journal articles take time to print. Coworkers may or may not remain current on emergency preparedness and should not be the primary source of information. 4. The nurse is assessing a diabetic patient who has presented at the clinic reporting several hypoglycemic episodes during the past 3 weeks. The nurse questions the patient about the use of herbal or alternative therapies, suspecting what herbal remedy could cause the hypoglycemic episodes? A) St. John’s wort B) Kava C) Fish oil D) Ginseng Ans: D Feedback: Ginseng is known to decrease blood sugar levels. If the patient used this in combination with his or her oral antidiabetic agent, diet, and exercise, his or her blood sugar could drop below therapeutic levels. St. John’s wort interacts with many drugs, but not with antidiabetic agents. Kava is associated with liver toxicity. Fish oil has been associated with decreased coronary artery disease. 5. A 22-year-old patient calls the clinic and tells the nurse that she has been depressed and is thinking about taking St. John’s wort but wants to know if it is safe first. The nurse begins by questioning what other medications the patient takes and would be concerned about a drug-alternative drug interaction if the patient is also taking what type of medication? Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) A) Antihistamines B) Analgesics C) Antibiotics D) Oral contraceptives Ans: D 88 Feedback: St. John’s wort can interact with oral contraceptives that alter drug metabolism, which can decrease the effectiveness of the contraceptive. Analgesics, antibiotics, and antihistamines can be taken in combination with St. John’s wort without known adverse effects. 6. A patient tells the clinic nurse that he or she has been taking over-the-counter (OTC) Pepcid to relieve acid indigestion for several years. This is the first time the patient has ever reported this issue to a health care provider. As part of the teaching plan for this patient, the nurse explains what risk associated with not sharing OTC drug use with the provider? A) The OTC drug could be more expensive than seeking health care advice. B) The drug could mask symptoms of a serious problem that is undiagnosed. C) Use of the drug could cause a rebound effect of Pepcid. D) The drug could interact with several cold medicines. Ans: D Feedback: OTC drugs allow patients to self-diagnose and treat routine signs and symptoms without seeing a health care provider. This self-prescribed treatment, however, could mask a more serious underlying medical problem and result in a poor outcome for the patient. The issues of drug rebound and drug interaction need to be considered, but the safety issue related to self-diagnosis and self-prescription presents the greatest risk to the patient. Patients should always be encouraged to discuss the use of OTC products with their health care provider. 7. A) What patient populations would the nurse expect is most likely to be prescribed a drug for an off-label use? Adolescent and middle-aged adult patients Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) B) Patients with diabetes or heart disease C) Obstetric and neonatal patients D) Pediatric and geriatric patients Ans: D 89 Feedback: Drugs being used for an off-label purpose are commonly prescribed for pediatric and geriatric populations due to the lack of drug trial information and minimal premarket testing. Often a trial-anderror method is used in treating both the pediatric and geriatric populations when only adult information is known. The geriatric population responds to medication more like children because of their decreased ability to metabolize medications. Adolescents, especially later adolescents, use medications similarly to young adults as do middle-aged adults. Patients with different diagnoses are often involved in drug testing including those with diabetes and heart disease. Drugs are discouraged for use in obstetric patients. 8. A patient calls the clinic and asks to speak to a nurse. The patient questions the nurse about the use of a drug that was advertised on TV. The patient tells the nurse he or she is sure that the drug will make him or her feel the same way as described in the commercial. What response is most appropriate for the nurse to make? A) I’m glad that you want to be involved in treatment decisions but you are not qualified to decide what medications are best for your condition. B) It’s important to remember that drug advertisements emphasize the positive effects of drug therapy and not the adverse effects or contraindications. C) You need to remember that the drugs being advertised are much more expensive than other drugs that have the same effect. D) I’ve seen those advertisements and I would want to take that medication too if I had the condition it was designed to treat. Ans: B Feedback: It would be important for the nurse to remind the patient that advertisements always emphasize the positive effects of drug therapy. The patient should not be discouraged from contributing to the plan of care by being told she is not adequately qualified to make decisions because no one is more qualified to make decisions about her own body. Although the drug may be more expensive, this is not a reason to choose or avoid a medication that could be more effective. Agreeing with the patient is not meeting the nurse’s obligation to teach and inform. 9. The clinic nurse is talking with a patient about information concerning a drug her or she bought online. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 90 What is the nurse’s responsibility to the patient concerning this information? A) Encourage the patient to seek information about drugs from a pharmacist. B) Explain that information obtained from the Internet is not always accurate. C) Offer the patient a drug reference guide to read and learn more about the drug. D) Interpret the information and explain it in terms that the patient will understand. Ans: D Feedback: The Internet can be a good reference for drug information. However, the amount and reliability of the information can be overwhelming. The nurse should always try to interpret the information and explain it in terms that the patient will understand. A pharmacist is a good resource person but may not be able to teach from a holistic perspective. Drug reference guides may be hard for the patient to understand and he or she would still need someone to interpret the information. 10. The triage nurse in the emergency department sees a patient suspected of abusing amphetamines brought in by friends. While assessing this patient, what would the nurse be likely to find if steroids are being abused? A) Hypertension B) Bradycardia C) Drowsiness D) Elated mood Ans: A Feedback: Increases in blood pressure, tachycardia, and insomnia are symptoms of amphetamine abuse. Elation can indicate abuse of cannabis. 11. The nursing instructor is discussing the off-label use of drugs. What group of drugs would the instructor tell the nursing students is often used for off-label indications? A) Drugs used to treat psychiatric problems B) Drugs used to treat gastrointestinal (GI) problems Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) C) Drugs used to treat cardiovascular problems D) Drugs used to treat musculoskeletal problems Ans: A 91 Feedback: Drugs often used for off-label indications include the drugs used to treat various psychiatric problems. Drugs used to treat GI, cardiovascular, or musculoskeletal problems do not fall in the category of frequent off-label uses. 12. The patient calls the clinic nurse and says, I looked this medication up on the Internet after it was prescribed yesterday and there is nothing in the literature about this drug being used to treat my disorder. Should I still take it? What is the nurse’s best response? A) No, stop taking it immediately until I can consult with the doctor because it is obvious a mistake was made. B) Oh, that’s okay. Go ahead and take it because the doctor wouldn’t order it if he or she didn’t think it would be effective. C) It is quite common for drugs to be found to have positive effects for a condition not originally intended so it is safe to take. D) Let me talk with the physician about why this medication was ordered for you and I will call you back. Ans: D Feedback: Off-label use is relatively common because new information is gathered when the drug is used by large numbers of people that may indicate another condition for which the drug is effective. However, if the nurse does not know for a fact that the drug prescribed is the right drug for the patient’s condition, it is always best to consult with the prescriber to make sure the patient is taking the right drug and to avoid a medication error. The medication may be perfectly safe so the patient should not be told the doctor made a mistake. 13. When a drug is ordered off-label, what must the nurse be clear about before administering the drug? (Select all that apply.) A) Why the drug is being given B) Its potential for problems Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) C) The research that has been done D) The age group it was pretested on E) The intended use Ans: A, B, E 92 Feedback: Liability issues surrounding many of these uses are very unclear, and the nurse should be clear about the intended use, why the drug is being given, and its potential for problems. Knowing the age group it was pretested on and knowing the research that has been done are not factors the nurse needs to know before administering the drug. 14. It is important for the nurse to be aware of what related to the way drugs are marketed? A) The adverse effects the advertisements do not mention B) What magazines and Web sites contain the advertisement C) What patients are seeing in the advertisements about these drugs D) The name of the cheerful, happy models who are advertising these drugs Ans: C Feedback: As the marketing power for prescription drugs continues to grow, the nurse must be constantly aware of what patients are seeing, what the ads are claiming, and the real data behind the indications and contraindications for these hot drugs. The Food and Drug Administration regulates the information that needs to be contained within medication ads. Where the patient saw the ad and the actors in the ads are unimportant. 15. When evaluating information accessed over the Internet, an important question the nurse should teach the patient to ask is what? A) Is the information anecdotal? B) Where has this information been obtained? C) Is this information paid for by the drug company? D) How many patients have had input into the information? Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) Ans: 93 A Feedback: Many people do not know how to evaluate the drug-related information that they can access over the Internet. Is it accurate or anecdotal is an important concept for the nurse to teach the patient to assess to verify the accuracy of the information. Where the information came from is unimportant. It would be expected that all drug advertising is paid for by the drug company and this is not an important concern. Number of patients with input into the information is most likely none because information is gathered from health care professionals. 16. How has the patient’s access to drug information changed the way the patient interacts with the nurse and other health care providers? A) Patients share information from research reports with health care providers. B) Patients are contacting drug companies to see what their latest reports say. C) Patients are more likely to challenge the health care provider with their own research. D) Patients are more likely to self-prescribe and not obtain prescriptions from their health care provider. Ans: C Feedback: Access to consumer advertising, mass media health reports, and the Internet influence some patients to request specific treatments, to question therapy, and to challenge the health care provider. Consumers do not generally read research reports from medical facilities and contact drug companies to see what their reports say, and they cannot self-medicate because many of these drugs require a prescription to obtain them. 17. What can make a nurse or any health care provider lose credibility with the patient? A) Being unprepared to deal with the disease of the week B) Refusing to write prescriptions for the drug the patient requests C) Not being knowledgeable about diseases described on House D) Being prepared to discuss the role of concierge doctor Ans: A Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 94 Feedback: Some health care providers have learned to deal with the disease of the week as seen on talk shows; others can be unprepared to deal with what was presented and may lose credibility with the patient. 18. Today, an abundance of information is available in the health care arena for consumers, resulting in the nurse encountering patients who have a much greater use of what? A) Over-the-counter (OTC) therapies B) Alternative therapies C) Prescription drugs D) Off-label drugs Ans: B Feedback: The patient now comes into the health care system burdened with the influence of advertising, the Internet, and a growing alternative therapy industry. Many patients no longer calmly accept whatever medication is selected for them. Indeed, an increasing number of patients are turning to alternative therapies with the belief that they will treat their disorder and reduce risk of adverse effects. Although more prescription drugs are used today, that is not related to abundant information. No indication exists of an increase in use of OTC or off-label drugs. 19. Because of the amount of care now being done in the home care setting, it is imperative that the nurse teach the patients what? (Select all that apply.) A) Care givers educational level. B) Generic names of medication C) Over-the-counter (OTC) drugs that need to be avoided D) Alleviation of adverse effects E) How to calculate safe dosages Ans: B, C, D Feedback: The responsibility of meeting the tremendous increase in teaching needs of patients frequently resides Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 95 with the nurse. Patients need to know exactly what medications they are taking (generic and brand names), the dose of each medication, and what each is supposed to do. Patients also need to know what they can do to alleviate some of the adverse effects that are expected with each drug (e.g., small meals if gastrointestinal upset is common, use of a humidifier if secretions will be dried and make breathing difficult), which OTC drugs or alternative therapies they need to avoid while taking their prescribed drugs, and what to watch for that would indicate a need to call the health care provider. 20. What concerns might the nurse legitimately have related to the use of alternative therapies? (Select all that apply.) A) The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) does not test or regulate active ingredients. B) The incidental ingredients are clearly marked on the label. C) The dosage contained in each tablet may vary greatly. D) No alternative therapies have been found to be effective. E) Advertising of alternative products is not as restrictive or accurate. Ans: A, C, E Feedback: Alternative products are not controlled or tested by the FDA and advertising is not as restrictive or accurate as with classic drugs. Incidental ingredients are often unknown and strength of tablets may vary within the bottle depending on the conditions under which they were grown. While some alternative therapies have been found to be effective, there are others who have not been studied. 21. The nurse provides teaching to the patient using herbal therapies and includes what important information related to the effects of the herbal therapy? A) They can interact with prescription drugs. B) They always contain known ingredients. C) They are natural so they are effective and safe. D) The ingredients are natural, meaning toxicity is not a concern. Ans: A Feedback: Herbal therapies can produce unexpected adverse effects and toxic reactions, can interact with prescription drugs, and can contain various unknown ingredients that alter the therapies’ effectiveness Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 96 and toxicity. 22. When patients do not understand the information provided with their medication, whose responsibility is it to help them sort through and comprehend the meaning? A) Care giver B) Nurse C) Patient D) Physician Ans: B Feedback: Many pharmacies provide written information with each drug that is dispensed, but trying to organize these sheets of information into a usable and understandable form is difficult for many patients. The nurse is often the one who needs to sort through the provided information to organize, simplify, and make sense of it for the patient. 23. The nurse is providing an inservice on alternative therapies for peers and explains that the term alternative therapies includes what? A) Holistic drug therapy B) Hospice care C) Nondrug measures D) Home care Ans: C Feedback: Herbal medicines and alternative therapies are found in ancient records and have often been the basis for discovery of an active ingredient that is later developed into a regulated medication. Today, alternative therapies can also include non-drug measures, such as imaging and relaxation. Options A, B, and D are not included in alternative therapies. 24. The patient calls the clinic and talks to the nurse saying, I found the same drug the provider prescribed on the Internet and it is much cheaper. Is it safe for me to order my drug from this site? What is the nurse’s best response? Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) A) It is usually safe to order drugs from Internet Web sites if it is a reliable site. B) Most drugs ordered online come from another country and are safely used there. C) The drug you get will be the same chemical prescribed but the dosage may differ. D) The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has issued warnings to consumers about the risk of taking unregulated drugs. Ans: D 97 Feedback: The FDA has begun checking these drugs when they arrive in this country and have found many discrepancies between what was ordered and what is in the product, as well as problems in the storage of these products. Some foreign brand names are the same as brand names in this country but are associated with different generic drugs. The FDA has issued many warnings to consumers about the risk of taking some of these drugs without medical supervision, reminding consumers that they are not protected by U.S. laws or regulations when they purchase drugs from other countries. 25. With the need to protect our environment, what is it now important for the nurse to teach patients to do? A) Dispose of drugs no longer used on an annual basis. B) Flush drugs down the toilet. C) Bury unused in the yard. D) Throw unused pill bottles in the trash in original containers. Ans: A Feedback: Patients should go through their medicine cabinet annually and dispose of drugs no longer used. Unused drugs should not be flushed down the toilet or buried in the yard because they seep into the community water supply. Pills should be removed from their bottle and mixed with an undesirable substance to prevent someone from using the medication if found. 26. The nurse receives a call from a frantic mother saying, My child swallowed some of my birth control pills. Should I give Ipecac? What is the nurse’s best response? A) Yes, give Ipecac and follow the dosage directions on the bottle. B) Ipecac is not effective for this use so you should not give it to your child. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) C) Give the Ipecac only if you are absolutely sure your child swallowed the pills. D) No, don’t give Ipecac because it will cause your child to vomit and make a mess. Ans: B 98 Feedback: Ipecac is a drug that the Food and Drug Administration tested in 2003 and found, despite its use for many years, that it was not effective in inducing vomiting in children suspected of poisoning. As a result, it is no longer used. The mother should be instructed not to give it and to call poison control to get up-to-date instructions on how to deal with this emergency. Whether the pills were swallowed, this child requires appropriate intervention because it is better to err on the side of caution. Making a mess is not a concern. 27. The patient tells the nurse that he or she has begun ordering his or her medications over the Internet because it is cheaper. What statement made by the nurse in response to this information is accurate? A) All drugs are manufactured with the same quality controls. B) Any drug that is shipped into this country is safe to use. C) Foreign drugs may have the same name as domestic drugs, but they are not the same drug. D) If you order from Canada or Mexico, the drugs are safe because they undergo testing. Ans: C Feedback: The Food and Drug Administration has begun checking these drugs when they arrive in this country and have found many discrepancies between what was ordered and what is in the product, as well as problems in the storage of these products. Some foreign brand names are the same as brand names in this country but are associated with different generic drugs. Options A, B, and D are incorrect because not all drugs are manufactured the same and they are not always safe coming from another country. 28. The increasing number of patients who go to their health care provider and request a drug they have seen advertised on television or in a magazine has created what continuing challenge to health care providers? A) Treating infections appropriately B) Treating sicker patients C) Prescribing cost-effectively Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) D) Staying knowledgeable about drug therapy Ans: D 99 Feedback: As the marketing power for prescription drugs continues to grow, the health care provider must be constantly aware of what patients are seeing (or reading), what the commercials and ads are promising, and the real data behind the indications and contraindications for these hot drugs. It is a continuing challenge to stay up-to-date and knowledgeable about drug therapy. 29. Ipecac, formerly used as the drug of choice by parents for treatment of suspected poisoning in children, was tested by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2003. What was the finding of this testing? A) Ipecac is ineffective for its intended use. B) Ipecac is the safest treatment for poisoning in children. C) Ipecac was grandfathered in as an ineffective drug. D) Ipecac induces vomiting. Ans: A Feedback: Ipecac, a formerly standard over-the-counter drug, was used for many years by parents to induce vomiting in children in cases of suspected poisoning or suspected drug overdose. The drug was finally tested and in 2003, the FDA announced that it was not found to be effective for its intended use. Although it was grandfathered in as an effective drug, this was not what the study researched. Ipecac is not effective and does not consistently induce vomiting. 30. Federal guidelines state that when advertising a drug, if the company states what the drug is used for, what other information must also be included in the advertisement? (Select all that apply.) A) Symptoms B) Contraindications C) Adverse effects D) Precautions E) Cost Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) Ans: 100 B, C, D Feedback: If a drug advertisement states what the drug is used for, it must also state contraindications, adverse effects, and precautions. The advertisement does not have to state symptoms or cost. 31. The parent of a 2-year-old child is visiting his or her pediatric health care provider and shows the nurse the advertisement for allergy medication found in a magazine in the waiting room saying, This drug sounds like it would be far more effective to treat my son’s asthma and I’d only have to give it once a day. What is the nurse’s best response? A) Talk with your health care provider about this drug, but be aware that advertisements do not always provide all the important information you need to know. B) Oh, I need to throw that magazine away because so many people show me that ad and it is all complete nonsense with no truth to it at all. C) I’ve been seeing amazingly positive results from that medication so you are absolutely right to want to give it to your child. D) That drug is dangerous and should not be given to children under the age of 5 unless there are no other good options. Ans: A Feedback: The health care provider should make the decision about what medications are to be prescribed, not the nurse. However, the nurse can make the mother aware of the fact that there is often more that goes into choosing the correct drug than the bit of information disclosed in the advertisement. Becoming upset with the mother, agreeing with the mother, or frightening the mother about the medication is the wrong approach for the nurse to use. 32. The local news has been discussing a specific rare disorder that killed a child in the community this week, describing the symptoms of the disease as including nasal congestion, ear pain, and a cough. The pediatrician’s office is receiving numerous calls asking to make appointments to rule out this rare disease. What is the nurse’s best action? A) Prepare a handout that describes the disorder discussed in the news in greater detail. B) Tell parents their child is experiencing the common cold and do not need to be seen. C) Direct all calls to the local news agency to answer questions and provide details. D) Become familiar with the disorder and screen each call for more specific symptoms. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) Ans: 101 A Feedback: The nurse needs to not only become more familiar with the disorder in the news, but also needs to be prepared to teach parents about the disease of the week to allay fears so a handout with detailed information would allow the parents to have something to consult after leaving the provider’s office. Turning parents away without seeing their child will increase fears and the office will lose credibility for lack of interest in their child’s well-being. Directing calls to the news agencies will not provide parents with essential information. Screening calls without seeing the child could be potentially very dangerous. 33. The nurse is teaching the patient how to safely use the Internet for health information and includes what information in the teaching plan? A) The Web site where information is obtained needs to be evaluated for credibility. B) Most information found on the Internet is accurate. C) Information on the Internet is most reliable when people give their reviews of the drug. D) Only a health care professional can tell whether a Web site is reliable. Ans: A Feedback: There are excellent sites for reliable drug information, but each site must be evaluated for credibility and the nurse can teach the patient things to look for to increase confidence in the site. However, a lot of information on the Internet is not accurate; the patient needs to learn how to recognize unreliable information when he or she comes across these sites. Just because a person reviews a drug and gives it multiple stars or a thumbs up does not mean the drug is any more effective or useful in the patient’s care. 34. The nursing instructor is teaching the class about how prescription drugs become over-the-counter (OTC) drugs and lists what factor as preventing a drug from becoming classified as OTC? A) If the patient cannot reliably self-diagnose the condition the drug is intended to treat B) If it would mask signs and symptoms of an underlying problem, the drug remains available by prescription only. C) If the drug would cause toxic effects if not taken as directed, it remains a prescription drug. D) OTC drugs must not have any adverse effects that could harm the patient. Ans: A Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 102 Feedback: If a diagnosis requires medical intervention, such as hyperlipidemia, which can only be diagnosed through laboratory studies, there is no point in making the drug an OTC medication. Most, if not all, OTC drugs have the capacity to mask signs and symptoms of an underlying disease so this is not a factor in deciding if a drug can be sold OTC. All drugs have the potential for toxic effects if not taken as directed and virtually all drugs have the potential for adverse effects. 35. The nurse needs to ask what specific questions when collecting a drug history? (Select all that apply.) A) Do you take any over-the-counter medications? B) Do you take any herbal supplements? C) Do you use any alternative therapies? D) Do you take any natural supplements or vitamins? E) What unusual therapies do you take? Ans: A, B, D Feedback: The nurse needs to specifically question the patient’s use of over-the-counter drugs, herbal supplements, natural supplements, and vitamins. Use of terms like alternative therapies or unusual therapies is too vague and may not elicit the kind of information needed. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 103 Chapter 07 - Introduction to Cell Physiology 1. A researcher is studying chromosomal disorders. What part of the human cell would the researcher be interested in studying? A) Cytoplasm B) Membrane C) Nucleus D) Organelles Ans: C Feedback: The nucleus of a cell contains all of the genetic material that is necessary for cell reproduction. The nucleus also contains genes or sequences of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). Genes are responsible for the formation of messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) and transcription RNA, which are involved in production of proteins unique to the cells. This is the area where chromosomal disorders originate. The cell cytoplasm lies within the cell membrane and is the site of activities of cellular metabolism and special cellular functions. The organelles are contained within the cytoplasm and are structures with specific functions. They include the mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, free ribosomes, Golgi apparatus, and lysosomes. The membrane is a thin barrier, which separates the intracellular fluid from the extracellular fluid and is essential for cellular integrity; it also maintains cell homeostasis. 2. Which of these body cells has the greatest number of mitochondria? A) Tibia bone cells B) Breast tissue C) Cardiac muscle D) Subcutaneous skin Ans: C Feedback: Mitochondria are very abundant in cells that consume energy. The cardiac muscle cells, which must work continually to keep the heart contracting, contain a great number of mitochondria. Milk-producing cells in breast tissue, which are normally dormant, contain very few. Cells of bone and of subcutaneous Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 104 tissue do not consume a great deal of energy; therefore, they have smaller numbers of mitochondria than cardiac muscle. 3. When hormones, formed within the cell, move across the cell membrane, the process is called what? A) Endocytosis B) Exocytosis C) Phagocytosis D) Pinocytosis Ans: B Feedback: Exocytosis is the movement of substances such as waste products, hormones, and neurotransmitters out of the cell. Pinocytosis is the movement of nutrients and needed substances into the cell through specific receptors on the cell surface. Phagocytosis involves the destruction of engulfed proteins or bacteria. Endocytosis involves incorporation of material into the cell. 4. What substances move freely in and out of a cell by diffusion? A) Electrolytes B) Enzymes C) Hormones D) Proteins Ans: A Feedback: Sodium, potassium, calcium, carbonate, oxygen, bicarbonate, and water move freely in and out of cells. These substances move through channels or pores in the cell membrane through movement from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. Hormones, enzymes, and proteins are considered carriers. If a substance cannot move freely on its own, it may attach itself to another carrier to be diffused. 5. A) There can be interference with cancer chemotherapy in what phase of the cell cycle? G0 phase Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) B) G1 phase C) G2 phase D) S phase Ans: A 105 Feedback: During the G0 phase, the cell is stable. Cells in this phase can interfere with cancer chemotherapy because these drugs usually work on actively dividing cells, leaving resting cells mostly untouched. When the resting cells are stimulated to become active and regenerate, the cancer can return. This is the reason that cancer chemotherapy regimens are complicated and extended over a period of time. In the G1 phase, a cell is stimulated to emerge from its resting phase. During this time, the cell synthesizes the substances needed for DNA formation. The S phase involves the actual synthesis of DNA, and during the G2 phase, the cell produces all the substances that are required for the manufacture of the mitotic spindles. 6. The pharmacology instructor is discussing the histocompatibility of the cell. What is the importance of a cell’s histocompatibility antigen? A) It reproduces cells when other cells die. B) It recognizes cells as self-cells that belong in the body. C) The antigen produces antibodies to viral invaders. D) The antigen stimulates the production of white blood cells. Ans: B Feedback: The histocompatibility antigens are proteins that are seen on the top of the cell membrane. T cells use these antigens as the identifying proteins that identify a cell as a self-cell. If these antigens are not present on a cell membrane, the T cells will destroy that cell, determining that it is foreign. The histocompatibility antigens are not involved in reproduction. They do not produce antibodies nor do they stimulate white blood cell production. 7. A) A patient on the unit has a deep decubitus ulcer. The family asks why the nurse debrides the ulcer and removes the dead cells. What is the nurse’s best response to explain to the family why debridement is performed? The lysosomes released by the dead cells in the area continue to kill other cells, destroying more Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 106 tissue. B) The dead cells no longer contain histocompatible antigens causing a greater inflammatory response. C) Removing dead tissue forces oxygen to enter the damaged cells to regenerate them and to promote healing. D) The doctor ordered the procedure to be performed so it is done the way it is ordered because orders are always followed. Ans: A Feedback: When a cell dies, its cell membrane ruptures and the lysosomes release lysozymes, which dissolve protein. When many cells die, lysozymes accumulate and dissolve the proteins that the dead cells leave behind, but the lysozymes also destroy the cell membrane of healthy cells in the area. Those cells then die, releasing lysozymes, which destroy more cells, and a vicious cycle occurs. A decubitus ulcer is an area of many dead cells, which are killing healthy cells. The area needs to be scraped clean to remove the dead cells so that the lysozymes will stop destroying healthy cells and allow oxygen to return to the area through the capillary bed, which allows healing to occur. Many treatments exist for decubitus ulcers, all of which depend on the return of blood flow to the area and removal of the dead tissue. No procedure should ever be performed only because it was ordered. The nurse should understand why each procedure is needed. 8. A patient is extremely dehydrated from vomiting and diarrhea causing his or her blood to become hypertonic. What effect does the nurse expect this will have on the red blood cells? A) They will swell and eventually rupture. B) Red blood cells will migrate to the bone narrow. C) The cells will shrink and shrivel, decreasing their oxygen-carrying ability. D) The red cells will precipitate out of circulation. Ans: C Feedback: A hypertonic solution will draw the water out of the red blood cell, causing it to shrink and shrivel, decreasing the oxygen carrying ability of the red blood cell. A hypotonic solution would result in water moving into the red blood cell, causing it to swell and burst. Red blood cells will not migrate back to the bone marrow or precipitate out of circulation. 9. The nurse is caring for four patients. Which patient would the nurse expect to have a faster recovery Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 107 period based only on the process of mitosis? A) A 32-year-old female patient who had surgery for ulcerated colitis B) A 72-year-old man who had surgery for colon cancer C) A 28-year-old woman who had breast reduction surgery D) A 65-year-old man who had surgery for breast cancer Ans: A Feedback: Cells lining the GI tract reproduce very quickly (72 hours) compared with breast tissue, which takes 2 to 3 months to reproduce. The older the person is, the longer it will take for recovery due to the aging process that reduces rate of circulation of blood cells carrying oxygen to and from cells. 10. When chemotherapeutic agents interfere with cellular physiology, it results in what? A) Cellular death or alterations B) Diffusion C) Endocytosis D) Homeostasis Ans: A Feedback: Drugs may alter the cell membrane, causing the cell to rupture and die or they may deprive the cell of certain nutrients, altering the proteins that the cell produces. This could interfere with normal cell functioning and cell division. Diffusion is the movement of a substance from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. Endocytosis involves gathering of material into a cell. Homeostasis refers to keeping the cytoplasm stable within the cell membrane. Diffusion, endocytosis, and homeostasis are not the result of chemotherapeutic agents but may be impacted by the agent. 11. When learning about the physiology of the human body, a student would learn that cellular metabolism takes place where? A) Organelles B) Mitochondria Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) C) Endoplasmic reticulum D) Cytoplasm Ans: D 108 Feedback: The cell cytoplasm lies within the cell membrane and outside the nucleus and is the site of activities of cellular metabolism and special cellular functions. Organelles, mitochondria, and endoplasmic reticulum are all part of the cytoplasm of the cell and each has a specific function that contributes to cellular function. 12. What is the function of the rough endoplasmic reticulum (ER) within a cell? A) Produces proteins B) Combines protein with other components of the cytoplasm C) Exports protein from the cell D) Destroys ribosomes Ans: A Feedback: Many granules that contain enzymes and ribosomes, which produce protein, are scattered over the surface of the rough endoplasmic reticulum. Production of proteins, phospholipids, and cholesterol takes place in the rough endoplasmic reticulum. The rough ER segregates (rather than combines) these proteins from other components of the cytoplasm and modifies their structure for a specific function. Rough ER does not transport anything through the cell membrane. Rough ER is studded with ribosomes; it does not destroy them. 13. What is one purpose of the Golgi apparatus? A) Produces bile B) Prepares hormones or other substances for secretion-producing excretory granules C) Stimulates production of new red blood cells D) Produces small carbohydrate molecules Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) Ans: 109 B Feedback: The Golgi apparatus is a series of flattened sacs that may be part of the endoplasmic reticulum. These structures prepare hormones or other substances for secretion by processing them and packaging them in vesicles to be moved to the cell membrane for excretion from the cell. Golgi bodies do not produce bile. They produce secretory, not excretory, granules and they produce large carbohydrate molecules rather than small ones. 14. Mitochondria produce energy in the form of what? A) Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) B) Red blood cells C) Lactic acid D) Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) Ans: D Feedback: Mitochondria are rod-shaped power plants within each cell that produce energy in the form of ATP, which allows the cell to function. Red blood cells and DNA are not formed in the mitochondria. If oxygen is not available, lactic acid builds up as a by-product of cellular respiration. Lactic acid leaves the cell and is transported to the liver for conversion to glycogen and carbon dioxide. 15. The physiology instructor is explaining cell death to the nursing students. The instructor explains that what organelle digests worn or damaged sections of a cell when the cell dies? A) Golgi apparatus B) Lysosomes C) Endoplasmic reticulum D) Mitochondria Ans: B Feedback: Lysosomes are membrane-covered organelles that contain specific digestive enzymes that can break Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 110 down proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, and lipids. They are responsible for digesting worn or damaged sections of a cell when the membrane ruptures and the cell dies. The Golgi apparatus prepares substances for secretion by processing and packaging them in vehicles to move through the cell membrane. The endoplasmic reticulum provides a large surface for chemical reactions within the cell. Mitochondria are the power plants of the cell. 16. What is the function of the mitochondria within the cell? A) Convert small substances into energy B) Convert hormones into secretory substances C) Produce energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) D) Move electrolytes into and out of a cell Ans: C Feedback: Mitochondria are rod-shaped organelles that produce energy in the form of ATP for use by cells. They do not convert small substances into energy; they do not convert hormones into secretory substances; and they do not move electrolytes into and out of a cell. 17. Two types of ribosomes exist within a cell. Ribosomes that are not bound to the endoplasmic reticulum exist throughout the cytoplasm of the cell and produce proteins with what purpose? A) Bind themselves to the Golgi apparatus B) Bind to produce the endoplasmic reticulum C) Denature unnecessary enzymes within the cell D) Contribute to the structure of the cell Ans: D Feedback: Ribosomes that are not bound to the surface of the endoplasmic reticulum exist throughout the cytoplasm. These free-floating ribosomes produce proteins that are important to the structure of the cell and some of the enzymes that are necessary for cellular activity. Free-floating ribosomes do not bind themselves to Golgi apparatus; produce endoplasmic reticulum; or denature any part of the cell or its contents. 18. When a cell uses energy to move ions against an electrical or chemical gradient, what is the process Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 111 called? A) Passive transport B) Neutral transport C) Cotransport D) Active transport Ans: D Feedback: Active transport is what happens when cells use energy to move ions against an electrical or chemical gradient. Passive transport is another term for diffusion. There is no such thing as neutral transport. Cotransport is when the sodium ion and the solute are transported in the same direction. 19. When making a presentation on the cell, what would the students say are the main parts of the cell? (Select all that apply.) A) The nucleus B) The cytoplasm C) The cell membrane D) The mitochondria E) The organelles Ans: A, B, C Feedback: The cell is composed of a nucleus, which contains genetic material and controls the production of proteins by the cell; a cell membrane, which separates the inside of the cell from the outside environment; and cytoplasm, which contains various organelles important to cell function. The mitochondria and the organelles are units within the cytoplasm but are not main parts of the cell. 20. A) The cell membrane has embedded within it a series of peripheral proteins that function in several ways. One of these proteins is known as a receptor site. What does this receptor site do? Maintains contact with outside proteins to prevent lysis of the cell wall Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) B) Maintains contact with inside proteins to prevent lysis of the cell wall C) Reacts with specific chemicals inside the cell to stimulate a reaction outside the cell D) Reacts with specific chemicals outside the cell to stimulate a reaction within a cell Ans: D 112 Feedback: Embedded in the cell membrane are a series of peripheral proteins with several functions. One type of protein located on the cell membrane is known as a receptor site. This protein reacts with specific chemicals outside the cell to stimulate a reaction within a cell. Receptor sites do not prevent lysis of the cell wall nor do they stimulate a reaction outside of the cell. 21. Proteins within the cell wall allow the passage of several substances into and out of the cell. What is one of these substances? A) Calcium B) Phosphorous C) Magnesium D) Manganese Ans: A Feedback: Channels or pores within the cell membrane are made by proteins in the cell wall that allow the passage of small substances in or out of the cell. Specific channels have been identified for sodium, potassium, calcium, chloride, bicarbonate, and water; other channels may also exist. Some drugs are designed to affect certain channels specifically. For example, calcium channel blockers prevent the movement of calcium into a cell through calcium channels. Options B, C, and D are not known to have their own channels at this time. 22. After the cell has produced all substances necessary for the formation of a new cell, mitosis occurs in what phase of the cell cycle? A) G0 phase B) M phase C) S phase Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) D) G2 phase Ans: B 113 Feedback: After the cell has produced all substances necessary for formation of a new cell, or daughter cell, it undergoes cell division. This occurs during the M phase of the cell cycle. During this phase, the cell splits to form two identical daughter cells, a process called mitosis. The S phase involves the actual synthesis of DNA. In the G2 phase, the cell produces all the substances required for manufacture of the mitotic spindles. 23. During the cell cycle, the cell is stimulated to emerge from its resting phase and enter what stage? A) M phase B) S phase C) G1 phase D) G2 phase Ans: C Feedback: When a cell is stimulated to emerge from its resting phase, it enters what is called the G1 phase, which lasts from the time of stimulation from the resting phase until the formation of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). During this period, the cell synthesizes substances needed for DNA formation. The cell is actively collecting materials to make these substances and producing the building blocks for DNA. 24. When a substance must attach to another molecule, called a carrier, to move into or out of a cell, it is called what? A) Active transport B) Osmosis C) Passive transport D) Facilitated diffusion Ans: D Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 114 Feedback: Sometimes a substance cannot move freely on its own in or out of a cell. Such a substance may attach to another kind of molecule, called a carrier, to be diffused. This form of diffusion, known as facilitated diffusion, does not require energy, only the presence of the carrier. Active transport requires energy to move the substance against the concentration gradient. Osmosis is a special form of diffusion where water moves across a semipermeable membrane from an area low in solutes to one that is higher in solutes to dilute solutes. Passive transport does not require energy to move solutions across a semipermeable membrane and includes diffusion, osmosis, and facilitated diffusion. 25. A group of students are diagramming the cycle of a cell. What phase would they diagram as actually synthesizing deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)? A) S phase B) G0 phase C) M phase D) G2 phase Ans: A Feedback: The next phase, called the S phase, involves the actual synthesis of DNA, which is an energyconsuming activity. The cell remains in this phase until the amount of cellular DNA has doubled. The G0 phase is considered the resting phase of the cell cycle. The M phase is when cell replication occurs. The G2 phase is when the cell produces all substances it needs to replicate. 26. What is the purpose of the G1 phase of the cell cycle? A) Reproduction B) Synthesizes substances needed for deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) formation C) Rest D) Production of mitotic spindles Ans: B Feedback: The G1 phase lasts from the time of stimulation from the resting phase until the formation of DNA. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 115 During this period, the cell synthesizes substances needed for DNA formation. Mitotic spindles are produced in the S phase; rest is accomplished in the G0 phase; and reproduction is in the M phase. 27. What is the cell membrane composed of? (Select all that apply.) A) Glycolipids B) Lysosomes C) Cholesterol D) Glycoprotein E) Phospholipids Ans: A, C, E Feedback: The cell membrane is a lipoprotein structure, meaning it is mainly composed of proteins and lipidsphospholipids, glycolipids, and cholesterol; bipolar arrangement of the lipids monitors substances passing in and out of the cell. Lysosomes are organelles within the cytoplasm. Glycoprotein is a distracter. 28. The Krebs cycle provides a common pathway for the metabolism of nutrients by the body. The Krebs cycle uses carbohydrates, proteins, and what other nutrient to make adenosine triphosphate (ATP)? A) NADH + H+ B) Vitamins C) Fat D) H2O Ans: C Feedback: The mitochondria can take carbohydrates, fats, and proteins from the cytoplasm and make ATP via the Krebs cycle, which depends on oxygen. Cells use the ATP to maintain homeostasis, produce proteins, and carry out specific functions. NADH + H+ is an end-product of glycolysis. Vitamins are not used to make ATP and neither is water. 29. A patient is discussing a liver transplant with the transplant team. The physician is explaining the effort Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 116 made to match what in the donor tissue? A) Histocompatability antigens B) Lipoproteins C) Non-self-markers D) Receptor sites Ans: A Feedback: The body’s immune system recognizes these proteins and acts to protect self-cells and to destroy nonself-cells. When an organ is transplanted from one person to another, a great effort is made to match as many histocompatibility antigens as possible to reduce the chance that the new body will reject the transplanted organ. 30. The cell membrane, an integral part of the cell, is essential for what? (Select all that apply.) A) Cell movement B) Cellular integrity C) Cell life D) Cell homeostasis E) Cell maturation Ans: B, C, D Feedback: The membrane is essential for cellular integrity and is equipped with many mechanisms for maintaining cell homeostasis. Options A and E are distracters for this question. 31. The pharmacology instructor explains to the nursing students that drugs will have the least effect on the cell during what phase of the cell cycle? A) G0 phase B) G1 phase Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) C) S phase D) G2 phase Ans: A 117 Feedback: During the G0 phase, or resting phase, the cell is stable. It is not making any proteins associated with cell division and is basically dormant in terms of reproduction. These cells are functioning to do whatever they are supposed to do. Most drugs, particularly chemotherapy for cancer, work on active cells so cells that are resting are less susceptible to chemical action. The other options are active phases when drugs will be most effective. 32. The nurse is caring for a patient with acute renal failure with an elevated potassium level. The health care provider orders administration of insulin that causes potassium to return to the cell, thereby lowering serum potassium levels and the risks associated with hyperkalemia. The nurse recognizes this as a type of what? A) Passive transport B) Active transport C) Osmosis D) Diffusion Ans: A Feedback: Moving potassium back into the cell, an area with a higher concentration gradient than the bloodstream, requires energy. Insulin helps to activate the sodium–potassium pump. Passive transport is a means of moving substances in and out of the cell without the use of energy. Potassium levels are elevated and will not diffuse into the cell independently because potassium levels are higher inside the cell than outside and require energy to cross the concentration gradient. Osmosis involves diffusion of water. 33. The nurse is caring for a patient with edema caused by escape of fluid from the intravascular compartment to the extracellular compartment. An IV solution will be administered to draw the fluid back into the intravascular compartment. What type of solution will the nurse expect to administer? A) Isotonic solution B) Hypertonic solution Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) C) Hypotonic solution D) Osmotic solution Ans: B 118 Feedback: Hypertonic solutions are those with a higher concentration of solutes than human plasma. They draw water from cells, which would help to draw fluid back into the intravascular space. Hypotonic solutions are fluids that contain a lower concentration of solutes than human plasma, which causes water to be pushed into the cells. Isotonic fluids contain the same concentration of solutes as human plasma and will not cause fluids to shift from one compartment to another. Osmotic solution is a distracter. 34. The cytoplasm within the cell is stable so that the cell is said to be in what state? A) Homeostasis B) Activity C) Excitability D) Mitosis Ans: A Feedback: The main goal of a cell is to maintain homeostasis, which means keeping the cytoplasm stable within the cell membrane. Options B, C, and D are distracters for the question. 35. The patient has been diagnosed with multiple sclerosis, a disease that reduces the amount of available adenosine triphosphate (ATP) in the body. The nurse recognizes that this reduction in ATP is caused by the impact of the disease on what part of the cell? A) Cell neuron B) Endoplasmic reticulum C) Golgi bodies D) Mitochondria Ans: D Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 119 Feedback: The mitochondria are rod-shaped power plants within each cell that produce energy in the form of ATP, which allows the cell to function. Inadequate production of ATP would indicate damage to the functioning of the mitochondria. The neuron, endoplasmic reticulum, and Golgi bodies do not produce ATP. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 120 Chapter 08 - Antiinfective Agents 1. A patient asks the nurse how an anti-infective produces a therapeutic effect. What key point will the nurse explain to this patient? A) Drugs used to treat infections date back to the 17th century. B) All anti-infectives work in the same way to destroy organisms. C) Selective toxicity determines the appropriate drug dosage needed. D) The goal of anti-infectives is to interfere with normal functioning of the organism. Ans: D Feedback: The goal of anti-infectives is to interfere with the normal function of the invading organism to prevent it from reproducing and to cause cell death without affecting host cells. Each class of anti-infectives works in a different way, but all have the same goal. Because bacteria cells have a slightly different composition than human cells, the bacteria are destroyed without interfering with the host. The first drugs used to treat systemic infections were developed in the early 20th century. The term selective toxicity refers to the ability to affect certain proteins or enzyme systems that are used by infecting organisms, but not by human cells. 2. The nursing student learns about anti-infectives in class and demonstrates the need to study more when making what statement about how anti-infectives work? A) Some anti-infectives interfere with biosynthesis of the pathogen’s cell wall. B) Some anti-infectives prevent the cells of the organism from using essential substances. C) Many anti-infectives interfere with the steps involved in protein synthesis. D) Some anti-infectives interfere with ribonucleic acid (RNA) synthesis in the cell leading to cell death. Ans: D Feedback: Some anti-infectives interfere with deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) synthesis, not RNA synthesis, in the cell, leading to inability to divide and causing cell death. The fluoroquinolones work in this way. The other three options are correct and would not indicate the need for further study time. Penicillins Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 121 interfere with biosynthesis of the cell wall, sulfonamides prevent organisms from using substances essential to their growth and development, whereas aminoglycosides, macrolides, and chloramphenicol interfere with protein synthesis. 3. The nurse administers a drug to treat Neisseria gonorrhoeae that works on no other bacteria. How would the nurse describe this drug? A) Broad spectrum B) Narrow spectrum C) Bactericidal D) Bacteriostatic Ans: B Feedback: Without knowing the name of the antibiotic and how it works to treat N. gonorrhoeae, the only thing that can be said is that it is a narrow-spectrum anti-infective because it only treats one specific organism. Broad-spectrum anti-infectives treat multiple organisms. The name of the drug and how it works would need to be known to determine whether it is bacteriocidal or bacteriostatic. 4. The nurse has provided patient teaching for a patient who will be discharged to home on an antiinfective. What statement made by the patient indicates the nurse needs to provide additional teaching concerning the use of anti-infectives? A) Antibiotics will not help me when I have a viral infection. B) A bacterial culture will be done before antibiotics are prescribed for me. C) I could develop diarrhea as a result of taking an antibiotic. D) I will stop taking the antibiotic as soon as I feel better. Ans: D Feedback: Compliance with anti-infective therapy is a concern. Patients tend to stop taking the drugs when they begin to feel better. A nurse should instruct the patient to take the entire course of prescribed drug to ensure a sufficient period to rid the body of pathogens and to help prevent the development of resistance. Antibiotics are not prescribed for viral infections. It is important that cultures be performed before antibiotics are prescribed to determine what organism is causing the infection so that the correct drug is prescribed. Diarrhea is the most common adverse effect from anti-infectives. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 5. 122 The nurse attends a class on preventing resistance to anti-infectives and learns that the critical concept in preventing the development of resistant strains of microbes is what? A) Exposure of pathogens to an antimicrobial agent without cellular death B) Drug dosages that are below a therapeutic level C) The duration of drug use D) Frequency of drug ingestion Ans: C Feedback: Exposure of pathogens to an antimicrobial agent without cellular death leads to the development of resistance so it is important to limit the use of these agents to treat pathogens with a known sensitivity to the drug being used. Drug dosages are also important in preventing the development of resistance. However, the duration of drug use is critical to ensure that microbes are completely eliminated and not given the chance to grow and develop resistant strains. It is hard to convince patients that they must always complete the entire course of antimicrobial agents when they begin to feel better, because stopping early favors the emergence of drug-resistant strains. 6. The pathophysiology class is learning how microorganisms develop resistance to anti-infective drugs. What is one way the nursing students would learn that microorganisms develop resistance to antiinfective drugs? A) By rearranging their deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) to produce membranes that are permeable to the drug B) By producing an enzyme that stimulates the drug C) By changing the cellular membrane to allow the drug entry into the cell D) By altering binding sites on the membrane or ribosomes so that the drug cannot enter the cell Ans: D Feedback: Microorganisms have developed resistance by changing cellular permeability to prevent the drug from entering the cell by altering binding sites on the membranes or on ribosomes so the drug can no longer be accepted and by producing enzymes that deactivate the drug. Microorganisms have not been found to be able to rearrange their DNA to change their membrane structure. 7. The nurse, writing a care plan for a patient on an aminoglycoside, includes what intervention to reduce Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 123 the accumulation of the drug in the kidney? A) Avoid caffeine intake. B) Increase fluids. C) Decrease activity. D) Increase consumption of fruits and vegetables. Ans: B Feedback: To prevent the accumulation of anti-infective drugs in the kidneys, which can damage the kidney, patients taking anti-infective drugs should be well hydrated. Decreasing the dosage will likely reduce the therapeutic action and increase risk of resistance. There is no evidence of association between caffeine intake and drug accumulation in the kidney. Decreasing activity and increasing fruits and vegetables in the diet would not be effective in decreasing drug accumulation. 8. When conducting patient teaching about using antibiotic medications, what is it critical for the nurse to include to help stop the development of resistant strains of microorganisms? A) Antibiotics should be used quickly to treat colds and other viral infections before the invading organism has a chance to multiply. B) Antibiotic dosage should be reduced and used for shorter periods of time to reduce unnecessary exposure to the drug. C) Prescriptions for antibiotics should be readily available so they can be filled as soon as patients suspect they have an infection. D) It is very important to take the full course of an antibiotic as prescribed and not save remaining drugs for future infections. Ans: D Feedback: Teaching patients to take the full course of their antibiotic as prescribed can help to decrease the number of drug-resistant strains. Antibiotics should only be used to treat bacterial infections that have been cultured to identify the antibiotic sensitivity and then patients should be instructed to use the antibiotic for the prescribed course, which will help to eliminate drug-resistant strains. Reducing dosage and time intervals increases the chance for drug resistance because anti-infectives are most effective when taken exactly as indicated. 9. A patient is told that he or she will have to undergo extensive dental surgery. The dentist prescribes a Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 124 course of antibiotic therapy before beginning the procedures and continuing for 5 days after the procedure. What is this is an example of? A) Chemotherapy B) Curative treatment C) Prophylaxis D) Synergism Ans: C Feedback: In a situation where an infection is likely to occur, antibiotics can be used to prevent it. This is called prophylaxis. Synergism is using two antibiotics at the same time to improve their effectiveness. Chemotherapy is the use of drugs to destroy abnormal cells, usually cancer cells. Curative treatment involves treating an actual infection to promote a cure. 10. A patient is receiving meropenem (Merrem IV). What drug-related reaction will the nurse assess for? A) Gastrointestinal toxicity B) Hepatic toxicity C) Nephrotoxicity D) Neurotoxicity Ans: A Feedback: This drug has been associated with potentially fatal pseudomembranous colitis, which affects the gastrointestinal tract. This drug is not associated with liver, kidney, or nerve toxicity. 11. A patient is admitted to the unit and the nurse assesses whether he or she is at increased risk for infection when what factors are determined? (Select all that apply.) A) Malnutrition B) Hypertension Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) C) Suppression of immune system D) Advanced age E) Decreased amylase levels Ans: A, C, D 125 Feedback: Factors that suppress the host defense mechanisms include malnutrition, suppression of immune system, and advanced age. Hypertension does not predispose a person to infection neither does a decreased amylase level. 12. The nurse is caring for a patient receiving penicillin. The nurse knows this type of antibiotic works by what mechanism? A) Inhibiting growth and development of the organism B) Inhibiting protein synthesis C) Inhibiting cell wall biosynthesis D) Stimulating bacterial reproduction Ans: C Feedback: Some anti-infectives interfere with biosynthesis of the bacterial cell wall. Because bacterial cells have a slightly different composition than human cells, this is an effective way to destroy the bacteria without interfering with the host (see Box 8.2). The penicillins work in this way. The sulfonamides inhibit growth and development of the organism’s cells. Aminoglycosides, macrolides, and chloramphenicol interfere with protein synthesis. Fluoroquinolones interfere with synthesis of deoxyribonucleic acid, resulting in the inability to reproduce. 13. A nurse collects a culture sample of infected tissue. What does the result of testing the culture contribute to the patient’s care? A) Identifies the specific organism causing the infection B) Pinpoints the exact site of the infection C) Identifies individualized patient factors contributing to infection Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) D) Describes the length of time the patient has experienced infection Ans: A 126 Feedback: A culture is collected to identify the causative organism of an infection. It can help with determining the site of infection in some cases if the infection is limited only to the site where the culture is collected. It does not individualize patient factors contributing to infection. These must be determined through assessment. It cannot indicate how long the patient has had the infection, which is often determined by the white blood cell count and differential. 14. A patient calls the clinic to talk to the nurse. The patient states that he or she saw the physician last week and was prescribed penicillin for a strep throat. The patient goes on to say that they feel so much better they stopped taking the drug today, even though there are a few pills left. What is the nurse’s best response? A) Okay, thank you for letting me know. I will document in your medical record that the treatment was effective. B) It is important that you take all the medication so all the germs are killed. Otherwise they could come right back and be even stronger. C) What you have described is the halo effect of the drug, making you feel better when you are still infected. You’ll feel sick again when the drug is out of your system. D) You will need to come to the clinic and be evaluated by your physician to make sure the infection is really gone. Ans: B Feedback: The duration of drug use is critical to ensure that the microbes are completely, not partially, eliminated and are not given the chance to grow and develop resistant strains. The nurse must explain the importance of taking all of the prescribed medication and should not agree with the patient. This is not related to a halo effect and the patient may feel well until drug levels decrease rather than being completely eliminated from the body. The patient does not need to be seen if the infection is responding to treatment, but they must take the rest of the antibiotic. 15. When administering anti-infectives to patients, the nurse is aware of the risk for what potentially fatal adverse effect? A) Gastrointestinal toxicity B) Eighth cranial nerve damage Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) C) Anaphylaxis D) Toxic effects on the kidney Ans: C 127 Feedback: Anaphylaxis is an acute, systemic allergic response to a substance that can be fatal if medical intervention does not occur almost immediately because the airway closes due to tissue edema making it impossible to breathe. Gastrointestinal toxicity, hearing loss due to eighth cranial nerve damage and, toxic effects to the kidney are all adverse effects that may be seen with some anti-infectives. Although these adverse effects can be serious, they are not usually fatal. 16. A group of nursing students are giving a report on the emergence of drug-resistant microbial agents. What could the students cite as a good way to minimize the emergence of drug-resistant microbial agents? (Select all that apply.) A) Avoid the use of broad-spectrum antibacterial drugs when treating trivial or viral infections. B) Use narrow-spectrum agents if they are thought to be effective. C) Do not use vancomycin unnecessarily. D) Antibiotics are best started before the culture and sensitivity report returns. E) Administer the smallest effective dosage available. Ans: A, B, C Feedback: Exposure to an antimicrobial agent leads to the development of resistance, so it is important to limit the use of antimicrobial agents to the treatment of specific pathogens known to be sensitive to the drug being used. Drug dosage is important in preventing the development of resistance. Doses should be high enough and the duration of drug therapy should be long enough to eradicate even slightly resistant microorganisms. It is best to wait until cultures return before initiating antibiotics when possible, but patients with severe infections may be started on broad -spectrum antibiotics while waiting for culture results. 17. The home care nurse is taking care of a patient on IV vancomycin for cellulitis of the left calf. How would the nurse explain how microorganisms develop resistance to anti-infective medications? A) Microorganisms can alter the blood supply to the infection. B) Microorganisms can stop the cell from reproducing. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) C) Microorganisms produce a chemical that acts as an antagonist to the drug. D) Microorganisms change their cell membrane to make it look like the drug. Ans: C 128 Feedback: Microorganisms develop resistance in a number of ways, including the following: changing cellular permeability to prevent the drug from entering the cell or altering transport systems to exclude the drug from active transport into the cell; altering binding sites on the membranes or ribosomes, which then no longer accept the drug; and producing a chemical that acts as an antagonist to the drug. Microorganisms do not alter the blood supply to the infection, stop a cell from reproducing, or change the appearance of the cell membrane. 18. Overuse of anti-infective agents is known to contribute to the onset of superinfections in the body. What is a causative agent of a superinfection? A) Escherichia coli B) Probenecid C) Protozoans D) Pseudomonas Ans: D Feedback: Common superinfections include vaginal or gastrointestinal yeast infections, which are associated with antibiotic therapy, and infections caused by Proteus and Pseudomonas throughout the body, which are a result of broad-spectrum antibiotic use. Probenicid is a medication, not a causative organism. Protozoa and E. coli do not usually cause superinfections. 19. The pharmacology instructor is explaining combination drugs to the nursing class. The instructor tells the students that a combination of anti-infective agents may be used for several reasons. What is one of them? A) Some drugs are synergistic. B) Increased likelihood of killing the microorganisms C) Requires larger doses of the drugs Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) D) Absorption of drugs increased Ans: A 129 Feedback: Some drugs are synergistic, which means that they are more powerful when given in combination. The health care provider may be encouraged to use a smaller dosage of each drug, leading to fewer adverse effects, but still having a therapeutic impact on the pathogen. Many microbial infections are caused by more than one organism; each pathogen may react to a different anti-infective agent. Combination drugs do not have a better chance at killing the microorganism and they do not increase the absorption of the drugs. 20. Bactericidal agents do not prevent compounds fight infection and destroy microorganisms by inhibiting what? A) Protein synthesis B) Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) replication C) Cell wall synthesis D) Leukocytes Ans: A Feedback: Some anti-infectives are so active against the infective microorganisms that they actually cause the death of the cells they affect. These drugs are said to be bactericidal. Bactericidal action inhibits protein synthesis. Bacteriocidal agents do not prevent DNA replication , do not inhibit cell wall synthesis, and do not impact leukocytes. 21. The nurse is caring for a child who weighs 30 kg. The physician orders gentamicin (Garamycin) tid. The recommended dosage range is 6 to 7.5 mg/kg/day. Why is it important to give a dosage within this recommended range? (Select all that apply.) A) To avoid toxic effects B) To protect other patients C) To reduce the risk of drug-resistant organisms D) To eradicate the bacteria E) To promote lactic acid removal Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) Ans: 130 A, B, C, D Feedback: By administering the correct dosage, you avoid overdosage and reduce the risk of toxic effects. The correct dosage reduces the risk of creating drug-resistant organisms; it also protects both the patient and the other patients who might be susceptible to the drug-resistant organisms as well. The proper dosage is needed to eradicate the bacteria. Lactic acid removal is not related to the proper dosage and is a distracter for this question. 22. The nurse is administering an anti-infective to a pediatric patient. What will the nurse assess for related to adverse effects in this patient? A) Cardiovascular function and perfusion B) Hydration and nutritional status C) Liver and pancreatic function D) Rest and sleep status Ans: B Feedback: Because children can have increased susceptibility to the gastrointestinal and nervous system effects of anti-infectives, monitor hydration and nutritional status carefully. Patients should be encouraged to drink fluids. Cardiovascular, hepatic, and pancreatic function are not at greater risk in children. Rest and sleep status are important but are not impacted by anti-infectives. 23. A parasitic infection is suspected. What type of culture is the nurse likely to collect? A) Blood B) Urine C) Stool D) Sputum Ans: C Feedback: Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 131 When investigators search for parasitic sources of infection, the stool is examined for ova and parasites. Blood, urine, and sputum are unlikely to reflect signs of parasitic infection. 24. The nurse is caring for a patient receiving IV aminoglycosides for an intractable infection in his or her leg. What would it be important for the nurse to monitor this patient for? A) Visual disturbances B) Liver dysfunction C) Serum glucose levels D) Renal dysfunction Ans: D Feedback: When patients are taking aminoglycosides, it is important they be monitored closely for any sign of renal dysfunction. Aminoglycosides do not generally cause visual disturbances, liver dysfunction, or altered serum glucose levels. 25. The nurse collects the past medical history of a patient new to the clinic. The patient states he or she is allergic to penicillin. What would the nurse question next? (Select all that apply.) A) What signs and symptoms were displayed with the reaction? B) What treatment was required to control the allergic reaction? C) How was the medication administered? D) How many dosages were administered before the reaction occurred? E) Had the medication ever been prescribed before the time when the reaction occurred? Ans: A, D, E Feedback: It is important to determine what the allergic reaction was and when the patient experienced it (e.g., after first use of drug, after years of use). If she had been prescribed this medication before with no reaction and then had a reaction the next time it was prescribed, this would be important information to know. Some patients report having a drug allergy, but closer investigation indicates that their reaction actually constituted an anticipated effect or a known adverse effect to the drug. It would not necessarily be important to find out what was done to stop the reaction or who the caregiver was at the time of the reaction or what type of allergic reaction it was. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 26. 132 A patient comes to the clinic to talk with the nurse about planned overseas travel. The patient tells the nurse that he or she is planning a trip to an area of the world where malaria is common. He wants to know how to prevent contracting the disease. What should the nurse respond? A) We can ask the physician to give you some anti-infectives in case you get malaria. B) We can ask the physician for some anti-infectives for you to take prophylactically. C) Don’t worry, if you get malaria they have some good doctors where you are going. D) If you get malaria, you can always be treated on the way home. Ans: B Feedback: Some anti-infectives are used as a means of prophylaxis when patients expect to be in situations that will expose them to a known pathogen, such as travel to an area where malaria is endemic, or undergoing oral or invasive gastrointestinal surgery in a person who is susceptible to subacute bacterial endocarditis. After the patient contracts malaria, it is much harder to treat so he would not start the medication or obtain treatment after being infected. 27. The nurse is caring for a patient who is receiving a broad-spectrum anti-infective agents. The nurse would assess the patient for what common adverse effect of broad spectrum anti-infective agents? A) Destruction of pathogens B) Decrease in infection C) Destruction of the normal flora D) Decrease in inflammation Ans: C Feedback: One offshoot of the use of anti-infectives, especially broad-spectrum anti-infectives, is destruction of the normal flora resulting in superinfections. Destruction of pathogens is the therapeutic effect and not an adverse effect resulting in a decrease in infection. Inflammation is reduced by resolution of infection. 28. Selective toxicity, or the ability to affect certain proteins or enzyme systems in the infecting organism, is a much sought-after quality in an anti-infective agent. How many anti-infective agents have this quality? Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) A) 75% B) 50% C) 25% D) 0% Ans: D 133 Feedback: Although anti-infective agents target foreign organisms infecting the body of a human host, they do not possess selective toxicity, which is the ability to affect certain proteins or enzyme systems used by the infecting organism but not by human cells. Because all living cells are somewhat similar, however, no anti-infective drug has yet been developed that does not affect the host. Therefore Options A, B, and C are incorrect. 29. The nursing instructor teaches the students about selective toxicity when one of the students asks, What happens when a drug doesn’t have selective toxicity? What is the instructor’s best response? A) Healthy cells are damaged. B) All pathogens are destroyed in the body. C) Reduced enzymes are produced. D) Protein malnutrition Ans: A Feedback: When a drug does not display selective toxicity, healthy cells are damaged because the drug does not specifically target only the pathogen. Anti-infectives work by a variety of different means so one drug is not likely to kill every type of pathogen in the body. Selective toxicity does not impact enzyme production or cause protein malnutrition. 30. The nursing instructor is talking with the students about anti-infective medication and explains that drugs that are very selective in their actions are said to be what? A) Broad spectrum B) Narrow spectrum Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) C) Bactericidal D) Bacteriostatic Ans: B 134 Feedback: Some anti-infectives are so selective in their action that they are effective against only a few, or possibly only one, microorganism with a very specific metabolic pathway or enzyme. These drugs are said to have a narrow spectrum of activity. They are not called broad spectrum, which applies to a drug with little selectivity; bactericidal, which is a substance that causes death of bacteria; or bacteriostatic, which prevents replication of a bacterium. 31. The nurse administers polymyxin B to a patient with a gram-negative bacterial infection. What symptoms would cause the nurse to suspect drug fever, hold the medication, and call the health care provider immediately? (Select all that apply.) A) Fever B) Dizziness C) Ataxia D) Increased activity E) Reduced urine output Ans: A, B, C, E Feedback: The actions of polymyxin B on cell membranes means it can be toxic to the human host, leading to nephrotoxicity, neurotoxicity (e.g., facial flushing, dizziness, ataxia, paresthesias, drowsiness), and drug-related fever and rash. This drug is reserved for infections that do not respond to less toxic drugs; the nurse needs to be alert for serious reactions and hold the drug until notifying the provider. 32. The charge nurse, working on a pediatric unit, sees an order was written to administer chloramphenicol (Chloromycetin) to one of the children assigned to a new graduate nurse. The charge nurse would make sure the new graduate was familiar with what possible adverse effects of this medication? (Select all that apply.) A) Gray syndrome B) Bone marrow depression Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) C) Aplastic anemia D) Liver failure E) Hearing loss Ans: A, B, C 135 Feedback: Chloramphenicol (Chloromycetin), an older antibiotic, prevents bacterial cell division in susceptible bacteria. Because of the potential toxic effects of this drug, its use is limited to serious infections for which no other antibiotic is effective. Chloramphenicol produces a gray syndrome in neonates and premature babies, which is characterized by abdominal distention, pallid cyanosis, vasomotor collapse, irregular respirations, and even death. In addition, the drug may cause bone marrow depression, including aplastic anemia that can result in death. Liver failure and hearing loss are not usually associated with this drug. 33. The patient in the clinic receives a prescription for an anti-infective to treat a urinary tract infection. The patient asks the nurse, Would you ask the doctor to give me refills on this prescription? I get a urinary tract infection almost once a year it seems and I’d like to have a refill I can store for the next time so I don’t have to come back to the clinic. What is the nurse’s priority response? A) Sure, I’d be glad to ask. How many refills would you like to have? B) Most medications, if not used, should be discarded after a year so it is better to get a new prescription next year when you need it. C) This antibiotic doesn’t destroy every pathogen that could cause a urinary tract infection so it is better to get the right antibiotic next time. D) Saving antibiotics for another time and self-diagnosing when antibiotics are needed lead to resistant organisms that no longer respond to drugs. Ans: D Feedback: Option A is incorrect because the patient should not be given refills to use indiscriminately. The remaining options are all important teaching points for this patient, but the priority is teaching this patient about drug-resistant organisms and how they can be prevented, as well as what happens if an infection results from a resistant organism. 34. The nurse admits a patient with septicemia (i.e., infection in the bloodstream). The patient denies any allergies and the doctor has ordered cefuroxime based on blood culture results that report the active pathogen is susceptible to this drug. The patient asks what antibiotic was ordered, and when the nurse says cefuroxime, the patient says, Call my doctor and tell him I want vancomycin because I’ve been reading about drug-resistant bacteria and I don’t want to take any chances. What is the nurse’s best Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 136 response? A) Vancomycin is a powerful drug with many adverse effects and it is reserved for when no other drug will work against the infection. B) There are some resistant infections that require vancomycin so you are right to prefer a stronger antibiotic. C) I appreciate your concern but your doctor ordered the right medication for you so don’t worry about it. D) You can’t believe anything you read on the Internet because most of it is just someone’s opinion and not fact. Ans: A Feedback: The patient is right in saying that vancomycin is effective against drug-resistant bacteria but needs help to understand that he or she does not have a resistant infection as indicated by the culture and sensitivity and that use of such a powerful drug when it is not needed increases risk of developing a vancomycin-resistant infection. It is never right to tell a patient not to worry because they have every right to participate in his or her own care and should not be patronized. Although some information on the Internet may not be accurate, it would be incorrect to say it is all just someone’s opinion and not fact, especially given that the patient’s information is accurate. 35. The mother brings her 18-month-old toddler to the pediatrician because the child has a fever and has been tugging on his or her left ear. Examination of the tympanic membrane confirms an ear infection and the toddler also has a cold with nasal congestion, rhinorrhea, and a cough. The provider tells the mother to apply heat and gives her a prescription for an otic anesthetic to make the ear more comfortable until the infection resolves. The mother is not happy and says she wants a prescription for an antibiotic. What important teaching points will the nurse include in the teaching plan? (Select all that apply.) A) Ear infections that accompany viral respiratory infections do not respond to antibiotics. B) Habitual use of antibiotics for viral infections contribute to development of resistant strains. C) Adverse effects from antibiotics in children can cause diarrhea and dehydration. D) Antibiotics will only be prescribed if a culture indicates the presence of bacteria in the ear. E) The pediatrician knows more than the mother and she should trust what she is being told. Ans: A, B, C Feedback: Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 137 When the child has a viral respiratory infection, the organism involved in ear infections is usually viral as well. As a result, antibiotics will have no effect on the infection that will resolve independently and only comfort care is indicated. Habitual use of antibiotics for viral infections contributes to the development of resistant strains of bacteria and the adverse effects can make the child more uncomfortable causing diarrhea and dehydration. Cultures of ear fluid are almost never done because it would be an invasive procedure to remove fluid from the middle ear. It is never right for the nurse to patronize the mother, who has every right to advocate for her child, and it is more important she understand why the antibiotic is not being prescribed than telling her the pediatrician knows more. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 138 Chapter 09 - Antibiotics 1. A 32-year-old female patient is admitted to the floor with a superinfection. Her orders read tigecycline (Tygacil) 100 mg IV followed by 50 mg IV every 12 hours infused over 30 to 60 minutes for 5 days. What would be important for the nurse to educate this patient about? A) Analgesics B) Antihistamines C) Contraceptives D) Decongestants Ans: C Feedback: Many antibiotics interfere with the effectiveness of oral contraceptives and unplanned pregnancies can occur. Women should be advised to use a barrier form of contraceptives when taking this drug. No known serious drugdrug interactions involve analgesics, antihistamines, or decongestants. 2. A patient with a gram-negative infection is being treated with an aminoglycoside. What system should the nurse expect to monitor closely while the patient is taking this medication? A) Respiratory system B) Ophthalmic system C) Renal system D) Musculoskeletal system Ans: C Feedback: Renal function should be tested daily because aminoglycosides depend on the kidney for excretion and if the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) is abnormal it may be toxic to the kidney. The results of the renal function testing could change the daily dosage. Aminoglycosides do not usually adversely affect respiratory, hepatic, or musculoskeletal function, although baseline data concerning these systems is always needed. 3. How would the nurse describe selective toxicity? Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 139 A) Selective toxicity interferes with a biochemical reaction common to many different organisms. B) Selective toxicity will decrease invading bacteria by interfering with the pathogens’ ability to reproduce. C) Selective toxicity will eliminate bacteria by interrupting protein synthesis and damaging the pathogen’s cell wall. D) Selective toxicity is the ability of the drug to kill foreign cells without causing harm to one’s own body cells. Ans: D Feedback: The choice of antibiotics in a clinical situation is determined by assessing which drug will affect the causative organism and lead to the fewest adverse effects. Selective toxicity is the ability of the drug to kill foreign cells without causing harm to the human body cells. How the antibiotic works to kill bacteria varies by drug type and may reduce the ability to reproduce, damage the cell wall, or interfere with a biochemical reaction, but this is a description of how the antibiotic works and does not describe selective toxicity 4. A local bioterrorism medical team is learning about germ warfare. The team is instructed that a fluoroquinolone may be used to prevent an outbreak of anthrax infection. What fluoroquinolone would the nurse be most likely to administer for this purpose? A) Ciprofloxacin (Cipro) B) Gemifloxacin (Factive) C) Norfloxacin (Noroxin) D) Sparfloxacin (Zagam) Ans: A Feedback: Ciprofloxacin (Cipro) is the most widely used fluoroquinolone and is indicated for the prevention of anthrax infection. Gemifloxacin and sparfloxacin are most useful in treating acute episodes of chronic bronchitis and community-acquired pneumonia. Norfloxacin is recommended only for certain types of urinary tract infections. 5. A clinic nurse is caring for a 66-pound child who has acute otitis media. The physician has ordered ceftibuten (Cedax) 9 mg/kg per day PO for 10 days. The drug comes in an oral suspension of 90 mg/5 mL. How many mL will the nurse administer? Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) A) 5 mL B) 10 mL C) 15 mL D) 20 mL Ans: C 140 Feedback: First, using the formula: 2.2 lb/1 kg = 66 lb/X kg, determine the child’s weight in kg (66/2.2 = 30 kg). Next, determine the desired dose by using the formula: amount of prescribed drug times weight in kg (9 mg/kg times 30 kg = 270 mg). To determine the volume of medication to administer, use the formula: amount of drug available/volume available = amount of drug prescribed/volume to administer (90 mg/5 mL = 270 mg/X mL, 90mg/(X) = 1,350 mg/mL, X = 15 mL). 6. A 78-year-old woman, who lives alone and is forgetful, is being seen by her home health nurse. In reviewing the patient’s medication, the nurse discovers that the patient is taking Azithromycin (Zithromax) for urethritis. Why would this be a good choice of antibiotics for this patient? A) The half-life of the drug is 3 to 7 hours. B) It is taken only once a day. C) It has very few adverse effects. D) It can be given without consideration to drugdrug interactions. Ans: B Feedback: Given that the patient is forgetful and lives alone, a daily dose would likely promote improved compliance. Azithromycin can be administered once daily because the half-life is 68 hours. Azithromycin is associated with GI adverse effects and can cause pseudomembranous colitis; neurological symptoms can occur as well. Azithromycin (Zithromax) may adversely interact with cardiac glycosides, oral anticoagulants, theophyllines, carbamazepine, and corticosteroids to name a few agents. 7. A) A 12-year-old patient with a complicated skin infection has been admitted to the pediatric unit. The physician has ordered Ertapenem (Invanz). What is the nursing priority? Transcribe the order to the medication administration record (MAR). Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) B) Perform hand hygiene before preparing the medication. C) Assess the patient’s renal and hepatic functions. D) Question the order by calling the physician who prescribed it. Ans: D 141 Feedback: The nurse should call the physician and question the order Because this drug is not recommended for children younger than 18 years of age. Following clarification of the order, the drug would be transcribed and listed in the MAR. The nurse would then wash her hands before preparing the drug for administration. Assessment of renal and hepatic function is good practice before administering any medication but is not the nursing priority. 8. A 22-year-old female is diagnosed with mycobacterial tuberculosis. The physician orders rifampin (Rifadin) 600 mg PO daily. What should the nurse question the patient about? A) Her diet B) Sun exposure C) Type of exercise she does D) Use of contact lenses Ans: D Feedback: Some antimycobacterial drugs can cause discoloration of body fluids. The orange tinged discoloration can cause permanent stain to contact lenses. The patient should avoid wearing them while on the antimycobacterial therapy. With antimycobacterial drugs there is not a concern is warranted about photosensitivity or exercise. However, due to the GI adverse effects, the nurse may want to discuss an appropriate diet if the patient experiences GI upset after beginning treatment. 9. The nurse is providing discharge teaching to a patient who is being sent home on oral tetracycline (Sumycin). What instructions should the nurse include? A) Take the medication only once a day. B) Check pulse rate and hold the drug if lower than 60 beats per minute (bpm). Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) C) Take the drug on an empty stomach. D) Take the medication with 2 ounces of water. Ans: C 142 Feedback: Tetracycline should be taken on an empty stomach 1 hour before or 2 hours after meals with a full 8 ounces of water to ensure full absorption. Tetracycline is usually taken at least once every 12 hours. Checking the pulse and holding the dose if below 60 bpm is an action specific to the use of cardiac glycosides. 10. A 28-year-old patient has been prescribed penicillin for the first time. What nursing diagnosis would be most appropriate for this patient? A) Acute pain related to gastrointestinal (GI) effects of the drug B) Deficient knowledge regarding drug therapy C) Imbalance nutrition: less than body requirements related to multiple GI effects of the drug D) Constipation Ans: B Feedback: Because this is the first time the patient has taken penicillin, she is likely to have limited knowledge about the drug. She may not understand the importance of taking the medication as ordered to increase effectiveness of the drug or to report adverse effects. because the patient has not started the drug yet, there is no way to know what adverse effects, if any, she will experience. Only if she develops acute pain related to GI effects of the drug would this be appropriate. If GI symptoms develop it may lead to imbalanced nutrition, but that remains to be seen. No indication about constipation exists. 11. The pharmacology instructor is discussing antimicrobials with the nursing class. What would the instructor tell the students about the mechanism of action of antimicrobials? (Select all that apply). A) Preventing cell division B) Causing cell death C) Inhibiting cell wall synthesis D) Causing leakage of cell wall allowing fluid to leak in Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) E) Inhibiting synthesis of ribonucleic acid (RNA) Ans: A, B, C 143 Feedback: Sites of cellular action of carbapenems, ketolides, lincosamides, aztreonam, penicillins, sulfonamides, tetracyclines, and antimycobacterials. Carbapenems, ketolides, and lincosamides change protein function and prevent cell division or cause cell death. Aztreonam alters cell membranes to allow leakage of intracellular substances and causes cell death; it does not cause leakage of fluid into the cell. Penicillins prevent bacteria from building their cells during division. Sulfonamides inhibit folic acid synthesis for RNA and deoxyribonucleic acid production but does not inhibit RNA synthesis 12. The nurse is preparing to contact the physician for an antibiotic order for the patient’s infection. What information will the nurse be prepared to provide for the physician to choose the proper antibiotic? A) First day of infection symptoms B) Culture and sensitivity test results C) The patient’s intake and output for past 2 days D) Results of complete blood count with differential Ans: B Feedback: Antibiotics are best selected based on culture results that identify the type of organism causing the infection and sensitivity testing that shows what antibiotics are most effective in eliminating the bacteria. First day of symptoms of infection is likely already known if culture and sensitivity testing has been performed. Although measurement of intake and output is one indicator of renal function, a bloodureanitrogen test and assessment of creatinine levels would be better ways of assessing renal function, which will be used to determine dose of medication but not for selection of the correct antibiotic. The white blood cell count and differential would indicate the possibility of an infection but are not needed in choosing the proper antibiotic. 13. A nursing student asks the pharmacology instructor for ways to minimize the emergence of drugresistant microbial agents. What would be an appropriate response by the instructor? (Select all that apply.) A) Avoid the use of broad-spectrum antibacterial drugs when treating trivial or viral infections. B) Use narrow-spectrum agents if they are thought to be effective. C) Do not use vancomycin unnecessarily. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) D) Prescribe antibiotics when the patient believes they are warranted. E) Start the antibiotics, do culture and sensitivity tests, and provide patient education. Ans: A, B, C 144 Feedback: To prevent or contain the growing threat of drug-resistant strains of bacteria, it is very important to use antibiotics cautiously, to complete the full course of an antibiotic prescription, and to avoid saving antibiotics for self-medication in the future. You would not give antibiotics every time the patient wants them, nor would you do a culture and sensitivity test after starting antibiotics. Therefore, Options D and E are incorrect. 14. A student asks the pharmacology instructor if there is a way to increase the benefits and decrease the risks of antibiotic therapy. What would be an appropriate response by the instructor? A) Taking drugs not prescribed for the particular illness tends to maximize risks and minimize benefits. B) Never use antibiotics in combination with other prescriptions or in combination with other antibiotics. C) Maximize antibiotic drug therapy by administering the full dose when the patient has a fever. D) Use antibiotics cautiously and teach patients to complete the full course of an antibiotic prescription. Ans: D Feedback: To prevent or contain the growing threat of drug-resistant strains of bacteria, it is very important to use antibiotics cautiously, to complete the full course of an antibiotic prescription, and to avoid saving antibiotics for self-medication in the future. A patient and family teaching program should address these issues, as well as the proper dosing procedure for the drug (even if the patient feels better) and the importance of keeping a record of any reactions to antibiotics. Thus, taking drugs not prescribed for the particular illness tends to maximize risks and minimize benefits. Also, if the infection is viral, antibacterial drugs are ineffective and should not be used. 15. What is the priority reason for the nurse to consider questioning an order for tetracycline in a child younger than 8 years of age? A) Children younger than 8 years of age cannot take tetracyclines. B) Weight-bearing joints have been impaired in young animals given the drugs. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) C) Tetracyclines can damage developing teeth and bone in children younger than 8 years of age. D) Liver and kidney function may be damaged when it is given to children under 8 years of age. Ans: C 145 Feedback: Use tetracyclines with caution in children younger than 8 years of age because they can potentially damage developing bones and teeth. Although the drug does not cause damage to liver and kidneys, it may be contraindicated in patients with hepatic or renal dysfunction because it is concentrated in the bile and excreted in the urine. Fluoroquinolones, not tetracyclines, are generally contraindicated for use in children (i.e., those younger than 18 years of age) because weight-bearing joints have been impaired in young animals given the drugs. Clindamycin (Dalacin C) warrants monitoring hepatic and renal function when it is given to neonates and infants. Trimethoprimsulfamethoxazole (Nu-Cotrimox) is used in children, although children younger than 2 months of age have not been evaluated. Children under 8 years of age can take tetracycline, but it should be used with caution. 16. After administering an antibiotic, the nurse assesses the patient for what common, potentially serious, adverse effect? A) Rash B) Pain C) Constipation D) Hypopnea Ans: A Feedback: Examine skin for any rash or lesions, examine injection sites for abscess formation, and note respiratory statusincluding rate, depth, and adventitious sounds to provide a baseline for indications of an allergic or adverse response to the drug. Report nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, rash, recurrence of symptoms for which the antibiotic drug was prescribed, or signs of new infection (e.g., fever, cough, sore mouth, drainage). These problems may indicate adverse effects of the drug, lack of therapeutic response to the drug, or another infection. Pain, constipation, and hypopnea are not common adverse effects of antibiotic drugs. 17. The nurse is caring for a 62-year-old patient who is receiving IV gentamicin (Garamycin). The patient complains of difficulty hearing. What should the nurse do? A) Hold the dose and notify the physician immediately. B) Administer the dose and speak in a louder voice when talking to the patient. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) C) Administer the dose and report this information to the oncoming nurse. D) Administer the dose and document the finding in the nurse’s notes. Ans: A 146 Feedback: Aminoglycosides are contraindicated in the following conditions: known allergy to any of the aminoglycosides; renal or hepatic disease that could be exacerbated by toxic aminoglycoside effects and that could interfere with drug metabolism and excretion, leading to higher toxicity; preexisting hearing loss, which could be intensified by toxic drug-related adverse effects on the auditory nerve. Ototoxicity should be reported and the drug should be stopped. You would not administer the dose and then call the physician, administer the dose and report information to oncoming nurse, or administer the dose and document the finding in the nurse’s notes because each additional dose administered could potentially worsen hearing loss. 18. The nurse is providing patient teaching before discharging a patient home. The patient is taking ciprofloxacin (Cipro). What would the nurse teach this patient is the best way to prevent crystalluria caused by ciprofloxacin (Cipro)? A) Eliminate red meat and seafood from the diet. B) Encourage at least 2 liters of fluid per day. C) Avoid caffeine and alcohol. D) Spend time in the sun each day to optimize vitamin D levels. Ans: B Feedback: Provide the following patient teaching: Avoid driving or operating dangerous machinery because dizziness, lethargy, and ataxia may occur; try to drink a lot of fluids and maintain nutrition (very important), even though nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea may occur. There is no need to eliminate red meat, seafood, caffeine, or alcohol from the diet, although alcohol may increase the risk of GI irritation. Patients should be taught to avoid the sun due to possible photosensitivity. 19. The nurse is caring for a child weighing 30 kg. The physician orders gentamicin (Garamycin) 100 mg tid for the patient. The recommended dosage range is 6 to 7.5 mg/kg/day. What action should the nurse take? A) Administer the medication and assess hearing frequently. B) Question the physician about the frequency of administration. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) C) Question the physician about the dosage of the medication. D) Administer the medication and assess renal function frequently. Ans: C 147 Feedback: The dosage is outside the recommended dosage range at 10 mg/kg/day so the nurse should question the dosage before administering the medication. It is appropriate to administer gentamicin tid to pediatric patients so there would be no need to question frequency of dosage. The drug should not be administered until the correct dosage is ordered so there is no need to assess hearing or renal function. 20. The nurse is caring for a patient with a gram-positive infection. What antibiotic would be most effective in treating this infection? A) Cefaclor (Ceclor) B) Cefoxitin (generic) C) Cefotaxime (Claforan) D) Cefazolin (Zolicef) Ans: A Feedback: First-generation cephalosporins are largely effective against gram-positive bacteria and include cefadroxil (generic), cefazolin (Zolicef), and cephalexin (Keflex). Second-and third-generation cephalosporins are less effective against gram-positive bacteria. Cefoxitin (generic) is a secondgeneration cephalosporin and cefotaxime (Claforan) and cefazolin (Zolicef) are third-generation cephalosporins. 21. What severe reaction would the nurse assess for if it were necessary to administer trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole (TMP/SMX) to an older adult? A) Diarrhea B) Bone marrow depression C) Vomiting D) Decreased gastrointestinal (GI) motility Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) Ans: 148 B Feedback: TMP/SMX is associated with an increased risk of severe adverse effects in patients with reduced liver and kidney function. Because kidney function is known to decline as a natural part of aging, older adults would be at more increased risk of severe reactions and would require more careful monitoring. Severe skin reactions and bone marrow depression are the most frequently reported severe reactions. Diarrhea and vomiting are possible adverse effects of most medications but are not examples of severe reactions, although they would require proper intervention to prevent dehydration. GI motility is more likely to increase than to decrease. 22. What medication would the nurse question if ordered for a pediatric patient? A) Amikacin B) Cefazolin C) Streptomycin D) Levofloxacin Ans: D Feedback: Fluoroquinolones are contraindicated in patients who are younger than 18 years of age. Levofloxacin is the only fluoroquinolone among the answer options and is contraindicated for pediatric patients under age 18. 23. The nurse is caring for a patient who is receiving an aminoglycoside. What would be a priority assessment on this patient? A) Respiratory function B) Vision C) Cardiac function D) Liver function Ans: A Feedback: Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 149 Aminoglycosides come with a black box warning alerting health care professionals to the serious risk of ototoxicity and nephrotoxicity. Central nervous system effects include ototoxicity, possibly leading to irreversible deafness; vestibular paralysis resulting from drug effects on the auditory nerve; confusion; depression; disorientation; and numbness, tingling, and weakness related to drug-related adverse effects on other nerves. Visual alterations are not usually reported in relation to this drug. Respiratory function and liver function are not usually impacted by this drug. 24. The nurse provides discharge teaching for a patient who will receive a prescription for cefaclor (Ceclor). What important information will the nurse provide this patient? A) Avoid alcohol until 72 hours after stopping this medication. B) Genital itching will go away after the drug is discontinued. C) Monitor for yellowing of the skin or eyes and call the doctor if it occurs. D) Avoid grapefruit juice when taking this medication to prevent adverse effects. Ans: A Feedback: Patients should be taught to avoid alcohol for up to 72 hours after discontinuing cefaclor (Ceclor) to prevent a disulfiram-like reaction that results in unpleasant symptoms such as flushing, throbbing headache, nausea and vomiting, chest pain, palpitations, dyspnea, syncope, vertigo, blurred vision, and in extreme reactions, cardiovascular collapse, convulsions, or even death. Genital itching in women indicates the possibility of a superinfection and the patient should see her health care provider. Liver damage, indicated by jaundice, is not a likely adverse effect with this drug. There is no need to avoid grapefruit juice. 25. The nurse is teaching the patient about amoxicillin prior to discharge and includes what important teaching point? A) Blackening of the tongue may occur but will subside when the drug is discontinued. B) Even if it seems like the infection is not improving, the drug is still working. C) Yeast infections are unlikely to occur with this medication because it is narrow spectrum. D) Appearance of a rash is common and does not indicate an allergic reaction. Ans: A Feedback: One of the adverse effects of ampicillin is blackening of the tongue but the discoloration goes away after stopping the drug. If it is accompanied by swelling, the patient should be instructed to call the Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 150 prescribing health care provider immediately. Many penicillin-resistant pathogens exist, so if the infection does not seem to be responding to the drug, the patient should notify the health care provider because a different antibiotic may be required. Yeast infections are very likely after taking ampicillin because it is a broad-spectrum antibiotic. Appearance of a rash should be evaluated by a health care professional because allergic reactions to this class of antibiotic are very common. 26. What drug administered by the nurse belongs to the group of Carbapenems? A) Primaxin B) Gemifloxacin C) Demeclocycline D) Cefuroxime Ans: A Feedback: The group consists of three drugs: imipenem-cilastatin (Primaxin), meropenem (Merrem), and ertapenem (Invanz). Gemifloxacin is a Fluoroquinolones, Cefuroxime is a second-generation cephalosporin, and demeclocycline is a tetracycline. 27. An intensive care unit nurse is caring for a patient taking kanamycin. What is the nurse’s priority action? A) Giving the drug for no longer than 7 days B) Assessing liver function daily C) Contacting the ordering physician D) Monitoring renal function daily Ans: D Feedback: The potential for nephrotoxicity and ototoxicity with amikacin is very high, so the drug is used only as long as absolutely necessary and should not be administered for longer than 7 to 10 days because of its potentially toxic adverse effects, which include renal damage, bone marrow depression, and gastrointestinal (GI) complications. The nurse cannot stop administering the drug after 7 days if the doctor orders it to be given longer but the nurse could question the order and promote change to another antibiotic if necessary. Monitoring renal function is the priority action when this drug is administered and the provider should be notified if signs of renal failure occur. Liver function is not usually impacted by this drug, although a patient with preexisting liver alterations may require a change in dosage to Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 151 prevent toxicity. There is no indication of a need to contact the health care provider. 28. The clinic nurse is providing health teaching to a patient who has been prescribed doxycycline (Doxycin). What is a priority teaching point for this patient? A) Stay out of the sun. B) Avoid sexual activity. C) Take an antacid with the drug if nausea occurs. D) Chew the tablets completely before swallowing. Ans: A Feedback: Encourage the patient to apply sunscreen and wear protective clothing if sun exposure cannot be avoided to protect exposed skin from rashes and sunburn associated with photosensitivity reactions. If the patient is a woman the nurse may advise the patient to use barrier methods of contraceptives (if she is taking oral contraceptives) due to the drugdrug interaction but the patient would not be told to avoid sexual activity. Antacid therapy and chewing the tablets would be inaccurate information. 29. The mother of a 5-year-old asks the nurse why it seems amoxicillin is always prescribed when her child needs an antibiotic. What is the priority rationale the nurse should give the mother? A) It is better absorbed. B) It is less costly. C) It has a less frequent dosing schedule. D) It tastes better in oral form. Ans: A Feedback: Most penicillins are rapidly absorbed from the GI tract, reaching peak levels in 1 hour. Although amoxicillin is less expensive, that fact has far less impact on choosing the proper antibiotic than the effectiveness of the drug. Most oral antibiotics for children are available in pleasant tasting syrups so taste would not be a factor. Ampicillin is often given up to 4 times a day so it actually has a frequent dosing schedule. 30. When discussing cephalosporins with the nursing class, the pharmacology instructor explains that this classification of drug is primarily excreted through which organ? Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) A) Lung B) Liver C) Kidney D) Skin Ans: C 152 Feedback: The cephalosporins are primarily metabolized in the liver and excreted in urine. These drugs cross the placenta and enter breast milk. They are not excreted through the lungs, liver, or skin. 31. The nurse is caring for a patient receiving an antimycobacterial who reports dizziness, headache, and drowsiness. What is the priority nursing diagnosis? A) Imbalanced nutrition: less than body requirements B) Disturbed sensory perception (kinesthetic) related to central nervous system (CNS) effects of the drug C) Acute pain related to gastrointestinal (GI) effects of the drug D) Deficient knowledge regarding drug therapy Ans: B Feedback: The priority concern for this patient right now is the disturbed sensory perception related to the CNS effects of the drug. Acute Pain could also be used but it would be related to CNS effects, not GI effects. There is no indication of imbalanced nutrition or deficient knowledge in the question. 32. The patient is admitted to the acute care facility with acute septicemia and has orders to receive gentamicin and ampicillin IV. The nurse is performing an admission assessment that includes a complete nursing history. What information provided by the patient would indicate the need to consult the health care provider before administering the ordered medication? A) Takes furosemide (Lasix), a potent diuretic, daily B) Had prostate surgery 3 months ago Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) C) History of hypothyroidism D) Allergic to peanuts and peanut products Ans: A 153 Feedback: Aminoglycosides should be avoided if the patient takes a potent diuretic because of the increased risk of ototoxicity, nephrotoxicity, and neurotoxicity. Learning the patient takes a potent diuretic would indicate the need to consult with the health care provider before administering gentamicin. Prostate surgery, hypothyroidism, and an allergy to peanuts would not preclude administration of these medications and would not indicate a need to consult with the provider. 33. When the nurse cares for a patient receiving an antibiotic, what instructions will the nurse provide no matter what medication is prescribed? (Select all that apply.) A) Drink plenty of fluids to avoid kidney damage. B) Take all medications as prescribed until all of the medication is gone. C) Report difficulty breathing, severe headache, or changes in urine output. D) Take antibiotic with food to avoid gastrointestinal (GI) upset. E) Take safety precautions such as changing position slowly. Ans: A, B, C Feedback: The patient taking any antibiotic needs to drink plenty of fluids to avoid kidney damage and improve excretion of the metabolized drug; take all medications as prescribed until all of the medication is gone to avoid developing a resistant strain of bacteria; and report any difficulty breathing, severe headache, or changes in urine output because these are primary manifestations of serious adverse effects. Although some antibiotics need to be taken with food, others may be best taken on an empty stomach so this does not apply to all antibiotics. Not all antibiotics are associated with central nervous system (CNS) toxicity so taking safety precautions need only be included in patient teaching if they are taking a drug associated with CNS adverse effects. 34. The nurse is admitting a 12-year-old girl to the acute care facility and notices discolored secondary teeth. The mother says she doesn’t know why the teeth are discolored because the child is very good about brushing and flossing and sees the dentist regularly. What question would the nurse ask? A) Has she ever received tetracycline? B) Has she ever received gentamicin? Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) C) Has she ever received ampicillin? D) Has she ever received cephalexin? Ans: A 154 Feedback: The nurse would question whether the child was ever given tetracycline because this drug is commonly associated with discoloration of secondary teeth when it is administered to children who still have their primary teeth. Gentamicin, ampicillin, and cephalexin are not associated with discoloration of the teeth. 35. The nurse is caring for a female patient whose tests confirm she is 10 weeks pregnant and has contracted tuberculosis. The health care provider orders a combination of antimycobacterials. What combination of drugs would the nurse identify as safest for this pregnant patient? A) Isoniazid, ethambutol, and rifampin B) Rifabutin, streptomycin, and rifampin C) Capreomycin, cycloserine, and ethionamide D) Dapsone, ethambutol, and cycloserine Ans: A Feedback: The antituberculosis drugs are always used in combination to affect the bacteria at various cellular stages and first-line drugs are always the first choice, using second-line drugs only when the patient is unable to take the first-line medications. Because this patient is pregnant, the safest choices would be isoniazid, ethambutol, and rifampin but no drug is administered during pregnancy unless the benefit outweighs the risk. The other drug choices would be less safe and would not be used unless the safer drugs were contraindicated. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 155 Chapter 10 - Antiviral Agents 1. The nurse explains why viruses are so difficult to treat when making what statement? A) Viruses are contained inside the human cell and cannot be destroyed without destroying the cell. B) Release of interferons by the host cell makes the virus replicate more quickly allowing the virus to spread. C) Drugs exist to treat all viral infections but they carry serious adverse effects and the benefit often does not outweigh the risk. D) Individual antiviral drugs are often effective in treating many different viruses because one virus in a category behaves like others in the same category. Ans: A Feedback: Because viruses are contained inside human cells while they are in the body, researchers have difficulty developing effective drugs that destroy a virus without harming the human host. Interferons are released by the host in response to viral invasion of a cell and act to prevent the replication of that particular virus. Some interferons that affect particular viruses can now be genetically engineered to treat particular viral infections. Other drugs that are used in treating viral infections are not natural substances and have been effective against only a limited number of viruses. Very few viruses are treatable with medications; a few more can be prevented through immunization but most have no known treatment. Each antiviral is generally only suited to treat the single virus it was developed for and will not be effective against other viruses. 2. While calculating the drug dose of antiviral medications for children who have AIDS a pediatric nurse uses what? A) The viral complications B) The child’s age C) The severity of the virus D) The child’s weight Ans: D Feedback: Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 156 Antiviral medication dosages for children are calculated according to weight. There is no scientific data available concerning dosages based on complications or severity of illness. The ethical dilemma using children in drug studies is always a concern. Children must be monitored very carefully for adverse effects on kidneys, bone marrow, and the liver. The complications and severity of the disease may determine which drug is prescribed. 3. A patient taking nevirapine (Viramune) as part of combination therapy for treatment of HIV took 200 mg/daily PO for 14 days. The patient is now taking 200 mg PO bid. How many mg of the medication is the patient taking daily? A) 100 mg B) 200 mg C) 300 mg D) 400 mg Ans: D Feedback: The patient is to take 200 mg bid, which means twice a day. (200 times 2 equals 400 mg daily.) 4. What medication is only administered intravenously and is used to treat cytomegalovirus (CMV)? A) Cidofovir (Vistide) B) Foscarnet (Foscavir) C) Valacyclovir (Valtrex) D) Valganciclovir (Valcyte) Ans: B Feedback: Foscarnet (Foscavir) is administered IV only. Ganciclovir and (Cytovene) can be administered by IV and orally. Valganciclovir (Valcyte) and Valacyclovir (Valtrex) are administered only by the oral route. 5. A) A hospitalized patient is receiving an antiviral drug to treat cytomegalovirus. What is the nurse’s priority action after administering the antiviral drug? Monitor vital signs every hour. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) B) Decrease fluid intake. C) Keep side rails up. D) Encourage the patient to ambulate 10 minutes after each dose. Ans: C 157 Feedback: Antiviral drugs for herpes and cytomegalovirus can cause confusion, dizziness, and other central nervous system (CNS) effects. Side rails should be up after administration to protect the patient from injury until risk for these adverse effects is lowered because not every patient will experience these effects. The patient should not be encouraged to walk after each dose because of the risk of falls if adverse effects occur. Fluid intake should be slightly increased to help decrease risk of nephrotoxicity. Vital signs should be monitored, but it would not be necessary to take them every hour unless serious adverse effects occur. 6. A nurse is caring for a patient with HIV. What lab tests would the nurse monitor when a protease inhibitor has been ordered for this patient? A) A fasting blood sugar and 2-hour postprandial blood sugar B) Urine specific gravity and urine pH C) Serum alanine aminotransferase and bilirubin D) Arterial blood gases and O2 saturation Ans: C Feedback: Serum alanine aminotransferase and bilirubin are monitored when a protease inhibitor is used due to the risk of liver damage and the need to monitor liver function. Cholesterol and triglycerides may also be elevated by the drug and should be monitored. Protease inhibitors are metabolized in the liver and partially by the cytochrome P450 oxidase system. Although some cases of kidney stones have been related to protease inhibitors use, the greatest risk is to the liver and therefore urine specific gravity and urine pH, which indicate renal function, would be less critical to assess. Lab tests for blood sugar and arterial blood gases would not be directly affected by hepatic function. 7. A) A patient with renal impairment and HIV has had a medication change. What drug would be considered the drug of choice for this patient? Atazanivir (Reyataz) Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) B) Lopinavir (Kaletra) C) Nelfinavir (Viracept) D) Ritonavir (Norvir) Ans: C 158 Feedback: Nelfinavir is the best choice for a patient with renal impairment because very little of the drug is excreted through the kidney, with most being excreted in feces. The other drugs are all excreted through both the urine and feces, so patients with renal impairment might need dosage adjustments to avoid toxicity. 8. The nurse is caring for a patient with hepatitis B. The patient is taking adefovir (Hepsera). Which medication would the nurse question if it were ordered? A) Cimetidine (Tagament) B) Diltiazem (Cardizem) C) Diphenhydramine (Benadryl) D) Telbivudine (Tyzeka) Ans: D Feedback: Telbivudine is an antihepatitis B agent, and when given with adefovir (Hepsera) can result in severe hepatomegaly with steatosis, sometimes fatal. Cimetidine is a histamine-2 antagonist, diltiazem is a calcium channel blocker, and diphenhydramine is a first-generation antihistamine. These drugs are normally not considered nephrotoxic and could be used with adefovir. 9. A nurse is caring for a stroke victim in the intensive care unit. The nurse notices a cold sore and requests medication. Docosanol (Abreva) is ordered. Before applying the medication, the nurse would first? A) Clean the area to be treated and then pat it dry. B) Assess the area for open lesions or abrasions. C) Put gloves on to protect herself. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) D) Prepare applicator for drug administration. Ans: B 159 Feedback: The nurse would assess the area first to make sure no open lesions or abrasions could allow for systemic absorption of the drug. Then the nurse would clean the area and pat it dry. The nurse may apply the medication using gloves or an applicator. 10. A patient with AIDS is taking an antiviral agent. What comment by the patient would indicate that the teaching plan was effective? A) I feel like I do when I have the flu. B) I will continue to take the over-the-counter medication for my allergies. C) Excessive fatigue and a severe headache are common adverse effects of my medication. D) This drug will cure AIDS. Ans: A Feedback: Common adverse effects of antiviral agents are flu-like symptoms, which may be related to the underlying disease. Excessive fatigue and a severe headache can indicate a serious complication and should be reported immediately. Antiviral agents do not cure the disease. HIV causes loss of helper Tcell function. This causes the immune system to be depressed and allows opportunistic infections to occur. Antiviral agents reduce the number of mutant viruses that are formed and spread to noninfected cells. 11. The school nurse is preparing a lecture on hepatitis B for a health class in high school. What is an important teaching point for the nurse to include about the transmission of hepatitis B? (Select all that apply.) A) Hepatitis B is transmitted through the bite of an insect. B) Hepatitis B is transmitted through sexual contact. C) Hepatitis B is transmitted through blood-to-blood contact. D) Hepatitis B is transmitted from the mother to her unborn baby. E) Hepatitis B is transmitted through nonsexual household contact. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) Ans: 160 B, C, D Feedback: Hepatitis B is transmitted from one person to another through sexual contact, blood-to-blood contact, or perinatally. It is not transmitted through casual contact. Several studies involving more than 1,000 uninfected, nonsexual household contacts with persons with hepatitis B infection (including siblings, parents, and children) have shown no evidence of casual transmission. Hepatitis B is not spread by mosquitoes or other insect vectors. 12. A 21-year-old woman presents with cytomegalovirus (CMV). The LPN says, I’ve never heard of CMV before. The nurse explains to the LPN that this infection is most often seen with patients diagnosed with what? A) HIV B) Influenza C) Autoimmune disorder D) Hepatitis B Ans: A Feedback: CMV is an opportunistic infection that is most often diagnosed in patients with HIV or who are immunocompromised because those with a healthy immune system can fight off CMV. CMV would not be diagnosed in patients with influenza, an autoimmune disorder, or hepatitis B because the immune system would be strong enough to destroy the CMV pathogen. 13. The nurse is assessing a patient admitted with AIDS who is taking a nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor. What nursing diagnosis is most likely to be appropriate for this patient? A) Risk for injury related to central nervous system (CNS) effects of the drug B) Excess fluid volume related to renal failure C) Imbalanced nutrition: Less than body requirements, related to gastrointestinal (GI) effects of the drugs D) Ineffective health maintenance related to spiritual distress Ans: C Feedback: Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 161 The adverse effects most commonly experienced with these drugs are GI relateddry mouth, constipation or diarrhea, nausea, abdominal pain, and dyspepsia. As a result, this patient is most at risk for imbalanced nutrition; less than body requirements. CNS effects are not common with this classification of drug. Renal failure is not a common adverse effect. Nothing indicates the possibility of spiritual distress in this situation. 14. A patient has just been diagnosed with HIV. When developing the teaching plan, what information would the nurse share with this patient related to use of alternative or complementary therapies? A) Complementary therapies such as acupuncture or herbal therapy are dangerous to patients with HIV and you are discouraged from exploring these types of therapy. B) Researchers have not looked at the benefits of alternative therapy for patients with HIV, so it is suggested you avoid these therapies until research data are available. C) Alternative therapies have benefits and risks. Are there any types of alternative or complementary therapies that you follow or are there any herbs or supplements that you take? D) You do not take herbs or practice some type of alternative medicine such as acupuncture, massage therapy, hypnosis, or diet therapy, do you? Ans: C Feedback: With a new diagnosis of HIV, it is important for the nurse to assess the patient for use of alternative therapies because some alternative therapies are contraindicated while on antiviral medication. Options A and D are negative statements that discourage the patient from sharing information with the nurse. Option B gives the patient information, but does not elicit information in return and is therefore inappropriate for the nurse to use. 15. The nurse is caring for a patient hospitalized with hepatitis B. The family comes to visit and a family member asks the nurse if it is safe to visit. What is the nurse’s best response? A) You seem fearful. Why do you think you are at risk? B) Don’t worry, you will not contract the disease from the patient. C) There is no risk unless you come in contact with blood and body fluids. D) The patient should be isolated and have limited visitation. Ans: C Feedback: Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 162 Visitors should be reassured that they are not at risk of contracting the virus unless they come in contact with blood or body fluids. It is never appropriate to tell someone not to worry because it is neither effective nor appropriate. The reason the family member is fearful is obvious, so these questions are demeaning. Visitation does not need to be limited. 16. A patient newly diagnosed with HIV is receiving patient teaching from the clinic nurse about antiviral medications. What would the nurse tell the patient needs to be reported to a health care provider? A) Dizziness B) Constipation C) Vomiting D) Rash Ans: D Feedback: All options provided have the potential to be an adverse effect of antiviral medications prescribed to treat HIV. Most can be managed through diet or over-the-counter medications but a rash needs to be reported immediately because it could indicate a potentially serious reaction and requires immediate intervention. 17. The nurse is planning care for an AIDS patient admitted with chronic severe diarrhea secondary to adverse effects of the antiviral drugs prescribed. What would be the most appropriate goal for this patient? A) Patient will show improved nutritional status evidenced by weight gain. B) Alleviation or reduction of signs and symptoms of AIDS. C) Patient will be able to demonstrate the effectiveness of the teaching plan. D) Patient will state that comfort and safety measures are effective and show compliance with the regimen. Ans: A Feedback: Severe chronic diarrhea is likely to result in malnutrition and weight loss along with potential alterations in fluid and electrolyte balance. The best indicator of improvement would be an improvement in nutritional status as indicated by weight gain. Although the other outcomes might be applicable to a patient with AIDS, weight gain is the priority concern for a patient with severe chronic diarrhea. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 18. 163 A nurse practitioner is teaching a health class in the local high school. The NP informs the class about hepatitis B. What occupation does the NP inform the class is at the greatest risk for contracting hepatitis B? A) Policemen B) Health care workers C) Educators D) Fire fighters Ans: B Feedback: Health care workers are at especially high risk for contracting hepatitis B due to needle sticks and contact with the blood of infected patients. Policemen, educators, and fire fighters are not considered at high risk for contracting hepatitis B although they do face some risk because of contact with blood and body fluids. 19. What liver function test is a sensitive indicator of injury to liver cells and useful in detecting acute liver disease such as hepatitis? A) Clotting factors B) SGGT C) Serum aminotransferases D) Alkaline phosphatase Ans: C Feedback: Antiviral drugs are indicated for the treatment of adults with chronic hepatitis B who have evidence of active viral replication and evidence of either persistent elevations in serum aminotransferases or histologically active disease. The drugs inhibit reverse transcriptase in the hepatitis B virus and cause DNA chain termination, leading to blocked viral replication and decreased viral load. Clotting factor alterations will be seen only in cases of severe liver damage. Serum gamma-glutamyl transferase and alkaline phosphatase may elevate with liver damage, but serum aminotransferases are the best indicator of hepatitis B 20. What drug would the nurse administer to treat chronic hepatitis C in children and adults who relapse Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 164 after interferon-alfa therapy? A) Zanamivir (Relenza) B) Acyclovir (Zovirax) C) Cidofovir (Vistide) D) Ribavirin (Virazole) Ans: D Feedback: Ribavirin is used in combination with interferon alfa-2b as an oral drug for the treatment of chronic hepatitis C in children and adults who relapse after inferferon alfa therapy. Cidofovir is used to treat cytomegalovirus (CMV) in AIDS patients. Virazole is used to treat uncomplicated infuenza infections. Acyclovir is used for herpes infections. 21. Some antiviral agents are given locally to treat local viral infections. How do these medications work? (Select all that apply.) A) Interfere with viral metabolic processes B) Interfere with viral cellular replication C) Interfere with host metabolic processes D) Interfere with viral transcription E) Increase antibody production Ans: A, B Feedback: These antiviral agents act on viruses by interfering with normal viral replication and metabolic processes. They are indicated for specific local viral infections. The medications do not interfere with the invaded cell or with viral transcription and they do not increase antibody production. 22. A) What drug used to treat influenza A should not be used by nursing mothers? Ribavirin (Rebetron) Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) B) Rimantadine (Flumadine) C) Valganciclovir (Valcyte) D) Acyclovir (Zovirax) Ans: B 165 Feedback: Rimantadine is embryotoxic in animals and should be used during pregnancy only if the benefits clearly outweigh the risks. The drug should not be used by nursing mothers because it crosses into breast milk and can cause toxic reactions in the neonate. Valganciclovir is used to treat cytomegalovirus-related retinitis in AIDS patients. Acyclovir is used to treat herpes simplex outbreaks. Ribavirin is used as a treatment of influenza A, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), and herpes virus infections; treatment of children with RSV; has undergone testing for use in several other viral conditions. It is teratogenic and is rated pregnancy category X, but no warnings are related to breastfeeding mothers. 23. A 25-year-old female patient presents at the clinic with fever, chills, and achy joints. The patient is diagnosed with influenza A, and ribavirin is prescribed. What should the nurse include in patient teaching about this medication? A) Advise women of childbearing age to remain on oral contraceptives for at least 1 month after finishing this medication. B) Advise women of childbearing age that this drug is also an abortifacient. C) Advise women of childbearing age to use barrier contraceptives. D) Advise women of childbearing age that this drug is safe for the fetus. Ans: C Feedback: For ribavirin, advise women of childbearing age to use barrier contraceptives if they are taking this drug. The drug has been associated with serious fetal effects, but it has not been associated with spontaneous abortions. Oral contraceptives should not be stopped and barrier contraceptives should be used in addition. 24. A patient has been prescribed ribavirin for influenza A. The patient is experiencing nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. What would the nurse be sure to include in the patient teaching about this medication? A) Do not take with anticholinergic medications. B) Do not take with acetaminophen or aspirin. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) C) Do not take with antiarrhythmics. D) Do not take with antacids. Ans: D 166 Feedback: Ribavirin levels may be reduced if given with antacids. Patients who receive amantadine or rimantadine may experience increased atropine-like effects if either of these drugs is given with an anticholinergic drug. Patients taking rimantadine may also experience a loss of effectiveness of aspirin and acetaminophen if these are also being used. Rifampin is known to decrease the effectiveness of many drugs, including antiarrhythmics. 25. The nurse is caring for a patient who is prescribed cidofovir, IV. What other medication will the nurse administer with cidofovir? A) Probenecid B) Paroxetine hydrochloride C) Penciclovir D) Prostigmin Ans: A Feedback: Cidofovir, which is given by IV infusion, reaches peak levels at the end of the infusion; in studies, it was cleared from the system within 15 minutes after the infusion was completed. It is excreted unchanged in the urine and must be given with probenecid to increase renal clearance of the drug. Paroxetine hydrochloride is Paxil, an antidepressant; Penciclovir is an antiviral cream; Prostigmin is an anticholinesterase agent used in myasthenia gravis. None of these drugs are used with cidofovir except for probenecid. 26. The nurse admits a patient for treatment of cytomegalovirus (CMV). The patient has been ordered foscarnet (Foscavir), 40 mg/kg q812h given over 2 hours. By what route would the nurse administer this drug? A) Sub q B) IV C) IM Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) D) PO Ans: B 167 Feedback: Foscarnet is available in intravenous (IV) form only. It reaches peak levels at the end of the infusion and has a half-life of 4 hours. About 90% of foscarnet is excreted unchanged in the urine making it highly toxic to the kidneys. Use caution and at reduced dosage in patients with renal impairment. Options A, C, and D are incorrect. 27. A patient comes to the clinic with a herpes outbreak. The nurse notes from the patient’s chart that the patient is just beginning a course of antibiotics prescribed by another physician in the clinic. What classification of antibiotic should not be taken with an antiviral medication used to treat herpes? A) Penicillin B) Beta-Lactam C) Aminoglycoside D) Macrolide Ans: C Feedback: The risk of nephrotoxicity increases when agents indicated for the treatment of herpes and cytomegalovirus are used in combination with other nephrotoxic drugs, such as the aminoglycoside antibiotics. No contraindication exists for penicillins, beta-lactams, or macrolide antibiotics. 28. A nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor has direct effects on the HIV virus activities within the cell. What drug is a nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor? A) Econazole nitrate (Spectazole) B) Oxaliplatin (Eloxatin) C) Olanzapine (Zyprexa) D) Efavirenz (Sustiva) Ans: D Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 168 Feedback: The nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors now available include: delavirdine (Rescriptor), efavirenz (Sustiva), and nevirapine (Viramune). Econazole nitrate is an antifungal cream, olanzapine is an atypical antipsychotic, and oxaliplatin is an antineoplastic agent. 29. An immunocompromised 3-year-old has been exposed to avian flu. The patient is brought to the clinic and the mother reports that the patient has had flu-like symptoms for the past 12 hours. What medication would you expect the physician to order for this patient? A) Oseltamivir (Tamiflu) B) Amantadine (Symmetrel) C) Ribavirin (Rebetron) D) Zanamivir (Relenza) Ans: A Feedback: Oseltamivir is the only antiviral agent that has been shown to be effective in treating avian flu. Therefore Options B, C, and D are incorrect. 30. The nurse is providing discharge teaching for a patient going home on the medication entecavir (Baraclude). What is the priority teaching point for this patient? A) Take the whole course of the medication as prescribed. B) Take this medication with grapefruit juice. C) Do not stop taking this medication or allow the prescription to run out. D) The patient will take this medication for the rest of his life. Ans: C Feedback: A potential risk for hepatitis B exacerbation could occur when the drugs are stopped. Therefore, teach patient the importance of not running out of the drugs and using extreme caution when discontinuing these drugs. Options A, B, and D are incorrect responses. 31. The nurse is caring for a patient who is taking adefovir to treat hepatitis B. The nurse would hold the Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 169 medication and notify the health care provider if assessing the signs and symptoms of what? (Select all that apply.) A) Lactic acidosis B) Hepatotoxicity C) Headache D) Nausea E) Asthenia Ans: A, B Feedback: Withdraw the drug and monitor the patient if he or she develops signs of lactic acidosis or hepatotoxicity because these adverse effects can be life threatening. Headache, nausea, and asthenia are potential adverse effects but are not life threatening and would not require withdrawal of the drug. 32. The nurse is caring for an asymptomatic preschool-aged child who has cystic fibrosis and has been exposed to influenza A before receiving the appropriate immunization. What antiviral medication might the nurse administer to this child? A) Rimantadine (Flumadine) B) Zanamivir (Relenza) C) Oseltamivir (Tamiflu) D) Amantadine (Symmetrel) Ans: C Feedback: Amantadine is indicated for the prevention of respiratory virus infections and can be given to children older than 1 year of age. This would be appropriate in a child with a chronic respiratory illness who could die as the result of developing a respiratory virus. Zanamivir is not indicated for children younger than 7 years of age. Rimantadine is administered as prophylaxis against influenza A virus in children older than 10 years of age. Oseltamivir is indicated for patients who are symptomatic for less than 2 days, but this child is asymptomatic. 33. For what viruses might the nurse administer acyclovir (Zovirax)? (Select all that apply.) Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) A) Herpes simplex virus B) Shingles C) Chickenpox D) HIV E) Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Ans: A, B, C 170 Feedback: Acyclovir is indicated for the treatment of herpes simplex virus, shingles, and chickenpox as well as topically for treating herpes labialis. Acyclovir is not effective against HIV or CMV. 34. The nurse is caring for a patient whose condition has continued to decline on other antiviral medications and is now prescribed nevirapine (Viramune). What other medications will the nurse assess for to avoid a drugdrug interaction with this new prescription? (Select all that apply.) A) Oral contraceptives B) Protease inhibitors C) St. John’s wort D) Ergot derivatives E) Antiarrhythmics Ans: A, B, C Feedback: Effectiveness may be lessened if nevirapine is combined with hormonal contraceptives or protease inhibitors. St. John’s wort should not be used with this drug or any nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors because a decrease in antiviral effects can occur. Antiarrhythmics are contraindicated when taking delavirdine, not nevirapine. Ergot derivatives are contraindicated with efavirenz, not nevirapine. 35. A) The nurse is caring for a pregnant woman diagnosed with HIV on prenatal drug screening. What medication would the nurse expect to administer to reduce the risk of maternal to fetal transmission of the virus? Lamivudine (Epivir) Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) B) Zidovudine (Retrovir) C) Stavudine (Zerit XR) D) Tenofovir (Viread) Ans: B 171 Feedback: AZT, or zidovudine is administered to prevent the transmission of HIV from mother to child and can be administered to both after birth to treat symptomatic HIV. The other medications (options A, C, and D) are not used for this purpose. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 172 Chapter 11 - Antifungal Agents 1. A 17-year-old male patient with athlete’s foot is extremely upset that he cannot get rid of it. He calls the clinic and asks the nurse whether the doctor can give him an antibiotic to cure the infection. What should the nurse include in the explanation of treatment for fungal infections? A) Fungi differ from bacteria in that the fungus has flexible cell walls that allow for free transfer into and out of the cell. B) Protective layers contain sterols, which change the membrane permeability. C) The composition of the protective layers of the fungal cell makes the organism resistant to antibiotics. D) Fungi cell walls contain Candida, which makes the cells rigid. Ans: C Feedback: The nurse should tell the patient that the composition of the protective layers of the fungal cell makes the organism resistant to antibiotics so that antibiotics would not have any positive effect. Fungi do differ from bacteria, but the fungus has rigid cell walls that allow for free transfer in and out of the cell. The protective layers contain ergosterol, not Candida, that helps keep the cell wall rigid, not permeable. 2. The nurse admits a 1-year-old child to the pediatric intensive care unit (ICU) with cryptococcal meningitis. What drug will the nurse anticipate receiving an order for to treat this child? A) Amphotericin B (Fungizone) B) Fluconazole (Diflucan) C) Griseofulvin (Fulvicin) D) Ketoconazole (Nizoral) Ans: B Feedback: Fluconazole is used in the treatment of cryptococcal meningitis and is safe to use in a 1-year-old child. Amphotericin B has many unpleasant adverse effects and is very potent, so it would not be the first or best medication to administer initially but would be reserved for use if fluconazole was not effective. Griseofulvin is given to treat tinea pedis and tinea unguium in children. Ketoconazole is not given to Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 173 children younger than 2 years because safety has not been established. 3. The nurse is teaching the patient about a newly prescribed systemic antifungal drug. What sign or symptom will the nurse instruct the patient to report to the provider immediately? A) Unusual bruising and bleeding B) Constipation or diarrhea C) Red and dry eyes D) Increased appetite with weight gain Ans: A Feedback: Unusual bruising and bleeding can be an indication of hepatic toxicity, which should be reported immediately. Yellowing of the eyes, not redness, and tearing are also indicative of hepatic toxicity. Usually GI symptoms include nausea and vomiting with antiviral drugs, which could cause decreased appetite and weight loss. These symptoms should be reported if they persist but are not emergency symptoms to report immediately. 4. A patient who has a tinea infection calls the clinic and complains of intense local burning and irritation with use of a topical antifungal drug. Even before asking the patient, the nurse suspects he or she is applying what medication? A) Butoconazole (Gynazole I) B) Ciclopirox (Loprox) C) Econazole (Spectazole) D) Haloprogin (Halotex) Ans: C Feedback: Econazole can cause intense local burning and irritation in treatment of tinea infections. Butoconazole is used to treat vaginal Candida infections. Ciclopirox is used to treat toenail and fingernail tinea infections and does not produce intense burning and irritation. Haloprogin is used to treat athlete’s foot, jock itch, and ringworm infections and is not associated with burning or irritation. 5. A patient asks the nurse if he or she should use a topical antifungal. The nurse is aware that the most important contraindication to topical antifungals is what? Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) A) Hepatic impairment B) Renal impairment C) Congestive heart failure D) Known allergy to any of the antifungal drugs Ans: D 174 Feedback: Topical antifungals are not absorbed systemically so they are not metabolized and excreted. As a result, the only contraindication would be an allergy to the drug. Hepatic and renal impairment and congestive heart failure would not be a contraindication because these drugs do not enter the bloodstream and impact these organ systems. 6. A patient with high cholesterol is taking lovastatin (Mevacor). What drug would the nurse question if it was ordered for this patient? A) Nifedipine (Procardia) B) Ciprofloxacin (Cipro) C) Itraconazole (Sporanox) D) Oxazepam (Serax) Ans: C Feedback: Itraconazole is an azole antifungal drug that has been associated with severe cardiovascular events when taken with lovastatin. Nifedipine, ciprofloxacin, and oxazepam have no drug interactions with lovastatin. Nifedipine is an antihypertensive drug whose effects can be increased when taken with cimetidine. The effects of ciprofloxacin are altered when taken with antacids and theophyllines. Oxazepam is an antianxiety drug that should not be taken with alcohol or theophyllines. 7. An 85-year-old man who is a resident in an extended-care facility has athlete’s foot. After applying an antifungal cream, what is the nurse’s next action? A) Wipe away excess medication from the affected area. B) Wrap a sterile kling dressing around both feet. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) C) Elevate the feet for 30 minutes. D) Apply clean dry socks. Ans: D 175 Feedback: Clean dry socks should be applied when treating athlete’s foot to help eradicate the infection because they will keep the feet dry as well as prevent the cream from being wiped away. A kling dressing is not necessary as it would bind the feet and interfere with mobility and increase the risk of systemic absorption. Medication should not be removed once applied, and there is no need to elevate the feet unless another medical condition warrants this action. 8. A patient comes to the clinic and is diagnosed with a vaginal fungal infection. The nurse provides patient information for self-administration of a vaginal antifungal medication. What will the nurse include in the instructions? A) Insert low into the opening of the vagina. B) Discontinue use during menstruation. C) Remain recumbent for at least 15 minutes after insertion. D) Rub the cream into the vaginal wall after insertion. Ans: C Feedback: The patient should remain recumbent at least 10 to 15 minutes after the medication is deposited high in the vagina so that leakage will not occur and absorption will take place. The effectiveness of the medication is determined by the consistent application for each specified dose for maximal results. The nurse would instruct the patient to continue the medication during menstruation. Stopping the drug and restarting it later can lead to the development of resistant strains of the drug. The cream need not be rubbed into the vaginal wall as it will coat the wall naturally after insertion. 9. A patient who is using a topical antifungal agent to treat mycosis calls the clinic to report a severe rash that is accompanied by blisters. What will the nurse instruct the patient to do? A) Continue the drug as the prescription indicates. B) Scrub the rash with soap and water. C) Stop using the drug immediately. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) D) Decrease the amount of the medication used. Ans: C 176 Feedback: The patient should stop using the drug. The rash could indicate sensitivity to the drug or worsening of the condition being treated. Scrubbing the rash could cause further irritation and increase the risk for other infections. Continuing the drug could cause further complications. Decreasing the medication would be ineffective in treating the infection while continuing to risk further complications. 10. The nurse admitted a 25-year-old woman to the unit. What would be the most important thing for the nurse to assess before administering ketoconazole? A) Complete blood count (CBC) and blood glucose B) Eating and sleeping habits C) Height and weight D) Renal and hepatic function Ans: D Feedback: It would be important for the nurse to know the patient’s CBC, blood glucose level, eating and sleeping habits, and height and weight. All of these factors could help determine a specific dosage. However, the most important factor would be the patient’s renal and hepatic function because hepatic or renal toxicity could occur quickly if the organs are not functioning properly. 11. What drug would the nurse administer orally without the need to question when treating infections caused by Candida albicans? A) Amphotericin B (Abelcet) B) Tolnaftate (Tinactin) C) Griseofulvin (Fulvicin) D) Fluconazole (Diflucan) Ans: D Feedback: Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 177 Fluconazole is available for oral use and is effective in treating C. albicans. Amphotericin B is reserved for severe and potentially fatal infections, so it would not be used for a C. albicansinfection. Tolnaftate is used to treat athlete’s foot and is applied topically, not given orally. Griseofulvin is applied topically and is used to treat tinea, not C. albicans. 12. When administering a topical antifungal via the vaginal route, what action would the nurse take? A) Place the patient in left lateral Sims’ position. B) Applied using sterile technique C) Administered high into the vagina. D) Insert a tampon after insertion. Ans: C Feedback: Vaginal antifungals should be administered high into the vagina. The patient should be placed in a recumbent position for insertion. Clean technique (not sterile) should be used. Inserting a tampon after administration is not necessary. 13. By what route would the nurse administer amphotericin B? A) Intravenously B) Intramuscularly C) Orally D) Topically Ans: A Feedback: Amphotericin B is only administered by the IV route. It cannot be given intramuscularly, orally, or topically. 14. A) What classification of medication will the nurse administer concurrently with amphotericin B (Fungizone) to help minimize the adverse reactions to this medication? Sedatives Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) B) Antipyretics C) Beta-adrenergic blockers D) Diuretics Ans: B 178 Feedback: Amphotericin B is often given with antipyretics to improve patient comfort and to minimize adverse reactions. Sedatives, beta-adrenergic blockers, and diuretics are not indicated for use with amphotericin B unless the patient has a coexisting diagnosis that would indicate a need for these drugs. 15. The nurse provides teaching about amphotericin B (Fungizone) for an 82-year-old patient. The nurse evaluates the patient understood teaching when he says he could develop what condition? A) Diabetes B) Liver necrosis C) Kidney damage D) Pancreatitis Ans: C Feedback: Amphotericin B is nephrotoxic so the patient needs to understand the risk of kidney damage. Other risks of amphotericin B include bone marrow suppression; GI irritation with nausea, vomiting, and potentially severe diarrhea; anorexia and weight loss; and pain at the injection site with the possibility of phlebitis or thrombophlebitis, but it does not cause diabetes, liver necrosis, or pancreatitis. 16. The nurse is reviewing the patient’s medications and sees fluconazole has been ordered. The nurse will question this order when finding the patient is taking what other medication? A) Digoxin B) Humulin insulin C) Acetaminophen D) Hydrochlorothiazide Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) Ans: 179 A Feedback: Fluconazole strongly inhibit the cytochrome P450 (CYP450) enzyme system in the liver and are associated with many drugdrug interactions, such as increased serum levels of the following agents: cyclosporine, digoxin, oral hypoglycemics, warfarin, oral anticoagulants, and phenytoin. Diphenhydramine, acetaminophen, and hydrochlorothiazide have no impact on fluconazole. There is no indication that humulin insulin, acetaminophen, and hydrochlorothiazide are contraindicated when taking fluconazole. 17. The nurse administers nystatin (Mycostatin) to a patient with thrush (oral candidiasis). How does the medication work in the body? A) Changes membrane permeability B) Prevents reproduction of fungal cells C) Fungistatic D) Inhibits glucan synthesis Ans: A Feedback: Nystatin binds to sterols in the cell wall, changing membrane permeability and allowing leaking of the cellular components, which will result in cell death. Nystatin is not a fungistatic (prevents reproduction of fungal cells) and it does not inhibit glucan synthesis. 18. The nurse teaches the patient to administer butoconazole (Gynazole) for vaginal candidal infection. What instructions will the nurse supply? A) Fill the applicator with the medication and insert it into the vagina at bedtime. B) Apply the medication to the perineal area twice a day and wear white cotton underwear. C) Soak in a sitz bath twice daily and insert the medication into the vagina after the bath. D) Take one tablet by mouth and be sure to follow the medication with a full glass of water. Ans: A Feedback: Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 180 Butoconazole (Gynazole) is administered once daily and should be inserted high into the vagina with the patient remaining recumbent for at least 10 to 15 minutes after insertion. Using the medication at bedtime helps decrease losing the medication by gravity and extends the time the medication will be in contact with the vaginal wall. The medication is not usually applied to the perineum unless the infection has traveled outside the vagina. Sitz baths are contraindicated because fungi flourish in moist environments. This medication is not administered orally and can only be applied topically. 19. What medication could the nurse administer in a single dose for effective treatment of the patient’s vaginal candidal infection? A) Caspofungin (Cancidas) B) Terbinafine (Lamisil) C) Ketoconazole (Nizoral) D) Tioconazole (Monistat-1) Ans: D Feedback: Tioconazole may be given as one dose for treatment of vaginal candidal infection. Caspofungin is given IV to treat invasive aspergillosis in patients who did not respond to other treatments and would not be used for a vaginal candidal infection. Terbinafine is administered twice daily for 1 to 4 weeks to treat topical mycosis. Ketoconazole is administered orally or topically to treat aspergillosis, leishmaniasis, cryptococcosis, blastomycosis, moniliasis, coccidioidomycosis, histoplasmosis, and mucormycosis but would not be used to treat vaginal candidal infections. 20. The nurse works on a renal transplant unit and receives an order for posaconazole (Noxafil) for the patient which the nurse interprets to mean the patient has what infection? A) Blastomycosis B) Aspergillus C) Mucormycosis D) Coccidioidomycosis Ans: B Feedback: Posaconazole is used for prophylaxis treatment of invasive Aspergillus and Candida infections in adults and children older than 13 years who are immunosuppressed secondary to antineoplastic, Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 181 chemotherapy, graft-versus-host disease following transplants, or hematological malignancies. Posaconazole would not be used to treat blastomycosis, mucormycosis, or coccidioidomycosis. 21. The nurse admits a patient diagnosed with a systemic fungal infection and is ordered IV fluconazole. When developing the plan of care for this patient, the nurse would use what nursing diagnosis related to this medication? A) Chronic pain related to the gastrointestinal (GI) system, central nervous system (CNS), and local effects of drug B) Risk for altered perfusion secondary to system cardiovascular effects of drug C) Disturbed sensory perception (kinesthetic) related to CNS effects D) Monitor IV sites to ensure that phlebitis or infiltration does not occur. Ans: C Feedback: Nursing diagnoses related to drug therapy might include disturbed sensory perception (kinesthetic) related to CNS effects. Cardiovascular effects are not a concern with this medication; acute, not chronic, pain is associated with GI, CNS, and local effects of the drug; option D is an intervention, not a nursing diagnosis. 22. The nurse is caring for a patient receiving an oral fungicide to treat a systemic fungal infection. What intervention would the nurse include in the plan of care? A) Maintain complete bed rest. B) Assess for cyanosis every 4 hours. C) Administer medication 1 hour before meals. D) Monitor nutritional status. Ans: D Feedback: Monitor nutritional status and arrange a dietary consultation as needed to ensure nutritional status secondary to gastrointestinal (GI) upset related to medication. Complete bed rest is unnecessary. Cyanosis is not an anticipated problem. Medications should be given with food not before meals. 23. What factors would the nurse indicate as contributing to an increase in diagnosed fungal infections? (Select all that apply.) Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) A) Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS)-related complex B) Increased prevalence of cancer C) Rise in birth rates across the country D) Greater number of older adults E) Increased use of immunosuppressants Ans: A, D, E 182 Feedback: The incidence of fungal infections has increased with the rising number of immunocompromised peoplepatients with AIDS and AIDS-related complex (ARC), those taking immunosuppressant drugs, those who have undergone transplantation surgery or cancer treatment, and members of the increasingly larger elderly population, who are no longer able to protect themselves from the many fungi that are found throughout the environment. Cancer rates and birth rates are declining and do not contribute to the increase in diagnosis of fungal infection. 24. A patient who has received a heart transplant is taking cyclosporine. The patient is found to have a systemic Aspergillus infection. What drug would the nurse question if ordered for this patient? A) Terbinafine B) Posaconazole C) Itraconazole D) Ketoconazole Ans: D Feedback: Ketoconzaole and fluconazole strongly inhibit the cytochrome P450 (CYP450) enzyme system in the liver and is associated with many drugdrug interactions such as increased serum levels of the following agents: cyclosporine, digoxin, oral hypoglycemics, warfarin, oral anticoagulants, and phenytoin. There is no known drug interaction between cyclosporins and terbinafine, posaconazole, or itraconazole. 25. When caring for a patient with a secondary immunodeficiency disease following kidney transplantation being treated for candidemia the nurse can anticipate receiving an order for what medication? Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) A) Amphotericin B B) Anidulafungin C) Flucytosine D) Butoconazole Ans: B 183 Feedback: Anidulafungin (Eraxis) is used for the treatment of candidemia (infection of the bloodstream) and other forms of candidal infections, intra-abdominal infections, and esophageal candidiasis. Amphotericin B is not indicated in the treatment of candidemia. Flucytosine is indicated for the treatment of candidemia but is excreted primarily in the urine so would be contraindicated in a patient with a transplanted kidney. Butoconazole is a topical medication that would not be appropriate for use treating a systemic bloodborne fungal infection. 26. Which antifungal would the nurse explain works by inhibiting glucan synthesis A) Flucytosine B) Terbinafine C) Micafungin D) Ketoconazole Ans: C Feedback: The antifungal medications called echinocandins work by inhibiting glucan synthesis and micafungin is one of the drugs in this classification. Flucytosine is a miscellaneous antifungal agent, whereas terbinafine and ketoconazole are topical agents. 27. What antifungal would be appropriate for the nurse to administer to treat a patient with an oropharyngeal candidiasis? A) Itraconazole B) Fluconazole C) Posaconazole Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) D) Clotrimazole Ans: D 184 Feedback: Clotrimazole is an effective treatment for oropharyngeal candidiasis (in troche form) or to prevent oropharyngeal candidiasis in patients receiving radiation or chemotherapy. Itraconazole, fluconazole, and posaconazole would not be appropriate for this patient because they do not treat oropharyngeal candidiasis infections. 28. What drug would the nurse recognize as contraindicated for pediatric use? A) Fluconazole B) Terbinafine C) Griseofulvin D) Flucytosine Ans: D Feedback: Flucytosine does not have proven safety and efficacy in children, and extreme caution should be exercised if it is ordered. Fluconazole, terbinafine, and griseofulvin have established pediatric doses and would be drugs of choice if appropriate for a particular infection. 29. When caring for a 92-year-old patient, the nurse would anticipate the need for what interventions related to administration of any antifungal medications? (Select all that apply.) A) Dose reduction B) Frequent monitoring C) Frequent testing of liver function D) Shorter course of treatment E) Continuous cardiorespiratory monitoring Ans: A, B, C Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 185 Feedback: Patients over age 85 are at increased risk for some liver dysfunction and require more careful monitoring, lower dosages, and frequent assessment of liver function studies. Course of treatment should not be shortened, but dosage should be reduced. Continuous cardiorespiratory monitoring is not indicated. 30. A 15-year-old patient is immunocompromised because of the adverse effects of chemotherapy. He or she has developed severe migraine headaches and is being treated with ergot. What drug would be contraindicated in this patient? A) Caspofungin B) Ketoconazole C) Posaconazole D) Terbinafine Ans: C Feedback: Patients being treated with voriconazole or posaconazole should be cautioned about the risk of ergotism if they combine this drug with ergot, an herb frequently used to treat migraine headache and menstrual problems. If the patient is using voriconazole, it should be suggested that ergot not be used until the antifungal therapy is finished. The other options do not have a known drug interaction with ergot. 31. The nurse is reading the patient’s medical record and discovers the patient has a mycosis and interprets this as meaning what? A) An infection caused by a fungus B) A fungus normally found on mucous membranes C) A systemic fungal infection D) A fungal infection with a secondary bacterial infection Ans: A Feedback: A mycosis is simply a fungal infection. It does not give any indication of type or where it is found and has nothing to do with a bacterial infection. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 32. 186 The nurse admits a patient suspected of having a fungal infection. What action will the nurse need to take before a systemic antifungal can be prescribed? (Select all that apply.) A) Initiate IV therapy. B) Assess history of liver or kidney disease. C) Obtain a culture of the fungus. D) Request the patient sign a consent form. E) Assess history of lymphatic disease. Ans: B, C Feedback: The nurse would assess the patient for history of liver or kidney disease because systemic antifungals carry a higher risk of adverse effects and toxicity in patients with disease of these organs. A culture to determine the type of fungus should also be performed to increase the likelihood of the correct medication being prescribed. Not all antifungals are administered IV so this may not be necessary and would not be initiated until a drug was prescribed. A consent form is not needed by most facilities. History of lymphatic disease would not be associated with concern related to antifungal medications. 33. The patient is admitted for IV administration of antifungal medication with the plan to discharge the patient on oral medication in a few days. What medication would the nurse be able to administer both IV and orally? A) Fluconazole B) Itraconazole C) Posaconazole D) Terbinafine Ans: A Feedback: Fluconazole and voriconazole are available in oral and IV preparations, making it possible to start the drug IV for a serious infection and then switch to an oral form when the patient’s condition improves and he or she is able to take oral medications. Itraconazole, posaconazole, and terbinafine are administered only orally. 34. The nurse admits a patient diagnosed with diabetes who has been undergoing fertility treatment in the Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 187 hopes of becoming pregnant but is not pregnant at this time. The patient has a life-threatening fungal infection and requires systemic antifungal therapy. What medication would be contraindicated in this patient? A) Ketoconazole B) Fluconazole C) Posaconazole D) Itraconazole Ans: A Feedback: Ketoconazole is not the drug of choice for patients with endocrine or fertility problems because of its effects on these processes. It is not known whether posaconazole crosses the placenta or enters breast milk, so it should not be used during pregnancy or lactation unless the benefits clearly outweigh the potential risks but has no risk to those with fertility or endocrine problems. Fluconazole and itraconazole would be safe for this patient. 35. The nurse is assessing the patient’s medication history and learns the patient received a prescription for voriconazole from one provider and a prescription for an ergot alkaloid from another provider. The nurse realizes this patient is at risk for, and needs to be assessed for, what condition? A) Liver toxicity B) Central nervous system (CNS) depression C) Ergotism D) Renal toxicity Ans: C Feedback: This patient is at risk for ergotism and would require an electrocardiographic or rhythm strip to assess the QT interval because ergotism manifests with prolonged QT intervals. The drug combination does not contribute to hepatic or renal toxicity or depression of the central nervous system. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 188 Chapter 12 - Antiprotozoal Agents 1. The patient is having an acute malarial attack with chills and fever. The nurse knows chills and fever are caused by what? A) Formation of sporozoites into the system B) Rupture of red blood cells due to invasion of merozoites C) Invasion of the tsetse fly into the central nervous system D) Release of amastigotes into the blood vessels Ans: B Feedback: The chills and fever associated with an acute malarial attack are caused by the rupture of red blood cells containing merozoites. These symptoms are related to the pyrogenic effects of the protozoa and the toxic effects of the red blood cell components on the system. The formation of sporozoites occurs in the stomach of the mosquito when the male and female gametocytes mate and produce a zygote. Invasion of the tsetse fly causes trypanosomiasis, which affects the central nervous system. The release of amastigotes occurs in leishmaniasis, which is caused by the sand fly and is part of a cyclic pattern that causes serious skin lesions. 2. The nurse is caring for a patient of Greek descent who plans to travel to an area of the world in which malaria is endemic. What should this patient be tested for before administering antimalarial medications? A) Tay-Sachs disease B) Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency C) Plasmodium D) Penicillin allergy Ans: B Feedback: Patients of Mediterranean descent, including Greeks, are more likely to have a G6PD deficiency. When patients with this deficiency take primaquine, chloroquine, or quinine, an acute hemolytic crisis may occur. Patients of Mediterranean descent should be tested for G6PD deficiency before any antimalarial Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 189 drugs are prescribed. Tay-Sachs disease is a disorder seen in those of middle-eastern descent that causes death of the child by age 5. Plasmodium is the genus strain that causes malaria. Penicillin allergy has no connection to this situation. 3. The nurse is caring for a patient who is being treated with quinine (Qualaquin) for drug-resistant malaria. The nurse will monitor the patient for cinchonism that will present with what manifestations? A) Diarrhea, nausea, and fever B) Yellowing of the sclera and skin C) Tremors and ataxia D) Vomiting, tinnitus, and vertigo Ans: D Feedback: Patients with cinchonism or quinine toxicity may complain of tinnitus, headache, dizziness, nausea, fever, tremors, and visual disturbances. Diarrhea, yellowing of the sclera or skin, and ataxia are not associated with cinchonism. 4. Patients receiving chloroquine (Aralen Phosphate) for malaria prophylaxis should receive patient teaching from the nurse, which includes instructions to receive what regularly? A) Cardiovascular studies B) Eye exams C) Immunizations D) Pulmonary studies Ans: B Feedback: Chloroquine is associated with visual disturbances and a patient receiving this drug should receive regular ophthalmic exams. Heart and lung toxicity is not associated with chloroquine use. Immunizations are not associated with chloroquine use. 5. A 28-year-old woman is planning to be part of a mission team going to Central Africa. She will take mefloquine (Lariam) once a week, beginning 1 week before traveling to Africa until 4 weeks after leaving Africa. What precaution will the nurse teach this patient is needed? Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) A) Avoid excessive weight gain. B) Have regular cancer screening. C) Use contraceptives to avoid pregnancy. D) Stop the medication if diabetes is diagnosed. Ans: C 190 Feedback: Mefloquine is teratogenic and should be avoided during pregnancy. The nurse will want to determine whether a possibility exists that the patient is pregnant and warn about the need to avoid pregnancy for 2 months after completing therapy. Avoiding weight gain and having regular cancer screenings are good preventive care but not associated with mefloquine. This medication is not contraindicated in patients with diabetes. 6. The nurse is writing a plan of care for a patient receiving antimalarial drug therapy. What nursing diagnosis would be appropriate for this patient if common adverse effects were indicated? A) Disturbed sensory perception (visual) related to central nervous system effects B) Imbalanced nutrition: more than body requirements C) Constipation D) Ineffective breathing pattern Ans: A Feedback: Visual disturbances, including blindness related to retinal damage from the drug, may occur. Patients usually have gastrointestinal (GI) upset including diarrhea, not constipation, which could produce loss of weight and not an increase. Respiratory disturbances are not associated with antimalarial agents. 7. During a lecture on intestinal parasites, the students learn that what is the most commonly diagnosed intestinal parasite infection in the United States? A) Amebiasis B) Giardiasis C) Leishmaniasis Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) D) Trichomoniasis Ans: B 191 Feedback: The most commonly diagnosed intestinal parasite in the United States is Giardiasis. It is transmitted through contaminated water or food. Amebiasis is found in the United States but is not the most common. Leishmaniasis is transmitted through sand flies, which are not common in the United States. Trichomoniasis is a flagellated protozoan and most often is seen in the vagina and is spread during sexual intercourse by men who have no signs and symptoms of infection, it is not the most commonly diagnosed. 8. A patient has been diagnosed with trichomoniasis. Before beginning tinidazole (Tindamax) therapy, what should the nurse question the patient about? A) Working conditions B) Use of alcohol C) Recent visit to a beach or desert D) Possibly having AIDS Ans: B Feedback: Tinidazole is prescribed for trichomoniasis, which is transmitted during sexual intercourse. The drug should not be used when there is a history of alcohol use. Alcohol use could interfere with the drug’s metabolism in the liver and cause toxicity and patients should be warned to avoid consuming all alcoholic beverages while taking this medication. There is no need to question about working conditions unless transmission involved environmental contamination of food and water, which is not indicated by the question. A recent visit to a beach or desert would be indicated if the patient was diagnosed with leishmaniasis and questioning the patient concerning AIDS would be indicated if the patient had a diagnosis of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia and would not involve trichomonas. 9. The nurse is caring for a patient with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) who has been diagnosed with Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia. The patient is taking multiple oral agents to treat AIDS. What would be the drug of choice for this patient? A) Nitazoxanide (Alinia) B) Chloroquine C) Metronidazole Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) D) Pentamidine Ans: D 192 Feedback: Pentamidine is available as an inhalation product for the direct treatment of P. jiroveci in patients with AIDS. Because the patient is already taking multiple oral drugs, inhaler administration would be the best choice. Nitazoxanide, chloroquine, and metronidazole are not effective against P. jiroveci pneumonia. 10. A patient with giardiasis is being treated with metronidazole. What comment by the patient would indicate that the nurse needs to provide further teaching? A) I can continue to work delivering pizza because the disease is not contagious. B) I will not lose my hair during drug therapy. C) I know I will experience diarrhea during this time. D) I shouldn’t experience irregular menstrual periods. Ans: A Feedback: Although giardiasis is not contagious, the patient should be encouraged not to drive or operate heavy equipment until the effects of the drug can be assessed because metronidazole can lead to central nervous system adverse effects, including dizziness and lack of coordination. The drug may also cause diarrhea. Loss of hair and irregular menstrual periods are not associated with this drug, so these statements would be correct and would not indicate the need for further teaching. 11. During treatment of amebiasis with chloroquine (Aralen Phosphate), the nurse assesses the patient for what adverse effects? A) Diarrhea B) Weight gain C) Hypertension D) Seizures Ans: A Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 193 Feedback: With amebicides, observe for anorexia, nausea, vomiting, epigastric burning, and diarrhea that can lead to malnutrition and significant weight loss, which the nurse assesses for with each visit to intervene before significant malnutrition occurs. Weight gain, hypertension, or seizures are not associated adverse effects. 12. The clinic nurse provides teaching for a patient prescribed pyrimethamine (Daraprim) to prevent malaria and instructs on the need to notify the prescriber immediately if what signs and symptoms occur? A) Diarrhea, fatigue, weight loss, and anemia B) Irritation, rash, or inflammation C) Headache, nausea, or constipation D) Anorexia, nausea, or vomiting Ans: A Feedback: If signs of folate deficiency develop, pyrimethamine will need to be discontinued so the prescriber needs to be notified immediately. Folate deficiency presents with diarrhea, fatigue, weight loss, and anemia. The other signs and symptoms would need to be reported if significant and/or long-lasting. 13. The mother of a 6-month-old infant comes to the clinic. The mother is diagnosed with a protozoal infection. What would be a priority for the nurse to assess for? A) Whether she is breast-feeding B) Whether she has a support network C) Whether she has money to pay for the medication D) Whether she eats a protein-rich diet Ans: A Feedback: Assess for lactation because antiprotozoal drugs could enter the breast milk and be toxic to the infant. The other options are part of a complete nursing history but do not specifically relate to treatment for a protozoal infection. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 14. 194 A patient is prescribed mefloquine (Lariam) for malaria prophylaxis. When should the nurse instruct mefloquine be started? A) 1 week prior to entering an endemic area B) 1 to 2 days prior to entering an endemic area C) On arrival to an endemic area D) When mosquitoes are present Ans: A Feedback: Lariam should be taken 1 week prior to entering a malarial area. Therefore, options B, C, and D are incorrect. 15. What statements made by the 36-year-old patient leads the nurse to believe that he or she has understood the teaching regarding metronidazole (Flagyl)? A) I will refrain from operating heavy machinery while I am taking this medication. B) I will avoid foods high in vitamin C. C) I will not drink alcohol while I am taking this medication. D) I will contact my physician if I have a cold. Ans: C Feedback: Patients should avoid all forms of alcohol while taking metronidazole. Patients do not need to avoid operating heavy machinery,and foods high in vitamin C, and will not contact the physician if they have colds. 16. The emergency room nurse admits a patient suspected of having giardiasis. What symptoms would the nurse expect the patient to present with? A) Voluminous soft unformed stool B) Frothy voluminous pale stool Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) C) Pale and mucous-filled stool D) Frothy tan stool Ans: C 195 Feedback: Diarrhea, rotten-egg-smelling stool, and pale and mucous-filled stool are commonly seen. Diarrhea is often accompanied by epigastric distress, weight loss, and malnutrition as a result of the invasion of the mucosa. Therefore, options A, B, and D are incorrect. 17. A 91-year-old man is being treated for Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia with pentamidine (NebuPent). What should the nurse measure when assessing this patient for adverse effects of the medication? A) Liver function tests B) Serum potassium C) Daily blood pressure D) Blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and creatinine Ans: A Feedback: Patients receiving antiprotozoal agents should be monitored regularly to detect any serious adverse effects. Liver function tests are of particular importance to determine the appropriateness of therapy and to monitor for toxicity. Serum potassium, BUN, and creatinine would indicate kidney damage, which is not normally a risk with this drug. Blood pressure is not indicated for this medication but is an early indicator of health deterioration and is usually included in all provisions of care. 18. What is the priority teaching point to be provided by the nurse to a patient being treated for trichomoniasis to prevent reinfection? A) Meats should be fully cooked before eaten. B) Sexual partners should be treated. C) Wash hands before eating. D) Purify all drinking water when camping. Ans: B Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 196 Feedback: Trichomoniasis is usually spread during sexual intercourse and men often have no symptoms. Women present with red, inflamed vaginal mucosa, itching, burning, and a yellowish green discharge. Women should be taught the importance of having their partners tested and treated simultaneously to prevent reinfection. The other options are healthy lifestyle choices but are not the primary means of preventing reinfection. 19. How does the nurse teach the patient to take chloroquine (Aralen Phosphate)? A) On an empty stomach B) With 8 ounces of water C) With meals D) With orange juice followed by 8 ounces of water Ans: C Feedback: Chloroquine should be taken with meals to reduce gastrointestinal (GI) upset; small frequent meals may also reduce negative GI effects. Taking medications, any medication, with adequate amounts of water is always good practice but not specific to this medication. There is no indication that ingestion of orange juice makes any practical difference. 20. The nurse, learning about malaria, discovers that the transmission of malaria occurs when what is injected into the human body by the infected mosquito? A) Sporozoites B) Gametocytes C) Schizonts D) Merozoites Ans: A Feedback: Gametocytes are sucked with the blood from an infected person by the mosquito. The gametocytes mate in the stomach of the mosquito and produce a zygote that goes through several phases before forming sporozoites (spore animals) that make their way to the mosquito’s salivary glands. The next Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 197 person who is bitten by that mosquito is injected with thousands of sporozoites. Schizonts are the primary tissue organisms resulting from asexual cell division and reproduction after the sporozoites are introduced into the body. Merozoites are then formed from the primary schizonts. 21. The nurse is caring for a patient who is taking antimalarial medications. The nurse teaches the patient about the medication and explains the need to report what signs and symptoms immediately because of its association with a serious adverse effect? A) Loss of appetite B) Loss of hair C) Loss of vision D) Loss of sensation Ans: C Feedback: Report blurring of vision, which could indicate retinal damage; loss of hearing or ringing in the ears, which could indicate central nervous system toxicity; and fever or worsening of condition, which could indicate a drug-resistant strain or noneffective therapy. Loss of appetite is such a common result of the gastrointestinal (GI) effects of the drug that the nurse should provide anticipatory guidance to teach the patient how to maintain adequate nutrition, but the patient does not need to report this unless it becomes serious or unmanageable. Loss of sensation is not a typical adverse effect the nurse would anticipate and teach about. 22. The nurse is caring for a patient who just returned from a trip to South America and was infected by the protozoan Trypanosoma cruzi. What will the nurse assess for in this patient? A) Serious lesions in the skin B) Sleeping sickness C) Severe cardiomyopathy D) Yellowish green vaginal discharge Ans: C Feedback: Chagas’ disease, which is caused by T. cruzi, is passed to humans by the common house fly. This protozoan results in a severe cardiomyopathy that accounts for numerous deaths and disabilities in certain regions. Sleeping sickness results from T. brucei gambiense; leishmaniasis produces serious lesions in the skin, and trichomoniasis produces a yellowish green discharge. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 23. 198 A patient with malaria is taking primaquine. What would indicate to the nurse caring for this patient that the patient has cinchonism? A) Diarrhea B) Abdominal cramping C) Tan, frothy stool D) Vertigo Ans: D Feedback: Cinchonism (nausea, vomiting, tinnitus, and vertigo) may occur with high levels of primaquine. Symptoms of cinchonism do not include diarrhea, abdominal cramping, or tan, frothy stool. 24. A patient has been prescribed an antimalarial as prophylaxis for the disease. What assessment finding would the nurse recognize as indicating the patient has a common adverse effect? A) Dyspepsia B) Hematemesis C) Tarry stool D) Tachycardia Ans: A Feedback: Nausea, vomiting, dyspepsia, and anorexia are associated with direct effects of the antimalarial medications on the GI tract and the effects on central nervous system control of vomiting caused by the products of cell death and protein changes. Adverse effects from antimalarial drugs do not usually include hematemesis, tarry stool, or tachycardia. 25. A patient presents at the emergency department complaining of sudden onset of high fever and swelling and reddening of the limbs. Assessment shows severe hypotension. The nurse taking the patient’s history notes that the patient has recently returned to the United States from the African continent. The patient is admitted to the intensive care unit (ICU) suspected of having malaria caused by what protozoan? Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) A) Plasmodium ovale B) Plasmodium falciparum C) Plasmodium vivax D) Plasmodium malariae Ans: B 199 Feedback: P. falciparum is considered to be the most dangerous type of protozoan. Infection with this protozoan results in an acute, rapidly fulminating form of the disease with high fever, severe hypotension, swelling and reddening of the limbs, loss of red blood cells, and even death. The other options are pathogens that cause milder forms of the disease and P. ovale is rarely encountered. 26. Pyrimethamine (Daraprim) has been ordered for the patient as prophylactic treatment of malaria. The nurse recognizes the action of this drug prevents relapse of the disease by acting on what? A) Changing the metabolic pathways for reproduction B) Disrupting the mitochondria of the plasmodium C) Blocking the use of folic acid D) Increasing the acidity of plasmodial food vacuoles Ans: C Feedback: Pyrimethamine is used in combination with agents that act more rapidly to suppress malaria; it acts by blockings the use of folic acid in protein synthesis by the plasmodium, eventually leading to inability to reproduce and cell death. Chloroquine changes the metabolic pathways for reproduction of the plasmodium and is toxic to parasites that absorb it. Primaquine disrupts the mitochondria of the plasmodium. Mefloquine increases the acidity of plasmodial food vacuoles causing cell rupture and death. 27. A patient, recently returned from a vacation in the tropics, is diagnosed with leishmaniasis. The patient asks the nurse how he or shes got this disease. What is the nurse’s best response? A) You got this disease from a mosquito bite. B) You got this disease from unsanitary drinking water. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) C) You got this disease from eating unsanitary food. D) You got this disease from the bites of sand flies. Ans: D 200 Feedback: Leishmaniasis is a disease caused by a protozoan that is passed from sand flies to humans. Therefore, options A, C, and D are incorrect. 28. The patient, newly diagnosed with African sleeping sickness, asked what caused the disease. What is the nurse’s best response? A) Trypanosoma brucei gambiense B) Giardia lamblia C) Promastigote D) Trypanosoma cruzi Ans: A Feedback: African sleeping sickness, which is caused by Trypanosoma brucei gambiense, is transmitted by the tsetse fly. After the pathogenic organism has lived and grown in human blood, it eventually invades the central nervous system, leading to acute inflammation resulting in lethargy, prolonged sleep, and even death. G. lamblia causes giardiasis; T. cruzi causes Chagas’ disease. A promastigote is a flagellated protozoan that causes leishmaniasis. 29. The patient, a physician returning from a trip to the tropics, is prescribed chloroquine and asks the nurse how it works. What is the nurse’s best response? A) Blocks the plasmodium’s ability to synthesize ribonucleic acid B) Changes the metabolic pathways necessary for the reproduction of the plasmodium C) Interrupts the cell wall preventing entry of nutrients into the plasmodium D) It is alkaline and decreases the ability of the parasite to synthesize deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). Ans: B Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 201 Feedback: Chloroquine is currently the mainstay of antimalarial therapy. This drug enters human red blood cells and changes the metabolic pathways necessary for the reproduction of the plasmodium (see Figure 12.1). In addition, this agent is directly toxic to parasites that absorb it, it is acidic, and it decreases the ability of the parasite to synthesize DNA, leading to a blockage of reproduction. 30. What antimalarial medication is used as a radical cure of Plasmodium vivax malaria? A) Chloroquine B) Mefloquine C) Pyrimethamine D) Primaquine Ans: D Feedback: Primaquine (generic) is the only drug indicated for the prevention of relapses of P. vivax and P. malariae infections and a radical cure of P. vivax malaria. It may be given in combination with other drugs that interrupt the cell cycle at other stages. None of the other options are indicated for this use. 31. The nurse, working in a pediatric clinic, admits a patient who will be traveling to a country where malaria is endemic. What is the safest treatment for this child? A) No prophylaxis is administered because of the severity of adverse effects. B) Call the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) or local health department for the safest possible treatment. C) Administer extremely small doses of chloroquine. D) Any antimalarials in appropriate dosages can be administered. Ans: B Feedback: Although dosages for prophylaxis have been calculated to treat malaria in children, many drugs have not been proven to be safe and efficient in that population and extreme caution is needed .If a child needs to travel to an area with endemic protozoal infections, the CDC or local health department should be consulted about the safest possible preventive measures. As a result, the other options are incorrect. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 32. 202 What statement, if made by the nurse, would be correct? A) Malaria can live without a host and be contracted from drinking standing water. B) Any mosquito can carry the plasmodium that transmits malaria. C) A major problem with controlling malaria is the mosquito that is resistant to insecticide. D) Widespread efforts at mosquito control have never been helpful. Ans: C Feedback: Widespread efforts at mosquito control have been successful, with fewer cases of malaria being reported each year. However, the rise of insecticide-resistant mosquitoes has allowed malaria to continue to flourish, increasing the incidence of the disease. Malaria requires a host to live, whether it is human or mosquito. Only the female Anopheles mosquito harbors the protozoal parasite and carries it to humans. 33. The nurse is caring for a patient diagnosed with amebiasis caused by Entamoeba histolytica that resulted in the patient having amebic dysentery. What questions might the nurse ask in an attempt to discover how the patient came in contact with the organism? (Select all that apply.) A) Have you traveled outside the country recently? B) Have you been swimming in a lake or pond recently? C) Have you been eating fresh fruits or vegetables without washing them first? D) Have you been bitten by a mosquito? E) Have you had unprotected sex recently? Ans: A, B, C Feedback: The disease is transmitted while the protozoan is in the cystic stage in fecal matter, from which it can enter water and soil. It can be passed to other humans who drink this water or eat food that has been grown in this ground. It is not passed by a mosquito or from sexual activity. 34. The nurse explains that the drugs metronidazole (Flagyl) or tinidazole (Tindamax) can be administered to treat what protozoan infections? (Select all that apply.) Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) A) Trichomoniasis B) Giardiasis C) Amebiasis D) Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia E) Cryptosporidium parvum Ans: A, B, C 203 Feedback: Metronidazole or tinidazole are effective treatments for trichomoniasis, giardiasis, and amebiasis. They are not effective for P carinii pneumonia or C. parvum. 35. How does the nurse adapt the plan of care when caring for an older adult receiving an antiprotozoal agent? A) Patients should be monitored more closely for toxic adverse effects. B) The drug dosage should be lowered for all older adults. C) Antiprotozoal agents should not be administered to older adults. D) Female patients of appropriate age should be advised to use barrier contraceptives. Ans: A Feedback: Older patients may be more susceptible to the adverse effects associated with these drugs. They should be monitored closely. Dosage should only be lowered if the patient has hepatic dysfunction or if hepatic dysfunction is anticipated. Antiprotozoal agents can be administered to older adults with caution when the benefit outweighs the risk. It is not necessary for older adult women to use barrier methods of contraceptives because they are no longer of childbearing age. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 204 Chapter 13 - Anthelmintic Agents 1. A public health nurse is speaking to parents of first graders. When discussing worm infection, the nurse will explain that the most common type found in U.S. school-aged children is what? A) Pinworms B) Roundworms C) Threadworms D) Whipworms Ans: A Feedback: The most common worm infection encountered in U.S. school-aged children is pinworms. These worms are endogenous to the area and easily spread. Roundworms, whipworms, and threadworms are not as common. 2. A mother of a 3-year-old child brings her child to the clinic. The child is diagnosed with pinworms. What drug would be the best choice for the patient? A) Pyrantel (Pin-Rid) B) Ivermectin (Stromectol) C) Mebendazole (Vermox) D) Albendazole (Albenza) Ans: C Feedback: Mebendazole is the most commonly used anthelmintic for pinworms because it is available in a chewable tablet. This is a good choice for the 3-year-old patient. Pyrantel is also prescribed for pinworms but is not available in a chewable form. Ivermectin is prescribed for treatment of threadworm disease and albendazole is given to treat active lesions caused by pork tapeworm and cystic disease of the liver, lungs, and peritoneum caused by dog tapeworm. 3. A nurse is teaching a young mother about administering pyrantel (Pin-Rid, others) to her 5-year-old child. What will the nurse emphasize about how the agent is given? Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) A) In 3 doses as a 1-day treatment B) In a morning dose and an evening dose for 3 days C) B.I.D. for 10 days D) Give only once Ans: D 205 Feedback: Pyrantel is administered orally as a single dose. Albendazole is prescribed for hydatid disease and is given twice a day for 8 to 30 days of treatment. Mebendazole is used in the treatment of diseases caused by pinworms, roundworms, whipworms, and hookworms and is given in a morning and evening dose for 3 days. Praziquantel is used to treat schistosomes and is taken in three doses as a 1-day treatment. 4. A patient has been diagnosed with roundworms and is to be treated with albendazole. A priority nursing assessment of this patient would be to determine if the patient is taking what? A) Cimetidine (Tagamet) B) Pioglitazone (Actos) C) Alprazolam (Xanax) D) Loperamide (Imodium) Ans: A Feedback: The adverse effects of albendazole, which are already severe, may increase if the drug is combined with dexamethasone, praziquantel, or cimetidine. These combinations should be avoided if at all possible; if they are necessary, patients should be monitored closely for the occurrence of adverse effects. Pioglitazone is an oral antidiabetic agent that could be taken with albendazole. Loperamide is an antidiarrheal drug that may be used for treatment of diarrhea as a result of the mebendazole and pyrantel. Alprazolam should not be a concern. 5. A) What would be a priority nursing action related to the care of a patient taking albendazole (Albenza)? Check blood pressure, pulse, and respirations Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) B) Weigh the patient C) Monitor renal function D) Encourage small, frequent meals Ans: C 206 Feedback: It is important that the patient’s kidney function be monitored because a serious adverse effect of this drug is renal failure. Even though vital signs, weight, and nutrition are important and should be monitored, if the patient exhibits any signs of renal failure the drug should be stopped immediately. 6. The nurse is caring for an adult patient receiving a prescription for an anthelmintic drug. What is a possible nursing diagnosis for this patient? A) Constipation B) Disturbed body image C) Acute confusion D) Imbalanced nutrition: More than body requirements Ans: B Feedback: A potential nursing diagnosis for the patient would be disturbed body image related to diagnosis and treatment. There is a stigma associated with having helminthic infections. Treatment can cause diarrhea, loss of hair, and pruritus, which could be noticed by others and further impact the patient’s body image. Usually these drugs do not cause constipation; they have not been linked to confusion. 7. A nurse is teaching a patient who has been diagnosed with trichinosis. The nurse will include in the discussion that trichinosis is caused by roundworms having what effect? A) Disruption of the host’s normal cellular functions causing cell death and resulting in disease B) Invasion of body tissues seriously damages lymphatic tissue, lungs, the central nervous system, heart, and liver C) Exposure to the delicate mucous membranes of the anus and colon producing local irritation D) Easily passed from one individual to another resulting in rapid spreading within a work place Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) Ans: 207 B Feedback: Trichinosis is a disease caused by the ingestion of the encysted larvae of the roundworm from undercooked pork. These worms exist outside the intestinal tract and can seriously damage the tissues they invade. The worms do not spread rapidly through a large group of people unless they have all eaten the undercooked pork. They do not enter cells to alter human cellular function. 8. When instructing a patient about the therapeutic effectiveness of an anthelmintic drug, the nurse would be sure to include what? A) Any person exposed to the patient should also be treated. B) The drugs should never be taken with food. C) The infected person should be isolated. D) Strict hygiene measures are important in eradicating the worm. Ans: D Feedback: When treating a patient with an anthelmintic drug, the patient should be instructed to follow strict hand washing and hygiene measures as an adjunct in eradicating the worm. Isolation is not necessary and prophylactic treatment is not effective with worms. Anthelmintics are often taken with food to decrease the gastrointestinal (GI) adverse effects. 9. The nurse is caring for a patient diagnosed with hookworms. The patient is receiving mebendazole (Vermox). What would the nurse expect to see in this patient? A) Increased bilirubin B) Decreased hematocrit and hemoglobin C) Increased aspartate transaminase levels D) Decreased blood sugar Ans: B Feedback: Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 208 Hookworms can cause anemia and fluid and electrolyte imbalances because of the amount of blood that is sucked from the walls of the intestine. A decreased hematocrit and hemoglobin would indicate anemia and is often found in patients with hookworm. Bilirubin and aspartate transaminase indicate liver function. Because mebendazole is not absorbed systemically, adverse effects are limited to abdominal effects such as discomfort, diarrhea, or pain so this drug would not impact bilirubin or aspartate transaminase levels. Neither the disease nor drug should decrease blood sugar. 10. A patient is taking an anthelmintic that is absorbed systemically. What adverse effect should the nurse inform the patient might be experienced? A) Abdominal discomfort B) Diarrhea C) Loss of hair D) Pain Ans: C Feedback: Anthelmintics that are absorbed systemically could cause headache, dizziness, fever, shaking, chills, malaise, pruritus, and loss of hair. Mebendazole and pyrantel are anthelmintics that are not generally absorbed systemically and may cause abdominal discomfort, diarrhea, and pain. 11. A mother brings her child to the clinic where the child is diagnosed with hookworms. The mother asks how the child got hookworms. What would the nurse tell the mother is the route of entry for hookworm? A) Inhalation B) Contact with skin C) Ingestion of undercooked foods D) Blood-borne exposure Ans: B Feedback: The larvae penetrate the skin and then enter the blood and within about a week, reach the intestine. Inhalation, ingestion, and blood-borne exposure are incorrect. 12. A patient is diagnosed with an ascaris infection. The patient asks what the best way is to prevent ascaris Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 209 infections. What is the nurse’s best response? A) Wash hands before eating. B) Do not share hairbrushes or hats. C) Wash fresh fruits and vegetables before eating. D) Avoid heavily populated areas. Ans: C Feedback: Ascaris infection occurs where sanitation is poor. Eggs in the soil are ingested with vegetables or other improperly washed foods containing the worm. The patients may be unaware until a worm in their stool is seen or the patient becomes quite ill. Teaching patients the importance of washing fresh fruit and vegetables will help them reduce risk of infection. Washing hands, avoiding sharing hairbrushes or hats, and being aware in populated areas will reduce the risk of other infections but do not relate to ascaris. 13. What is an appropriate nursing diagnosis for a patient with tapeworm? A) Imbalanced nutrition: less than body requirements B) Chronic pain C) Constipation D) Impaired mobility Ans: A Feedback: Tapeworm affects the body’s ability to absorb food products and weight loss and malnutrition often follow unless treatment is received promptly. As a result, the best nursing diagnosis is imbalanced nutrition: less than body requirements. Patients with tapeworm are often symptom-free but may experience some abdominal discomfort and distention as well as weight loss so they do not have chronic pain, constipation, or impaired mobility. 14. A) Why is it important for a nurse to inquire about any foreign travel of a patient with a suspected lymphatic or hematologic disorder? To determine the varied sexual history of the patient, if any Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) B) To determine the potential exposure to infectious agents C) To determine whether the patient has had any blood transfusions D) To determine whether the patient adopted any specific dietary habits Ans: B 210 Feedback: Knowledge of recent travel can help the nurse to pinpoint potential exposure to helminths, parasites, or other infection exposure common in the area visited. The nurse should specifically ask about foreign travel to countries where malaria or parasitic roundworms are common. Sexual history, dietary habits, or any blood transfusions that the patient may have had before would not be adequately explored by questioning travel history. 15. What helmintic infestation occurs in tropical areas and is carried by snails? A) Schistosomiasis B) Platyhelminths C) Trichinosis D) Filariasis Ans: A Feedback: Schistosomiasis is a common problem in many tropical areas where the snail that is necessary in the life cycle of the fluke lives. Trichinosis is caused by eating undercooked pork and can occur in any part of the world. Filariasis and platyhelminths are not restricted to tropical areas. 16. The nursing instructor is discussing helmintic infections with the nursing students. How would the instructor explain the action of anthelmintic drugs? A) Destroy the nervous system of the invading worm B) Act on metabolic pathways that are present in the invading worm C) Interfere in the reproductive cycle of the invading worm D) Cause fatal mutations in the deoxyribonucleic acid of the invading worm Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) Ans: 211 B Feedback: The anthelmintic drugs act on metabolic pathways that are present in the invading worm, but that are absent or significantly different in the human host. Other options are incorrect descriptions of how anthelmintic drugs work. 17. What anthelmintics would the nurse expect will be readily absorbed from the gastrointestinal (GI) tract? (Select all that apply.) A) Mebendazole B) Pyrantel C) Albendazole D) Praziquantel E) Ivermectin Ans: D, E Feedback: Praziquantel and ivermectin are readily absorbed from the GI tract. Mebendazole, pyrantel, and albendazole are not. 18. A mother brings her 18-month-old son into the clinic. The child is diagnosed with pinworms. Which anthelmintic would the nurse expect to be prescribed? A) Pyrantel B) Mebendazole C) Ivermectin D) Praziquantel Ans: B Feedback: Mebendazole is available in the form of a chewable tablet that would be preferable for a young child. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 212 Because little of the drug is absorbed systemically, it is safe for children and has few adverse effects, thus making it safer to administer to a child. Pyrantel is not approved for children younger than 2 years old. Ivermectin and praziquantel effects are systemic and would a greater number of adverse effects. 19. The nurse is caring for a 26-year-old patient diagnosed with roundworms who is prescribed pyrantel. What adverse effect would the nurse teach the patient about? A) Vomiting B) Itching C) Diarrhea D) Constipation Ans: C Feedback: Mebendazole and pyrantel, which are not absorbed systemically, may cause abdominal discomfort, diarrhea, or pain, but have very few other effects and are well-tolerated. Therefore options A, B, and D are incorrect. 20. The nurse is caring for a patient taking albendazole. When reviewing the patient’s medication history what drug would cause the nurse to question administering albendazole? A) Propranolol B) Fexofenadine C) Furosemide D) Dexamethasone Ans: D Feedback: The effects of albendazole, which are already severe, may increase if the drug is combined with dexamethasone, praziquantel, or cimetidine. These combinations should be avoided if at all possible; if they are necessary, patients should be monitored closely for occurrence of adverse effects. No contraindications are noted for propranolol, fexofenadine, or furosemide. 21. Why is a filariae infestation potentially fatal? Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) A) Worm-like embryos overwhelm the lymphatic system B) Worm-like embryos invade the central nervous system (CNS) C) Worm-like embryos destroy the gastric mucosa D) Worm-like embryos hibernate in the brain Ans: A 213 Feedback: Filariasis refers to infection of the blood and tissues of healthy individuals by worm embryos, which enter the body via insect bites. These thread-like embryos, or filariae, can overwhelm the lymphatic system and cause massive inflammatory reactions. While any system can be impacted due to the effect on the blood and lymphatic system, the filariae do not invade the CNS, gastric mucosa, or the brain specifically. 22. The nurse is caring for a patient diagnosed with threadworm infestation. What is the nurse’s priority assessment related to common manifestations of this infestation? A) Gastroenteritis B) Pneumonia C) Hematuria D) Tarry stools Ans: B Feedback: Threadworm is a pervasive nematode that can send larvae into the lungs, liver, and central nervous system and can cause severe pneumonia or liver abscess. Threadworms do not cause gastroenteritis, hematuria, or tarry stools. 23. What infestation would the nurse suspect when the patient manifests with intestinal obstruction caused by the adult worms clogging the lumen of the intestine? A) Platyhelminth B) Trichinosis C) Nematode Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) D) Cestode Ans: C 214 Feedback: Nematode are roundworms such as the commonly encountered pinworm, whipworm, threadworm, Ascaris, or hookworm that cause a common helminthic infection in humans and can cause intestinal obstruction as the adult worms clog the intestinal lumen or severe pneumonia when the larvae migrate to the lungs and form a pulmonary infiltrate. Options A, B, and D are incorrect. 24. The nurse is caring for a 17-year-old girl who has just been diagnosed with a tapeworm. What is a priority nursing action for this patient? A) Monitor hepatic and renal function before and periodically during treatment. B) Provide small, frequent, nutritious meals if GI upset is severe. C) Instruct the patient about the appropriate dosage regimen. D) Offer support and encouragement. Ans: D Feedback: Frequently, patients have a very difficult time dealing with a diagnosis of worm infestation. It is very important for the nurse to understand the disease process and to explain the disease and treatment carefully to help the patient to cope with both the diagnosis and the treatment. Options A, B, and C are correct nursing interventions for this patient, but they are not the priority nursing intervention. 25. The nurse is counseling a patient who has been prescribed mebendazole for a worm infestation. What adverse effects would the nurse caution this patient about? A) Fever B) Constipation C) Nausea D) Hematuria Ans: A Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 215 Feedback: Mebendazole is not absorbed systemically so it has few adverse effects. Adverse effects include transient abdominal pain, diarrhea, and fever. Adverse effects do not include constipation, nausea, or hematuria. 26. When teaching a class of her peers about use of the drug ivermectin, what would the nurse say is the primary route of excretion? A) Urine B) Feces C) Sweat D) Both urine and feces Ans: B Feedback: Ivermectin is readily absorbed from the gastrointestinal (GI) tract and reaches peak plasma levels in 4 hours. It is completely metabolized in the liver with a half-life of 16 hours and excretion is fecal. Options A, C, and D are incorrect. 27. Which anthelmintic medication is poorly absorbed from the gastrointestinal (GI) tract and primarily excreted in the urine? A) Ivermectin B) Praziquantel C) Albendazole D) Mebendazole Ans: C Feedback: Albendazole is poorly absorbed from the GI tract, reaching peak plasma levels in about 5 hours. It is metabolized in the liver and primarily excreted in urine. Although praziquantel is excreted in the urine, it is rapidly absorbed from the GI tract. Mebendazole and ivermectin are excreted in feces. 28. The nurse is presenting at an educational event about pinworms at the local elementary school during Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 216 an outbreak of the infestation. What suggestion would the nurse give the attendees to prevent a recurrence of the infestation? A) Tell the children not to share combs and brushes. B) Tell the children not to drink out of other peoples drinks. C) Avoid pajamas in favor of night gowns. D) Shower the children every morning. Ans: D Feedback: Some suggested hygiene measures that might help to control the infection include the following: Keep the child’s nails cut short and hands well scrubbed, because reinfection results from the worm’s eggs being carried back to the mouth after becoming lodged under the fingernails when the child scratches the pruritic perianal area. Give the child a shower in the morning to wash away any ova deposited in the anal area during the night. Change and launder undergarments, bed linens, and pajamas every day. Open gowns, rather than pajamas with pants, would not be the best choice because this would allow for greater perianal scratching. 29. An adult presents at the clinic complaining of a cough, fever, abdominal distention, and pain. The patient is diagnosed with pneumonia and a helminth infection. What type of worm would the nurse suspect the patient has? A) Ascaris B) Platyhelminth C) Hookworm D) Schistosomiasis Ans: A Feedback: Ascaris manifestations include cough, fever, pulmonary infiltrates, abdominal distention, and pain. Platyhelminth is a flatworm that can live in the human intestine or can invade other human tissues causing malnutrition as the worm competes for the food eaten by the human. Hookworms attach to the small intestine leading to severe anemia, lethargy, fatigue, and weakness. Schistosomiasis presents with a rash and then symptoms of diarrhea and liver and brain inflammation. 30. A mother asks the nurse what to look for if her child has pinworms. What would be the nurse’s best response? Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) A) Hard stools full of worms B) Perianal itching C) Upset stomach D) Bloody diarrhea Ans: B 217 Feedback: Pinworms manifestation includes perianal itching, and occasionally, vaginal itching particularly at night when the pinworms are most active around the anal opening. Pinworms do not usually present in any other manner so the other options are incorrect. 31. A patient with hookworm infection states that he has a hard time following medication regimens. The nurse knows that what medication would be preferred for this patient? A) Pyrantel (Antiminth) B) Mebendazole (Vermox) C) Ivermectin (Stromectol) D) Albendazole (Albenza) Ans: A Feedback: Pyrantel can be administered as a single dose, which makes it a good choice for patients who have trouble remembering to take their medications, or have trouble following medication regimens. Mebendazole requires twice-daily dosing, which makes it less optimal for a patient who has trouble with medication regimens. Ivermectin is used to treat threadworm disease (strongyloidiasis) and river blindness (onchocerciasis). Albendazole is used to treat active lesions caused by pork tapeworm and cystic disease of the liver, lungs, and peritoneum caused by dog tapeworm. 32. What benefit would the nurse describe for treating pinworms and roundworms with a prescription for pyrantel instead of mebendazole? A) Pyrantel needs only be taken once. B) Mebendazole has many serious adverse effects. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) C) Pyrantel is excreted in the feces. D) Pyrantel is safer for children younger than 2 years. Ans: A 218 Feedback: Pyrantel’s big advantage is that it needs only be taken one time so it is a better choice for those who may not remember to take repeated doses. Mebendazole has very few side effects because very little of the medication is absorbed systemically so that is not a reason to prescribe pyrantel. Pyrantel is mostly excreted in the feces but some is also found in urine while mebendazole is only excreted in the feces so this does not benefit prescribing pyrantel. Pyrantel has not been established as safe for use in children under 2 years old. 33. What laboratory test will the nurse obtain to determine what type of helminth is infecting the patient? A) Stool culture B) Stool for ova and parasite C) Renal function studies D) Liver function studies Ans: B Feedback: The only test to specifically determine what helminth is involved is a stool culture for ova and parasite. A simple stool culture would not be likely to identify the helminth. Renal and liver function studies would indicate the functioning of these organ systems but would not identify the helminth. 34. What assessment findings would raise the nurse’s level of suspicion that the patient may be infected with cestodes? (Select all that apply.) A) Abdominal discomfort and distention B) Weight loss without dieting C) Pneumonia D) Heart failure Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) E) Encephalitis Ans: A, B 219 Feedback: Cestodes enter the body as larvae that are found in undercooked meat or fish; they sometimes form worms that are several yards long, people with a tapeworm may experience some abdominal discomfort and distention, as well as weight loss, because the worm eats ingested nutrients. Trichinosis can result in fatal pneumonia, heart failure, and encephalitis if not treated early, but these symptoms would not be expected with cestode infection. 35. The nurse is caring for an 85-year-old woman diagnosed with a roundworm infection in addition to heart disease, chronic renal failure, and history of a stroke. The patient is prescribed mebendazole. What assessments will be of particular importance for this patient related to drug therapy? (Select all that apply.) A) Hydration B) Nutritional status C) Liver function D) Cognitive function E) Respiratory function Ans: A, B, D Feedback: Mebendazole is a relatively safe drug with few adverse effects. However, infection by a helminth that impacts absorption of nutrients in a frail older woman could lead to significant dehydration and malnutrition so it would be of particular importance to assess this patient frequently and regularly. Respiratory function, liver function, and cognition would not be impacted by the helminth or the medication, but altered cognition could occur with malnutrition and/or dehydration. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 220 Chapter 14 - Antineoplastic Agents 1. The process of cancerous cells exhibiting a loss of cellular differentiation and organization leading to a loss of their ability to function normally is called what? A) Anaplasia B) Angiogenesis C) Autonomy D) Metastasis Ans: A Feedback: Cancerous cells exhibit anaplasia, which is a loss of cellular differentiation and organization that leads to a loss of their ability to function normally. Angiogenesis refers to the abnormal cells releasing enzymes that generate blood vessels in the area to supply both oxygen and nutrients to the cells. Cancerous cells exhibit autonomy, which is the ability to grow without the usual homeostatic restrictions that regulate cell growth and control. Metastasis is the process of the cancerous cells traveling from the place of origin to develop new tumors. 2. The mitotic inhibitors interfere with the ability of a cell to divide and they block or alter deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) synthesis, thus causing cell death. What is important for the nurse to remember when administering these drugs? A) The nurse should encourage the patient to eat six small meals a day. B) The nurse should avoid any skin, eye, or mucous membrane contact with the drug. C) The nurse should avoid using a distal vein. D) The nurse should check for extravasation when the infusion is over. Ans: B Feedback: Special care needs to be taken when administering these drugs. The nurse should avoid any skin, eye, or mucous membrane contact with the drug. This type of contact can cause serious reactions and toxicity for the nurse. The nurse should check for extravasation frequently during the infusion and not wait until the infusion is completed, a distal vein should be used, nausea and vomiting are commonly Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 221 experienced adverse effects of these drugs, and small meals may help the patient to maintain adequate nutrition but this is not the important concern when administering the drug. 3. A nurse is preparing an antineoplastic agent for a 9-year-old cancer patient. Before administering an antineoplastic agent, what is the nurse’s priority action? A) Wash his or her hands. B) Identify the child by checking the arm band and asking him or her to state his or her name. C) Ensure a quiet environment so the patient can sleep during administration of the drug. D) Check laboratory studies to determine most recent measures of bone marrow function. Ans: D Feedback: The most important action of the nurse before administering the drug would be to check indexes of bone marrow functioning because these results will help to determine the proper dosage. Smaller dosages are administered if bone marrow function declines, whereas larger dosages can be given if bone marrow function is good. Only after this is checked will the nurse begin the process of actually administering the medication by performing hand hygiene, identifying the patient, and creating a quiet environment. 4. A patient with leukemia receives rasburicase (Elitek) before administering chemotherapy. What is the nurse’s priority assessment after administration of this medication? A) Blood glucose levels B) Serum potassium levels C) Serum calcium levels D) Uric acid levels Ans: D Feedback: Rasburicase is approved for the management of plasma uric acid levels in patients with leukemia, lymphoma, and solid malignancies who are receiving antineoplastic therapy associated with tumor lysis and elevated serum uric acid levels. Uric acid levels should be analyzed within 4 hours of each dose of rasburicase. Blood glucose, potassium, and calcium levels should not be affected by administration of the drug. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 5. 222 The nurse is caring for a patient at risk of severe-to-fatal interstitial lung disease. What antineoplastic agent is the nurse administering that carries this risk? A) Valrubicin (Valstar) B) Erlotinib (Tarceva) C) Histrelin acetate (Vantas) D) Triptorelin pamoate (Trelstar Depot) Ans: B Feedback: Erlotinib inhibits tyrosine kinase associated with epidermal growth factor found on surfaces of normal and cancer cells and causes serious-to-fatal interstitial lung disease. Histrelin inhibits gonadotropic secretion and decreases follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) and testosterone levels and suppresses testosterone production. Hot flashes are very common with this drug. Triptorelin pamoate decreases FSH and LH levels and also suppresses testosterone production. It has also been associated with sexual dysfunction, urinary tract symptoms, bone pain, and hot flashes. Valrubicin is used in intravesical therapy for carcinoma in situ of the bladder. It is also associated with severe bladder spasms. 6. The nurse is caring for a patient who has just been diagnosed with adenocarcinoma of the pancreas. What antineoplastic does the nurse suspect the patient will receive? A) Bleomycin (Blenoxane) B) Daunorubicin (DaunoXome) C) Idarubicin (Idamycin) D) Mitomycin (Mutamycin) Ans: D Feedback: Mitomycin is used in before the treatment of disseminated adenocarcinoma of the stomach and pancreas. Bleomycin is used for palliative treatment of squamous cell carcinomas, testicular cancers, and lymphomas. Daunorubicin is the first-line treatment of advanced HIV infection and associated Kaposi’s sarcoma. Idarubicin is used in combination therapy for treatment of acute myeloid leukemia in adults. 7. The nurse is caring for a patient receiving cyclophosphamide (Cytoxan). What is the priority nursing action for this patient? Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) A) Monitor urinalysis results. B) Provide small, frequent meals. C) Administer an antiemetic when needed. D) Provide oral care. Ans: A 223 Feedback: The priority nursing action would be to monitor the patient’s urinalysis results because hemorrhagic cystitis is a potentially fatal adverse effect of cyclophosphamide. Providing small frequent meals, and oral care and administering an antiemetic are necessary to maintain nutrition when GI effects are severe but, assessments come before interventions and these interventions are of lower priority than monitoring for hemorrhagic cystitis. 8. A 42-year-old woman with breast cancer has had a radical mastectomy. She will have radiation therapy and then begin chemotherapy. Drug therapy will consist of a combination of doxorubicin, cyclophosphamide, and paclitaxel. What will the nurse include in her teaching plan concerning the drug therapy? A) Stay on a low-fat diet during the course of the drug therapy. B) Take special care when shaving or when brushing her teeth. C) Continue to go to church or to the mall just as she did before the diagnosis of cancer. D) Stay in bed 2 days after each administration. Ans: B Feedback: Special care should be taken when shaving or when brushing her teeth because she may bruise more easily than normal and gums may bleed. A cancer patient should not be on a diet during chemotherapy unless prescribed. Care should be taken to avoid crowds and public places where risk of infection is greater. Cancer patients should remain as active as tolerated, but they should be careful not to overextend themselves physically to promote optimal health. 9. A) The nurse should exercise caution when administering antimetabolites to a patient diagnosed with what? Bone marrow suppression Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) B) Diabetes mellitus C) Hypertension D) Seizure activity Ans: A 224 Feedback: Bone marrow is often the index for dosing and redosing levels. Caution should be used and strict monitoring done for patients with suppressed bone marrow who are receiving an antimetabolite. Diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and seizure activity have not been identified as interfering with this drug therapy. 10. The nurse is caring for a patient who is receiving a combination of antineoplastic agents. The patient will most likely lose his or her hair. Why would the nurse suggest that he or she get a wig or use appropriate head cover? A) People may be uncomfortable seeing his or her bald head. B) The hair will likely grow back if the head is covered at all times. C) His or her self-esteem will be better if the head is covered. D) Heat is lost through the head and it is important to cover it during extremes in temperature. Ans: D Feedback: Most of the heat is lost through the head and it is important to cover the head to prevent extreme changes in core temperature, which could affect all biochemical processes in the body. Other people’s feelings should not be an issue in whether she wears a wig or not. Even though loss of hair could decrease self-esteem, patients are usually more concerned about their prognosis. Whether the head is covered or not has nothing to do with hair growing back. 11. A patient diagnosed with a malignancy is receiving an antimetabolite as part of his or her medication therapy. What would the nurse be sure to teach this patient about his or her antimetabolite medication? (Select all that apply.) A) Report all other drugs and alternative therapies he or she is taking. B) Use safety measures due to possible dizziness, headache, and drowsiness. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) C) Cover the head at extremes of temperature. D) Plan for appropriate exercise regimens. E) Avoid being alone as much as possible. Ans: A, B, C 225 Feedback: Provide the following patient teaching: Follow the appropriate dosage regimen, including dates to return for further doses. Patients need to be reminded to report all other drugs and alternative therapies that they might be using; maintain nutrition if GI effects are severe; cover the head at extremes of temperature if alopecia is anticipated; plan for appropriate rest periods because fatigue and weakness are common adverse effects of the drugs; avoid infection including avoiding crowded places, sick people, and working in soil; and use safety measures such as not driving or using dangerous equipment due to possible dizziness, headache, and drowsiness. The nurse would not tell the patient to plan for appropriate exercise regimens because patients are more likely to need encouragement to rest; there is no reason he cannot be alone. 12. The nurse explains that the signs and symptoms caused by cancer are a result of what? A) Overgrowth of tumor cells B) Enzymes that generate blood vessels C) Tumor cells invading healthy tissue D) Metastasis Ans: C Feedback: As cancer cells grow, they invade and damage healthy host tissues and this is what causes signs and symptoms of cancer. When cancer metastasizes, the tumor cells invade new tissue and other signs and symptoms occur. Cancer cells do overgrow and the abnormal cells do release enzymes that generate blood vessels, but this is not what causes the signs and symptoms of cancer. The effects of neoplasms are not caused by overgrowth of tumor cells, enzymes that generate blood vessels, or metastasis. 13. The nurse is caring for a patient newly diagnosed with a primary brain tumor. The patient asks the nurse where his or her tumor came from. What is the nurse’s best response? A) Your tumor originated from somewhere outside the CNS from a cell just like other cells. B) Your tumor is from the pituitary gland in origin. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) C) Your tumor originated from a single cell that is genetically different from nearby cells. D) Your tumor is from nerve tissue somewhere in your body. Ans: C 226 Feedback: All cancers start with a single cell that is genetically different from the other cells in the surrounding tissue. Determining the site of the first cell to genetically mutate in this patient would require more information so it is impossible to say if the originating cell was in the CNS, the pituitary gland, or peripheral nerve tissue. 14. A nurse on the oncology unit is caring for a patient with an astrocytoma. The patient has just been told that the tumor is growing very fast. The patient asks the nurse how these tumors grow. What is the nurse’s best response? A) Brain tumors infiltrate the surrounding tissue. B) Brain tumors grow by invading the surrounding grey matter. C) Brain tumors grow by invading the surrounding white matter. D) Brain tumors spread down the spinal cord. Ans: A Feedback: Over time, these neoplastic cells grow uncontrollably, invading and damaging healthy tissue in the area and even undergoing metastasis (traveling from the place of origin to develop new tumors in other areas of the body where conditions are favorable for cell growth). The abnormal cells release enzymes that generate blood vessels. Brain tumors can invade either grey or white matter or they can spread down the spinal cord. These responses do not answer the patient’s question. 15. A patient asks the nurse what a cancer cell’s growth rate is called. What is the nurse’s best response? A) Cancer cell’s growth rate is called proliferation. B) Cancer cell’s growth rate is called anaplasia. C) Cancer cell’s growth rate is called pleomorphism. D) Cancer cell’s growth rate is called neoplasm. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) Ans: 227 A Feedback: A cancer cell growth rate is called proliferation. Anaplasia is the loss of organization and structure, pleomorphism is the occurrence of more than one shape of the cell, and a neoplasm is the term for a new or cancerous growth occurring when abnormal cells have the opportunity to multiply and grow. 16. The nurse is caring for a patient receiving a combination of different antineoplastic medications. The patient asks why they use so many different medications instead of just one drug. The nurse explains that a combination does what? (Select all that apply.) A) Decreases the development of cell resistance B) Increases the length of treatment C) Increases the quantity of each medication used D) Decreases the side effects of each medication E) Targets different phases of the cell cycle Ans: A, E Feedback: Malignant cells that remain in a dormant phase for long periods are difficult to destroy. These cells can emerge long after cancer treatment has finishedafter weeks, months, or yearsto begin their division and growth cycle all over again. For this reason, antineoplastic agents are often given in sequence over periods of time, in the hope that the drugs will affect the cancer cells as they emerge from dormancy or move into a new phase of the cell cycle. A combination of antineoplastic agents targeting different phases of the cell cycle is frequently most effective in treating many cancers. Combinations of drugs do not increase the length of treatment, increase the quantity of medication used, or decrease the adverse effects of the medications used. 17. The nurse is caring for a patient who is taking bicalutamide (Casodex). For what type of cancer would the nurse administer this drug? A) Bladder B) Colon C) Breast D) Prostate Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) Ans: 228 D Feedback: Bicalutamide (Casodex) is administered in combination with a luteinizing hormone for the treatment of advanced prostate cancer. This medication would not be effective for treating bladder, colon, or breast cancer because it is a hormone modulator and works only on hormone-requiring cancers. 18. What nursing diagnosis is a priority for the 87-year-old woman, who has stomatitis secondary to the administration of methotrexate? (Select all that apply.) A) Impaired skin integrity B) Risk for infection C) Imbalanced nutrition D) Risk for bleeding E) Hopelessness Ans: A, B, C, D Feedback: Because of the common adverse effects of severe bone marrow suppression, fatigue, malaise, rashes, alopecia, ulcerative stomatitis, hepatic toxicity, interstitial pneumonitis, chills, fever, and anaphylaxis, priority nursing diagnosis would include impaired skin integrity related to rash, risk for infection, and risk for bleeding related to severe bone marrow suppression. Because the patient has stomatitis, there is a risk for imbalanced nutrition less than body requirements because eating is uncomfortable and not feeling well will also reduce her appetite. Although fear and anxiety are common with any cancer diagnosis, hopelessness is usually not as common unless the patient receives a terminal diagnosis and, even then, many patients are able to remain hopeful. 19. What measure protects the nurse when preparing cytotoxic drugs? A) Wearing protective equipment such as gloves, mask, and gown B) Washing hands before preparation C) Mixing medication in a 1-L bag D) Administering medication IM Ans: A Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 229 Feedback: Cytotoxic drugs are toxic chemicals and the nurse who administers them must take adequate precautions to avoid self-exposure. These precautions include protective equipment. Hand hygiene should be performed before administering any medication but this measure does not protect the nurse. Whether mixing the medication in a 1-L bag or administering it IM, the nurse must wear protective equipment. 20. The patient has just been started on an alkylating agent to treat cancer. What is the most common adverse effect of most alkylating agents that the nurse will monitor for? A) Bone marrow suppression B) Nephrotoxicity C) Confusion D) Depression Ans: A Feedback: Hematological effects include bone marrow suppression, with leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, anemia, and pancytopenia, secondary to the effects of the drugs on the rapidly multiplying cells of the bone marrow. Therefore, options B, C, and D are not correct. 21. The patient is taking ifosfamide as part of his or her cancer treatment. Mesna (Mesnex) is added to the treatment regimen to prevent cystitis induced by the ifosfamide. The nurse explains that mesna works by what action? A) By increasing urine output B) By shielding the kidney from ifosfamide C) By increasing white blood cell production D) By combining with a metabolite of ifosfamide Ans: D Feedback: Mesna combines with a urotoxic metabolite of ifosfamide to reduce the damaging effects of ifosfamide. It has no effect on urine output, does not provide a shield for the kidney, and has no impact on white blood cell production. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 22. 230 Chlorambucil has been ordered for a patient with Hodgkin’s disease. The patient’s son asks the nurse what adverse effects this drug has. What will the nurse include when responding to this question? (Select all that apply.) A) Tremors B) Muscle twitching C) Confusion D) Gynecomastia E) Alopecia Ans: A, B, C Feedback: Chlorambucil is a palliative treatment for chronic lymphocytic leukemia, malignant lymphomas, and Hodgkin’s disease. Adverse effects include tremors, muscle twitching, confusion, nausea, hepatotoxicity, bone marrow suppression, sterility, and cancer. 23. A patient with acute myeloblastic leukemia is taking doxorubicin. What medication, if ordered, would the nurse recognize as a cardioprotective drug used in combination with doxorubicin? A) Dexrazoxane (Zinecard) B) Ixabepilone (Ixempra) C) Teniposide (Vumon) D) Vinblastine (Velban) Ans: A Feedback: Dexrazoxane is a powerful chelating agent that is a cardioprotective drug that interferes with the cardiotoxic effects of doxorubicin. Ixabepilone (Ixempra) is given in combination with capecitabine for the treatment of patients with metastatic or locally advanced breast cancer. Teniposide is given in combination with other drugs for induction therapy in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Vinblastine is given in combination with other medications as part of the treatment for advanced testicular germ cell cancer. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 24. 231 A patient taking tamoxifen to reduce the risk of contralateral breast cancer asks the nurse about adverse effects of the drug. What is an adverse effect of tamoxifen? A) Stomatitis B) Mucositis C) Thrombocytopenia D) Cerebrovascular accidents Ans: D Feedback: Adverse effects of tamoxifen include hot flashes, rash, nausea, vomiting, vaginal bleeding, menstrual irregularities, edema, pain, cerebrovascular accident, and pulmonary emboli. They do not include stomatitis, mucositis, or thrombocytopenia. 25. A female patient prescribed methotrexate for meningeal leukemia is asking the nurse about adverse effects of the drug. What would the nurse tell this patient should be avoided while taking methotrexate? A) Pregnancy B) Aerobic exercise C) Smoking D) Alcohol Ans: A Feedback: Antimetabolites are contraindicated for use during pregnancy and lactation because of the potential for severe adverse effects on the fetus and neonate. The nurse would not caution the patient against aerobic exercise, smoking, or alcohol use because of the medication she was taking. 26. What is the nurse’s priority intervention to reduce the risk of cystitis caused by cyclophosphamide (Cytoxan)? A) Encourage the patient to drink cranberry juice. B) Promote adequate rest and sleep. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) C) Encourage fluids to maintain hydration. D) Instruct the patient to wear only cotton underwear. Ans: C 232 Feedback: Hemorrhagic cystitis is a potentially fatal adverse effect. Ensure that the patient is well hydrated. Drinking cranberry juice or milk helps to hydrate the patient, but what he or she drinks is less important than that he or she drinks adequate amounts of fluid. Wearing cotton underwear is not an intervention the nurse would teach the patient. 27. A young man asks the nurse about the goal of the cancer therapy his mother is receiving. What is the nurse’s best response? A) The goal is to limit the cancer cells so the immune system can respond without causing too much toxicity to your mother. B) The goal is to kill the cancer cells as quickly as possible before they can spread so your mother will be well again. C) The goal is to control the speed at which new cancer cells grow so the medication has a better chance to work. D) The goal is to keep the cancer cells from spreading all over your mother’s body and choose the drug with the fewest adverse effects. Ans: A Feedback: The goal of cancer therapy, much like that of anti-infective therapy, is to limit the offending cells to the degree that the immune system can then respond without causing too much toxicity to the host. Therefore, options B, C, and D are not correct. 28. The nurse is acting as a mentor for a new graduate nurse who is delivering chemotherapy to a patient in the short-stay unit. What action performed by the new graduate would the mentor teach is not appropriate and requires correction? A) Checking the IV line frequently B) Using an infusion pump to administer the medication C) Premedicating the patient as ordered Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) D) Starting the IV in a large, distal vein Ans: B 233 Feedback: If at all possible, do not use an infusion pump to administer one of these drugs because it will continue to deliver the drug under pressure and can cause a severe extravasation. This would be the least beneficial to the patient. Checking the line frequently, premedicating the patient as ordered, and using a large, distal vein would be much more beneficial to the patient. 29. A patient with rhabdomyosarcoma has been admitted for chemotherapy with vincristine. While preparing a plan of care for this patient, what would be an appropriate nursing diagnosis? A) Altered body image due to severe fluid retention B) Risk for bleeding due to possible hemorrhagic cystitis C) Risk for injury related to muscle wasting and weight loss D) Risk of infection related to possible nosocomial infection Ans: C Feedback: Adverse effects of vincristine include ataxia, cranial nerve manifestations, neuritic pain, muscle wasting, constipation, leukopenia, weight loss, loss of hair, and death. As a result, the risk for injury due to weakness and falls is a significant concept. Risk for bleeding and severe fluid retention is unlikely with this drug. The risk of infection is related to bone marrow suppression, not a possible nosocomial infection. The patient is more at risk for a nosocomial infection because of the bone marrow suppression. 30. A patient newly diagnosed with chronic myelocytic leukemia (`) has been prescribed treatment with imatinib. The patient asks the nurse how imatinib works. What would be the nurse’s best response? A) imatinib alkylates cellular DNA. B) imatinib inhibits folic acid reductase, leading to inhibition of DNA synthesis and inhibition of cellular replication. C) imatinib binds to DNA and inhibits DNA synthesis in susceptible cells, causing cell death. D) imatinib inhibits the enzyme created by the Philadelphia chromosome abnormality in CML. Ans: D Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 234 Feedback: Imatinib is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor that selectively inhibits the Bcr-Abl tyrosine kinase created by the Philadelphia chromosome abnormality in CML and some tumor cells present in gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST); blocking this enzyme inhibits proliferation and induces cell division. Alkylating agents alkylate cellular DNA; antimetabolites inhibit folic acid reductase, leading to inhibition of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) synthesis and inhibition of cellular replication; and antineoplastic antibiotics bind to DNA and inhibit DNA synthesis in susceptible cells, causing cell death. 31. The patient, diagnosed with chronic myelocytic leukemia (CML), has not been responding to chemotherapy and the provider changes the patient to imatinib. The patient asks the nurse, What adverse effects am I going to have to deal with from this drug? What is the nurse’s best response? A) Adverse effects from this drug are more serious but this drug is stronger and more effective. B) Adverse effects are similar to other drugs including bone marrow suppression, nausea, and hair loss. C) Adverse effects are much less likely or severe including GI upset, headache, and muscle pain. D) Adverse effects vary from patient to patient and depend on your overall health as to what will occur. Ans: C Feedback: Patients who have CML and who have been switched to imatinib after traditional chemotherapy have been amazed at how good they feel and how much they have recovered from the numerous adverse effects of traditional chemotherapy. Administer with a meal and a full glass of water, arrange for small frequent meals if GI upset is a problem, provide analgesics for headache and muscle pain, monitor CBC, and examine for edema. Options A, B, and D are not correct. 32. The nursing instructor teaches the students that antineoplastic drugs are often carcinogens. The students are surprised to hear this and ask why. The instructor’s best response includes what information? A) The drugs kill cells resulting in a need for more cellular growth with risk of a mutant cell. B) These drugs do so much damage to so many human cells that the patient is debilitated. C) If the patient remains cancer free for 2 years and then cancer is found, it is caused by the drugs. D) Palliative therapy promotes the growth of new cancer cells because it is not strong enough. Ans: A Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 235 Feedback: Many neoplastic drugs result in the adverse effect of cancer because cell death caused by the agents increase the need for cellular growth, placing the patient at increased risk for a mutant cell to develop. Patients often recover completely from the adverse effects after chemotherapy is completed and do not remain debilitated. Most cancer patients are not considered to be cured until they have remained cancer free for 5 years because no cells have been identified that can remain dormant for 5 years. Palliative therapy does not promote growth of new cancer cells. 33. What classification of antineoplastic medication would the nurse administer that acts by inhibiting microtubular reorganization? A) Alkylating agents B) Hormone modulators C) Mitotic inhibitors D) Antimetabolites Ans: C Feedback: Mitotic inhibitors such as docetaxel and paclitaxel inhibit microtubular reorganization. Alkylating agents interfere with ribonucleic acid (RNA), deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), or other cellular proteins. Hormone modulators react with specific receptor sites to block cell growth and activity. The antimetabolite cladribine and miscellaneous agent hydroxyurea block DNA synthesis. 34. The nurse transfers from the adult oncology unit to the pediatric oncology unit. What will the nurse need to add to the patient’s plan of care that was not a part of the adult patient’s care plan? A) Social, emotional, and intellectual stimulation B) Concerns related to combination drug therapy C) Double checking dosage calculations and appropriateness of drug dosage D) Monitor for hydration and nutritional status Ans: A Feedback: Children need to play and learn so meeting the child’s social, emotional, and intellectual needs is a part of the care plan that was not as significant with adults. Administration of combination drugs, Double- Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 236 checking dosage calculations and appropriateness of drug dosage, and Monitoring for hydration and nutritional status are all components of adult care as well as pediatric care. 35. The nurse is conducting a class for nurses hired to work on the oncology unit. What statement, if made by the nurse, would be correct regarding chemotherapy for older adults? (Select all that apply.) A) Older adults may be more susceptible to the central nervous system (CNS) and GI effects of these drugs. B) Older patients are at risk for dehydration and diminished nutritional status. C) Safety precautions should be instituted as soon as any drug is initiated. D) Dosage will need to be adjusted based on the age of the older adult. E) Older adults are already somewhat immunosuppressed, so further suppression is a concern. Ans: A, B, E Feedback: Older adults may be more susceptible to the CNS and GI effects of some of these drugs. Older patients should be monitored for hydration and nutritional status regularly. Safety precautions should be instituted if CNS effects occur but are not needed for every drug as soon as it is initiated. Dosage is adjusted based on hepatic and renal function, not the patient’s age. Protecting these patients from exposure to infection and injury is a very important aspect of their nursing care because older patients are naturally somewhat immunosuppressed because of age. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 237 Chapter 15 - Introduction to the Immune Response and Inflammation 1. The body’s first-line barrier defense is considered to be what? A) Mast cells B) Mucous membranes C) Skin D) T cells Ans: C Feedback: The skin is the first line of barrier defense. It acts as a physical barrier to protect the internal tissues and organs of the body. Mast cells are part of cellular defense. They are found in the respiratory and GI tracts and are fixed basophils that do not circulate. Mucous membranes are a barrier defense that line the areas of the body that are exposed to external influences but do not have the benefit of skin protection. T cells are part of the immune response and provide cell-mediated immunity. Activation of a T cell by a nonself-cell results in responses that destroy foreign cells. 2. The nurse recognizes what patient has lost a barrier defense increasing his risk for infection? A) A 68-year-old man diagnosed with prostate cancer B) A 24-year-old man diagnosed with partial thickness burns C) A 13-year-old boy diagnosed with chickenpox D) A 72-year-old man diagnosed with bacterial pneumonia Ans: B Feedback: A burn patient loses the protective barrier of the skin and is at risk for infection. In a partial thickness burn, the glands of the skin secrete chemicals that destroy many pathogens and also the normal flora that live on the skin. A cancer patient has decreased cellular defenses. The patient with chickenpox and the patient with pneumonia both have a diminished immune defense along with the prostate cancer patient but still are at less risk for infection than the burn patient. 3. After reviewing the results of a complete blood count on a patient who is diagnosed with an acute Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 238 infection, what will the nurse expect to see elevated? A) Basophil count B) Eosinophil count C) Hematocrit D) Neutrophil count Ans: D Feedback: During an acute infection, the neutrophils are rapidly produced in response to the interleukins released by active white blood cells. They move to the site of insult to attack the foreign substance. Eosinophils are often increased in an allergic response. Basophils would only increase with generalized bone marrow stimulation. The hematocrit level is increased in polycythemia. 4. A new mother calls the clinic and tells the nurse her toddler has a temperature of 102ºF. How does the nurse explain why the mother should not be alarmed? A) A fever is the body’s way of fighting an infection and supporting the body’s immune system. B) Neutrophils release pyrogen, a fever-causing substance, which helps act as a catalyst for the body’s inflammatory and immune responses. C) Leukotrienes activated by arachidonic acid attract neutrophils to start the process of fighting inflammation. D) Inflammation causes the activation of a chemical called Hageman factor that initiates a process to bring more blood to the injured area and allows white blood cells to escape into the tissues. Ans: A Feedback: The best response by the nurse would be that a fever actually increases the efficiency of the immune and inflammatory responses, helping the body to fight the infection. While the other three statements are correct, they are more technical and include terminology that a new mother may not understand or even care about. If the appropriate response does not suffice and the mother still has questions, the nurse would then go into more detail and use the rationale from the other options to explain in greater detail. 5. A patient presents to the emergency department with an infected wound on his left forearm. The nurse explains the inflammatory response caused by the injury will occur in what sequence? Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) A) Heat, pain, redness, swelling B) Swelling, pain, redness, heat C) Redness, swelling, heat, pain D) Pain, redness, swelling, heat Ans: C 239 Feedback: The inflammatory response will begin with redness in the direct line of the infected wound. Next, swelling will occur because of the fluid that leaks into the tissue as a result of the change in capillary permeability. The heat can be detected due to the increased blood flow to the area. Pain will be felt due to the activation of fibers by histamine and the kinin system as well as stretching of the tissue caused by the edema. 6. The patient with AIDS asks the nurse why his cytotoxic T cells are so important. What is the nurse’s best response to explain the actions of cytotoxic T cells? A) Cells that are programmed to identify specific proteins or antigens B) Cells that can either destroy a foreign cell or mark it for aggressive destruction C) Cells that respond to chemical indicators of immune activity and stimulate other lymphocytes to be more aggressive and responsive D) Cells that respond to rising levels of chemicals associated with an immune response to suppress or slow the reaction Ans: B Feedback: Effector or cytotoxic T cells either destroy a foreign cell or make it available for aggressive destruction. Cells that identify specific proteins or antigens are B cells. Cells that respond to chemical indicators to stimulate other cells are helper T cells. Cells that suppress or slow the reaction are suppressor T cells. 7. A) A patient has a minor laceration on the left arm. What does the nurse know that will cause a patient to experience muscle and joint aches, a low-grade fever, and sleepiness when an inflammatory reaction is initiated? Bacterial toxins Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) B) Interferon activity C) Leukotriene activity D) Phagocytosis Ans: C 240 Feedback: The leukotrienes (autocoids activated through the kinin system) affect the brain to induce slow-wave sleep, believed to be an important energy conservation measure for fighting the invader. They also cause myalgia and arthralgia (muscle and joint pain)common signs and symptoms of various inflammatory diseases, which also cause reduced activity and save energy. Interferons are released in response to viral infection. Phagocytosis destroys engulfed foreign material in the body. Bacterial toxins cause local reactions unless the infection is intense and the bacteria enter the bloodstream. 8. What body defense needs to be reduced in the patient following organ transplantation? A) Major histocompatibility complex B) Barrier defenses C) Lymphoid tissues D) Eosinophils Ans: A Feedback: The major histocompatability complex is the genetic identification code carried on chromosomes and produces several proteins called histocompatibility antigens located on the cell membrane that allow the body to recognize cells that are self-cells. Cells without these proteins, such as those in a transplanted organ, are identified as foreign and are targeted for destruction so this defense must be minimized to prevent damage to the transplanted organ. Barrier defenses prevent entry of pathogens into the body. Lymphoid tissue creates cellular components of the mononuclear phagocyte system, differentiates T cells, and regulates actions of the immune system. Eosinophils respond to allergic responses. Barrier defenses, lymphoid tissue, and eosinophils are not involved in the transplant rejection process. 9. The nurse is teaching a class on the inflammatory response for other nurses and discusses the role of factor XII or the Hageman factor. What substance does Hageman’s factor activate to cause kininogen to be converted to bradykinin? A) Arachidonic acid B) Prostaglandins Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) C) Leukotrienes D) Kallikrein Ans: D 241 Feedback: Hageman’s factor activates kallikrein, a substance found in the local tissues, which causes the precursor substance kininogen to be converted to bradykinin and other kinins. Bradykinin causes the release of arachidonic acid from the cell membrane. Arachidonic acid causes the release of other substances called autocoids, including prostaglandins, leukotrienes, and thromboxanes 10. A patient who has received a heart transplant has been given an order for drugs that block T cell activity. What is the rationale behind this order? A) To manufacture antibodies to the foreign proteins B) To stimulate wound healing C) To combine with a complement to cause a massive inflammatory reaction D) To prevent an inflammatory reaction against the transplanted heart Ans: D Feedback: Effector or cytotoxic T cells are aggressive against nonself-cells, releasing cytokines that can either directly destroy a foreign cell or mark it for aggressive destruction. If the transplanted organ is attacked by cytokines, it will be destroyed, referred to as organ rejection. As a result, inhibition of these killer T cells is essential to continued organ function in the transplanted organ. Blocking T cells would not manufacture antibodies, stimulate wound healing, or trigger a massive inflammatory response. 11. The nurse anticipates what generalized response to the patient’s cellular injury? A) Decreased pH B) Increased protein catabolism C) Inhibition of cell growth D) Inflammation Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) Ans: 242 D Feedback: The inflammatory response is the local reaction of the body to invasion or injury. Any insult to the body that injures cells or tissues sets of a series of events and chemical reactions known as the inflammatory response. Protein catabolism is the breakdown of protein into particles small enough to be carried into the cell and is an incorrect choice. Cellular injury does not inhibit cell growth or lower pH. 12. The nurse takes a class to better understand the immune and inflammatory responses and learns what cells help to slow or suppress the immune response? A) Cytotoxic T cells B) Helper T cells C) Suppressor T cells D) B cells Ans: C Feedback: Suppressor T cells respond to rising levels of chemicals associated with an immune response to suppress or slow the reaction. Helper T cells respond to the chemical indicators of immune activity and stimulate other lymphocytes, including B cells, to be more aggressive. Cytotoxic T cells are aggressive against nonself-cells. 13. The nurse plans care for patients with the knowledge that loss of body defenses can increase the patient’s risk for infection. What barrier defenses need to remain intact to prevent infection? (Select all that apply.) A) Skin B) Mucous membranes C) Gastric acid D) Leukocytes E) T cells Ans: A, B, C Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 243 Feedback: The skin is the first line of barrier defense, creating a physical barrier to prevent pathogens from entering the internal tissues. Mucous membranes are another barrier defense protecting the area without skin protection (e.g., the respiratory tract, gastrointestinal tract, genitourinary tract). Gastric acids destroy many pathogens that are ingested or swallowed, preventing them from entering the bloodstream or internal organs. Leukocytes and T cells are cellular defenses and not barrier defenses. 14. What is the nurse referring to when discussing B-cell immunity when the B cells are programmed to identify specific proteins or antigens? A) T-cell immunity B) Autoimmunity C) Passive immunity D) Humoral immunity Ans: D Feedback: B cells are programmed to identify specific proteins, or antigens. They provide what is called humoral immunity. Autoimmunity occurs when the body attacks its own self-cells. Passive immunity is the transfer of antibodies from one person to another. Active immunity is immunity produced by the body in response to an organism. 15. When antibodies and antigens react, they create an antigenantibody complex. This structure reveals a new receptor site that activates a series of plasma proteins called what? A) Complement B) Neutralization of viral toxins C) Opsonization D) Histamine Ans: A Feedback: When the antigens and antibodies react, they form an antigenantibody complex. This new structure reveals a new receptor site on the antibody that activates a series of plasma proteins in the body called complement proteins. Options B, C, and D are distracters for this question and are not involved in this Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 244 process. 16. The pharmacology instructor is discussing activated complement with the nursing students. What would the instructor tell the students that activated complement stimulates? A) Opsonization B) Chemotaxis C) Agglutination D) Phagocytosis Ans: B Feedback: Activated complement stimulates chemotaxis (movement of monocytes, neutrophils, basophils, and eosinophils toward the antigen) and the release of hydrolytic enzymes; actions that result in the destruction or inactivation of the invading antigen. Opsonization is the coating of the antigen so that it is more readily recognized by phagocytic cells. Agglutination is the clumping of cells. Phagocytosis is the destruction of pathogens or cells. 17. The nursing instructor explains that future exposure to an antigen previously encountered elicits a much faster response as the result of what cells forming memory cells? A) T cells B) Lymphocytes C) Monocytes D) B cells Ans: D Feedback: After being activated, the B cells form memory cells that will produce antibodies for immediate release in the future if the antigen is encountered again. Although lymphocytes, monocytes, and T cells will then join in the battle to destroy the antigen, they do not produce memory cells as the B cells do. 18. When explaining the immune response the nursing instructor explains the role of neutrophils as doing what? Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) A) Phagocytosis B) Producing memory cells C) Marking cells for destruction D) Initiating an immune response Ans: A 245 Feedback: Neutrophils engulf and digest foreign material through the process of phagocytosis. B cells produce memory cells. Cytoxic T cells mark cells for destruction. Basophils initiate the immune response. 19. What specific drug group has both antiviral and antiproliferative actions? A) Interferons B) Interleukins C) Monoclonal antibodies D) Hematopoietic growth factors Ans: A Feedback: Interferons are chemicals that are secreted by cells that have been invaded by viruses and possibly by other stimuli. The interferons prevent viral replication and also suppress malignant cell replication and tumor growth. Therefore, options B, C, and D are incorrect. 20. Tumor necrosis factors (TNF) participate in the inflammatory response of the human body. What do they cause in the inflammatory response? A) Enhancing macrophage activity B) Tumor regression C) Binding of target cells D) Delaying or stopping macrophage migration Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) Ans: 246 B Feedback: TNF, a cytokine, is a chemical released by macrophages that inhibits tumor growth and can cause tumor regression. It also works with other chemicals to make the inflammatory and immune responses more aggressive and efficient. Therefore, options A, C, and D are incorrect. 21. Stressors are a variety of factors that have long been thought to have an important connection with the immune response. What could the nurse classify as a stressor? (Select all that apply.) A) Trauma B) Foreign cells C) Viruses D) Extremes of environmental conditions E) Self-cells Ans: A, B, C, D Feedback: The term stressors can include bacteria, viruses, other foreign pathogens or nonself-cells, trauma, and exposure to extremes of environmental conditions. Self-cells are not considered a stressor on the body. 22. The nurse is caring for a patient with newly diagnosed multiple sclerosis (MS). The patient asks why MS is called an autoimmune disease. What is the nurse’s best response? A) The body attacks its own cells because it responds to specific self-antigens to produce antibodies. B) A result of response to a cell that was invaded by bacteria, leading to antibody production to similar cells. C) Production of autoantibodies is a normal process that goes on all the time, but immunosuppression limits B-cell response. D) People with multiple sclerosis have a genetic predisposition to destroy autoantibodies. Ans: A Feedback: Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 247 Autoimmune disease occurs when the body responds to specific self-antigens to produce antibodies or cell-mediated immune responses against its own cells. The actual cause of autoimmune disease is not known, but theories speculate that (1) it could be a result of response to a cell that was invaded by a virus, leading to antibody production to similar cells; (2) production of autoantibodies is a normal process that goes continuously, but in a state of immunosuppression, the suppressor T cells do not suppress autoantibody production; or (3) a genetic predisposition to develop autoantibodies is present. 23. The nurse is caring for a patient with an acute infection that resulted in an immune reaction. What symptoms exhibited by the patient would the nurse recognize as being caused by interleukins? (Select all that apply.) A) Fever B) Joint pain C) Muscle pain D) Hyperactivity E) Insomnia Ans: A, B, C Feedback: Interleukins cause many of the symptoms associated with flu-like symptoms, all things that help the body to conserve energy including fever, joint pain (arthralgia), muscle pain (myalgia), and slow-wave sleep induction. Hyperactivity and insomnia are incorrect options. 24. What immunoglobulin (Ig) is present in small amounts and is thought to be related to allergic responses? A) IgM B) IgG C) IgE D) IgA Ans: C Feedback: Five different types of immunoglobulins have been identified: IgE is present in small amounts and seems to be related to allergic responses and to the activation of mast cells. The first immunoglobulin Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 248 released is M (IgM). It contains the antibodies produced at the first exposure to the antigen. IgG, another form of immunoglobulin, contains antibodies made by the memory cells that circulate and enter the tissue; most immunoglobulin found in the serum is IgG. IgA is found in tears, saliva, sweat, mucus, and bile. It is secreted by plasma cells in the GI and respiratory tracts and in epithelial cells. These antibodies react with specific pathogens that are encountered in exposed areas of the body. 25. Our bodies contain various immunoglobulins (Ig). Which of these immunoglobulins is found in sweat, tears, mucus, and bile? A) IgG B) IgA C) IgM D) IgE Ans: B Feedback: Five different types of immunoglobulins have been identified: IgA is found in tears, saliva, sweat, mucus, and bile. It is secreted by plasma cells in the GI and respiratory tracts and in epithelial cells. IgE is present in small amounts and seems to be related to allergic responses and to the activation of mast cells. The first immunoglobulin released is M (IgM); it contains the antibodies produced at the first exposure to the antigen. IgG, another form of immunoglobulin, contains antibodies made by the memory cells that circulate and enter the tissue; most of the immunoglobulin found in the serum is IgG. These antibodies react with specific pathogens that are encountered in exposed areas of the body. 26. A 44-year-old man has come to the clinic with an exacerbated asthma attack, asthma exacerbation. He tells the nurse that his father and brother also suffer from asthma, as does his 15-year-old son. The nurse explains that there is most likely an allergic component based on a genetic predisposition. The specific allergen initiated by immunological mechanisms is usually mediated by what? A) Immunoglobulin A B) Immunoglobulin M C) Immunoglobulin G D) Immunoglobulin E Ans: D Feedback: Allergic reactions characterized by the action of IgE antibodies and a genetic predisposition to allergic Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 249 reactions are found in diseases like asthma. IgG is the most common immunoglobulin and is found in intravascular and intercellular compartments. IgA and IgM are found in mucous secretions. 27. Injury to a cell membrane causes the local release of histamine. What does histamine do? A) Stimulates pain perception B) Causes vasoconstriction C) Decreases capillary permeability D) Inhibits phagocytosis Ans: A Feedback: Pain comes from the activation of pain fibers by histamine and the kinin system, occurring any time a cell is injured. Histamine also causes vasodilation, increases capillary permeability, and facilitates phagocytosis. 28. An adolescent comes to the free clinic with complaints of allergic rhinitis. The adolescent asks the nurse what makes his nose get so stuffy. What is the nurse’s best response? A) The inside of the nose swells because of the dilation of the blood vessels. B) Allergies make the sinuses drain into the nasal passages and it stuffs them up. C) The inside of the nose swells closed because of drainage from the sinuses. D) Leukotrienes are attacking the mucous membranes of your nose and causing irritation. Ans: A Feedback: Histamine is the major mediator of allergic reactions in the nasal mucosa. Tissue edema results from vasodilation and increased capillary permeability. Tissue edema is not caused by drainage from the sinuses or from leukotrienes. 29. A) In a discussion about cancer, a student asks why the body does not phagocytize a tumor. What would be the instructor’s best response? Sometimes tumor cells trick the T cells into allowing them to survive. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) B) Some tumor cells do not develop an antigenantibody reaction. C) Some tumor cells develop a strong mast cell reaction. D) Tumor cells are too small to be seen by the immune system. Ans: A 250 Feedback: Neoplasms occur when mutant cells escape normal surveillance of the immune system and begin to grow and multiply. Aging reduces efficiency of the immune system; location of mutant cells can make it difficult for lymphocytes to get to them or that mass can grow so quickly that the tumor becomes too large for the immune system to deal with. Tumors can produce antibodies that cover antigen receptor sites on the tumor and prevent recognition by cytotoxic T cells, or a weak antigenic tumor may elicit a mild response from the immune system and tricks the T cells into allowing it to survive. 30. What systems are activated by Hagemans factor? (Select all that apply.) A) Kinin system B) Histamine release system C) Clotting cascade D) Plasminogen system E) Chemotaxis system Ans: A, C, D Feedback: Hagemans factor is responsible for activating at least three systems in the body: the kinin system; the clotting cascade, which initiates blood clotting; and the plasminogen system, which initiates the dissolution of blood clots. Histamine release is stimulated by cell damage. Arachidonic acid activates some leukotrienes that have a property called chemotaxis, which is the ability to attract neutrophils and to stimulate them and other macrophages to be very aggressive. 31. The nurse assesses the patient’s postoperative wound and determines that the wound is inflamed, most likely because of an infection, when noting what classic symptoms? (Select all that apply.) A) Heat around the site of the wound B) Redness around the site of the wound Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) C) Increase in reports of pain D) Edema at the site of the wound E) Serosanguineous drainage from the wound Ans: A, B, C, D 251 Feedback: Activation of the inflammatory response produces a characteristic clinical picture. Heat occurs because of the increased blood flow to the area. Swelling occurs because of the fluid that leaks into the tissues as a result of the change in capillary permeability. Redness is related to the increase in blood flow caused by the vasodilation. Pain comes from the activation of pain fibers by histamine and the kinin system. 32. When assessing the patient with tissue injury, the nurse correlates signs and symptoms to the responses occurring within the patient’s body. Put the inflammatory responses in the order they will occur. A) Activation of Hageman’s factor B) Kininogen activates release of bradykinin C) Release of leukotrienes and prostaglandins D) Prekallikrein becomes kallikrein E) Release of arachidonic acid Ans: A, B, C, D, E Feedback: Tissue injury is followed by exposure of plasma to the injured cell, which results in activation of Hageman’s factor. This stimulates prekallikrein to become active kallikrein. Kininogen activates bradykinin. Arachidonic acid is released, which activates release of leukotrienes and prostaglandins. 33. The patient tells the nurse she was reading about interferons on the Internet but still does not exactly understand what they do. What actions would the nurse describe as being performed by interferons? (Select all that apply.) A) Prevent viral replication B) Suppress malignant cell replication Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) C) Suppress tumor growth D) Stimulate T and B cells to initiate an immune response E) Stimulate the body to produce more T cells Ans: A, B, C 252 Feedback: Interferons are chemicals that are secreted by cells that have been invaded by viruses and possibly by other stimuli. The interferons prevent viral replication and also suppress malignant cell replication and tumor growth. Interleukins stimulate T and B cells to initiate an immune response and to produce more T cells. 34. The nurse is caring for a patient waiting for a heart transplant. The patient’s spouse asks the nurse, Why don’t they just choose any heart until the right heart can be found? What is the nurse’s best response? A) The more closely the new heart matches the patient’s tissue, the less aggressive the immune reaction will be. B) When the body responds to specific self-antigens to produce antibodies against its own cells, a severe immune response results. C) Graft-versus-host disease would result making the patient very ill. D) The patient would need to have suppressor T cells infused daily to maintain the heart. Ans: A Feedback: Transplantation of foreign tissue (e.g., moving a heart from a donor to a sick patient) results in an immune reaction. Matching a donor’s human leukocyte antigen markers is important as closely as possible to those of the recipient because histocompatability is essential. The more closely the transplanted heart matches the recipient, the less aggressive the immune response will be to the donated tissue. Graft-versus-host disease occurs only in stem cell or bone marrow donations, not organ transplantation. Suppressor T cells cannot be transfused like blood because they must be produced by the body to function appropriately. 35. The patient, recently diagnosed with HIV, is waiting for results of his lab work to determine his T cell count and says to the nurse, What exactly is a T cell? What is the nurse’s best response? A) T cells are monocytes, which are a type of white blood cell that helps to fight off infections and other foreign bodies that enter the body. B) T cells are neutrophils, which are a type of white blood cell that helps to fight off infections and Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 253 other foreign bodies that enter the body. C) T cells are lymphocytes, which are a type of white blood cell that helps to fight off infections and other foreign bodies that enter the body. D) T cells are basophils, which are a type of white blood cell that helps to fight off infections and other foreign bodies that enter the body. Ans: C Feedback: T cells are lymphocytes, a type of white blood cells with large, varied nuclei that can be either T cells or B cells. T cells are not neutrophils, which are capable of moving outside the bloodstream and phagocytizing foreign material. Basophils are myelocytic leukocytes containing chemical substances important for initiating and maintaining an immune or inflammatory response. Monocytes are macrophages capable of phagocytizing an antigen and help to remove foreign material from the body. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 254 Chapter 16 - Antiinflammatory, Antiarthritis, and Related Agents 1. A nurse has admitted a 10-year-old child to the short-stay unit. The child has complained of chronic headaches and his or her mother reports that he or she gives him or her acetaminophen (Tylenol) at least twice a day. What will the nurse evaluate? A) Renal function B) Hepatic function C) Respiratory function D) Cardiac function Ans: B Feedback: The nurse should evaluate the patient’s hepatic function. Severe hepatotoxicity can occur from overuse of acetaminophen. Significant interferences do not occur in the kidney, heart, or lung with acetaminophen. 2. The nurse is discussing ethnic differences in response to medication with your nursing students. What group of people would the nurse tell the students may have a decreased sensitivity to pain-relieving effects of anti-inflammatory drugs and should be educated concerning signs and symptoms of gastrointestinal bleeding from use of these drugs? A) African Americans B) White Americans C) Hispanics D) Asians Ans: A Feedback: African Americans have a documented decreased sensitivity to pain-relieving effects of many antiinflammatory drugs. They also have an increased risk of developing GI adverse effects to these drugs. In general, White Americans, Hispanics, and Asians are at lower risk for these problems. 3. A patient, newly diagnosed with ulcerative colitis, has been admitted to the short-stay unit. What Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 255 salicylates does the nurse anticipate will be ordered for this patient? A) Balsalazide (Colazal) B) Sodium thiosalicylate (generic) C) Choline magnesium trisalicylate (Tricosal) D) Salsalate (Argesic) Ans: A Feedback: Balsalazide is delivered intact to the colon, where it delivers a local anti-inflammatory effect that is most effective for patients with ulcerative colitis. Choline salicylate and salsalate are used to treat pain, fever, and inflammation. Sodium thiosalicylate is used mainly for episodes of acute gout, for muscular pain, and to treat rheumatic fever. 4. The nurse is caring for a 66-pound child with orders for choline magnesium trisalicylate (Tricosal). The orders read 50 mg/kg/d PO in two divided doses. How many milligram will the patient receive per dose? A) 250 mg B) 500 mg C) 750 mg D) 1,000 mg Ans: C Feedback: First, the nurse must determine the child’s weight in kilogram. One kg is equal to 2.2 pounds. Divide 2.2 into 66 to equal 30 kg. Multiply 50 mg times 30 kg to equal 1,500 mg. Divide 1,500 by 2 for the divided doses, which will equal 750 mg per dose. 5. A) A nurse is caring for a patient with severe rheumatoid arthritis who takes anti-inflammatory agents on a regular basis. What medication should the nurse question if ordered by the physician to be taken in addition to the anti-inflammatory agent? Oral antidiabetic agent Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) B) Calcium channel blocker C) Beta-blocker D) Antibiotic Ans: C 256 Feedback: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs have the potential to decrease antihypertensive effects from beta blockers if these drugs are taken at the same time. Patients who receive these combinations should be monitored closely and appropriate dosage adjustments made if needed. Drug interactions do not usually occur with oral antidiabetic agents, calcium channel blocking medications, or antibiotics. 6. A nurse is assessing a patient who has been taking nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID). What statement by the patient indicates to the nurse that the patient has a good understanding of the use of this therapy? A) I drink a glass of wine just about every night. B) I asked my doctor to check for blood in my stool regularly. C) I do not like to swallow tablets so I crush them. D) I drink as little water as possible when I take my medication. Ans: B Feedback: Taking certain anti-inflammatory drugs can irritate the gastric mucosa and increase the risk of bleeding; therefore, by asking his or her doctor to check his or her stool for bleeding, the nurse knows that the patient is aware of this. Alcohol and crushing the tablets can interfere with anti-inflammatory metabolism. A full glass of water should be taken with this medication to increase absorption. 7. A salicylate has been prescribed for a 15-year-old patient who has been diagnosed with arthritis. The mother is concerned about giving her child a salicylate. What salicylates could the nurse tell this mother are recommended for use in children? A) Salsalate (Argesic) B) Olsalazine (Dipentum) C) Sodium thiosalicylate (generic) Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) D) Choline magnesium trisalicylate (Tricosal) Ans: D 257 Feedback: Aspirin and choline magnesium trisalicylate are the only salicylates recommended for use in children. They should not be used when any risk of Reye’s syndrome exists. Salsalate (Argesic), olsalazine (Dipentum), and sodium thiosalicylate (generic) have not been approved for pediatric use and do not provide pediatric dosing guidelines as a result. 8. A mother has brought her 6-year-old child to the clinic. The child has a fever of 102.8ºF and is diagnosed with the flu. What medication will the nurse suggest for this child? A) Etanercept (Enbrel) B) Penicillamine (Depen) C) Acetaminophen (Tylenol) D) Aspirin (Bayer) Ans: C Feedback: Acetaminophen would be the suggested medication. It is prescribed for relief of pain and fever for influenza in children. Aspirin would be contraindicated because it increases the risk for Reye’s syndrome. Etanercept and penicillamine are given for severe rheumatoid arthritis therapy. 9. A nurse is presenting an educational event for a group of new parents. One topic that the nurse addresses is the overuse of acetaminophen, which can cause liver toxicity. What would the nurse tell the parents it is important to do? A) Do not give acetaminophen (Tylenol) unless you receive a doctor’s order. B) Check the label of over-the-counter (OTC) medications carefully to watch for inclusions of acetaminophen in the ingredients. C) Monitor their child’s temperature carefully and regulate the Tylenol dose based on the fever. D) Mix OTC children’s medications to get the best coverage for their child’s symptoms. Ans: B Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 258 Feedback: Inadvertent overdose with acetaminophen frequently occurs because of the combining of OTC drugs that contain the same ingredients. Parents should be taught to carefully check the labels of OTC products and follow the dosage guidelines. A prescription is not required for acetaminophen. Dosage guidelines are the best guide to follow to prevent overdose. 10. A mother asks the nurse how acetaminophen works. What statement best describes the therapeutic action of acetaminophen? A) Acetaminophen (Tylenol) works by blocking the increase of interleukin-1. B) Acetaminophen reacts with free-floating tumor necrosis (TNF) factor released by active leukocytes. C) Acetaminophen acts directly on the hypothalamus to cause vasodilation and sweating. D) Acetaminophen is taken up by macrophages, thus inhibiting phagocytosis and release of lysosomal enzymes. Ans: C Feedback: Acetaminophen acts on the hypothalamus to cause vasodilation and sweating to reduce fever. The mechanism of action as an analgesic is not understood. Anakinra (Kineret) blocks the increased interleukin-1, which is responsible for the degradation of cartilage in rheumatoid arthritis. Etanercept (Enbrel) reacts with free-floating TNF released by active leukocytes in autoimmune inflammatory disease to prevent the damage caused by TNF. Gold compounds are taken up by macrophages, which, in turn, inhibits phagocytosis and releases lysosomal enzymes, which causes damage associated with inflammation. 11. Antipyretic drugs (e.g., aspirin, ibuprofen, acetaminophen) often are used to alleviate the discomforts of fever and to protect vulnerable organs, such as the brain, from extreme elevations in body temperature. However, the use of aspirin in children is limited due to the possibility of what disease? A) Munchausen’s syndrome B) Guillain-Barré syndrome C) Angelman’s syndrome D) Reye’s syndrome Ans: D Feedback: Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 259 Salicylates like aspirin are contraindicated for the treatment of childhood fevers because of the risk of Reye’s syndrome in children and teenagers. Munchausen’s syndrome is an unusual condition characterized by habitual pleas for treatment and hospitalization for a symptomatic but imaginary acute illness. Guillain-Barré syndrome is an idiopathic, peripheral polyneuritis that occurs 1 to 3 weeks after a mild episode of fever associated with a viral infection or with immunization. Angelman’s syndrome is an autosomal recessive syndrome characterized by jerky puppet-like movements, frequent laughter, mental and motor retardation, a peculiar open-mouthed facial expression, and seizures. Salicylates like aspirin are not contraindicated for patients with Munchausen’s syndrome, Guillain-Barré syndrome, or Angelman’s syndrome. 12. A patient has been diagnosed with severe rheumatoid arthritis and hylan G-F 20 has been ordered. How is this drug given? A) Injected into the joint B) Orally C) IM D) Sub Q Ans: A Feedback: Hyaluronidase derivatives (e.g., hylan G-F 20, sodium hyaluronate) have elastic and viscous properties. These drugs are injected directly into the joints of patients with severe rheumatoid arthritis of the knee. They seem to cushion and lubricate the joint and relieve the pain associated with degenerative arthritis. They are given weekly for 3 to 5 weeks and are not given by any other route. 13. A nurse is caring for a patient in the early stage of rheumatoid arthritis. The nurse would expect what medication classification to be used in the treatment of this patient? A) Antimalarial agents B) Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) C) Xanthine oxidase inhibitors D) Uricosuric agents Ans: B Feedback: Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 260 NSAIDs are indicated for relief of the signs and symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis, for relief of mild to moderate pain, for treatment of primary dysmenorrhea, and for fever reduction. Antimalarial agents are used in the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus. Xanthine oxidase inhibitors and uricosuric agents are used in the treatment of gout. 14. The nurse is caring for a patient who receives anakinra (Kineret) for arthritis. By what route will the nurse administer this medication? A) Into the affected joint directly B) Oral C) Intramuscular D) Subcutaneous Ans: D Feedback: Anakinra is administered subcutaneously every day and is often used in combination with other antiarthritis drugs. No other route is appropriate. 15. The nurse is preparing to administer a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) to an older patient. What NSAID is associated with increased toxicity and should be avoided if possible? A) Naproxen (Aleve) B) Ibuprofen (Motrin) C) Indomethacin (Indocin) D) Etodolac (Lodine) Ans: A Feedback: Geriatric warnings have been associated with naproxen, ketorolac, and ketoprofen because of reports of increased toxicity when they are used by older patients. These NSAIDs should be avoided in this population if possible. No such warnings exist for ibuprofen, indomethacin, or etodolac. 16. What medication used to treat rheumatic arthritis not only has anti-inflammatory effects but is also used in premature infants to close a patent ductus arteriosus? Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) A) Penicillamine B) Indomethacin C) Antimalarials D) Prednisone Ans: B 261 Feedback: Indomethacin given IV is used in premature infants to close a patent ductus arteriosus and avoid a surgical procedure. Penicillamine, antimalarials, and prednisone are not used for this purpose. 17. When the nurse learns that the patient with rheumatic arthritis is complaining of stomatitis, the nurse should further assess the patient for the adverse effects of what medication? A) Corticosteroids B) Gold-containing compounds C) Antimalarials D) Salicylate therapy Ans: B Feedback: Various adverse effects are common with the use of gold salts and are probably related to their deposition in the tissues and effects at that local level: stomatitis, glossitis, gingivitis, pharyngitis, laryngitis, colitis, diarrhea, and other GI inflammation; gold-related bronchitis and interstitial pneumonitis; bone marrow depression; vaginitis and nephrotic syndrome; dermatitis, pruritus, and exfoliative dermatitis; and allergic reactions ranging from flushing, fainting, and dizziness to anaphylactic shock. The disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (DMARD) category of antimalarials may cause visual changes, GI upset, rash, headaches, photosensitivity, and bleaching of hair. Tinnitus is associated with salicylate therapy. Hirsutism is associated with corticosteroid therapy. 18. A patient with rheumatoid arthritis is taking gold salts. What drugs should the nurse teach this patient that are contraindicated when taking gold salts? (Select all that apply.) A) Antimalarials B) Cytotoxic drugs Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) C) Salicylates D) Penicillamine E) Anticoagulants Ans: A, B, D 262 Feedback: These drugs should not be combined with penicillamine, antimalarials, cytotoxic drugs, or immunosuppressive agents other than low-dose corticosteroids because of the potential for severe toxicity. No contraindication exists for therapy involving gold salts and salicylates or anticoagulants. 19. The nurse teaches a patient with rheumatic disease who is being prescribed salicylate therapy to monitor himself or herself for what? A) Tinnitus B) Visual changes C) Stomatitis D) Hirsutism Ans: A Feedback: Tinnitus is associated with salicylates. The disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (DMARD) category of antimalarials may cause visual changes, GI upset, skin rash, headaches, photosensitivity, and bleaching of hair. Eighth cranial nerve damage and stomatitis are associated with gold therapy. Hirsutism is associated with corticosteroid therapy. 20. The nurse assesses laboratory results related to blood clotting when the assigned patient takes what drug regularly? (Select all that apply.) A) Salicylates B) Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) C) Gold compounds D) Acetaminophen Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) E) Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) Ans: A, B 263 Feedback: Salicylates and NSAIDs can both inhibit blood clotting resulting in bleeding if not monitored. Gold compounds, acetaminophen, and DMARDs do not have a known impact on blood clotting. 21. What is chrysotherapy? A) Treatment with antimalarials B) Treatment with salicylates C) Treatment with disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) D) Treatment with gold salts Ans: D Feedback: Chrysotherapy is the clinical name for treatment with gold salts in which gold is taken up by macrophages, which then inhibit phagocytosis. It is reserved for use in patients who are unresponsive to conventional therapy and can be very toxic. Options A, B, and C are incorrect. 22. What drugs used to treat rheumatoid arthritis are contraindicated in a patient who has a history of toxic levels of heavy metals? A) Gold salts B) COX-2 inhibitors C) Propionic acids D) Fenamates Ans: A Feedback: Gold salts can be extremely toxic and are contraindicated in the presence of any known allergy to gold, severe diabetes mellitus, congestive heart failure, severe debilitation, renal or hepatic impairment, Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 264 hypertension, blood dyscrasias, recent radiation treatment, history of toxic levels of heavy metals, and pregnancy or lactation. COX-2 inhibitors, propionic acids, and fenamates have no contraindications related to prior toxic levels of heavy metals. 23. Which of these anti-inflammatory drugs have geriatric warnings? (Select all that apply.) A) Sulindac (Clinoril) B) Indomethacin (Indocin) C) Ketorolac (Toradol) D) Naproxen (Naprosyn) E) Ketoprofen (Orudis) Ans: C, D, E Feedback: Geriatric warnings have been associated with naproxen, ketorolac, and ketoprofen because of reports of increased toxicity when they are used by older patients. These nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs should be avoided if possible. Sulindac and indomethacin are not associated with toxicity in older patients. 24. A patient presents at the emergency department complaining of dizziness, mental confusion, and difficulty hearing. What should the nurse suspect is wrong with the patient? A) Anakinra toxicity B) Ibuprofen toxicity C) Salicylism D) Acetaminophen toxicity Ans: C Feedback: Salicylism can occur with high dosage of aspirin. Dizziness, ringing in the ears, difficulty hearing, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, mental confusion, and lassitude can occur. This combination of adverse effects is not associated with anakinra toxicity, ibuprofen toxicity, or acetaminophen toxicity. 25. A mother brings her 3-year-old child to the emergency department telling the nurse the child has eaten Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 265 a bottle of baby aspirin. The mother cannot tell the nurse how many tablets were in the bottle. What dose of salicylate would be toxic in a child? A) 2g B) 3g C) 4g D) 5g Ans: C Feedback: Acute salicylate toxicity may occur at doses of 20 to 25 g in adults or 4 g in children. Therefore, options A, B, and D are incorrect. 26. A patient arrives at the emergency department brought by his or her friends. The friends tell the nurse that the patient has taken a whole bottle of aspirin. Blood work for salicylate toxicity is run. What does the nurse expect the results to be? A) >5 g B) >10 g C) >15 g D) >20 g Ans: D Feedback: Acute salicylate toxicity may occur at doses of 20 to 25 g in adults or 4 g in children. Options A, B, and C would not be high enough to indicate salicylate toxicity. 27. The nursing instructor is discussing COX-2 inhibitors with her nursing students. Where would the instructor tell her students that COX-2 inhibitors work? A) At sites of trauma and injury B) Wherever prostaglandins are present Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) C) At the sites of blood clotting D) In the kidney Ans: A 266 Feedback: The COX-2 inhibitors are thought to act only at sites of trauma and injury to more specifically block the inflammatory reaction. COX-1 is present in all tissues and seems to be involved in many body functions including blood clotting, protecting the stomach lining, and maintaining sodium and water balance in the kidney. 28. The clinic nurse is caring for a patient who is taking a COX-2 inhibitor and knows that this patient needs to be assessed for what? (Select all that apply.) A) Bleeding time B) Liver function C) Altered hearing D) Gastrointestinal (GI) effects E) Water retention Ans: A, D, E Feedback: COX-2 inhibitors have an impact on many body functions and patients receiving this therapy should be assessed for GI effects, changes in bleeding time, and water retention. Patients taking COX-2 inhibitors do not need to be evaluated for liver function or altered hearing because these are not common adverse effects. 29. Why do COX-2 inhibitors increase the risk for cardiovascular problems? (Select all that apply.) A) Vasoconstriction is blocked. B) Vasodilation is blocked. C) Platelet clumping is blocked. D) Water and sodium balance is altered. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) E) Gastrointestinal (GI) integrity is altered. Ans: B, C 267 Feedback: Recent studies suggest that COX-2 inhibitors may block some protective responses in the body, such as vasodilation and inhibited platelet clumping, which is protective if vessel narrowing or blockage occurs. Blocking this effect could lead to cardiovascular problems. Vasoconstriction is not blocked, water and sodium balance is not altered, and GI integrity is not impacted by COX-2 inhibitors but can be impacted by COX-1 inhibitors. 30. When nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are combined with loop diuretics, there is a potential for what? A) Decreased antihypertensive effect B) Decreased diuretic effect C) Lithium toxicity D) Anaphylactoid reactions Ans: B Feedback: Diuretic effect is often decreased when NSAIDs are taken with loop diuretics. There is a potential for decreased antihypertensive effect of beta-blockers if NSAIDs are combined and there have also been reports of lithium toxicity, especially when lithium is combined with ibuprofen. 31. The nurse is caring for a patient who reports taking 800 mg of ibuprofen three times a day for relief of menstrual cramps. What lab results will the nurse find most significant in assessing this patient? A) Complete blood count B) White blood cell differential C) Arterial blood gas D) Cholesterol and triglyceride profile Ans: A Feedback: Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 268 Ibuprofen, like all nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, can cause irritation to the GI mucosa and block platelet clumping, both of which can result in bleeding. Blood loss due to dysmenorrhea can exacerbate these risks so it is important to assess the complete blood count to monitor for excessive blood loss. White blood cell differential would be impacted by infection, which is not indicated here. Arterial blood gas, cholesterol, and triglyceride levels would not be impacted by ibuprofen. 32. When caring for a patient diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis, the patient tells the nurse that he or she has had insufficient response to nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and his or her condition continues to worsen. What drug does the nurse anticipate will be ordered next for this patient? A) Auranofin (Ridaura) B) Ibuprofen (Motrin) C) Acetaminophen (Tylenol) D) Ketorolac (Toradol) Ans: A Feedback: Gold compounds such as auranofin are prescribed when more usual anti-inflammatory therapies are ineffective and the patient’s condition worsens despite weeks or months of standard pharmacological treatment. Ibuprofen and ketorolac are NSAIDs, which have been tried without good results. Acetaminophen is not an anti-inflammatory and would not be appropriate to control this patient’s condition. 33. The patient has been diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis. She also reports pain in various muscle groups secondary to a diagnosis of fibromyalgia and dysmenorrhea with painful cramping during menses. What drug would be most effective in treating all three of this patient’s problems? A) Naproxen (Naprosyn) B) Acetaminophen (Tylenol) C) Etanercept (Enbrel) D) Sodium hyaluronate (Hyalgan) Ans: A Feedback: Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 269 Naproxen is effective in treating muscle pain, arthritis, and dysmenorrhea. Acetaminophen has no antiinflammatory effects and would not be helpful for treating arthritis or dysmenorrhea other than some pain relief. Etanercept is useful only for treating rheumatoid arthritis; sodium hyaluronate is used to treat rheumatoid arthritis when other traditional treatment has been ineffective and the condition continues to worsen. 34. The nurse is teaching the patient, who has been newly prescribed etanercept (Enbrel), how to administer the medication. What statement is accurate? A) Be sure to drink a whole glass of water when swallowing the pill. B) Do not take this medication for at least 1 hour after taking an antacid. C) You can use each of the subcutaneous injection sites to avoid tissue damage. D) Inject this medication deeply into the muscle to promote absorption. Ans: C Feedback: Etanercept is given by injecting it into the subcutaneous tissues. The injection sites should be rotated to avoid tissue damage. Because it is not taken orally, there is no requirement related to amount of water to be taken or waiting an hour after taking an antacid. Etanercept is not injected into the muscle but rather into the subcutaneous tissue. 35. The pediatric patient has a fever and the nurse is preparing to administer an antipyretic. What drug would be the best choice for this patient? A) Balsalazide (Colazal) B) Naproxen (Naprosyn) C) Indomethacin (Indocin) D) Aspirin Ans: B Feedback: Naproxen is approved for pediatric use and has antipyretic properties. Balsalazide is used to treat ulcerative colitis and would not be appropriate for treating a fever. Indomethacin has anti-inflammatory effects but does not have antipyretic effects. Aspirin would not be appropriate for treating a child with a fever of unknown origin due to risk of Reye’s syndrome. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 270 Chapter 17 - Immune Modulators 1. A patient has been diagnosed with hairy cell leukemia. The patient is to begin taking interferon alfa 2b. What will the nurse include in her instructions to the patient concerning this drug? A) Avoid drinking alcohol while taking the drug. B) Continue to maintain maximal physical activity. C) Increase fluid intake while taking the drug. D) Treat constipation with over-the-counter laxatives. Ans: C Feedback: Interferon alfa 2b is metabolized in the kidney so adequate fluid intake is needed to promote metabolism and excretion of the drug as well as to minimize common adverse effects including dry skin and dizziness. Maintaining maximal physical activity is a good idea but has no relationship to the use of the drug. Fluids should be increased not decreased while taking the drug. Constipation is not an associated adverse effect of this medication. 2. The health care provider plans to inject an interferon directly into the patient’s wart. What interferon will the nurse prepare? A) Interferon alfa 2a (Roferon-A) B) Interferon alfacon 1 (Infergen) C) Interferon alfa n3 (Alferon N) D) Interferon beta 1a (Avonex) Ans: C Feedback: Interferon alf n3 is used for intralesional treatment of warts. Interferon alfa 2a is used in the treatment of leukemia. Interferon alfacon 1 is used in the treatment of chronic hepatitis C infection in adults. Interferon beta 1a is used to treat multiple sclerosis in adults. 3. A 30-year-old woman has been diagnosed with leukemia and will be using an immune modulator for treatment. What will be important to discuss with the patient when the nurse provides patient teaching Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 271 about her treatment? A) The need to continue oral contraceptives B) The need to use barrier contraceptives while taking the drug C) The need to avoid sexual intercourse while taking the drug D) The importance of taking an aspirin daily to decrease the adverse effects of the drug Ans: B Feedback: A patient taking an immune modulator would be advised to use barrier contraceptives to prevent pregnancy. The interaction of the immune modulator and the oral contraceptive may interfere with the oral contraceptive’s ability to work properly. Asking patients to avoid sexual intercourse is not necessary if barrier methods are properly used. Daily aspirin would not decrease adverse effects of this drug. 4. The nurse has an order to administer oprelvekin (Neumega) to a patient for the first time. Before administering the drug, what allergy would the nurse want to specifically question the patient about? A) Egg products B) Escherichia coliproduced products C) Lactose intolerance D) Penicillin Ans: B Feedback: The interleukins are produced using deoxyribonucleic acid technology and E. coli bacteria. Patients with known allergy to E. coli products should not receive oprelvekin. The allergies to penicillin, egg products, or lactose intolerance would not be of concern with this drug. 5. The physician has decided to prescribe T- and B-cell suppressors for a patient diagnosed with psoriasis. What drug will be ordered for this patient? A) Alefacept (Amevive) B) Azathioprine (Imuran) Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) C) Cyclosporine (Neoral) D) Glatiramer acetate (Copaxone) Ans: A 272 Feedback: Alefacept is prescribed for patients with severe chronic plaque psoriasis. Cyclosporine is used to suppress rejection in a variety of transplant situations. Azathioprine is used to treat patients with rheumatoid arthritis and in prevention of rejection in renal homotransplants. Tacrolimus is used for prevention of rejection after renal or liver transplantation. 6. A patient who is receiving an immune suppressant has been admitted to the unit. What would be a priority action by the nurse? A) Monitor nutritional status. B) Provide patient teaching regarding the drug. C) Protect the patient from exposure to infection. D) Provide support and comfort measures in relation to adverse effects of the drug. Ans: C Feedback: Patients taking immune suppressant drugs are more susceptible to infection because the patient’s normal body defenses will be diminished. As a result, the priority action by the nurse would to protect the patient from exposure to infection through room selection, good hand hygiene, and taking care to avoid exposure to sick staff members. Teaching will need to include avoiding crowded places and people with known infection and those working in soil. Nutritional status is important as are comfort and support measures and other instructions concerning the drug. However, protecting the patient from infection should be the priority action. 7. A nurse is discussing interferon alfa 2b with a patient. What will the nurse encourage the patient to do while taking this drug? A) To avoid crowds B) To increase salt intake C) To decrease milk intake Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) D) To eat three meals a day Ans: A 273 Feedback: Potential adverse effects in addition to the types of conditions interferon alfa 2b is prescribed to contribute to the need for the patient to take care to avoid people with infections so the patient should be taught to avoid crowds whenever possible. Adverse effects include dizziness, confusion, rash, dry skin, anorexia, nausea, bone marrow suppression, and flu-like syndrome. Salt, diet, and milk do not interfere with this drug. 8. A 70-year-old patient with acute myelocytic leukemia is receiving sargramostim (Leukine). What is a priority nursing action for this patient? A) Providing a quiet environment B) Increasing fluids C) Providing comfort measures related to nausea D) Encouraging appropriate dietary intake Ans: B Feedback: A common adverse effect of this drug is vomiting and diarrhea. Due to the patient’s age it would be important to keep him hydrated. Vomiting and diarrhea can cause dehydration quickly in the elderly. Providing a quiet environment and comfort measures for the nausea would be important but not as critical as increasing fluids. Diet is very important to this patient; however, usually this drug causes a loss of appetite. Therefore, increasing fluids would be extremely important to the patient’s nutritional status. 9. The nurse is caring for a patient in the immediate postoperative period following cardiac transplantation who is receiving mycophenolate (CellCept) twice a day IV. What will the nurse teach the patient regarding drug therapy? (Select all that apply.) A) The drug will be given orally as soon as possible. B) Take the medication three times a day. C) Avoid people with contagious diseases. D) Ask a pharmacist about drugdrug interactions before taking any over-the-counter (OTC) drug. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) E) Never miss a dose of medication. Ans: A, C, D, E 274 Feedback: The nurse will explain that the IV medication will be changed to oral therapy when the patient is able to tolerate oral medications. The patient will take the medication twice a day, not three times a day. Care should be taken to never miss a dose. The patient should avoid other medications that are hepatotoxic or nephrotoxic due to a risk of increased toxicity so the patient should be taught to always consult a doctor or pharmacist before beginning an OTC drug. Patients who have immune suppression must be taught how to reduce risk of infection, including avoiding people with contagious diseases, such as colds or viruses. 10. The nurse administers aldesleukin to a patient diagnosed with renal cell carcinoma. When assessing the patient a few days later, what abnormal findings would the nurse attribute to the medication? (Select all that apply.) A) Increased lymphocyte count B) Increased red blood cell count C) Increased platelet count D) Irregular pulse rate E) Increased blood pressure Ans: A, C, D Feedback: Aldesleukin activates human cellular immunity and inhibits tumor growth through increases in lymphocytes, platelets, and cytokines. Common adverse effects include hypotension, sinus tachycardia, arrhythmias, as well as pruritus, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, anorexia, GI bleeding, bone marrow suppression, respiratory difficulties, fever, chills, pain, mental status changes, and dizziness. There is no impact on red blood cell count. It does not raise blood pressure. 11. While studying for a pharmacology test, a student asks his peers about interferons. What statement about interferons is accurate? A) They stimulate B-lymphocyte activity. B) They interfere with multiplication of stem cells. C) They stimulate growth and differentiation of lymphoid cells into lymphocytes. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) D) They interfere with the ability of viruses in infected cells to replicate. Ans: D 275 Feedback: Interferons are substances naturally produced and released by human cells that have been invaded by viruses. They may also be released from cells in response to other stimuli, such as cytotoxic T-cell activity. Interferons do not stimulate B-lymphocyte activity, interfere with multiplication of stem cells, nor do they stimulate growth and differentiation of lymphoid cells into lymphocytes. 12. How do immune suppressants work when ordered for a patient who has had an organ transplant? A) Blocking normal effects of the immune system B) Stimulating immune system to fight off infection C) Working with corticosteroids to enhance healing D) Working with corticosteroids to promote suppressor cells Ans: A Feedback: Immune suppressants are used to block the normal effects of the immune system in cases of organ transplantation (in which nonself-cells are transplanted into the body and destroyed by the immune reaction) and in autoimmune disorders (in which the body’s defenses recognize self-cells as foreign and work to destroy them) in some cancers. Options B, C, and D are distracters for this question. 13. A patient has just been told that her cancer has metastasized to her right kidney. An interferon (Aldesleukin) has been prescribed to treat this metastasis. The patient asks why this interferon is ordered. What is the nurse’s best response? A) Aldesleukin has been shown to protect autologous tumor cells. B) Aldesleukin has been shown to inhibit tumor growth. C) Aldesleukin has been shown to enhance allogeneic stem-cell transplantation. D) Aldesleukin has been shown to have a direct proliferative effect on renal tumors. Ans: B Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 276 Feedback: Aldesleukin is prescribed for metastatic renal cell carcinoma in adults and treatment of metastatic melanomas (orphan drug use) working by activating human cellular immunity and inhibiting tumor growth through increases in lymphocytes, platelets, and cytokines. Aldesleukin does not protect autologous tumor cells, enhance allogeneic stem-cell transplantation, or have a direct proliferative effect on renal tumors. 14. The nurse admits a patient who was newly diagnosed with Kaposi’s sarcoma to the unit. The physician has ordered an IV infusion of an interferon. What drug would be appropriate? A) Interferon beta1a B) Interferon gamma 1b C) Interferon alfa 2b D) Peginterferon alfa 2b Ans: C Feedback: Interferon alfa 2b indications include hairy cell leukemia, melanoma, AIDS-related Kaposi’s sarcoma, chronic hepatitis B and C infection, intralesional treatment of condyloma acuminatum in patients 18 years of age or older. No other interferons are indicated for treatment of Kaposi’s sarcoma. 15. The pharmacology instructor is talking about interferon. The instructor explains that agents, such as interferons, have more than one biologic function. What are the functions of interferons? (Select all that apply.) A) Antibacterial B) Antiviral C) Immunomodulatory D) Antiproliferative E) Anticancer Ans: B, C, D Feedback: Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 277 Interferons act to prevent virus particles from replicating inside the cells. They also stimulate interferon receptor sites on noninvaded cells to produce antiviral proteins, which prevent viruses from entering the cell. In addition, interferons have been found to inhibit tumor growth and replication, to stimulate cytotoxic T-cell activity, and to enhance the inflammatory response. Options A and E are incorrect. 16. The nursing class is studying monoclonal antibodies. What monoclonal antibody reacts to human T cells, disabling them and acting as an immune suppressor? A) Adalimumab B) Cetuximab C) Rituximab D) Muromonab-CD3 Ans: D Feedback: Muromonab-CD3, the first monoclonal antibody approved for use, is a T-cellspecific antibody, that is available as an IV agent. It reacts as an antibody to human T cells, disabling the T cells, acting as an immune suppressor. Adalimumab is an antibody specific for human tumor necrosis factor. Cetuximab is an antibody specific to epidermal growth factor receptor sites. Rituximab is an antibody specific to sites on activated B lymphocytes. 17. What monoclonal antibody is used to prevent respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) in high risk children? A) Palivizumab B) Natalizumab C) Belimumab D) Eculizumab Ans: A Feedback: Palivizumab is specific to the antigenic site on respiratory syncytial virus (RSV); it inactivates that virus. It is used to prevent RSV disease in high-risk children. Natalizumab is an antibody specific to surface receptors on all leukocytes except neutrophils. Belimumab is a specific inhibitor of Blymphocyte stimulator that inhibits the survival of B-lymphocytes and their differentiation into immune-globulin producing cells. Eculizumab binds to complement proteins and prevents the formation of the complement complex. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 18. 278 The nurse is caring for a patient with an allograft transplant. The physician orders a monoclonal antibody to prevent rejection of the transplant. What monoclonal antibody would the nurse expect to be ordered? A) Alemtuzumab B) Daclizumab C) Erlotinib D) Omalizumab Ans: B Feedback: Daclizumab is specific to interleukin-2 receptor sites on activated T lymphocytes; it reacts with those sites and blocks cellular response to allograft transplants. Alemtuzumab is an antibody specific for lymphocyte receptor sites used to treat chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients who have been treated with alkylating agents and have been failed by fludarabine therapy. Erlotinib is effective against specific malignant receptor sites. Omalizumab is an antibody to immunoglobulin E, an important factor in allergic reactions. 19. The pharmacology instructor is explaining interleukins to the class. What would be the best definition of interleukins? A) They are substances naturally produced and released by human cells that have been invaded by viruses. B) They block the inflammatory reaction and decrease initial damage to cells. C) They are chemicals used to communicate between leukocytes and stimulate immunity. D) They attach to specific receptor sites and respond to very specific situations. Ans: C Feedback: Interleukins are chemicals produced by T cells to communicate between leukocytes and stimulate cellular immunity and inhibit tumor growth. Immune suppressants block the inflammatory reaction and decrease initial damage to cells. Interferons are naturally produced and released by human cells that have been invaded by viruses. Monoclonal antibodies attach to specific receptor sites and respond to very specific situations. 20. The nurse is caring for a female patient, aged 62, who has been admitted for treatment of metastatic Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 279 melanoma. What agent would the nurse anticipate the physician is likely to order? A) Aldesleukin B) Interferon alfa 2b C) Cyclosporine D) Ipilimumab Ans: D Feedback: Ipilimumab is a human cytotoxic T-cell antigen-4 blocking antibody. By blocking this site, T cells are activated and proliferate at a faster rate. It is used to treat patients with unresectable or metastatic melanoma. Aldesleukin is an interleukin, used for metastatic renal cell carcinoma in adults; a treatment of metastatic melanomas. Interferon alfa 2b is indicated for hairy cell leukemia, melanoma, AIDSrelated Kaposi’s sarcoma, chronic hepatitis B and C infections, intralesional treatment of condyloma acuminatum in patients 18 years of age or older. Cyclosporine is a T and B cell suppressor and is indicated for prophylaxis for organ rejection in kidney, liver, and heart transplants (used with corticosteroids); treatment of chronic rejection in patients previously treated with other immunosuppressants; treatment of rheumatoid arthritis; and recalcitrant psoriasis. 21. While studying the T- and B-cell immune suppressors, the nursing students learn that the most commonly used immune suppressant is what? A) Cyclosporine (Sandimmune) B) Azathioprine (Imuran) C) Pimecrolimus (Elidel) D) Glatiramer (Copaxone) Ans: A Feedback: Several T- and B-cell immune suppressors are available for use. Of the numerous agents available, cyclosporine is the most commonly used immune suppressant. Options B, C, and D are all T- and Bcell immune suppressors, they are simply not the most commonly prescribed. 22. What interleukin receptor antagonist would the nurse anticipate is most likely to be ordered for a patient, 25 years old, who has not responded to traditional antirheumatic drugs? Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) A) Natalizumab (Tysabri) B) Anakinra (Kineret) C) Eculizumab (Soliris) D) Adalimumab (Humira) Ans: B 280 Feedback: Anakinra is used to reduce the signs and symptoms of moderately to severely active rheumatoid arthritis in patients 18 years of age and older who have not responded to the traditional antirheumatic drugs. Options A, C, and D are monoclonal antibodies, therefore they are incorrect answers. 23. A patient with chronic hepatitis C has been prescribed peginterferon alfa 2b (PEG-INTRON). By what route would the nurse administer this drug? A) Subcutaneously (SQ) B) Intramuscularly (IM) C) Intralesionally (IL) D) Orally Ans: A Feedback: PEG-INTRON, like many of the interferons, is administered subcutaneously. Avonex is given intramuscularly. Interferon alfa n3 is given intralesionally. There are no interferons given orally. 24. The patient has arrived in the short stay unit for an infusion of tositumomab with 131 tositumomab (Bexxar). Before beginning the infusion, the nurse assesses the patient’s vital signs and finds the patient has a temperature of 101.5ºF, What is the nurse’s priority action? A) Holding the infusion until patient is afebrile B) Notifying the physician C) Starting the infusion and inform the physician Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) D) Treating the fever before beginning the therapy Ans: D 281 Feedback: Monoclonal antibodies should be used cautiously with fever (treat the fever before beginning therapy). This makes Options A, B, and C incorrect. 25. A 72-year-old male patient has arrived at the outpatient unit to receive an infusion of alemtuzumab (Compath). The patient tells the nurse this is the second time his chronic lymphocytic leukemia has relapsed and the second time he will receive this drug because he failed alemtuzumab therapy after being treated with an alkylating agent. What is the priority nursing action? A) Calling the physician and questioning the order B) Washing your hands C) Beginning an intravenous infusion D) Canceling the infusion Ans: A Feedback: Monoclonal antibodies should be used cautiously in patients who have had previous administration of the monoclonal antibody (serious hypersensitivity reactions can occur with repeat administration). The nursing priority would be to question the order because the patient has already received alemtuzumab (Compath) previously and if the order is verified, this patient should be monitored very carefully, perhaps starting to infuse more slowly until the patient’s reaction can be determined. Only after questioning the order and having it verified would the nurse perform hand hygiene and begin the infusion. 26. The nurse is writing a plan of care for a patient receiving immune suppressants for leukemia. What would be an appropriate nursing diagnosis for this patient? A) Anxiety related to diagnosis and drug therapy B) Acute pain related to central nervous system (CNS), gastrointestinal (GI), and flu-like effects C) Risk for infection related to immune stimulation D) Imbalanced nutrition: More than body requirements Ans: B Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 282 Feedback: Nursing diagnoses related to drug therapy might include: Acute pain related to CNS, GI, and flu-like effects. Anxiety related to diagnosis and drug therapy is a nursing diagnosis for a patient on an immune stimulant. There is no risk for infection related to immune stimulation unless an adverse effect occurs. Imbalanced nutrition would be less than body requirements due to flu-like symptoms resulting in diminished appetite. 27. The nurse is preparing a patient to receive immunosuppressant drugs on an outpatient basis. What is the priority for the nurse to arrange for this patient in the home environment? A) A caregiver who is skilled in cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) B) A caregiver who will provide adequate nutrition C) Supportive care and comfort measures D) Arrange for a home care nurse to administer injections Ans: C Feedback: Arrange for supportive care and comfort measures for flu-like symptoms (rest, environmental control, acetaminophen) to decrease patient discomfort and increase therapeutic compliance. Patients may also need support and comfort measures related to diagnosis and drug therapy. Although knowledge of CPR and providing appropriate nutrition are always positive actions, they are not related to administration of immunosuppressants. The patient or caregiver can be taught to administer injections unless the medication is to be given IV, in which case the patient would go to an infusion center. 28. The nurse is caring for a patient who has a diagnosis of chronic hepatitis B infection and has been prescribed an immune stimulant. After teaching the patient about the treatment plan, how might the nurse evaluate the effectiveness of teaching? A) The patient can state where to go to get the medication. B) The patient can state who will administer the medication. C) The patient can state what positive effects to watch for. D) The patient can state specific measures to avoid adverse effects. Ans: D Feedback: Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 283 The nurse would evaluate that the teaching plan was successful if the patient can name drug, dosage, adverse effects to watch for, and specific measures to avoid adverse effects. Knowing where to get the medication, who will administer it, and the positive effects to watch for would not be an adequate assessment of the teaching plan. 29. The patient underwent an allograft renal transplant 48 hours earlier and is showing signs of rejection. What drug would the nurse expect the physician to order? A) Muromonab B) Anakinra C) Mycophenolate D) Sirolimus Ans: A Feedback: Muromonab is indicated for the treatment of acute allograft rejection in patients undergoing renal transplantation. It also is indicated for the treatment of steroid-resistant acute allograft rejection in those receiving heart or liver transplants. Anakinra, mycophenolate, and sirolimus are useful for preventing renal or liver transplant rejection. 30. The nurse, working with a nursing student, is caring for a patient who is to receive interleukins. The student nurse asks you what happens physiologically when a patient receives interleukins. What is the nurse’s best response? A) It really helps the patient! B) The patient has increases in the number of natural killer cells. C) The patient has decreased cytokine activity. D) The patient gets really sick from flu-like symptoms and then they get better. Ans: B Feedback: When interleukins are administered, there are increases in the numbers of natural killer cells and lymphocytes, in cytokine activity, and in the number of circulating platelets. Options A, C, and D are incorrect. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 31. 284 The nurse is caring for a child requiring cyclosporine to prevent rejection. Cyclosporine is given to adults using a dosage of 15 mg/kg. The nurse calculates the child’s dosage is 20 mg/kg. What is the nurse’s priority action? A) Administer the drug. B) Hold the dose and question the ordering provider. C) Complete an incident report if this dosage has already been given before. D) Notify the nursing supervisor of the medication error. Ans: A Feedback: The nurse would administer the medication as ordered because doses larger than those given to adults are often needed when cyclosporine is administered to children. This is not an error so the nurse would not hold the drug, question the provider, complete an incident report, or notify the nursing supervisor. 32. When caring for older adults receiving immune modulators, what are the nurse’s priorities of care? (Select all that apply.) A) Assess carefully for infection. B) Obtain baseline liver function studies and monitor follow-up studies. C) Determine dosage based on renal and liver function. D) Minimize teaching to avoid causing confusion. E) Encourage the family to visit often, especially young children. Ans: A, B, C Feedback: Older patients may be more susceptible to the effects of the immune modulators, partly because the aging immune system is less efficient and less responsive. These patients need to be monitored closely for infection, GI, renal, hepatic, and central nervous system effects. Baseline renal and liver function tests can help to determine whether a decreased dosage will be needed before beginning therapy. Because these patients are more susceptible to infection, they need to receive extensive teaching, not less teaching, about ways to avoid infection and injury. Contact with young children and large groups of people increase the risk of infection. 33. The nurse teaches the female patient receiving immune modulating drugs about the need to use barrier Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 285 contraceptives. The patient says, I hate using barrier contraceptives. Why can’t I just take oral contraceptives? What is the nurse’s best response? A) Effects of oral contraceptives may be altered by liver changes or changes in immune response. B) Oral contraceptives increase the action of immune modulating drugs so dosage needs to be reduced. C) Immune modulators make oral contraceptives ineffective because of hormonal impact of drugs. D) Oral contraceptives are acceptable if barrier contraceptives are distasteful, but only high-estrogen pills can be used. Ans: A Feedback: The use of barrier contraceptives is advised because the effects of oral contraceptives may be altered by liver changes or by changes in the body’s immune response, potentially resulting in unexpected pregnancy. The other options conflict with this information and are incorrect. 34. The nurse is caring for a young adult woman taking immune modulating medications who has been advised to use barrier contraceptives but she wants to start her family. What information can the nurse provide about these drugs to help this patient with her decision-making? A) Discuss the desire to start a family with the provider so risk can be minimized. B) Immune modulating drugs will need to be discontinued if pregnancy occurs. C) Immune modulating drugs have been proven to be highly teratogenic. D) Pregnancy is not an option when taking immune modulating drugs but adoption is an option. Ans: A Feedback: If a patient taking immune modulators becomes pregnant or decides that she wants to become pregnant, she should discuss this with her health care provider and review the risks associated with use of the drug or drugs being taken. Monoclonal antibodies should be used with caution during pregnancy and lactation. Because results of long-term studies of most of these drugs are not yet available, it may be prudent to advise patients taking these drugs to avoid pregnancy if possible. Immune modulating drugs do not need to be discontinued, but the safest drug should be prescribed. Most immune modulating drugs have not been studied and there is not enough information to know whether they are teratogenic. The nurse cannot tell a patient that pregnancy is not an option. 35. The nurse is caring for a patient diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) who recently underwent a Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 286 liver transplant. What immunosuppressant could this patient be prescribed that would treat both diagnoses? A) Anakinra (Kineret) B) Adalimumab (Humira) C) Sirolimus (Rapamune) D) Cyclosporine (Sandimmune) Ans: A Feedback: Anakinra is used to prevent rejection after kidney or liver transplantation and also reduces signs and symptoms of RA in patients who have had inadequate response to other drugs. Adalimumab would be effective for the patient’s RA but would not prevent rejection of the transplanted liver. Sirolimus is used to prevent rejection of kidney transplants but would not be effective for either of the patient’s diagnoses. Cyclosporine would be appropriate to prevent liver rejection but would not treat RA. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 287 Chapter 18 - Vaccines and Sera 1. The nursing instructor is discussing immunity with her clinical group. What statement would the instructor make that would be accurate about immunity? A) Active immunity occurs with injected antibodies that react with specific antigens. B) Serum sickness results when the body fights antibodies injected as a form of active immunity. C) Passive immunity occurs when foreign proteins are recognized and the body produces antibodies. D) Passive immunity is limited, lasting only as long as the antibodies circulate. Ans: D Feedback: Unlike active immunity, passive immunity is limited. It lasts only as long as the circulating antibodies last because the body does not produce its own antibodies as found in active immunity. People are born with active immunity in which the body recognizes a foreign protein and begins producing antibodies to react with specific proteins or antigens. Serum sickness is a massive immune reaction against the injected antibodies that occur with passive immunity. 2. A mother brings her 18-month-old child into the clinic for a well-baby check-up. A nurse will administer measles, mumps, and rubella vaccine (MMR) to the child. What dosage will the nurse administer? A) 1.0 mL subcutaneously B) 0.75 mL subcutaneously C) 0.5 mL subcutaneously D) 0.25 mL subcutaneously Ans: C Feedback: The nurse will administer 0.5 mL. This is the recommended dose for adults and children older than 15 months of age. 3. A public health nurse is on a mission trip to Africa where she is administering Dryvax. The patient asks the purpose of this drug and the nurse explains it will prevent what? Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) A) Yellow fever B) Smallpox C) Chickenpox D) Rabies Ans: B 288 Feedback: Dryvax is the immunization for smallpox disease. Varivax is the immunization for chickenpox infection. YF-Vax is the immunization for yellow fever and RabAvert is the immunization for rabies. 4. The mother of a newborn is learning about immunization schedules. The nurse tells this mother her child will ideally receive the immunization for measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) on what schedule? A) 2 months, 4 months, between 6 and 18 months, and between 4 and 6 years B) 2 months, 4 months, 6 months, and between 12 and 15 months C) Between 12 and 15 months and between 4 and 6 years D) Between 24 months and 18 years of age Ans: C Feedback: The recommended schedule for the MMR is the first dose between 12 and 15 months and the second dose between 4 and 6 years. The schedule for inactivated poliovirus is 2 and 4 months, between 6 and 18 months, and between 4 and 6 years. Immunization for Haemophilus influenzae is 2, 4, and 6 months and between 12 and 15 months. The schedule for hepatitis A is between 24 months and 18 years of age. 5. A 14-year-old boy is brought to the clinic by his mother. The patient has a note from his basketball coach explaining that a member of the team has been diagnosed with hepatitis A infection. The nurse notes that the patient has an extensive list of allergies. What is the nurse’s priority action when administering the immune globulin? A) Perform a hepatitis A antibody check. B) Monitor the patient carefully and have emergency equipment ready if needed. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) C) Apply ice to the injection site to slow the absorption of the serum. D) Give the patient aspirin and a corticosteroid before the injection to modulate reaction. Ans: B 289 Feedback: If a patient has known allergies, it is important to monitor the patient carefully and have emergency equipment ready if needed after injection of proteins such as immune globulin. Severe allergic reactions, including anaphylaxis, could occur. Ice would slow absorption of the immune globulin, delaying the reaction and delivery of the immune globulin to the bloodstream where it can act on the hepatitis A virus. If a person had hepatitis A antibodies, the immune globulin would not be needed. The delay in getting that information could be problematic if the patient had been exposed to hepatitis A. Aspirin should be avoided in children due to risk of Reye’s syndrome. Corticosteroids can reduce immune response and so would be contraindicated. 6. A nurse is providing patient education to the mother of a child receiving a first immunization. The nurse tells the mother that after the injection, it is normal for the child to exhibit what signs and symptoms? A) Vomiting and diarrhea B) High fever and sweating C) Lethargy, drowsiness, and irritability D) Pain, redness, and swelling at site of injection Ans: D Feedback: Normal reactions to immunizations include pain, redness, and swelling at the site of the injection. Vomiting, diarrhea, high fever, sweating, lethargy, or drowsiness would not be expected and should be reported. The child could also be slightly irritable due to the pain at the injection site. 7. A 69-year-old patient comes to the clinic to talk to the nurse. The patient asks the nurse about when he should get the pneumonia vaccine. The patient’s medical record reveals that he received the vaccine at age 55. What should the nurse tell the patient? A) This vaccine is only given once and you have already had it. B) This vaccine is given every 10 years and you will be due next year. C) This vaccine is only repeated if the first dose was given before age 65. You should have another vaccine. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) D) This vaccine is no longer recommended. Don’t worry about getting pneumonia. Ans: A 290 Feedback: The pneumonia vaccine contains 23 strains and is believed to offer lifetime protection. The tetanus vaccine is given every 10 years. The vaccine is recommended for anyone at risk, especially those over age 65. Options C and D are distracters. 8. A mother has brought her infant to the clinic for the first immunization. What would the nurse be sure to include when providing patient education for the infant’s mother? A) Avoid having her child get more than one vaccine at a time. B) Stop the immunizations after 2 years of age. C) Keep a written record of the child’s immunizations. D) Omit immunizations if the injections are too upsetting for her child. Ans: C Feedback: Provide thorough patient teaching, including measures to avoid adverse effects, warning signs of problems, the need to keep a written record of immunizations, to increase knowledge about drug therapy, and to increase compliance with the drug regimen. Immunization records are often requested when the child is being enrolled in school so it is important for the mother to maintain these records. The nurse would not teach the mother to avoid having her child take more than one vaccine at a time, or to stop the immunizations after the age of 2, or to omit the immunizations if the injections are too upsetting to her child. 9. A mother brings her 18-month-old son into the clinic for his diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis vaccine. The child has a runny nose, a fever of 102.4ºF and is coughing. What should the nurse do? A) Administer the vaccine but monitor the child afterward for an extended time period. B) Give an antipyretic and administer vaccine when temperature is within normal range. C) Administer a reduced dose of the vaccine today and a normal dose when child is healthy. D) Hold the immunization until the child is free of allergic or cold-like symptoms. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) Ans: 291 D Feedback: The nurse should not administer the immunization if the child exhibits signs of acute infection because the vaccine can cause mild infection and can exacerbate acute infections. The child should be free of infection for several days before the immunization is given. Treating the fever, extended monitoring, or smaller doses will not overcome this risk and the only option is to hold the immunization until the child is healthy. 10. When discussing vaccines in class, a student asks the nursing instructor what an antitoxin is. What is the instructor’s best response? A) It is an immune serum for snake bites. B) It is a type of vaccine. C) It is a form of active immunity. D) It is a form of passive immunity. Ans: D Feedback: An antitoxin is an example of passive immunity. Antitoxins contain antibodies to very specific toxins. The antibodies are injected into the system and react with invading pathogens. Active immunity occurs when the body recognizes a foreign protein and begins producing antibodies to react against that specific protein or antigen. Vaccines are immunizations containing weakened or altered protein antigens that stimulate formation of antibodies against a specific disease. They are used to promote active immunity. Antivenin is used to refer to immune sera that have antibodies to venom that might be injected through spider or snake bites. 11. The nurse is presenting an educational event about vaccines at a local elementary school. When talking about vaccines, the nurse explains they are generally contraindicated in what situations? A) In people who have renal impairment B) In people who have hepatic failure C) In people who are immunosuppressed D) In people who are over 65 Ans: C Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 292 Feedback: The use of vaccines is contraindicated in the presence of immune deficiency because the vaccine could cause disease and the body would not be able to respond as anticipated if in an immunodeficient state, during pregnancy because of potential effects on the fetus and on the success of the pregnancy, in patients with known allergies to any of the components of the vaccine (refer to each individual vaccine for specifics, sometimes including eggs, where some pathogens are cultured), or in patients who are receiving immune globulin or who have received blood or blood products within the last 3 months because a serious immune reaction could occur. Vaccines are not contraindicated in people with renal impairment or who have hepatic failure nor are they contraindicated in people over the age of 65. 12. The clinic nurse is administering vaccines at well-baby checkups. Before administering a diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis (DTP) vaccine, what vital sign is most important for the nurse to check? A) Temperature B) Pulse C) Blood pressure D) Respirations Ans: A Feedback: Caution should be used whenever a vaccine is given to a child with a history of febrile convulsions or cerebral injury, or in any condition in which a potential fever would be dangerous. Caution also should be used in the presence of any acute infection. As a result, checking the child’s temperature is most important because this would be an indicator of potential infection. The nurse should ask the mother about history of febrile seizures or any condition that would make a fever dangerous. 13. The nurse is assigned to perform telephone triage for the clinic and receives a call from a young mother whose 6-month-old baby received her third diphtheriapertussistetanus immunization that morning. The mother reports the baby’s temperature is 99.8° axillary, the site of injection is a little red, and the baby is irritable. After checking the standing orders provided by the pediatrician, what teaching would the nurse provide this mother? (Select all that apply.) A) These are common adverse effects reported after immunizations. B) Bring the baby back to the clinic for an examination. C) Apply a warm moist compress to the baby’s leg. D) Aspirin can be given to manage fever symptoms. E) Symptoms should subside within 2 to 3 days. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) Ans: 293 A, C, E Feedback: The symptoms reported by this mother are all common adverse effects following immunization that will subside within 2 to 3 days. In the meantime, the mother can make the baby more comfortable by administering a weight appropriate dosage of acetaminophen, applying warm compresses to the injection site, and providing a quiet environment. If the symptoms do not subside within 2 to 3 days, the baby should be seen for follow-up care. Aspirin should not be given due to risk of Reye’s syndrome. 14. The nurse is describing the schedule for vaccinations to the parents of a new baby. The nurse explains the measlesmumpsrubella (MMR) vaccine is first administered at what age? A) 1 month B) 3 months C) 6 months D) 15 months Ans: D Feedback: MMR is administered initially as a combined vaccine at 15 months. Therefore, options A, B, and C are incorrect. 15. A male patient, aged 78 presents in the emergency department after stepping on a nail. The patient tells the nurse that he had his last tetanus shot 12 years ago and asks whether he will need another shot today. The nurse explains that tetanus boosters are required how often? A) Yearly B) Every 10 years C) Every 2 years D) Every 5 years Ans: B Feedback: Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 294 Having a tetanus booster shot every 10 years will help to protect older adults from exposure to that illness. Ask the patient about any adverse reaction to previous tetanus boosters, and weigh that risk against the possible exposure to tetanus. Options A, C, and D are incorrect information to give the patient. 16. The nurse works in a geriatric clinic and promotes administration of influenza immunizations to patients over age 65 how frequently? A) Once at age 65 B) Yearly C) Every 5 years D) As a one-time dose Ans: B Feedback: In addition, adults with chronic diseases are advised to be immunized yearly with an influenza vaccine, and also once with a pneumococcal pneumonia vaccine. Options A, C, and D are incorrect. 17. A group of nursing students are presenting information on the hepatitis B vaccine. What would the students prepare to tell others about the recommended population? A) Children under the age of 15 B) Infants and people at risk for contracting the disease C) People with diabetes mellitus or renal disease D) People over the age of 65 Ans: B Feedback: Patients indicated to receive the vaccine are susceptible people and infants. Indications for receiving the vaccine do not include children under the age of 15, people with diabetes or renal disease, or all people over the age of 65. 18. A patient, aged 72, is brought to the clinic by her daughter. The daughter asks how often her mother should receive the influenza vaccine. What would be the nurse’s best response? Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) A) Your mother only needs the influenza vaccine once in her lifetime. B) Your mother needs the influenza vaccine every 10 years. C) Your mother should receive the vaccine once, with two booster injections. D) Your mother needs the influenza vaccine yearly. Ans: D 295 Feedback: In general, all adults with chronic diseases are advised to be immunized yearly with an influenza vaccine, and once with a pneumococcal pneumonia vaccine. Options A, B, and C are incorrect information to give to the patient and her daughter. 19. The nursing instructor is explaining the best way to assess whether active immunity has developed from the administration of the hepatitis B series. What would the instructor cite as the best assessment method? A) Serum antibody levels B) Liver not palpable C) Aspartate aminotransferase within normal limits D) Absence of symptoms of hepatitis B infection Ans: A Feedback: In many cases, antibody titers (i.e., levels of the antibody in the serum) can be used to evaluate a patient’s response to an immunization and to determine the need for a booster dose. 20. A young mother asks the clinic nurse about the chickenpox vaccine. The mother states that she and her husband have both had chickenpox, but that she wants to protect her child if she can. What should the nurse tell the mother about the recommendation for the varicella vaccine? A) It is recommended for all children who have not been exposed to the varicella virus. B) It is not recommended for children under the age of 6. C) It is not recommended for children who have not been exposed to the varicella virus. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) D) It is recommended only for adults who have not had chickenpox. Ans: A 296 Feedback: ProQuad is an immunization against measles, mumps, rubella, and varicella virus vaccine indicated for children aged 12 months to 12 years. Varicella virus vaccine is indicated for adults and children older than 12 months of age. Immune globulin can be administered for short-term passive immunity to those exposed to chickenpox who are at high risk for complications from the disease such as those with immunoglobulin deficiency. 21. The clinic nurse is explaining recommended vaccines to the local parentteacher association. What vaccine would the nurse tell the attendees is recommended for children older than 7 years and for adults? A) Measlesmumpsrubella (MMR) B) Typhoid C) Diphtheria D) Varicella B Ans: C Feedback: Diphtheria and tetanus toxoids, combined, adsorbed (DT, Td) two IM injections of 0.5 mL at intervals of 4 to 8 weeks, with booster of 0.5 mL in 6 to12 months. Immunization is required for adults and children older than 7 years of age against diphtheria and tetanus. Tetanus booster is required every 10 years or with injury that could precipitate tetanus. Options A, B, and D are not correct. 22. A patient has come to the clinic for an allergy shot. The patient asks the nurse what immunoglobulin (Ig) is located in the body’s tissues and is thought to be responsible for allergic reactions. What is the nurse’s best response? A) IgG is thought to be responsible for allergic reactions. B) IgA is thought to be responsible for allergic reactions. C) IgM is thought to be responsible for allergic reactions. D) IgE is thought to be responsible for allergic reactions. Ans: D Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 297 Feedback: IgE is the immune globulin that is associated with allergic reactions. These antibodies react with mast cells, causing the release of histamine and other inflammatory chemicals when they have combined with the antigen. IgG, IgA, and IgM are not involved in allergic reactions. 23. A patient is brought to the emergency department after being bitten by a rattlesnake. The nurse asks the patient to describe the snake that bit him. Why would the nurse ask this question? A) Antivenin is very specific for antigens to which they can respond. B) Antivenin can only respond to cells that have not been attacked by the venom. C) Antivenin only responds to a specific group of spiders or snakes. D) Antivenin is very non-specific about a class of snakes or spiders. Ans: A Feedback: The term antivenin is used to refer to immune sera that have antibodies to venom that might be injected through spider or snake bites. These drugs are used to provide early treatment following exposure to known antigens. They are very specific for antigens to which they can respond. Therefore, options B, C, and D are incorrect. 24. A student asks the instructor how vaccines provide active immunity. The instructor’s best answer explains that active immunity is provided by stimulating production of antibodies to what? A) A bee sting B) A specific protein C) A foreign substance in the body D) A snake bite Ans: B Feedback: Vaccines provide active immunity by stimulating production of antibodies to a specific protein, which may produce the signs and symptoms of a mild immune reaction, but it protects the person from the more devastating effects of disease. This protein may be a foreign substance, a bee sting, or a snake Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 298 bite, but these answers are too narrow in focus. 25. The nurse at the pediatric clinic gives the mother of an infant a written record of the infant’s immune sera use. The nurse encourages the mother to keep the information. What is the rationale behind keeping a written record of immune sera use? A) To keep track of where the immune sera was given B) To identify who gave the immune sera C) To avoid future reactions D) To identify the lot number of the immune sera used Ans: C Feedback: Provide a written record of immune sera use and encourage the patient or family to store that information safely to ensure proper medical treatment and to avert future reactions. Written records are not kept to keep track of where the immune sera was given or to identify who gave the immune sera or to identify the lot number of the immune sera used as this information will have no value in the future. 26. What occurs when the host human responds to the injected antibodies circulating through the body? A) The host forms antigenantibody complexes with the injected antibodies. B) The host produces a passive immunity to the antibodies. C) The circulating antibodies attack the host cells. D) The host produces its own antibodies to the injected antibodies. Ans: D Feedback: In some cases, the host human responds to the circulating injected antibodies, which are foreign proteins to the host’s body, by producing its own antibodies to the injected antibodies. This results in serum sickness, a massive immune reaction that is manifested by fever, arthritis, flank pain, myalgia, and arthralgia. Options A, B, and C are incorrect answers to the question. 27. The nurse is developing a written plan of care for a patient receiving vaccines. What would be an appropriate nursing diagnosis for this patient? Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) A) Ineffective tissue perfusion if severe reaction occurs B) Chronic pain related to local, gastrointestinal (GI), and flu-like effects C) Monitoring effectiveness of comfort measures and adherence to the regimen D) Monitoring patient’s blood serum levels Ans: A 299 Feedback: Nursing diagnoses related to drug therapy might include ineffective tissue perfusion if severe reaction occurs. Option B is incorrect because vaccines do not generally cause chronic pain. Options C and D are implementations, not diagnoses. 28. A 55-year-old patient presents at the emergency department complaining of chest tightness and difficulty breathing. The patient tells the nurse he had immune sera earlier that day at the clinic. What does the nurse suspect is happening with this patient? A) Delayed hypersensitivity reaction B) An allergic reaction to the immune sera C) Serum sickness D) The response of the body to the immune sera Ans: B Feedback: Adverse effects can be attributed either to the effect of immune sera on the immune system (e.g., rash, nausea, vomiting, chills, fever) or to allergic reactions (e.g., chest tightness, falling blood pressure, difficulty breathing). Local reactions (e.g., swelling, tenderness, pain, muscle stiffness at the injection site) are very common. Serum sickness would manifest with fever, arthritis, flank pain, myalgia, and arthralgia. 29. An immune compromised patient is exposed to hepatitis A virus. The physician orders an injection of immunoglobulin as prophylaxis. What adverse effects would the nurse advise the patient might occur? (Select all that apply.) A) Fever B) Rhinitis Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) C) Angioedema D) Severe abdominal pain E) Urticaria Ans: A, C, E 300 Feedback: Adverse effects include tenderness, muscle stiffness at site of injection; urticaria, angioedema, nausea, vomiting, chills, fever, and chest tightness. An immune compromised patient would not be told to watch for rhinitis or severe abdominal pain because these are not anticipated adverse effects. 30. A patient is to receive a physical examination before starting immune sera therapy. What would the nurse assess for? A) Assess mental status changes B) Physical characteristics C) Pulse pressure D) Adventitious breath sounds Ans: D Feedback: Perform a physical assessment to determine baseline status before beginning therapy and for any potential adverse effects; inspect for presence of any skin lesions to monitor for hypersensitivity reactions; monitor temperature to monitor for possible infection, pulse, respirations, and blood pressure; auscultate lungs for adventitious sounds; assess level of orientation and affect to monitor for hypersensitivity reactions to the vaccine. 31. The mother of a preschool aged child brings her child to the clinic and asks what immunizations the child needs before starting school. What immunizations will the nurse expect this child needs if the child is healthy and has received immunizations on schedule in the past? (Select all that apply.) A) Diphtheria and tetanus toxoids and acellular pertussis vaccine, adsorbed (DTaP) B) Inactivated poliovirus vaccine (IPV) C) Measles, mumps, and rubella vaccine (MMR) Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) D) Hepatitis B E) Haemophilus influenzae type b vaccine (Hib) Ans: A, B, C 301 Feedback: The 4- to 6-year-old, preparing to enter school needs booster DTaP, IPV, MMR, influenza and varicella. High-risk groups, which does not include this child, will also need HepA and MCV. 32. The nurse is preparing for a visit with a 4-month-old infant. What immunizations will the nurse prepare? (Select all that apply.) A) Diphtheria and tetanus toxoids and acellular pertussis vaccine, adsorbed (DTaP) B) Inactivated poliovirus vaccine (IPV) C) Haemophilus influenzae type b vaccine (Hib) D) Varicella E) meningococcal Ans: A, B, C Feedback: At 4 months of age, the child will receive a DTaP, Hib, IPV, and PCV. Varicella vaccine is not given until the child is at least 1 year of age, and Meningococcal is usually given at age 11 to 12 years unless the patient is at high risk for development of the disease before that age. 33. The nurse explains the purpose of vaccines is to promote what? (Select all that apply.) A) Active immunity B) Passive immunity C) Short-term immunity D) Lifetime immunity E) Activation of the immune system Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) Ans: 302 A, D, E Feedback: The word vaccine comes from the Latin word for smallpox, vaccinia. Vaccines are immunizations containing weakened or altered protein antigens that stimulate the formation of antibodies against a specific disease. They are used to promote active immunity that will last for a lifetime, although some patients will require smaller booster doses to maintain immunity. 34. The mother of a 2-month-old child tells the nurse, I’ve been reading about how vaccines cause autism so I have decided not to give my child any of these vaccines. What is the nurse’s best response? A) Extensive studies have found no link between the measlesmumpsrubella (MMR) vaccine and autism. B) Extensive studies are being conducted and so far they have not found a link to autism. C) Research has found no link between the chickenpox vaccine and autism. D) Many parents agree that withholding vaccines is best and that is your choice to make. Ans: A Feedback: The Immunization Safety Review Committee Board of Health Promotion and Disease Prevention of the Institute of Medicine under the auspices of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the National Institutes of Health have concluded that no evidence supports any linkage between the use of MMR vaccine and the development of autism. The chickenpox virus is not involved in the debate. Although it is the mother’s choice to make, many parents make an uninformed decision out of fear, so it is important for the nurse to provide the necessary education because children who do not receive essential immunizations put the community at risk. A child who is exposed to measles and then comes in contact with a pregnant woman can cause fetal damage or death. 35. The nurse is caring for a 35-year-old woman who came to her gynecologist today to receive a Gardasil injection. The patient says she is sexually active since age 14, admitting to more than 10 sexual partners, and has used oral birth control as a contraceptive because I don’t like using barrier methods. The provider tells the patient she is not a good candidate for the injection and the patient asks the nurse why. What is the nurse’s best response? A) Gardasil is only given to women between the ages of 9 and 26 years of age. B) The drug is only effective if administered before exposure to human papillomavirus (HPV). C) The drug cannot be administered to a woman who is sexually active. D) The drug cannot be administered until further Food and Drug Administration (FDA) testing has Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 303 been completed. Ans: B Feedback: This patient is not a candidate for Gardasil primarily because she has most likely already been exposed to HPV and there would be no benefit to the injection. Gardasil is a vaccine that needs to be administered before exposure to be effective. Although the drug is normally given to women aged 9 to 26 years old, it could be given to an older person who has not become sexually active yet. Although sexual activity would not preclude administering the injection to a young girl who has had only one sexual partner, multiple partners increase the likelihood of exposure to HPV. The FDA continues to monitor testing related to the need for booster shots and the length of time the immunity remains active, as well as long-term adverse effects of the drug but the drug is available to the public by prescription. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 304 Chapter 19 - Introduction to Nerves and the Nervous System 1. What part of the neuron carries information into the neuron from other neurons? A) Axon B) Dendrite C) Nucleus D) Soma Ans: B Feedback: Dendrites carry information to the nerve and axons; they also carry information from a nerve to be transmitted to effector cells, which are found in muscles, glands, or another nerve. Soma refers to the cell body. The nucleus is the central part of a cell, which is responsible for the cell’s growth, reproduction, and metabolism. 2. When a neuron is stimulated and causes depolarization of the nerve, what occurs? A) Calcium rushes into the cell. B) Sodium rushes into the cell. C) Potassium rushes into the cell. D) Sodium and potassium are actively pumped out to the cell. Ans: B Feedback: When depolarization occurs, sodium rushes into the cell. During repolarization, potassium is pumped out of the cell and the resting membrane potential is reestablished. Calcium ions decrease the cell membranes’ permeability to sodium and increase the threshold needed to depolarize the cell. 3. A) What neurotransmitter inhibits overexcitability and is important in preventing seizure activity in a patient? Acetylcholine Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) B) Dopamine C) Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) D) Serotonin Ans: C 305 Feedback: GABA is found in the brain and inhibits nerve activity. It is important in preventing overexcitability or stimulation such as seizure activity. Acetylcholine communicates between nerves and muscles. Dopamine is involved in the coordination of impulses and responses, both motor and intellectual. Serotonin is found in the limbic system and is important in arousal and sleep as well as in preventing depression and promoting motivation. 4. The nurse is caring for a patient who has an injured hindbrain. What would the nurse expect to find altered when assessing the patient? A) Arousal and awareness B) Basic vital functions C) Coordination and motor activity D) Learning and motivation Ans: B Feedback: The hindbrain contains centers that control basic vital functions (e.g., blood pressure, respirations, vomiting). The reticular activating system in the medulla controls arousal and awareness. Learning and motivation occur in the cerebral cortex. Coordination and motor activity are controlled through the cerebellum and basal ganglia. 5. A female patient has experienced a stroke affecting the right side of her brain. What will the nurse expect to assess in this patient? A) Inability to recall the name of her best friend B) Inability to state her telephone number C) Inability to distinguish a spoon from a fork Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) D) Inability to recall how to apply her makeup Ans: C 306 Feedback: The right side of the brain is the artistic side and is concerned with forms and shapes. This patient could have difficulty distinguishing the roundness of the spoon with the straight line of the top of the fork. The left side of the brain is more analytical and is concerned with names, numbers, and process. 6. The nurse is caring for a patient with meningitis who is not responding to the prescribed antibiotic and whose condition continues to deteriorate. What rationale will the nurse give the family to explain why the antibiotic is not as effective as it was hoped? A) The meninges do not have a blood supply. B) The bloodbrain barrier prevents the antibiotics from crossing into the brain. C) The circle of Willis redirects the antibiotic elsewhere. D) The pressure in the hindbrain prevents entry into the skull. Ans: B Feedback: The bloodbrain barrier works to keep large molecules out of the brain and away from the nerves. Most antibiotics are protein bound and cannot pass through the bloodbrain barrier. When the infection becomes severe, the bloodbrain barrier will stop being effective and the antibiotics can pass into the brain. The brain has a unique blood supply to protect the neurons from lack of oxygen and glucose. After the bloodbrain barrier allows the antibiotic to pass through, the circle of Willis distributes the blood to the areas of need. If someone has an occluded carotid artery, which could build pressure up in the area, the circle of Willis can redirect the blood supply and provide a full blood supply to the affected areas. 7. An 87-year-old woman undergoes extensive surgery for an acoustic neuroma (a benign tumor of the inner ear), and 6 hours after surgery, she hemorrhages and goes into a coma. After awaking and 2 months of therapy, she is transferred to a long-term care facility. Due to damage in the midbrain, the nurse caring for the patient will expect the patient to exhibit what? A) Difficulty in sleeping B) Difficulty in hearing C) Difficulty in distinguishing hot and cold Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) D) Difficulty in speaking Ans: C 307 Feedback: The thalamus, located in the midbrain, is responsible for temperature control. The patient will have difficulty distinguishing hot and cold. Centers of control for sleep and hearing are found in the hindbrain and areas that control speech and communication are found in the forebrain. 8. A nurse is caring for a patient who is having an adverse drug reaction. The patient is experiencing tremors, is unable to hold his or her head up, and is having difficulty sitting up in bed. The nurse suspects that this is due to what? A) An interference with the extrapyramidal system B) A faulty engram C) An alteration in the reticular activating system D) An interference with a neurotransmitter Ans: A Feedback: The extrapyramidal system coordinates unconscious motor activity that regulates control of position and posture. An engram is a reverberating circuit of action potentials that becomes a long-term, permanent memory in the presence of the proper neurotransmitters and hormones. The reticular activating system, which is located in the hindbrain, controls arousal and awareness of stimuli and contains the sleep center. A neurotransmitter is a chemical that stimulates postsynaptic cells either by exciting or by inhibiting them. 9. A nurse is working on a surgical unit and has several patients who require preoperative teaching. Which patient demonstrates behavior indicating this is an appropriate time to begin teaching? A) A patient who is wide eyed and extremely frightened about being put to sleep B) A patient who appears to be unconcerned about what is happening and wants to watch his favorite TV show C) A patient who is clearing her throat several times while asking the nurse questions during their conversation and who appears to be slightly stressed D) A patient who is getting up and down from the bed, talking very fast, and appears to be extremely anxious Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) Ans: 308 C Feedback: Several substances appear to affect learning. Antidiuretic hormone (ADH), which is released during reactions to stress, is one such substance. Although too much stress prevents learning, feeling slightly stressed may increase a person’s ability to learn. A patient who is a little nervous about upcoming surgery, for example, seems to display a better mastery of facts about the surgery and postoperative procedures than a patient who is very stressed and scared or one who appears to show no interest or concern. 10. The nursing instructor explains the limbic system contains what neurotransmitters? A) Acetylcholine, epinephrine, and serotonin B) Gamma-aminobutyric acid, dopamine, and serotonin C) Epinephrine, dopamine, and gamma-aminobutyric acid D) Epinephrine, norepinephrine, and serotonin Ans: D Feedback: The limbic system contains high levels of epinephrine, norepinephrine, and serotonin. Dopamine, acetylcholine, and gamma-aminobutyric acid are found in the brain but not primarily in the limbic system. Options A, B, and C are incorrect. 11. The anatomy and physiology instructor is discussing neurotransmitters with the prenursing anatomy and physiology class. What neurotransmitter would the instructor tell the students is a catecholamine classified as a hormone when it is released from the adrenal medulla? A) Ephedrine B) Norepinephrine C) Dopamine D) Acetylcholine Ans: B Feedback: Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 309 Norepinephrine and epinephrine are catecholamines, which are released by nerves in the sympathetic branch of the autonomic nervous system and are classified as hormones when they are released from cells in the adrenal medulla. Therefore, options A, C, and D are incorrect. 12. A 46-year-old male patient sustained a closed-head injury 4 hours ago. He presents to the emergency department with difficulty breathing. What area of the brain does the nurse suspect is injured based on the patient’s symptoms? A) Thalamus B) Cerebrum C) Pituitary D) Medulla oblongata Ans: D Feedback: The hindbrain, which runs from the top of the spinal cord into the midbrain, is the most primitive area of the brain and contains the brainstem, where the pons and medulla oblongata are located. This area of the brain controls basic vital functions such as the respiratory centers, which control breathing; the cardiovascular centers, which regulate blood pressure; the chemoreceptor trigger zone and emetic zone, which control vomiting; the swallowing center, which coordinates the complex swallowing reflex; and the reticular activating system (RAS), which controls arousal and awareness of stimuli and contains the sleep center. The midbrain contains the thalamus and hypothalamus and the limbic system that transfer sensations into the cerebrum and control temperature. The pituitary gland is known as the master gland, controlling other glands with hormones secreted here. 13. The physiology instructor is discussing the limbic system. What would the instructor say occurs with stimulation of this area? A) Intelligence B) Heart rate C) Mood D) Reflexes Ans: C Feedback: The limbic system is an area of the brain that contains high levels of three neurotransmitters: epinephrine, norepinephrine, and serotonin. Stimulation of this area appears to be responsible for the Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 310 expression of emotions (e.g., anger, pleasure, motivation, stress). 14. The nursing instructor is talking about neurotransmitters, including which of these chemicals? A) Calcium ion B) Acetylcholinesterase C) Acetylcholine D) Monoamine oxidase Ans: C Feedback: The cholinergic system uses acetylcholine as its neurotransmitter. A calcium ion is an electrolyte circulating in the serum. Acetylcholinesterase is an enzyme that breaks down acetylcholine. Monoamine oxidase is an enzyme that breaks down the neurotransmitter norepinephrine. 15. What would a nurse describe to a peer as a factor in increasing synaptic transmission? A) Enzymes B) Electrical impulse C) Calcium reaction D) Neurotransmitter Ans: D Feedback: The nerve axon, called the presynaptic nerve, releases a chemical called a neurotransmitter into the synaptic cleft; the neurotransmitter reacts with a very specific receptor site on the postsynaptic cell to cause a reaction that increases synaptic transmission. Enzymes break down the neurotransmitter. The synaptic transmission is an electrical impulse. Calcium is an electrolyte but does not increase synaptic transmission. 16. A) Which neurotransmitter communicates between nerves and muscles? Acetylcholine Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) B) Dopamine C) Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) D) Serotonin Ans: A 311 Feedback: Acetylcholine, which communicates between nerves and muscles, is also important as the preganglionic neurotransmitter throughout the autonomic nervous system and as the postganglionic neurotransmitter in the parasympathetic nervous system and in several pathways in the brain. Dopamine is involved in the coordination of impulses and responses, both motor and intellectual. GABA inhibits nerve activity. Serotonin is important in arousal and sleep. 17. While discussing the central nervous system (CNS), the nursing instructor tells the students that the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the CNS is what? A) Acetylcholine B) Dopamine C) Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) D) Serotonin Ans: C Feedback: GABA, which is found in the brain, inhibits nerve activity and is important in preventing overexcitability or stimulation such as seizure activity. Acetylcholine, which communicates between nerves and muscles, is also important as the preganglionic neurotransmitter throughout the autonomic nervous system and as the postganglionic neurotransmitter in the parasympathetic nervous system and in several pathways in the brain. Dopamine is involved in the coordination of impulses and responses, both motor and intellectual. Acetylcholine, dopamine, and serotonin are not the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the CNS. Serotonin is important in arousal and sleep. 18. The anatomy and physiology instructor discusses the thalamus with the nursing class. The instructor tells the students that the thalamus does what? A) Relays motor impulses from the cortex to the spinal cord B) Is responsible for voluntary movement Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) C) Sends information into the cerebrum to transfer sensations D) Helps maintain red blood cell (RBC) production Ans: C 312 Feedback: The thalamus sends direct information into the cerebrum to transfer sensations, such as cold, heat, pain, touch, and muscle sense. Motor fibers from the cortex cross to the other side of the spinal cord before emerging to interact with peripheral effectors. In this way, motor stimuli coming from the right side of the brain affect motor activity on the left side of the body. The limbic system is not responsible for voluntary movement or RBC production. 19. Neurotransmission is important in the function of the central nervous system (CNS). For neurotransmission to occur, how do neurons communicate with other cells? A) Selectively B) Chemically C) Excitably D) Accessibly Ans: B Feedback: The transmission of information between two nerves or between a nerve and a gland or muscle is chemical. Options A, C, and D are incorrect. 20. Two nursing students are giving an oral presentation on the forebrain. What information will they include about this area? (Select all that apply.) A) Coordinates speech and communication B) Area where learning takes place C) Houses the extrapyramidal motor system D) Cranial nerves emerge from here. E) The swallowing center is here. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) Ans: 313 A, B, C Feedback: The forebrain is made up of two cerebral hemispheres joined together by the corpus callosum. The two hemispheres contain the sensory and motor neurons. It also contains areas that coordinate speech and communication and is thought to be where learning takes place. Cranial nerves emerge from the hindbrain, which is where the swallowing center is located as well. 21. A student asks the anatomy and physiology instructor to explain the two hemispheres of the brain and what they regulate. What statement, if made by the instructor, is accurate? A) The hemispheres regulate the electrical conduction system of the brain. B) The hemispheres regulate the afferent conduction system. C) The hemispheres regulate the efferent conduction system. D) The hemispheres regulate communication between sensory and motor neurons. Ans: D Feedback: The cerebral cortex consists of two hemispheres, which regulate the communication between sensory and motor neurons and are the sites of thinking and learning. Options A, B, and C are incorrect. 22. While diagramming the brain for their anatomy and physiology class, the nursing students would place the swallowing center where? A) Hindbrain B) Right hemisphere C) Forebrain D) Left hemisphere Ans: A Feedback: The pons and medulla oblongata are in the hindbrain and control basic, vital functions, such as the respiratory centers, which control breathing; the cardiovascular centers, which regulate blood pressure; the chemoreceptor trigger zone and emetic zone, which control vomiting; and the swallowing center, Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 314 which coordinates the complex swallowing reflex. Therefore, options B, C, and D are incorrect. 23. As the nursing students learn about the functioning of the nervous system, they learn that the energy required by the nerves is provided by what? A) Dopamine and electricity B) Oxygen and glucose C) Sodium and potassium D) Acetylcholine and serotonin Ans: B Feedback: Nerves require energy (i.e., oxygen and glucose) and the correct balance of the electrolytes sodium and potassium to maintain normal action potentials and transmit information into and out of the nervous system. Energy required by the nerves is not provided by dopamine, electricity, acetylcholine, or serotonin. 24. The nursing instructor is teaching the new nursing students about patient teaching. Where in the brain would the instructor tell the student nurses is the area where learning takes place? A) The area that coordinates sensation B) The area that coordinates movement C) The areas that coordinate speech and communication D) The areas that communicate between motor and sensory neurons Ans: C Feedback: The forebrain is made up of two cerebral hemispheres that contain areas that coordinate speech and communication and are thought to be the area where learning takes place. 25. A) When a person learns, this action begins as an electrical circuit called what? Impulse Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) B) Synapse C) Memory D) Engram Ans: D 315 Feedback: Learning begins as an electrical circuit called an engram, a reverberating circuit of action potentials that eventually becomes a long-term, permanent memory in the presence of the proper neurotransmitters and hormones. 26. The physiology instructor explains to the students that some substances increase actual learning. What is one of these substances? A) Oxytocin B) Acetylcholine C) Serotonin D) Dopamine Ans: A Feedback: Oxytocin and mild stress act to increase actual learning. Childbirth is the only time that oxytocin levels increase and this phenomenon is not clearly understood. Acetylcholine, serotonin, and dopamine do not increase actual learning; they function as neurotransmitters. 27. The sensory nerves enter the brain and react with related nerves to cause a reaction. What mediates this reaction? A) Muscles or glands B) The limbic system C) The cerebral cortex D) Neurotransmitters Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) Ans: 316 A Feedback: The sensory nerves that enter the brain react with related motor nerves to cause a reaction mediated by muscles or glands. The motor impulses that leave the cortex are further regulated or coordinated by the pyramidal system, which coordinates voluntary movement, and the extrapyramidal system, which coordinates unconscious motor activity that regulates control of position and posture. Therefore, the other options are incorrect. 28. What brings information from the central nervous system (CNS) to the peripheral nervous system (PNS)? A) Motor nerves B) Synapses C) Afferent neurons D) Sensory nerves Ans: D Feedback: The PNS is composed of sensory receptors that bring information into the CNS and motor nerves that carry information away from the CNS to facilitate response to stimuli. Synapses are the gaps between neurons. Afferent fibers are nerve axons that run from the peripheral receptors into the CNS. 29. The student nurses are learning about the nervous system. What would the students learn are capable of conducting along the entire membrane of the nerve? A) Action potentials B) Engrams C) Chemical synapses D) Sodiumpotassium channels Ans: A Feedback: Nerve membranes, which are capable of conducting action potentials along the entire membrane, send Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 317 messages to nearby neurons or to effector cells that may be located inches to feet away via this electrical communication system. Other options are incorrect. 30. A patient who nearly drowned is brought to the emergency department. The paramedics tell the nurse the patient was anoxic for approximately 5 minutes. Because of this anoxia, what might happen to the nerve cells? A) The nerves might not be able to repolarize. B) The nerves might not be able to depolarize. C) The nerves might not be able to maintain the sodiumpotassium pump. D) The nerves might not be able to maintain their action potential. Ans: C Feedback: If a person has anoxia or hypoglycemia, the nerves might not be able to maintain the sodiumpotassium pump, and with continued lack of oxygen and/or glucose, the nerve cell will die. Other options are incorrect. 31. What is the purpose of the myelin sheath? A) Protects the nerve from damage B) Speeds electrical conduction C) Produces Schwann cells D) Secretes neurotransmitters Ans: B Feedback: Long nerves are myelinated: They have a myelin sheath that speeds electrical conduction and protects the nerves from the fatigue that results from frequent formation of action potentials, not from damage. Although myelin sheaths have Schwann cells, they do not produce these cells and the myelin sheath does not secrete neurotransmitters. 32. The patient is diagnosed with myasthenia gravis, a condition in which antibodies block, alter, or destroy the receptors for acetylcholine. What symptom would the nurse expect this patient to display? Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) A) Muscle dysfunction B) Seizures C) Uncoordinated movements D) Sleep all the time Ans: A 318 Feedback: Acetylcholine communicates between nerves and muscles so inability of this neurotransmitter to function properly, whether blocking, altering, or destroying the receptors, would result in muscle dysfunction. Inadequate gamma-aminobutyric acid would result in seizures. Inadequate dopamine would result tin uncoordinated movements. Serotonin is important in arousal and sleep. 33. The nurse is caring for a patient with a malignant brain tumor. The patient asks the nurse why the tumor is being treated with radiation instead of chemotherapy. The nurse’s explanation involves what important information? A) Medications have difficulty crossing the bloodbrain barrier. B) Neurons in the brain are easily damaged by chemotherapy. C) Tumors arising from nervous tissue are not impacted by chemotherapy. D) Chemotherapy reduces nerve transmission and cannot be used. Ans: A Feedback: The bloodbrain barrier is a functioning boundary that plays a defensive role by keeping toxins, proteins, and other large structures out of the brain and preventing their contact with the sensitive and fragile neurons. As a result, medications like chemotherapy can have difficulty crossing this barrier to reach the tumor. The other answers are neither true nor the correct option. 34. The nurse is caring for a patient whose recent ultrasound of the carotids diagnosed a 90% occlusion of the right carotid artery and a 92% occlusion of the left carotid artery. The patient asks the nurse, If one of these arteries becomes completely occluded will I have a stroke? What is the nurse’s best response? A) A common vessel receiving all blood to the head called the circle of Willis will distribute blood from other arteries to the brain as needed. B) A stroke is caused by lack of blood supply to a part of the brain so if your right carotid artery Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 319 becomes blocked you’ll have a stroke on the right side of your brain. C) It is hard to predict exactly what will happen so you’ll have to wait until your provider sees you because only the provider can answer that question. D) With only 10% of the blood needed getting through your right artery and 8% through your left artery, you could have a stroke now. Ans: A Feedback: All the arteries that supply blood to the head deliver blood to a common vessel at the bottom of the brain called the circle of Willis, which distributes the blood to the brain when it is needed. The role of the circle of Willis becomes apparent when someone has an occluded carotid artery. Although the passage of blood through one of the carotid arteries may be negligible, the areas of the brain on that side will still have a full blood supply because of the blood sent to those areas through the circle of Willis. All other options are incorrect. 35. The nurse is caring for a patient whose emotions often swing from one extreme to the other. The patient’s spouse tells the nurse these mood swings started when the patient awoke from a coma following a serious head trauma. What area of the brain does the nurse suspect was damaged? A) The limbic system B) The forebrain C) The hindbrain D) The cerebellum Ans: A Feedback: Stimulation of the limbic system, which appears to be responsible for the expression of emotions, may lead to anger, pleasure, motivation, and stress. The forebrain is where thinking and coordination of sensory and motor activity occur. The hindbrain controls vital functions and arousal. The cerebellum controls motor functions that regulate balance. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 320 Chapter 20 - Anxiolytic and Hypnotic Agents 1. The nurse is caring for a patient in a state of hypnosis, which means the patient is in what state? A) A state of extreme sedation in which the person no longer senses or reacts to incoming stimuli. B) A state of tranquility in which the person can be made to do whatever is suggested by others. C) A feeling of tension, nervousness, apprehension, or fear with high levels of awareness. D) A state in which the brain is no longer sending out signals to the body. Ans: A Feedback: Hypnosis is an extreme state of sedation in which the person no longer senses or reacts to incoming stimuli. A state of tranquility is produced through minor tranquilizers by decreasing anxiety. Anxiety is a feeling of tension, nervousness, apprehension, or fear. Sedation is the loss of awareness and reaction to environmental stimuli, which may lead to drowsiness. The state of suggestibility often seen in television programs is not an appropriate definition of hypnosis. If the brain stopped sending signals, the patient would stop breathing and death would follow. 2. A nurse is caring for a 4-year-old child who is receiving a barbiturate. What common adverse effect would the nurse assess for? A) Decrease in respirations B) Vomiting C) Excitability D) Dry mucous membranes Ans: C Feedback: The barbiturates, being older drugs, have established pediatric dosages. These drugs must be used with caution because of the often unexpected responses. Children must be monitored very closely for central nervous system (CNS) depression and excitability. The most common adverse effects are related to general CNS depression. Other CNS effects may include drowsiness, somnolence, lethargy, ataxia, vertigo, a feeling of a hangover, thinking abnormalities, paradoxical excitement, anxiety, and hallucinations. Alteration in respirations and dried mucous membranes are adverse effects of Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 321 antihistamines, which can be given to calm children or induce sleep. Vomiting could occur with the use of paraldehyde due to the unpleasant taste and odor of the drug. 3. A nurse is caring for a 9-year-old patient and has received an order for diazepam (Valium) 10 mg given orally q.i.d. What is the nurse’s priority action? A) Perform hand hygiene and prepare the drug. B) Send the order to the hospital pharmacy. C) Determine when to administer the first dose. D) Call the physician and question the order. Ans: D Feedback: The first action of the nurse would be to call the physician and question the order. The normal oral dosage for a pediatric patient is 1 to 2.5 mg t.i.d. or q.i.d. The ordered dose would be unsafe for this patient. If the dosage was changed and the correct amount administered, the nurse would order the medication from the pharmacy if necessary and determine what time to start the medication. She would then wash her hands in preparation for administering the medication, but not until obtaining an appropriate dosage of medication. 4. A nurse is discussing the use of alprazolam (Xanax) with a 68-year-old patient. What statement indicates that the patient has an understanding of the drug? A) When I stop having panic attacks, I can stop taking the drug. B) This drug will calm me down in about 30 minutes after I take it. C) One dose will keep me calm for about 24 hours. D) I am taking an increased dose because of my age. Ans: B Feedback: The onset of alprazolam is about 30 minutes. The drug must be tapered after long-term use and the duration is approximately 4 to 6 hours. Elderly patients usually have a reduced dosage. 5. A nurse is about to administer a parenteral benzodiazepine to a female patient in the hospital before the performance of a procedure. What is the priority nursing action before administration of the drug? Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) A) Make sure that the side rails are up and the bed is in the lowest position. B) Close the blinds and ensure appropriate room temperature for the patient. C) Help the patient out of bed to the bathroom and encourage her to void. D) Ask all visitors to leave the room and remain in the waiting area. Ans: C 322 Feedback: The priority action would be to help the patient up to void. After the medication is administered the patient should not get out of bed because of possibly injury due to drowsiness. Safety should always be the priority concern. After administration of the drug the nurse would ask visitors to leave before beginning the procedure, make the room conducive to rest and sleep, and make sure that both side rails are up and the bed is in the lowest position. 6. The nurse is caring for a 36-year-old man who experienced a seizure 30 minutes before coming into the emergency room, where he begins to have another. What barbiturate has the fastest onset and would be most appropriate to give to the patient to quickly stop the seizure? A) Amobarbital (Amytal Sodium) B) Mephobarbital (Mebaral) C) Phenobarbital (Luminal) D) Secobarbital (Seconal) Ans: C Feedback: Phenobarbital’s onset is between 10 and 60 minutes, depending on the route administered, and most likely this would be given to the patient. Amobarbital is given for convulsions and the onset is between 15 and 60 minutes. Mephobarbital’s onset is between 30 and 60 minutes. Secobarbital is given for convulsive seizures of tetanus and has an onset of 1 to 4 hours. 7. What anxiolytic drugs would be given to a premenopausal patient who is a registered nurse planning to return to work at the hospital after anxiety is controlled? A) Alprazolam (Xanax) B) Buspirone (BuSpar) Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) C) Diazepam (Valium) D) Clorazepate (Tranxene) Ans: B 323 Feedback: Buspirone is a newer anxiolytic drug that does not cause sedation or muscle relaxation. It is preferred when the patient needs to be alert such as when driving or working. Alprazolam, diazepam, and clorazepate are benzodiazepines, which cause drowsiness, sedation, depression, lethargy, confusion, and decreased mental alertness. It would be unsafe for a nurse to function in her role while taking one of these drugs. 8. A patient arrives at the emergency room after attempting suicide by taking an entire bottle of diazepam. What antidote will the nurse most likely administer? A) Phenobarbital (Luminal) B) Dexmedetomidine (Precedex) C) Flumazenil (Romazicon) D) Ramelteon (Rozerem) Ans: C Feedback: Flumazenil is an antidote to benzodiazepine overdose and is administered to reverse the effects of benzodiazepines when used for anesthesia. Phenobarbital, a barbiturate, would further depress the body functions of this patient. Dexmedetomidine is a new hypnotic drug used in the intensive care unit for mechanically ventilated patients. Ramelteon is also new; it is used as a hypnotic. Adverse effects of this drug include depression and suicidal ideation. 9. The nurse is caring for a resident in a long-term care facility who is African American with a history of an anxiety disorder. The patient is receiving oral lorazepam (Ativan) 2 mg t.i.d. When developing this patient’s plan of care, what priority assessment will the nurse include? A) Depression B) Extreme sedation C) Phlebitis D) Nightmares Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) Ans: 324 B Feedback: Special care should be taken when anxiolytic or hypnotic drugs are given to African Americans. About 15% to 20% of African Americans are genetically predisposed to delayed metabolism of benzodiazepines. As a result, they may develop high serum levels of these drugs, with increased sedation and an increased incidence of adverse effects. Depression is not a common adverse effect. Phlebitis can occur at injection sites but this patient is taking the medication orally. Nightmares occur during drug withdrawal. 10. An elderly patient has been taking zolpidem (Ambien) as a sleep aid for the past 2 months. On admission to the assisted-living facility, it is determined that the drug is no longer needed. What is an important nursing consideration concerning this drug? A) Hallucinations are common. B) The drug needs to be withdrawn gradually. C) Another anxiolytic will need to be substituted. D) Sundowning is common with withdrawal from this drug. Ans: B Feedback: It is important for the nurse to understand that zolpidem must be withdrawn gradually over a 2-week period after prolonged use. If chloral hydrate is stopped suddenly, it will result in serious adverse effects. Hallucinations and sundowning are not common with withdrawal of the drug. The prescriber and the patient would determine the need for chloral hydrate to be substituted for another anxiolytic. 11. Why would the nurse expect the patient with liver disease to receive a smaller dose of benzodiazepines? A) Excretion of the drug relies on liver function. B) The drugs are metabolized extensively in the liver. C) They are lipid soluble and well distributed throughout the body. D) The drugs are well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Ans: B Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 325 Feedback: The benzodiazepines are metabolized extensively in the liver. Patients with liver disease must receive a smaller dose and be monitored closely. Excretion is primarily through the urine. All of the answer options are true, but only the fact that the benzodiazepines are metabolized in the liver explains why a patient with liver disease would require smaller dosages. 12. When compared with benzodiazepines, buspirone (BuSpar) stands out as unique among antianxiety drugs because of what factor? A) Increases the central nervous system (CNS) depression of alcohol and other drugs. B) Lacks muscle relaxant and anticonvulsant effects. C) Causes significant physical and psychological dependence. D) Rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal (GI) tract and metabolized in the liver. Ans: B Feedback: Buspirone, a newer antianxiety agent, has no sedative, anticonvulsant, or muscle-relaxant properties, and its mechanism of action is unknown. However, it reduces the signs and symptoms of anxiety without many of the central nervous system effects and severe adverse effects associated with other anxiolytic drugs. Most of the antianxiety drugs are rapidly absorbed from the GI tract, metabolized in the liver, have a significant drugdrug interaction with alcohol and other drugs, and can result in psychological dependence. 13. What would the nurse assess for when benzodiazepines are abruptly stopped? A) Urinary retention and change in sexual functioning B) Dry mouth, constipation, nausea, and vomiting C) Nausea, headache, vertigo, malaise, and nightmares D) In most cases nothing significant Ans: C Feedback: Abrupt cessation of these drugs may lead to a withdrawal syndrome characterized by nausea, headache, vertigo, malaise, and nightmares. When benzodiazepines are stopped abruptly the likelihood of withdrawal symptoms increases with the length of time the patient took the medication. Urinary Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 326 retention, change in sexual functioning, dry mouth, constipation, nausea, and vomiting are all common adverse effects of the medications classified as benzodiazepines. 14. The nurse is caring for a patient in intensive care unit receiving IV lorazepam (Ativan) to reduce anxiety related to mechanical ventilation. While injecting the medication the nurse notes a decrease in blood pressure and bradycardia. What is the nurse’s priority action? A) Discontinue drug administration. B) Give the IV drug more slowly. C) Notify the patient’s health care provider. D) Document the reaction to the drug. Ans: B Feedback: The nurse’s priority action is to slow the rate of injection because rapid injection of benzodiazepines can result in hypotension and bradycardia and can lead to cardiac arrest. 15. For what purpose would the nurse choose to administer a hypnotic instead of another classification of antianxiety drug? A) Treating insomnia B) Treating seizure disorder C) Treating panic attach D) Treating confusion and agitation Ans: D Feedback: Hypnotics are used to help people fall asleep by causing sedation. Drugs that are effective hypnotics act on the reticular activating system (RAS) and block the brain’s response to incoming stimuli. Hypnotics would not be the most effective drugs to treat seizure disorders, panic attack, or confusion with agitation. 16. The nurse assesses the patient who had an abrupt withdrawal of benzodiazepines for withdrawal syndrome and would recognize what symptoms as part of the syndrome? (Select all that apply.) Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) A) Headache B) Nightmares C) Malaise D) Bradycardia E) Hypotension Ans: A, B, C 327 Feedback: Abrupt cessation of benzodiazepines may lead to a withdrawal syndrome characterized by nausea, headache, vertigo, malaise, and nightmares. Withdrawal symptoms may be caused by the abrupt separation of benzodiazepine molecules from their receptor sites and the resulting acute decrease in gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) neurotransmission. Because GABA is an inhibitory neurotransmitter, less GABA may produce a less inhibited central nervous system (CNS) and therefore symptoms of hyperarousal or CNS stimulation. The nurse would not categorize hypotension or bradycardia as indicating benzodiazepine withdrawal. 17. A 75-year-old patient is brought to the emergency department by his family. The family relates that the patient is complaining of confusion, seizures, and abnormal perception of movement. The nurse reviews all of the medication bottles found in the house and suspects the patient overdosed on what medication? A) Benzodiazepine B) Antihypertensive C) Sedative D) Analgesic Ans: A Feedback: Common manifestations of benzodiazepine toxicity include increased anxiety, psychomotor agitation, insomnia, irritability, headache, tremor, and palpitations. Less common but more serious manifestations include confusion, abnormal perception of movement, depersonalization, psychosis, and seizures. These symptoms are not found in association with options B, C, or D. 18. The nurse is caring for a patient who experiences anxiety and insomnia and is prescribed benzodiazepines. When developing the plan of care, what would be an appropriate nursing diagnosis related to potential adverse effects of the drug? Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) A) Provide patient teaching about drug therapy. B) Anxiety related to drug therapy. C) Risk for injury related to central nervous system (CNS) effects. D) Avoid preventable adverse effects, including abuse and dependence. Ans: C 328 Feedback: The most appropriate nursing diagnosis related to adverse effects of the drug is risk for injury related to CNS effects because benzodiazepines can have many CNS adverse effects. Anxiety is the condition for which drug therapy is prescribed not related to drug therapy. Patient teaching and avoiding adverse effects are interventions and not nursing diagnoses. 19. A patient is being discharged home from the hospital after receiving treatment for pneumonia. The patient is going home and continuing to take the same drugs he or she was taking before he or she was hospitalized. These drugs include an antianxiety medication and a medication for insomnia. The home care nurse is following this patient. On the initial visit what is the nurse’s priority teaching point? A) The names and purposes of medications prescribed B) How to contact the provider if needed C) The importance of taking medications for insomnia only occasionally D) Warning signs that may indicate serious adverse effects Ans: D Feedback: The home care nurse should provide thorough patient teaching, with a priority teaching point being the warning signs the patient may experience that indicate a serious adverse effect. Although this may have been discussed by the discharging nurse in the hospital, this is essential information for the patient to thoroughly understand. By the time the home care nurse visits, the patient should already have filled the prescriptions and know the names and purposes of the medications prescribed from the hospital nurse but it is a good idea to review this information, although it is not a priority. Medications for insomnia should be taken as prescribed. The patient should have received the provider’s contact information when leaving the hospital but the home care nurse may need to review this, even though it is not the priority teaching point. 20. Hypnotic drugs are used to aid people in falling asleep. What physiological system does a hypnotic act on to be effective in helping a patient to sleep? Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) A) Limbic system B) Sympathetic nervous system C) Reticular activating system D) Lymph system Ans: C 329 Feedback: Hypnotics are used to help people fall asleep by causing sedation. Drugs that are effective hypnotics act on the reticular activating system and block the brain’s response to incoming stimuli. Hypnosis, therefore, is the extreme state of sedation, in which the person no longer senses or reacts to incoming stimuli. The other options are incorrect. 21. A patient presents at the emergency department with respiratory depression and excessive sedation. The family tells the nurse that the patient has been taking medication throughout the evening and gives the nurse an almost empty bottle of benzodiazepines. What other adverse effects would the nurse assess this patient for? A) Seizures B) Tachycardia C) Headache D) Coma Ans: D Feedback: Toxic effects of benzodiazepines include excessive sedation, respiratory depression, and coma. Flumazenil (Anexate) is a specific antidote that competes with benzodiazepines for benzodiazepine receptors and reverses toxicity. Seizures, tachycardia, and headache would not normally be associated with benzodiazepine toxicity. 22. A) A patient presents at the free clinic complaining of nervousness, worrying about everything, and feeling very tense. What diagnose would the nurse suspect? Neurosis Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) B) Psychosis C) Anxiety D) Depression Ans: C 330 Feedback: Anxiety is a common disorder that may be referred to as nervousness, tension, worry, or using other terms that denote an unpleasant feeling. The other options would not be described by these symptoms. 23. The nurse is caring for a patient who is taking a benzodiazepine. The nurse knows that caution should be used when administering a benzodiazepine to the elderly because of what possible adverse effect? A) Acute renal failure B) Unpredictable reactions C) Paranoia D) Hallucinations Ans: B Feedback: Use benzodiazepines with caution in elderly or debilitated patients because of the possibility of unpredictable reactions and in patients with renal or hepatic dysfunction, which may alter the metabolism and excretion of these drugs, resulting in direct toxicity. Dosage adjustments usually are needed for such patients. Acute renal failure, paranoia, and hallucinations are not commonly related to therapy with these medications in the elderly. 24. A 72-year-old patient presents at the emergency department with respiratory depression and excessive sedation. The family tells the nurse that the patient has been taking medication throughout the evening. The nurse suspects benzodiazepine overdose and would expect what drug to be ordered? A) Valium B) Phenergan C) Hydroxyzine D) Flumazenil Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) Ans: 331 D Feedback: Toxic effects of benzodiazepines include excessive sedation, respiratory depression, and coma. Flumazenil is an antidote for the benzodiazepines. Hydroxyzine is an antihistamine with anticholinergic effects and would not be appropriate for this patient. Valium would enhance the effects of benzodiazepines. Phenergan is not indicated for this patient; it is similar in actions to hydroxyzine. 25. The nurse is caring for a patient who has not been able to sleep. The physician orders a barbiturate medication for this patient. What adverse effect should the nurse teach the patient about? A) Double vision B) Paranoia C) Tinnitus D) Thinking abnormalities Ans: D Feedback: The most common adverse effects are related to general central nervous system (CNS) depression. CNS effects may include drowsiness, somnolence, lethargy, ataxia, vertigo, a resembling a hangover, thinking abnormalities, paradoxical excitement, anxiety, and hallucinations. Barbiturate drugs generally do not cause double vision, paranoia, or tinnitus. 26. An older adult African American patient comes to the clinic and is diagnosed with generalized anxiety disorder (GAD). The physician orders oral flurazepam 30 mg. What is the nurse’s priority action? A) Teach the patient about the prescribed medication. B) Administer the first dose of medication. C) Tell patient to take first dosage after driving home. D) Talk to the physician about the dosage. Ans: D Feedback: Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 332 If an anxiolytic or hypnotic agent is the drug of choice for an African American patient, the smallest possible dose should be used, and the patient should be monitored very closely during the first week of treatment. Dosage adjustments are necessary to achieve the most effective dose with the fewest adverse effects. In addition, older adults also require careful titration of dosage. Older patients may be more susceptible to the adverse effects of these drugs, from unanticipated central nervous system (CNS) adverse effects including increased sedation, dizziness, and even hallucinations. Dosages of all of these drugs should be reduced and the patient should be monitored very closely for toxic effects and to provide safety measures if CNS effects do occur. As a result, the priority action is to talk to the physician about the dosage. The other actions may be appropriate after a proper dosage is ordered. 27. The nurse is caring for a patient who has a sedative hypnotic ordered. The nurse would consider this drug contraindicated if the patient had what disorder? A) Neurological diseases B) Liver failure C) Endocrine disorders D) Heart disease Ans: B Feedback: Benzodiazepines undergo extensive hepatic metabolism. In the presence of liver disease, the metabolism of most benzodiazepines is slowed, with resultant accumulation and increased risk of adverse effects. Neurological disorders, endocrine disorders, and heart disease are not contraindications for the use of benzodiazepines. 28. The nurse evaluates teaching as effective when a patient taking a benzodiazepine states, A) I should always take the medication with meals. B) I should not stop taking this drug without talking to my health care provider first. C) I cannot take aspirin with this medication. D) I will have to take this medication for the rest of my life. Ans: B Feedback: The patient makes a correct statement when saying the drug should not be stopped without talking to the health care provider first because withdrawal of benzodiazepines require careful monitoring and should be gradually withdrawn. Medications do not have to be taken with food, aspirin is not Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 333 contraindicated, and the medication need only be taken while the condition being treated continues. Patients with anxiety may only need the medication for a few weeks whereas those with a seizure disorder may take it for longer periods of time. 29. The nurse is caring for a patient treated with flumazenil (Anexate) for benzodiazepine toxicity. After administering flumazenil what will the nurse carefully assess for? A) Agitation, confusion, and seizures B) Cerebral hemorrhage and dystonia C) Hypertension and renal insufficiency D) Hypotension, dysrhythmias, and cardiac arrest Ans: A Feedback: Administration of flumazenil blocks the action of benzodiazepines. If the patient has been taking these medications for an extended period of time, the blockage of the drug’s effects could precipitate an acute benzodiazepine withdrawal syndrome with symptoms including agitation, confusion, and seizures. Anexate does not cause cerebral hemorrhage and dystonia, hypertension, renal insufficiency, hypotension, dysrhythmias, and cardiac arrest. 30. The nurse administers promethazine (Phenergan) to the patient before sending the patient to the preoperative holding area. What is the rationale for administration of this drug? A) Sedation B) Oral secretions C) Hypotension and bradycardia D) Confusion Ans: A Feedback: Antihistamines (promethazine, diphenhydramine [Benadryl]) can be very sedating in some people. They are used as preoperative medications and postoperatively to decrease the need for narcotics. Promethazine is not given for hypotension, bradycardia, confusion, or oral secretions. 31. What reasons can the nurse give for why barbiturates are no longer considered the mainstay for treatment of anxiety? (Select all that apply.) Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) A) Adverse effects are more severe. B) There is an increased risk of physical tolerance. C) There is an increased risk of psychological dependence. D) The most common adverse effects are related to cardiac arrhythmias. E) Hypersensitivity reactions can sometimes be fatal. Ans: A, B, C, E 334 Feedback: The adverse effects caused by barbiturates are more severe than those associated with other, newer sedatives/hypnotics. For this reason, barbiturates are no longer considered the mainstay for the treatment of anxiety. In addition, the development of physical tolerance and psychological dependence is more likely with the barbiturates than with other anxiolytics. The most common adverse effects are related to central nervous system (CNS) depression. Hypersensitivity reactions to barbiturates are sometimes fatal. 32. The nurse is teaching a class for nurses working in prenatal clinics about the danger associated with use of benzodiazepines during pregnancy and explains that what fetal anomalies result from maternal use of benzodiazepines during the first trimester of pregnancy? (Select all that apply.) A) Cleft lip or palate B) Inguinal hernia C) Cardiac defects D) Microencephaly E) Gastroschises Ans: A, B, C, D Feedback: Benzodiazepines are contraindicated in pregnancy because a predictable syndrome of cleft lip or palate, inguinal hernia, cardiac defects, microcephaly, or pyloric stenosis occurs when they are taken in the first trimester. Gastroschises, when the abdominal organs are found outside the abdominal cavity, is not associated with use of benzodiazepine use in the first trimester. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 33. 335 The nurse is caring for a newborn who was delivered from a woman who took benzodiazepines for anxiety during the last 2 months of her pregnancy after her husband was killed in war. What will the nurse assess for in this newborn? A) Newborn withdrawal syndrome B) Hepatic dysfunction C) Failure to thrive D) Learning deficiencies Ans: A Feedback: Neonatal withdrawal syndrome may result in a baby born to a mother who was taking benzodiazepines in the final weeks of pregnancy. The neonate may be given very small doses of benzodiazepines that are withdrawn gradually to prevent symptoms. Hepatic dysfunction in the neonate is not associated with use of benzodiazepines. Failure to thrive and learning deficiencies would be long-term problems and are not assessed during the neonatal period. 34. The nurse is caring for a patient who received a new diagnosis of cancer. The patient exhibits signs of a sympathetic stress reaction. What signs and symptoms will the nurse assess in this patient consistent with an acute reaction to stress? (Select all that apply.) A) Profuse sweating B) Fast heart rate C) Rapid breathing D) Hypotension E) Inability to interact with others Ans: A, B, C Feedback: Anxiety is often accompanied by signs and symptoms of the sympathetic stress reaction that may include sweating, fast heart rate, rapid breathing, and elevated blood pressure. Chronically anxious people may be afraid to interact with other people but this is not usually seen in an acute stress reaction. 35. The nurse is caring for an older adult in the long-term care facility who has begun to display signs of anxiety and insomnia. What is the priority nursing action? Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) A) Assess the patient for physical problems. B) Call the provider and request an antianxiety drug order. C) Increase the patient’s social time, encouraging interaction with others. D) Suggest the family visit more often to reduce the resident’s stress level. Ans: A 336 Feedback: The patient should be screened for physical problems, neurological deterioration, or depression, which could contribute to the insomnia or anxiety. Only after physical problems are ruled out would the nurse consider nondrug measures such as increased socialization with other residents or family members. If nothing else is effective, pharmacological intervention may be necessary. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 337 Chapter 21 - Antidepressant Agents 1. The mental health nursing instructor is talking with the class about depression. What deficiency does the instructor explain will result in depression? A) Epinephrine, norepinephrine, and acetylcholine B) Norepinephrine, dopamine, and serotonin C) Acetylcholine, gamma-aminobutyric acid, and serotonin D) Gamma-aminobutyric acid, dopamine, and epinephrine Ans: B Feedback: A current hypothesis regarding the cause of depression is a deficiency of norepinephrine, dopamine, or serotonin, which are all biogenic amines, in key areas of the brain. Acetylcholine is a neurotransmitter that communicates between nerves and muscles. Epinephrine is a catecholamine that serves as a neurotransmitter that is released in the sympathetic branch of the autonomic nervous system and can be hormones when released from cells in the adrenal medulla. Gamma-aminobutyric acid is a neurotransmitter that inhibits nerve activity and prevents over excitability or stimulation. 2. What is the physiological action of tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs)? A) Inhibiting monoamine oxidase inhibitors that break down norepinephrine B) Inhibiting nerve activity, which prevents over excitability or stimulation C) Blocking the reuptake of serotonin, which increases the levels of norepinephrine D) Inhibiting reuptake of norepinephrine and serotonin Ans: D Feedback: TCAs inhibit presynaptic reuptake of norepinephrine and serotonin, which cause an accumulation of the neurotransmitters that is thought to create the antidepressant effect. Monoamine oxidase inhibitors irreversibly inhibit monoamine oxidase that breaks down norepinephrine and serotonin. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors block the reuptake of serotonin; gamma-aminobutyric acid inhibits nerve activity. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 3. 338 A nurse is working with a 9-year-old child who exhibits signs and symptoms of obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD). What drug will the nurse anticipate may be prescribed for the child? A) Phenelzine (Nardil) B) Amitriptyline (Elavil) C) Fluvoxamine (Prozac) D) Isocarboxazid (Marplan) Ans: C Feedback: Fluvoxamine is a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor that has established pediatric dosage guidelines for the treatment of obsessive-compulsive disorder. Isocarboxazid and phenelzine are monoamine oxidase inhibitors and should be avoided in pediatric use because of the potential drugfood interactions and other serious adverse effects. Amitriptyline is also a tricyclic antidepressant not recommended for pediatric use. 4. A patient explains to a nurse that he had been taking amitriptyline (Elavil) for depression and that his physician changed his medication to clomipramine (Anafranil). The patient is confused and does not understand why his medication was changed. The nurse’s best response to the patient would be what? A) These drugs are similar but some patients respond better to one drug than another. B) Did you take the amitriptyline like you should have? C) Maybe the old medicine wasn’t working anymore. D) Clomipramine is newer and will be much better for you. Ans: A Feedback: Because all tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) are similarly effective, the choice of which TCA depends on individual response to the drug and tolerance of adverse effects. A patient who does not respond to one TCA may respond to another drug from this class. In addition, the nurse might inform the physician of the patient’s question so the physician can explain his or her rationale for changing medications. By asking the patient if he took the medication as prescribed, the nurse is insinuating that he may not have and could damage the trusting nursepatient relationship. The nurse has no basis for commenting that the medication might not be working or that another drug would work better. 5. A patient comes to the mental health clinic for a regular appointment. The patient tells the nurse he has been taking oral fluoxetine (Prozac) 20 mg daily for the past 3 weeks and that he has lost 3 pounds Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 339 during that time due to a loss of appetite. What action should the nurse take? A) Teaching the patient about healthy eating to maintain weight B) Congratulating the patient on his weight loss and commenting how well he looks C) Encouraging the patient to increase fluid intake to avoid further weight loss D) Reassuring the patient that a decrease in weight is a common adverse effect with this medication Ans: D Feedback: Adverse effects of fluoxetine include anorexia and weight loss. Although teaching about healthy eating is a good idea, it is more important to teach the patient how to take the medication in a way that will reduce adverse effects as well as how to optimize healthy calories to maintain weight. The patient should increase caloric intake, not just fluid intake. The patient should continue the medication to see whether therapeutic effects are obtained and adjust nutritional intake if necessary. More information about the patient’s baseline weight is needed before congratulating the patient because a patient who is already too thin would not appreciate the nurse’s comment. 6. A patient diagnosed with type 1 diabetes mellitus is receiving insulin. The physician has prescribed a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) to treat this patient’s depression. What interaction will the nurse assess for with this drug combination? A) Increased risk of hypoglycemia B) Increased risk of hyperglycemia C) Increase in appetite D) Increased total cholesterol Ans: A Feedback: MAOIs can cause an additive hypoglycemic effect if taken with insulin or oral diabetic agents. This patient would have to be monitored closely and appropriate dosage adjustments made; he should be taught the importance of more frequent blood sugar monitoring. The drug combination in this question would not cause an increase in appetite or increased total cholesterol. 7. A patient has been taking Prozac (fluoxetine) for the past 3 years for depression. She is seeing her gynecologist for premenopausal symptoms and during the interview with the nurse she says that she would like to try Sarafem because her friend is taking it and she says it works great. The nurse’s best response is what? Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) A) Sarafem and Prozac are different brand names for the same generic medication. B) Before changing drugs it is important to consider how well you responded to Prozac. C) You cannot take both drugs at the same time so it will be important to decide which is best. D) When taking both of these drugs, it is best to take one in the morning and one at night. Ans: A 340 Feedback: Prozac and Sarafem are different brand names for fluoxetine, so there is no benefit in changing the patient’s medication regimen and, if taken together, would result in a drug overdose. The other three responses are incorrect or inappropriate because they do not recognize that both drugs are the same. 8. A 12-year-old patient is hospitalized with severe depression. The patient has been taking a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI). What is the priority nursing action for the patient? A) Monitor food intake for levels of tyramine. B) Assess for weight loss and difficulty sleeping. C) Monitor the patient for severe headaches. D) Implement suicide precautions. Ans: D Feedback: Recent studies have linked the incidence of suicide attempts to the use of SSRIs in pediatric patients (see box 21.3 Focus on the Evidence). The priority concern for the nurse would be safety for the patient. Severe headache and reactions to tyramine-containing foods are associated with monoamine oxidase therapy. Weight loss and difficulty sleeping are of a lower priority concern than the patient’s safety. 9. What drug, if prescribed for the patient, would indicate the need to assess the patient for depression characterized by anxiety and addictive behaviors? A) Imipramine (Tofranil) B) Venlafaxine (Effexor) Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) C) Fluvoxamine (Luvox) D) Tranylcypromine (Parnate) Ans: B 341 Feedback: Venlafaxine is used to treat and prevent depression in generalized anxiety disorder, social anxiety disorder; it also diminishes addictive behavior. Fluvoxamine is a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor, tranylcypromine is a monoamine oxidase inhibitor, and imipramine is a tricyclic antidepressant that are not indicated for treatment of anxiety disorder and addictive behavior. 10. A patient receives a new prescription for fluvoxamine (Luvox). What will the nurse instruct the patient about taking the medication? A) Take medication after eating breakfast. B) Take medication with at least 8 ounces of liquid. C) The dosage may need to be increased if the patient is not feeling better in 2 weeks. D) The medication should be taken once a day before bedtime. Ans: D Feedback: Fluvoxamine is a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor that should be taken once a day before bedtime. The medication does not require 8 ounces of fluid for absorption. It should be taken for at least 4 weeks before a therapeutic effect is noted. 11. The patient presents to the emergency department with a headache in the back of the head, palpitations, neck stiffness, nausea, vomiting, sweating, dilated pupils, tachycardia, and chest pain. Blood pressure measures 180/124 and heart rate is 168 beats per minute. The spouse says the only medication he takes is something for depression but she does not know the name of the drug and the patient is also unable to supply the name. What classification of antidepressant does the nurse suspect this patient is taking? A) Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) B) Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) C) Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) D) Antianxiety antidepressants Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) Ans: 342 A Feedback: MAOIs have several serious adverse effects that can be fatal. This patient’s symptoms indicate fatal hypertensive crisis characterized by occipital headache, palpitations, neck stiffness, nausea, vomiting, sweating, dilated pupils, photophobia, tachycardia, and chest pain. It may progress to intracranial bleeding and fatal stroke. SSRIs and TCAs are not associated with these particular symptoms. Antianxiety antidepressants are not a classification of antidepressants. 12. Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) is a disorder that remains under investigation as to its actual neurophysiology. What tricyclic antidepressant is now approved by the Food and Drug Administration to treat OCD? A) Clomipramine B) Imipramine C) Nortriptyline D) Amitriptyline Ans: A Feedback: Clomipramine is now also approved for use in the treatment of OCD. Imipramine, nortriptyline, and amitriptyline are not approved for use in treating OCD. 13. The nurse interviews the family of a patient hospitalized with severe depression who is prescribed a tricyclic antidepressant. What assessment data are important in planning this patient’s plan of care? (Select all that apply.) A) Recent suicide attempts B) Gastrointestinal (GI) obstruction C) Affect D) Physical pain E) Personal responsibilities Ans: A, B, C Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 343 Feedback: When caring for a patient with a diagnosis of depression it is always important for the nurse to assess for recent suicide attempts, suicidal ideation, and any suicidal plans. After starting the medication, as the patient begins to feel better, risk of suicide increases, so ongoing assessment is essential to the patient’s safety. Other assessments include allergies, liver and kidney function, glaucoma, benign prostatic hypertrophy, cardiac dysfunction, GI obstruction, surgery, or recent myocardial infarction, all of which could be exacerbated by the effects of the drug. Assess history of psychiatric problems, or myelography within the past 24 hours or in the next 48 hours, or is taking a monoamine oxidase inhibitor to avoid potentially serious adverse reactions. Physical pain and personal responsibilities may be assessed but are not priority assessments unless indicated by other diagnoses. 14. A patient is admitted to the unit with obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD). What drug might the nurse administer that has been found to be effective for treating OCD? A) Fluvoxamine B) Phenelzine C) Desipramine D) Amitriptyline Ans: A Feedback: Fluvoxamine is indicated for the treatment of OCD and is classified as a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI). SSRIs are indicated for the treatment of depression, OCD, panic attacks, bulimia, premenstrual dysphoria disorder, posttraumatic stress disorder, social phobias, and social anxiety disorders. Phenelzine is indicated for depression not responsive to other agents. Desipramine and amitriptyline are tricyclic antidepressants indicated for treatment of depression especially if accompanied by anxiety or sleep disturbances. 15. The patient has been severely depressed since her father died 6 months ago. The physician has prescribed amitriptyline. The nurse reviews the patient’s chart before administering the medication. What preexisting condition would require cautious use of this drug? A) Osteosarcoma B) Cardiovascular disorders C) Closed head injury D) Bleeding ulcer Ans: B Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 344 Feedback: Caution should be used with tricyclic antidepressants in patients with preexisting cardiovascular (CV) disorders because of the cardiac stimulatory effects of the drug and with any condition that would be exacerbated by the anticholinergic effects (e.g., angle-closure glaucoma, urinary retention, prostate hypertrophy, GI or genitourinary surgery). There is no indication that caution is needed with patients diagnosed with osteosarcoma, closed head injury, or bleeding ulcer. 16. What priority teaching point does the nurse include in the teaching plan for a patient on a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI)? (Select all that apply.) A) Take medication at bedtime. B) Monitor blood pressure. C) Do not take over-the-counter (OTC) drugs without talking to physician. D) Report double vision right away E) Reduce tyramine intake Ans: B, C, E Feedback: MAOIs can cause drugdrug and drugfood interactions, which can precipitate cardiovascular effects that include orthostatic hypotension, arrhythmias, palpitations, angina, and the potentially fatal hypertensive crisis. Priority teaching points include monitoring blood pressure which will elevate with tyramine ingestion and the importance of not taking any OTC without physician or pharmacist consultation due to multiple drugdrug interactions. When taking an MAOI, you would not necessarily take the drug at bedtime or drink lots of fluid. Blurred, but not double, vision is an adverse effect of an MAOI. 17. A patient with severe depression has been hospitalized and the physician has ordered amitriptyline. What common adverse effect will the nurse monitor and assess the patient for? (Select all that apply.) A) Fever B) Myocardial Infarction C) Stroke D) Dry mouth E) Gynecomastia Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) Ans: 345 B, C, D Feedback: Use of tricyclic antidepressants may lead to GI anticholinergic effects, such as dry mouth, constipation, nausea, vomiting, anorexia, increased salivation, cramps, and diarrhea. Cardiovascular effects (e.g., orthostatic hypotension, hypertension, arrhythmias, myocardial infarction, angina, palpitations, stroke) may occur. Fever and gynecomastia are not normally attributed to amitriptyline therapy. 18. The nurse is caring for an 8-year-old clinic patient who takes imipramine. The nurse assesses the patient who does not have a history for or signs of depression, so the nurse suspects this drug was prescribed as treatment for what? A) Enuresis B) Obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD) C) Peripheral neuropathy D) Panic disorder Ans: A Feedback: One of the indications for use of the drug imipramine is enuresis in children older than 6 years. Imipramine is not indicated for the treatment of OCD, peripheral neuropathy, or panic disorder. 19. A 10-year-old patient is being seen by a physician for severe depression. The physician prescribes an antidepressant. What antidepressant could the nurse safely administer to a child? A) Trazodone B) Nortriptyline C) Fluvoxamine D) Phenelzine Ans: B Feedback: Nortriptyline has established pediatric doses and can be used in children older than 6 years but such children should be monitored closely for adverse effects. Phenelzine is a monoamine oxidase inhibitor Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 346 (MAOI), a class of drugs that should be avoided in children if at all possible because of the potential for drugfood interactions and the serious adverse effects. Trazodone can be used with children but is not a first-line drug because it has many adverse effects on the central nervous system associated with its use. Luvox is an SSRI that can be used in children to treat obsessive-compulsive disorder but selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors can cause serious adverse effects in children. 20. The biogenic amine theory of depression states that depression results from a deficiency of biogenic amines in key areas of the brain. Why might a deficiency of these biogenic amines exist? A) A slowing of the action of the neurons may lead to their depletion. B) Monoamine oxidase (MAO) strengthens the impact of biogenic amines. C) The number or sensitivity of postsynaptic receptors may increase. D) Norepinephrine may be depleted because biogenic amines feed off of loose particles of the neurotransmitter. Ans: C Feedback: The three reasons for depression according to the biogenic amine theory include (1) MAO may break down biogenic amine to be recycled or restored in the neuron. (2) Rapid fire of the neurons may lead to their depletion. (3) The number or sensitivity of postsynaptic receptors may increase, thus depleting neurotransmitter levels. 21. It has been postulated that depression may be a syndrome that reflects either activity or lack of activity in what areas of the brain? (Select all that apply.) A) Limbic system B) Corpus callosum C) Reticular activating system (RAS) D) Substantia nigra E) Basal ganglia Ans: A, C, E Feedback: Depression also may occur as a result of other, yet unknown causes. This condition may be a syndrome that reflects either activity or lack of activity in a number of sites in the brain, including the arousal Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 347 center (i.e., RAS), the limbic system, and basal ganglia. It is not theorized that depression is associated with the corpus callosum or the substantia nigra. 22. What reason might the nurse give for why venlafaxine (Effexor) has become more popular with adults in treating their depression? A) It is taken orally. B) It does not have adverse effects. C) It can be taken during pregnancy. D) An extended release form is available. Ans: D Feedback: Venlafaxine mildly blocks reuptake of norepinephrine, 5-hydroxytriptamine, and dopamine. It has fewer adverse central nervous system effects than trazodone. Its popularity has increased with the introduction of an extended-release form that does away with the multiple daily doses that are required with the regular form. Venlafaxine is readily absorbed from the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, extensively metabolized in the liver, and excreted in urine. Adequate studies have not been done in pregnancy and lactation, so that it should be used during those times only if the benefit to the mother clearly outweighs the potential risk to the neonate. It is taken orally, which is the case with most antidepressants. 23. A 75-year-old male patient is brought to the emergency department by his family because he is talking to people who aren’t there. During the initial admission assessment, his daughter mentions that her mother died 4 months ago and Dad just hasn’t been the same. The doctor has even put him on antidepressant medication. I go by the house every day to make sure he takes his medication. What would the nurse suspect is happening to this patient? A) The patient is having hallucinations as an adverse effect of his antidepressant medication. B) The mental status change is due to the patient’s age. C) The patient probably has a urinary tract infection. D) The patient is having delusions because of his depression over the loss of his wife. Ans: A Feedback: Older patients may be more susceptible to the adverse effects of antidepressants from unanticipated central nervous system effects to increased sedation, dizziness, and even hallucinations. Although an infection cannot be ruled out without further testing, the history would lead the nurse to the Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 348 antidepressants as the most likely cause. 24. Antidepressants carry a black box warning about the increased risk of suicide in what age group? A) Infants and children B) Children and adolescents C) Adolescents and adults D) Adults and older adults Ans: B Feedback: A black box warning was added to all antidepressants bringing attention to the increase in suicidality, especially in children and adolescents, when these drugs were used. Therefore, the other age groups are incorrect. 25. A patient is prescribed sertraline (Zoloft). What adverse effects should the nurse warn of when developing a medication teaching plan? (Select all that apply.) A) Agitation B) Agglutination C) Insomnia D) Intermittent tachycardia E) Dry mouth Ans: A, C, E Feedback: The adverse effects associated with selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, which are related to the effects of increased 5-hydroxytriptamine levels, include central nervous system effects (e.g., headache, drowsiness, dizziness, insomnia, anxiety, tremor, agitation, seizures). Gastrointestinal effects (e.g., nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, dry mouth, anorexia, constipation, changes in taste) often occur, as do genitourinary effects (e.g., painful menstruation, cystitis, sexual dysfunction, urgency, impotence). Adverse effects of sertraline do not include agglutination of blood cells or intermittent tachycardia. 26. The nurse is caring for a patient who is taking amitriptyline for depression. What teaching will the Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 349 nurse include in the teaching plan to help the patient monitor for adverse effects? A) If chest pain occurs an over-the-counter pain reliever will help. B) Nasal congestion indicates a respiratory virus is beginning. C) Measure and record your blood pressure daily. D) Adverse effects will subside as you adjust to the medication. Ans: C Feedback: Cardiovascular effects of amitriptyline include orthostatic hypotension, hypertension, arrhythmias, myocardial infarction, angina, palpitations, and stroke. Miscellaneous reported effects include alopecia, weight gain or loss, flushing, chills, and nasal congestion. Teaching the patient how and when to monitor blood pressure would be an important teaching point. Chest pain could be a serious finding and patients should be taught to call 911. Nasal congestion is a possible adverse effect of the drug and not an indication of a respiratory virus infection. Adverse effects often will not subside and may continue so long as the drug is taken. 27. The nurse is caring for a patient who was referred to a psychiatrist for treatment of a severe anxiety disorder. What medication does the nurse consider appropriate for this patient? A) Chlorpromazine (Thorazine) 25 mg three times daily orally B) Benztropine (Cogentin) 2 mg twice daily orally C) Clozapine (Clozaril) 200 mg twice daily orally D) Paroxetine (Paxil) 10 mg once daily orally Ans: D Feedback: Paroxetine is a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor indicated for the treatment of depression, obsessive compulsive disorder, panic attacks, bulimia, premenstrual dysphoria disorder, posttraumatic stress disorders, social phobias, and social anxiety disorders. Chlorpromazine and clozapine are antipsychotic medications whereas benztropine is a drug used to treat Parkinson’s disease. None of these would be appropriate options to treat anxiety disorders. 28. A patient comes to the clinic because she is feeling depressed and has gained some weight. The physician prescribes oral tranylcypromine (Parnate) 10 mg twice daily for an atypical depression. When prescribed in this manner, when would the nurse tell the patient to expect the drug to reach peak levels in the body? Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) A) 1 to 2 hours B) 2 to 3 hours C) 3 to 4 days D) 4 to 5 weeks Ans: B 350 Feedback: The monoamine oxidase inhibitors are well absorbed from the GI tract, reaching peak levels in 2 to 3 hours. The other time frames are incorrect. 29. The nurse is creating a care plan for a patient taking a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI). What would be an appropriate nursing diagnosis for this patient? A) Risk for infection B) Establish suicide precautions C) Disturbed thought processes related to central nervous system (CNS) effects of medication D) Dysfunctional Family Processes Ans: C Feedback: Nursing diagnoses related to SSRI therapy might include: Disturbed thought processes related to central nervous system effects because adverse effects of SSRIs include headache, drowsiness, dizziness, insomnia, anxiety, tremor, agitation, and seizures. There would be no reason to expect the patient is at increased risk for infection, there is not enough information known about the patient’s family to know if processes are dysfunctional. Establishing suicide precautions is an intervention and not a nursing diagnosis. 30. A patient is admitted with a presumed diagnosis of colon cancer who takes a monoamine oxidase inhibitor for depression. What drug will the nurse keep on hand for this patient in case of the onset of an adverse reaction? A) Epinephrine B) Injectable naloxone (Narcan) Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) C) Phenylalanine D) Phentolamine Ans: D 351 Feedback: Have phentolamine or another adrenergic blocker on standby as treatment in case of hypertensive crisis. The other options are distracters for this question. 31. The nurse is working on the telemetry unit and has noted that many postmyocardial-infarction (MI) patients experience depression. What medication would the nurse question if ordered for one of these patients? A) Amitriptyline B) Escitalopram C) Fluoxetine D) Fluvoxamine Ans: A Feedback: Amitriptyline is a tricyclic antidepressant (TCA). One contraindication to the use of TCAs includes recent myocardial infarction because of the potential occurrence of reinfarction or extension of the infarct with the cardiac effects of the drug. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors would be the safest antidepressant to give so there would be no need to question an order for escitalopram, fluoxetine, or fluvoxamine. 32. The nurse works in a mental health clinic. When a new patient arrives reporting feelings of depression, what conditions are screened for before prescribing antidepressants? (Select all that apply.) A) Thyroid disease B) Hormonal imbalance C) Cardiovascular disorders D) Parkinson’s disease Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) E) Diabetes mellitus Ans: A, B, C 352 Feedback: Adults using these drugs should have physical causes for their depression ruled out before therapy is begun. Thyroid disease, hormonal imbalance, and cardiovascular disorders can all lead to the signs and symptoms of depression. There is no indication that Parkinson’s disease or diabetes is manifested by depression. 33. The nurse is teaching a patient taking a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) about dietary changes required to minimize adverse effects of the drug. The nurse determines the patient understands a low tyramine diet when what meal is chosen? A) A chop salad with blue cheese, sardines, and pepperoni B) A sandwich with turkey, avocado, and Swiss cheese C) Corned beef hash, eggs, and hash browns D) A hamburger, French fries, and a strawberry milkshake Ans: D Feedback: Hamburger, French fries, and a strawberry milkshake do not contain tyramine and, although high in fat, it would not be contraindicated for a patient taking an MAOI. Blue cheese, sardines, pepperoni, Swiss cheese, and corned beef are all high in tyramine and would indicate further teaching was needed. 34. What drugs would the nurse consider contraindicated for the patient taking a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI)? A) Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) B) Insulin C) Acetaminophen D) Docusate (Colace) Ans: A Feedback: Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 353 SSRIs are contraindicated because of a life-threatening serotonin syndrome that could occur. If a patient requires insulin the benefit outweighs the risk but careful monitoring of glucose levels is needed because effects of insulin may be additive with an MAOI. There is no known contraindication for acetaminophen or docusate. 35. The nurse is caring for a young female patient who is 5 weeks pregnant. What statement made by the nurse about the use of antidepressants during pregnancy is most accurate? A) Antidepressants are used very cautiously during pregnancy and only when benefit outweighs risk. B) Antidepressants are contraindicated and must be discontinued if pregnancy occurs. C) Antidepressants must be chosen carefully because only a few are safe during pregnancy. D) Most antidepressants are safe during pregnancy but those that are contraindicated should be avoided. Ans: A Feedback: Antidepressants should be used very cautiously during pregnancy and lactation because of the potential for adverse effects on the fetus and possible neurological effects on the baby. Use should be reserved for situations in which the benefits to the mother far outweigh the potential risks to the neonate. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 354 Chapter 22 - Psychotherapeutic Agents 1. A group of patients are being screened to see which patients would be the best candidate for a psychotherapeutic drug trial that helps people concentrate longer on activities. Which patient would be best suited for this trial? A) A 28-year-old salesperson who alternates between overactivity and periods of depression B) A 32-year-old hyperactive nursing student who cannot focus long enough to take a test C) A 55-year-old physician who suddenly falls asleep during the day without warning D) A 16-year-old youth who say he can make the light turn on by pointing at it and hears voices Ans: B Feedback: Attention-deficit disorders involve various conditions characterized by an inability to concentrate on one activity for longer than a few minutes. The nursing student needing accommodations has an attention-deficit disorder. The salesperson exhibits signs of mania, which are characterized by periods of extreme overactivity and excitement followed by extreme depression. The physician is experiencing narcolepsy, which is defined as daytime sleepiness and sudden periods of loss of wakefulness. The teenager is schizophrenic and is exhibiting paranoia, hallucinations, and delusions. 2. What nursing intervention is appropriate for a 70-year-old female patient receiving lithium? A) Instruct the patient to use barrier contraceptives. B) Monitor blood glucose levels. C) Monitor fluid and sodium intake. D) Encourage the patient to check daily for weight loss. Ans: C Feedback: Older patients, and especially those with renal impairment, should be encouraged to maintain adequate hydration and salt intake. Decreased dosages may also be necessary with the elderly. A 70-year-old patient would not be concerned about the use of contraceptives. These drugs alone do not affect glucose levels. Weight loss is usually not associated with lithium use. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 3. 355 A nurse is caring for a patient who is taking lithium for mania. The nurse’s assessment includes a notation of a lithium serum level of 2.4 mEq/L. The nurse anticipates seeing what? A) Fine tremors of both hands B) Slurred speech C) Clonic movements D) Nausea and vomiting Ans: C Feedback: Serum levels of 2 to 2.5 mEq/L may produce ataxia, clonic movements, possible seizures, and hypotension. Fine hand tremors, slurred speech, and nausea and vomiting are indicative of lithium levels less than 1.5 mEq/L. 4. The nurse administers chlorpromazine intramuscularly to the preoperative patient who is extremely anxious about surgery in the morning. What priority teaching point will the nurse provide this patient? A) Remain recumbent for at least 30 minutes after the injection. B) Do not eat for 1 hour after the drug is administered. C) Encourage fluids with the goal of 3,000 mL/d. D) Avoid eating avocados and oranges when taking this medication. Ans: A Feedback: When giving a parenteral form of an antipsychotic, the patient should remain recumbent to decrease the risk of injury if orthostatic hypotension occurs. Eating after drug injection should not interfere with the drug’s absorption and although adequate hydration should be maintained there is no need to increase fluid intake. Avocados and oranges are not contraindicated in patients receiving this medication. 5. A) The nurse is presenting an in-service at a children’s unit on hyperactivity. The nurse is told that a 6year-old on the unit is being treated with methylphenidate (Ritalin). The presenting nurse talks about discharge teaching for this patient and the importance of monitoring what? Long bone growth Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) B) Visual acuity C) Weight and complete blood count D) Urea and nitrogen levels Ans: C 356 Feedback: Methylphenidate is associated with weight loss, bone marrow suppression, and cardiac arrhythmias. Weight, blood count, and cardiac function should be monitored regularly. The drug is not associated with renal dysfunction, visual changes, or growth retardation, so those values would not need to be regularly evaluated as part of drug therapy. 6. The nurse is caring for a patient taking an oral neuroleptic medication. What is the nurse’s priority assessment to monitor for? A) Urge incontinence B) Orthostatic hypotension C) Bradycardia D) Tardive dyskinesia Ans: D Feedback: The nurse would monitor for and teach the patient and family about tardive dyskinesias because it is such a common adverse effect with continued use of the drug. Oral neuroleptic agents do not cause urge incontinence, orthostatic hypotension, or bradycardia. 7. A psychotic patient is admitted through the emergency department. The physician has ordered chlorpromazine (Thorazine) 25 mg intramuscularly. After administration of the medication, what is the nurse’s priority to evaluate? A) The patient’s ability to ambulate B) Return of the patient’s appetite C) A decrease in psychotic symptoms D) Blood pressure and pulse Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) Ans: 357 C Feedback: The nurse will evaluate the effectiveness of the drug in diminishing psychotic symptoms because this is the purpose of administering the drug. Monitoring blood pressure, pulse, and appetite is part of all patient care but is not the priority evaluation criterion for this patient. The ability to ambulate and maintain adequate nutrition would be assessed but is not the priority evaluation for this patient. 8. A patient diagnosed with bipolar disorder is to be discharged home in 48 hours. The nurse has completed patient teaching regarding the use of lithium. What statement by the patient indicates an understanding of their responsibility? A) I will increase my salt intake. B) I will increase my fluid intake. C) I will decrease my salt intake. D) I will decrease my fluid intake. Ans: B Feedback: To maintain a therapeutic lithium level, the patient must increase fluids. A decrease in consumption of fluids can lead to toxicity. An increase in salt intake can lead to lithium excretion and a decrease in effectiveness. A decrease in salt intake can cause retention, also leading to toxicity. Adequate salt intake is necessary to keep serum levels in therapeutic range but need not be increased or decreased. 9. A patient has just been prescribed a phenothiazine. During patient teaching about this drug, what would be important for the nurse to tell the patient? A) The urine can turn pink or reddish. B) The urine output will be decreased. C) Diarrhea can be an adverse effect. D) Hyperexcitability can occur. Ans: A Feedback: Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 358 Phenothiazines can cause the urine to turn pink or reddish. The patient should be informed that this is a simple color change and is not caused by blood in his urine. Decreased urine output is not associated with this drug. Constipation is usually an adverse effect of the drug. Drowsiness, not hyperexcitability, can occur. 10. A patient, in the manic phase of bipolar disorder, is being discharged home on an antimanic drug. What antimanic drug is used for long-term maintenance of bipolar disorders? A) Aripiprazole (Abilify) B) Lamotrigine (Lamictal) C) Quetiapine (Seroquel) D) Ziprasidone (Geodon) Ans: B Feedback: Lamotrigine is used for long-term maintenance of bipolar disorders. Aripiprazole and ziprasidone are used for acute manic and mixed episodes of bipolar disorders. Quetiapine is used as adjunct or monotherapy for the treatment of manic episodes associated with bipolar disorder. 11. A 16-year-old youth has just been diagnosed with schizophrenia. The parents ask the nurse what causes schizophrenia. What would be the nurse’s best response? A) Schizophrenia is caused by pain that the brain perceives. B) Schizophrenia is thought to occur due to trauma experienced in childhood. C) Schizophrenia is thought to reflect a fundamental biochemical abnormality. D) Schizophrenia is caused by seizure activity in the brain. Ans: C Feedback: This disorder, which seems to have a very strong genetic association, may reflect a fundamental biochemical abnormality. Mental disorders are now thought to be caused by some inherent dysfunction within the brain that leads to abnormal thought processes and responses. Schizophrenia is not caused by pain, childhood trauma, or seizure activity. 12. A patient on chlorpromazine is feeling better and decides they no longer need their medication. The nurse teaches the patient that abrupt withdrawal of a typical antipsychotic medication can result in Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 359 what? A) Insomnia B) Tardive dyskinesia C) Somnolence D) Constipation Ans: A Feedback: Sudden withdrawal can cause cholinergic effects such as diarrhea, gastritis, nausea, vomiting, dizziness, arrhythmias, drooling, and insomnia. Abrupt withdrawal of a typical antipsychotic generally does not cause tardive dyskinesia, somnolence, or constipation. 13. A patient’s medication has been changed to clozapine (Clozaril). The nurse evaluates this patient for which life-threatening adverse effect? A) Renal insufficiency B) Emphysema C) Neuroleptic malignant syndrome D) Cerebrovascular accident (CVA) Ans: C Feedback: Neuroleptic malignant syndrome can be a life-threatening adverse effect of atypical nonphenothiazines. Renal insufficiency, emphysema, and CVA are not commonly seen adverse effects of atypical non-phenothiazines. 14. The nurse is caring for an adolescent patient who began taking an antipsychotic drug last month to treat newly diagnosed schizophrenia. The drug has not been effective and the mother asks the nurse if this means the adolescent’s symptoms cannot be controlled by drugs. What is the nurse’s best response? A) Patients commonly have to try different drugs until the most effective drug is identified. B) Some patients do not respond to drugs and have to rely solely on behavior therapy. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) C) Most likely your child was not taking the medication properly as prescribed. D) He may need to take multiple drugs before effects will be seen that control his symptoms. Ans: A 360 Feedback: A patient who does not respond to one drug may react successfully to another agent. Responses may also vary because of cultural issues. The selection of a specific drug depends on the desired potency and patient tolerance of the associated adverse effects. It is not common to have a patient who does not demonstrate some improvement from medications so it would be incorrect to tell the mother the child won’t respond to any drug after trying only one medication. There is no indication the drug was taken improperly and even properly administered drugs will not work on all patients. Multiple drug therapy is not indicated by the question. 15. Haloperidol is a typical antipsychotic drug. What adverse effect is associated with this drug? A) Bradycardia B) Bradypnea C) Extrapyramidal effects D) Hypoglycemia Ans: C Feedback: Haloperidol produces a relatively low incidence of hypotension and sedation and a high incidence of extrapyramidal effects. Haloperidol does not generally produce bradycardia, bradypnea, or hypoglycemia. 16. The pharmacology instructor is explaining to their class the difference between the typical and the atypical groups of antipsychotic drugs. What medication would the instructor explain to the students has fewer extrapyramidal effects and greater effectiveness than older antipsychotic drugs in relieving negative symptoms of schizophrenia? A) Chlorpromazine (Thorazine) B) Clozapine (Clozaril) C) Thiothixene (Navane) D) Haloperidol (Haldol) Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) Ans: 361 B Feedback: Advantages of clozapine include improvement of negative symptoms without causing the extrapyramidal effects associated with older antipsychotic drugs. Chlorpromazine is a typical antipsychotic, one of the older drugs, which does cause the extrapyramidal effects. Navane is part of the thioxanthene group of typical antipsychotics. This group of drugs has low sedative and hypotensive effects but can cause extrapyramidal effects. Haloperidol is a butyrophenone group drug used in psychiatric disorders. Usually, it produces a relatively low incidence of hypotension and sedation and a high incidence of extrapyramidal effects. 17. The nurse, providing teaching about a typical antipsychotic newly prescribed for the patient, cautions against use of alcohol with the drug by explaining it will have what effect? A) Prolonged QT interval B) Increased central nervous system (CNS) depression C) Increased anticholinergic effects D) Increased gastrointestinal (GI) adverse effects Ans: B Feedback: Antipsychoticalcohol combinations combinations result in an increased risk of CNS depression, and antipsychoticanticholinergic combinations lead to increased anticholinergic effects, so dosage adjustments are necessary. Patients should not take thioridazine or ziprasidone with any other drug associated with prolongation of the QT interval. Increase in GI adverse effects is not associated with concurrent use of alcohol. 18. The nurse is caring for four patients. Which patient would the nurse know that clozapine (Clozaril) is contraindicated for? A) 17-year-old adolescent B) 23-year-old with diabetes insipidus C) 32-year-old with osteoarthritis D) 45-year-old with bone marrow depression Ans: D Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 362 Feedback: Clozapine is associated with bone marrow suppression, a life-threatening decrease in white blood cells. Because of their wide-ranging adverse effects, antipsychotic drugs may cause or aggravate various conditions. They should be used very cautiously in patients with liver damage, coronary artery disease, cerebrovascular disease, Parkinsonism, bone marrow depression, severe hypotension or hypertension, coma, or severely depressed states. Options A, B, and C are incorrect. 19. The physician has ordered olanzapine (Zyprexa) for a new patient. What laboratory test should be done before administration of olanzapine? A) Blood glucose B) Urine specific gravity C) Cholesterol D) Hemoglobin and hematocrit Ans: A Feedback: Olanzapine has been associated with weight gain, hyperglycemia, and initiation or aggravation of diabetes mellitus. Other options are not necessary for patients taking olanzapine unless a secondary diagnosis indicates a need. 20. Parents bring a 15-year-old boy into the clinic. The parents tell the nurse that there is a family history of schizophrenia and they fear their son has developed the disease. What symptoms, if described by the family, would support their conclusion? A) He hears and interacts with voices no one else can hear. B) He is overactive and always so excitable. C) He falls asleep in the middle of a sentence. D) He cannot concentrate and his grades are suffering. Ans: A Feedback: Characteristics of schizophrenia include hallucinations, paranoia, delusions, speech abnormalities, and affective problems. Overactivity and excitement are associated with mania. Falling asleep suddenly Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 363 describes narcolepsy. Difficulty concentrating and failing grades is associated with attention deficient disorders. 21. The patient taking an antipsychotic drug asks the nurse how long he will continue to feel the effects of the drug after stopping the medication. What is the nurse’s best response? A) 2 to 4 hours B) 2 to 4 weeks C) 2 to 4 months D) 6 months Ans: D Feedback: The antipsychotics are widely distributed in the tissues and are often stored there, being released for up to 6 months after the drug therapy has been stopped. 22. The nurse works on an inpatient mental health unit. When administering antipsychotic medications, what patient would the nurse expect to require a standard dosage? A) African American adolescent diagnosed with schizophrenia B) Malaysian middle adult diagnosed with bipolar disorder C) Iranian older adult diagnosed with schizophrenia D) Caucasian young adult diagnosed with bipolar disorder Ans: D Feedback: Only the Caucasian young adult has no indications for administering a smaller than usual dosage. African Americans respond more rapidly to antipsychotic medications and have a greater risk for development of disfiguring adverse effects, such as tardive dyskinesia. Consequently, these patients should be started off at the lowest possible dose and monitored closely. Patients in Asian countries (e.g., India, Turkey, Malaysia, China, Japan, Indonesia) receive lower doses of neuroleptics and lithium to achieve the same therapeutic response as seen in patients in the United States. Arab American patients metabolize antipsychotic medications more slowly than Asian Americans do and may require lower doses to achieve the same therapeutic effects as in Caucasians. 23. Psychosis is a severe mental illness characterized by what? Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) A) Disordered thought B) Increased social interaction C) Hypoactivity with aggressiveness D) Paranoid hallucinations Ans: A 364 Feedback: Antipsychotic drugs are used mainly for the treatment of psychosis, a severe mental disorder characterized by disordered thought processes; blunted or inappropriate emotional responses; bizarre behavior ranging from hypoactivity to hyperactivity with agitation, aggressiveness, hostility, and combativeness; social withdrawal in which a person pays less-than-normal attention to the environment and other people; deterioration from previous levels of occupational and social functioning (poor selfcare and interpersonal skills); hallucinations; and paranoid delusions. 24. The nurse is caring for a patient newly diagnosed with schizophrenia. His parents say they have heard the term before but do not really understand exactly what schizophrenia means. How would the nurse describe the disorder? (Select all that apply.) A) Thought disorder B) Difficulty functioning in society C) Hallucinations can be auditory, visual, or sensory D) Can be cured with the correct medications E) Enter into fugue state in most cases Ans: A, B, C, D Feedback: Mental disorders are thought process disorders that may be caused by some inherent dysfunction within the brain. A psychosis is a thought disorder, and schizophrenia is the most common psychosis in which delusions and hallucinations are hallmarks. Hallucinations can be auditory, visual, or sensory. Patients diagnosed with schizophrenia have difficulty functioning in society. Schizophrenic patients do not generally go into fugue states and it certainly is not a common disorder. 25. A 7-year-old boy is admitted to the pediatric behavioral health unit with a diagnosis of an acute psychotic episode. Aripiprazole has been ordered. Before administering the medication, what is the Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 365 nurse’s first priority? A) Weigh the patient. B) Obtain baseline vital signs. C) Call the physician. D) Administer the medication between meals. Ans: C Feedback: Of the antipsychotics, chlorpromazine, haloperidol, pimozide, prochlorperazine, risperidone, thioridazine, and trifluoperazine are the only ones with established pediatric regimens. Aripiprazole has dosages for children 13 to 17 years of age but would not be appropriate for a 7-year-old child. Weighing the patient and obtaining baseline vital signs is necessary assessment data but is not the first priority. There is nothing to indicate medications should be administered between meals. 26. The nurse admits a patient newly diagnosed with schizophrenia to the inpatient mental health unit. What is the priority reason for why the nurse includes the family when collecting the nursing history? A) The patient may not be able to provide a coherent history. B) The patient may not be able to speak due to reduced level of consciousness. C) The family will feel better if they are included in the process. D) The patient will be less anxious if the family listens while he answers questions. Ans: A Feedback: Schizophrenia, the most common psychosis, is characterized by delusions, hallucinations, and inappropriate responses to stimuli. As a result, the patient may be unable to provide a coherent history and may be unaware of his behaviors considered dysfunctional. There is no reason to suspect the patient cannot speak and reducing anxiety is not the priority rationale for including family. While family is included in treatment, the goal is to treat the patient and not make the family feel better if actions were not in the patient’s best interests. 27. A) The nurse is teaching the soon-to-be-discharged patient, diagnosed with schizophrenia, about his medications. What is a priority teaching point for this patient? The patient must eat three nutritious meals daily. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) B) Over-the-counter medications may be taken with antipsychotic drugs. C) Cough medicines potentiate the actions of antipsychotic drugs. D) Alcohol consumption should be avoided. Ans: D 366 Feedback: Alcohol consumption should be avoided because it increases the central nervous system (CNS) effects of the drug and may cause excessive drowsiness and decreased awareness of safety hazards in the environment. Some patients may find it easier and more effective to eat five small meals rather than three nutritious meals. While promoting good nutrition is good practice, it is not the priority. Drugdrug interactions with antipsychotic drugs are common so the nurse would teach the patient not to take any medication without consulting with the doctor or a pharmacist to make sure it is safe. 28. What antiepileptic medication might the nurse administer to treat bipolar disorder? A) Apriprazole (Abilify) B) Cyclobenzaprine (Flexeril) C) Lamotrigine (Lamictal) D) Temazepam (Restoril) Ans: C Feedback: Lamotrigine is an antiepileptic agent used for long-term maintenance of patients with bipolar disorders because it decreases occurrence of acute mood episodes. Apriprazole is an atypical antipsychotic and is not an antiepileptic medication. Flexeril is a muscle relaxant and Temazepam is a hypnotic agent. None of these medications are indicated for the treatment of bipolar disorder. 29. A patient, who is 77 years old, is admitted with a diagnosis of dementia. Haloperidol (Haldol) has been ordered for this patient. What nursing considerations would govern the nurse’s actions? (Select all that apply.) A) It is classed as an atypical antipsychotic. B) A lowered dosage is indicated for older adult. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) C) It often has a hyperactive effect on patients. D) It should not be used to control behavior with dementia. E) It should only be given every other day. Ans: B, D 367 Feedback: Haloperidol is classified as a typical antipsychotic with a high risk of extrapyramidal effects and lower risk for hypotension and sedation. Older patients may be more susceptible to the adverse effects of antipsychotic drugs. All dosages need to be reduced and patients monitored very closely for toxic effects and to provide safety measures if central nervous system effects do occur. They should not be used to control behavior with dementia. Haloperidol does not have a hyperactive effect on patients; it should not be given on an every-other-day schedule. 30. Which drug does not have a recommended pediatric dose? A) Pimozide (Orap) B) Lithium salts (Lithotabs) C) Haloperidol (Haldol) D) Risperidone (Risperdal) Ans: B Feedback: Lithium does not have a recommended pediatric dose; the drug should not be administered to children younger than 12 years old. Pimozide, haloperidol, and risperidone all have recommended pediatric doses. 31. The mother of a child diagnosed with attention-deficit syndrome receives a prescription for a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant to treat her child. The mother asks the nurse, I don’t understand why we’re giving a stimulant to calm him down? What is the nurse’s best response to this mother? A) It helps the reticular activating system (RAS), a part of the brain, to be more selective in response to incoming stimuli. B) It helps energize the child so they use up all of their available energy and then they can focus on quieter stimuli. C) No one truly understands why it works but it has been demonstrated to be very effective in treating Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 368 ADHD. D) The drugs work really well and you will see a tremendous change in your child within a few weeks without any other treatment. Ans: A Feedback: The paradoxical effect of calming hyperexcitability through CNS stimulation seen in attention-deficit syndrome is believed to be related to increased stimulation of an immature RAS, which leads to the ability to be more selective in response to incoming stimuli. CNS stimulants do not cause the child to use all his energy, the effect is thought to be understood, and telling the mother the drug just works without any explanation is not appropriate and may result in noncompliance with pharmacology therapy if the mother does not understand why the drug is given. 32. The nurse is teaching the mother of a child diagnosed with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder how to administer methylphenidate (Ritalin). When would the nurse instruct the mother to administer this drug? A) Administer at lunch every day. B) Administer at breakfast every day. C) Administer at dinner every day. D) Administer at bedtime. Ans: B Feedback: Several long-acting formulations of methylphenidate have become available that allow the drug to be given only once a day. It should always be given in the morning because administration at dinnertime or bedtime could result in insomnia. 33. A child was diagnosed with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder and methylphenidate was prescribed for treatment to be taken once a day in a sustained release form. On future visits what is a priority nursing assessment for this child? A) Weight and height B) Breath sounds and respiratory rate C) Urine output and kidney function Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) D) Electrocardiogram (ECG) and echocardiogram Ans: A 369 Feedback: The nurse needs to carefully track this child’s weight and height because the drug can cause weight loss, anorexia, and nausea that could result in slowed or absent growth. There would be no need to monitor breath sounds, respiratory rate, urine output, and kidney function. Although arrhythmias may occur as an adverse effect necessitating an ECG, there is no need to perform echocardiograms. 34. The nurse is preparing to administer methylphenidate to the child admitted to the pediatric unit after breaking a leg when jumping off the garage roof at home. Where will the nurse find the medication? A) In the patient’s drawer B) In the refrigerator C) At the patient’s bedside D) In the controlled substance cabinet Ans: D Feedback: Methylphenidate is a controlled medication due to risk for physical and psychological dependence. As a result, the drug would be found in the controlled substance cabinet. 35. The nurse is caring for a child receiving a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant who was admitted to the pediatric intensive care unit following repeated seizures after a closed head injury. The physician orders phenytoin to control seizures and lorazepam to be administered every time the child has a seizure. What is the nurse’s priority action? A) Call the doctor and question the administration of phenytoin. B) Call the doctor and question the administration of lorazepam. C) Wait 24 hours before beginning to administer phenytoin. D) Wait 24 hours before beginning to administer lorazepam. Ans: A Feedback: Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 370 The combination of CNS stimulants with phenytoin leads to a risk of increased drug levels. Patients who receive such a combination should be monitored for toxicity. There is no contraindication for use of lorazepam. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 371 Chapter 23 - Antiseizure Agents 1. A patient is admitted to the emergency department with severe recurrent convulsive seizures. What drug would the nurse expect to be ordered for use in emergency control of status epilepticus? A) Phenytoin (Dilantin) B) Diazepam (Valium) C) Phenobarbital (Luminal) D) Ethosuximide (Zarontin) Ans: C Feedback: Phenobarbital is used for emergency control of status epilepticus. This barbiturate inhibits impulse conduction in the ascending reticular activating system (RAS), depresses the cerebral cortex, alters cerebellar function, and depresses motor nerve output. Phenobarbital stabilizes nerve membranes throughout the central nervous system (CNS) directly by influencing ionic channels in the cell membrane, thereby decreasing excitability and hyperexcitability to stimulation. By decreasing conduction through nerve pathways, it reduces the tonicclonic, muscular, and emotional responses to stimulation. Phenobarbital depresses conduction in the lower brainstem and the cerebral cortex and depresses motor conduction. Phenytoin is used to prevent status epilepticus but is not used to stop seizures after they have started; diazepam is used for short-term treatment of status epilepticus. Ethosuximide is used for absence seizures. 2. The pharmacology instructor is discussing drugs used for the treatment of partial seizures. What accurately describes the physiological action of carbamazepine? A) Reduces electrical activity B) Alters sodium and calcium channels C) Increases gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) activity and blocks sodium and calcium channels to stop action potentials D) Depresses conduction in the brainstem and cortex Ans: C Feedback: Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 372 Carbamazepine increases GABA activity and blocks sodium and calcium channels to stop action potentials. Succinimides reduce electrical activity. Acetazolamides reduce electrical activity and alter sodium and calcium channels. Barbiturates depress conduction in the brainstem and the cortex. 3. A 7-year-old girl is brought to the clinic by her mother. The mother states that the child will be engaged in some activity at home and then will just stop for a few seconds and then pick up the activity again as if there had been no break in what she was doing. The nurse suspects the child might be demonstrating what type of seizure? A) Tonicclonic seizure B) Absence seizure C) Myoclonic seizure D) Status epilepticus Ans: B Feedback: Absence seizures involve abrupt periods of loss of consciousness lasting 3 to 5 seconds. Tonic-clonic seizures involve dramatic muscle contractions, loss of consciousness, and a recovery period characterized by confusion and exhaustion. Myoclonic seizures involve short, sporadic periods of muscle contractions lasting for several minutes. These types of seizures are rare. Status epilepticus seizures are the most dangerous and rapidly occur one after another. 4. A patient is brought into the emergency department in status epilepticus. The nurse administers phenobarbital 320 mg IV according to protocol. Family members ask the nurse how long it will take to stop the seizures. What is the nurse’s best response? A) The onset of action for the medication is 5 minutes. B) We should see results in about 10 minutes. C) It will probably take about 30 minutes before the seizures begin to subside. D) It may be an hour before the seizures stop. Ans: A Feedback: The onset of IV phenobarbital is 5 minutes; however, it is important not to confuse when the onset of action will occur and when the seizures will stop because additional interventions may be needed to stop the seizure activity in some cases. For intramuscular and subcutaneous administration, the onset should be between 10 and 30 minutes. Onset for an oral dose is between 30 and 60 minutes. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 5. 373 The nurse evaluates the patient’s serum phenytoin (Dilantin) level and determines the level is therapeutic when it is within what range? A) Between 5 and 12 mcg/mL B) Between 10 and 20 mcg/mL C) Between 15 and 50 mcg/mL D) Between 40 and 100 mcg/mL Ans: B Feedback: The therapeutic serum level range for phenytoin is between 10 and 20 mcg/mL. The other options are incorrect. 6. A nurse is teaching a patient about his or her newly prescribed drug, phenytoin (Dilantin) for a seizure disorder. What will the nurse alert the patient to as a serious adverse effect of this drug? A) Drowsiness B) Fatigue C) Rash D) Lethargy Ans: C Feedback: Serious liver, bone marrow, and potentially serious dermatological adverse effects can occur with phenytoin. Drowsiness, fatigue, and lethargy are adverse effects of hydantoins and classified as not serious. 7. A) An 8-year-old child has been diagnosed with a seizure disorder and phenytoin (Dilantin) has been prescribed for him or her. What nursing diagnosis would be appropriate if the child demonstrated adverse effects to the drug? Deficient fluid volume Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) B) Impaired skin integrity related to dermatological effects C) Noncompliance for drug therapy D) Sleep deprivation Ans: B 374 Feedback: Impaired skin integrity related to dermatological effects would be appropriate because phenytoin can cause potentially serious dermatological effects as well as gum disease and stained teeth. Usually this drug will cause the patient to be sleepy all day and should enhance sleep at night. Deficient fluid volume is not a concern with this drug. Noncompliance will probably not be an issue at this age because the parents and school nurse will administer the medication. 8. A patient is taking ethosuximide (Zarontin) for absence seizures. He or she complains of gastrointestinal (GI) upset associated with the drug. The nurse will encourage the patient to do what? A) Take the drug 1 hour before or 2 hours after a meal. B) Decrease the dosage. C) Take the drug with food. D) Discontinue the drug and ask his or her physician to prescribe another drug. Ans: C Feedback: If GI irritation occurs with ethosuximide, the patient should be encouraged to take the medication with food to reduce this adverse effect. A nurse would never tell a patient to decrease the dosage or discontinue a drug. That advice should only be given by the patient’s medication prescriber. Taking the drug 1 to 2 hours after meals would not reduce this effect. 9. The drug of choice for the treatment of partial seizures is what? A) Carbamazepine (Tegretol) B) Clorazepate (Tranxene) C) Felbamate (Felbatol) D) Gabapentin (Neurontin) Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) Ans: 375 A Feedback: Carbamazepine is often the drug of choice for treatment of partial seizures. It has the ability to inhibit polysynaptic responses and to block sodium channels to prevent the formation of repetitive action potentials in the abnormal focus. Clorazepate is indicated for anxiety and alcohol withdrawal and used as adjunctive therapy for partial seizures. Felbamate has been associated with severe liver failure and aplastic anemia and is now reserved for those patients who do not respond to other therapies. Gabapentin is used as adjunctive therapy in the treatment of partial seizures and for the treatment of postherpetic neuralgia. 10. A patient who has been taking lamotrigine (Lamictal) for the past 2 weeks calls the clinic and reports to the nurse that he or she has developed a rash. What should the nurse tell him or her to do? A) To continue taking the drug and that the rash will go away B) To talk to he or she physician and that he will prescribe a cream to apply to the rash C) To decrease the dosage by half for 2 weeks and then take the prescribed dose D) To discontinue the drug and return to the clinic immediately Ans: D Feedback: The nurse should inform the patient to discontinue the drug and return to the clinic. Rashes associated with the use of lamotrigine can be life-threatening. The patient needs to return to the clinic to be evaluated and will need a change of medication. Discontinuing the medication will cause the rash to clear. The nurse is not licensed to adjust the dosage of a drug for a patient. 11. The school nurse sees a child on the playground have an absence seizure identified by the occurrence of what characteristics? A) Alterations in consciousness that last seconds B) Automatic and repetitive movements C) Abnormal movements and bizarre behavior D) Sustained contraction of skeletal muscle Ans: A Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 376 Feedback: Absence seizures are characterized by abrupt alterations in consciousness that last only a few seconds. Characteristics of an absence seizure do not include automatic and repetitive movements, abnormal movements and bizarre behavior, or sustained contraction of skeletal muscle. 12. The nurse is providing patient education for a patient newly prescribed a hydantoin antiseizure medication. What would the nurse be sure to teach the patient regarding the dangers of abrupt withdrawal? A) Hypertensive crisis B) Cardiac dysrhythmias C) Respiratory arrest D) Status epilepticus Ans: D Feedback: Discontinuing hydantoins could result in status epilepticus so that drugs should be withdrawn, or added to the medication regimen, carefully to avoid danger. An abrupt withdrawal of antiseizure medications would not precipitate hypertensive crisis, dysrhythmias, or respiratory arrest. 13. A patient is brought to the emergency department in the midst of an active clonictonic seizure. What is the most appropriate antiseizure drug for the nurse to administer intravenously to terminate acute convulsive seizures? A) Diazepam (Valium) B) Phenytoin (Dilantin) C) Ethosuximide (Zarontin) D) Gabapentin (Neurontin) Ans: A Feedback: The drug of choice for acute seizures is intravenous benzodiazepine, usually diazepam. Phenytoin is administered to control and prevent seizures but is not the drug of choice to stop an active seizure. Gabapentin and ethosuximide are administered for partial seizures. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 14. 377 The nurse is caring for a patient receiving ethotoin to control seizure activity. When reviewing the patient’s laboratory results, the nurse would assess the patient is in a therapeutic level when the lab result is within what range? A) 5 to 15 mcg/mL B) 10 to 20 mcg/mL C) 15 to 50 mcg/mL D) 20 to 30 mcg/mL Ans: C Feedback: Therapeutic serum ethotoin levels range between 15 and 50 mcg/mL. Options A, B, and D are incorrect. 15. The nurse, working in the emergency room, admits a 13-month-old child reported by the parents to have had a clonictonic seizure at home with no history of a seizure disorder. What is the nurse’s priority intervention? A) Monitor serum phenytoin level. B) Take the child’s temperature. C) Place the child in a tepid bath. D) Administer an antipyretic medication. Ans: B Feedback: The first action of the nurse is to measure body temperature to determine whether the child has a fever, which could explain why the seizure occurred. Febrile seizures are common in young children. They are related to very high fevers and usually involve clonictonic seizure. Febrile seizures most frequently occur in children and they are usually self-limited and do not reappear. The nurse would not treat a fever by administering antipyretics or providing a tepid bath until temperature is measured. There would be no reason to check phenytoin levels if the child has no history of seizure disorder. 16. Richard, 15 years old, has been diagnosed with epilepsy. He is to be sent home on oral phenytoin 100 mg b.i.d. What statement by Richard’s mother leads the nurse to believe she has understood drug teaching? Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) A) I will make sure he takes the medication on an empty stomach. B) I will stop the drug immediately if any side effects occur. C) I will make sure he has routine visits to the dentist. D) I will weigh him daily and feed him a high-calorie diet. Ans: C 378 Feedback: Gingival hyperplasia is common in patients, especially children, who take phenytoin, which makes regular dentist visits important to oral health. Taking the medication on a full stomach or with meals reduces gastrointestinal (GI) adverse effects. The mother should call the health care provider if adverse effects are noted and needs to understand the risks associated with abrupt withdrawal of the medication. Daily weight taking and high-calorie diets are not associated with phenytoin administration. 17. The mother of a child newly diagnosed with drug-resistant epilepsy asks the nurse why two antiepileptic drugs have been prescribed for her daughter. What is the nurse’s best answer? A) To decrease overall cost B) To decrease risk of adverse effects C) To minimize seizures in resistant epilepsy D) To increase movement of sodium ions into the cell Ans: C Feedback: When monotherapy is ineffective, a second, and sometimes a third, drug may be added in an attempt to control seizures. It does not decrease overall cost or reduce the risk of side effects or increase movement of sodium ions into the cell. 18. The patient’s serum drug level is elevated and indicates a toxic level. What will the nurse assess for in this patient? (Select all that apply.) A) Liver toxicity B) Bone marrow suppression C) Serious dermatological reactions Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) D) Tooth loss E) Renal damage Ans: A, B, C 379 Feedback: Toxic levels of phenytoin increase the likelihood of adverse effects so the nurse would assess for liver toxicity, bone marrow suppression, or serious dermatological reactions. Gingival hyperplasia, not tooth loss, is associated with phenytoin toxic effects. Renal damage is not associated with phenytoin. 19. A patient has a new order for carbamazepine (Tegretol). What does the nurse know is a contraindication to administration of carbamazepine? A) Bone marrow depression B) Bipolar disorder C) Allergy to sulfonamides D) Diabetes Ans: A Feedback: Bone marrow suppression would be considered a contraindication to administration of carbamazepine therapy. Contraindications to the use of Tegretol do not include bipolar disorder, an allergy to sulfonamides, or diabetes. 20. A patient with liver impairment needs an antiepileptic drug. What drug would be safest for patients with liver impairment? A) Levetiracetam (Keppra) B) Lamotrigine (Lamictal) C) Phenobarbital D) Valproic acid (Depakene) Ans: A Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 380 Feedback: Levetiracetam is a newer drug chemically unrelated to other antiepileptic drug. Most of the drug is excreted by the kidneys and is not metabolized by the liver so it would be safer for the patient with liver disease. The other options are all metabolized by the liver, so the patient with liver disease will need a lower dosage. 21. The nurse is caring for a patient diagnosed with generalized seizures and will appropriately administer what classifications of medications to this patient? (Select all that apply.) A) Succinimides B) Acetazolamide C) Valproic acid D) Hydantoin E) Benzodiazepines Ans: D, E Feedback: Drugs used to treat generalized seizures include the hydantoins, barbiturates, and benzodiazepines. Drugs used to treat absence seizuresa particular type of generalized seizureinclude the hydantoins, succinimides, acetazolamide, valproic acid, and zonisamide. 22. The nurse is caring for a 4-year-old child diagnosed with a seizure disorder requiring an antiseizure agent. Using mg/kg as the comparison, how will the child’s dose compare with an adults dose? A) Children require a smaller mg/kg dose than an adult. B) Children require a larger mg/kg dose than an adult. C) Mg/kg dose is the same for adults and children. D) Dosing varies by medication. Ans: B Feedback: Older children (2 months to 6 years of age) absorb and metabolize many of these drugs more quickly than adults and require a larger dosage per kilogram to maintain therapeutic levels. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 23. 381 What factors contribute to determining the drug of choice for a patient with epilepsy? (Select all that apply.) A) Age B) Type of epilepsy C) Patient characteristics D) Preferred adverse effect E) Gender Ans: A, B, C Feedback: The drug of choice for any given situation depends on the type of epilepsy, patient age, specific patient characteristics such as cultural variations, and patient tolerance for associated adverse effects as opposed to preferred adverse effect. No adverse effects would be preferred but, because nearly all drugs have some adverse effects, determining what is tolerable to a particular patient is important to consider. Gender does not play a role in determining drug of choice. 24. The nurse anticipates a reduced dosage due to cultural differences when caring for patients from what cultural groups? (Select all that apply.) A) Arab Americans B) Asian Americans C) African Americans D) White American E) Native American Ans: A, B Feedback: Because of differences in liver enzyme functioning among Arab Americans and Asian Americans, patients in these ethnic groups may not metabolize antiseizure agents in the same way as patients in other ethnic groups. They may require not only lower doses to achieve the same therapeutic effects but also frequent dose adjustment. Nothing indicates a need to alter dosage for African Americans, Whites, or Native Americans. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 25. 382 A patient with a seizure disorder has had a recent change in medication. What data would the nurse collect to evaluate the effectiveness of the new drug? (Select all that apply.) A) Evaluate vital signs. B) Evaluate laboratory drug level. C) Assess for adverse effects. D) Assess for change in seizure activity. E) Assess for cost of therapy. Ans: B, C, D Feedback: Interview and assess for any change in seizure activity; interview and assess for avoidance of adverse drug effects, especially those that impair safety; when available, check laboratory reports of serum drug levels for therapeutic ranges or evidence of underdosing or overdosing. Measuring vital signs is part of every patient visit but does not contribute to evaluation of drug effectiveness. For example, if the patient has had a sudden increase in number of seizures, but is not currently having a seizure, vital signs will likely be within normal range. Cost of therapy does not indicate the effectiveness of drugs. Cost should be considered when prescribing drugs, not when they are being evaluated. 26. A patient is brought in to the emergency department by ambulance in status epilepticus. What drug may be used for this patient? A) Carbamazepine B) Clorazepate C) Ethotoin D) Fosphenytoin Ans: D Feedback: Only fosphenytoin is indicated for the treatment of status epilepticus. Carbamazepine is used to treat seizure disorders as well as trigeminal neuralgia and bipolar disorder but it is not indicated for status epilepticus. Clorazepate and ethotoin are used in long-term treatment of partial seizure disorders, alone, or with other antiepileptic drugs but would not be used for status epilepticus. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 27. 383 The patient has serum drug levels of an antiepileptic drug ordered. The patient asks the nurse why drug levels are measured. What is the nurse’s best response? A) To evaluate whetherthe therapeutic range is reached B) To measure the amount of toxicity C) To determine the effect of the drug on body systems D) To evaluate the effectiveness of therapy Ans: A Feedback: Measuring serum drug levels evaluates whether the therapeutic range of circulating drug can be found in the serum. It does not measure toxicity, which can occur even when the drug level is within prescribed range, and it does not evaluate effectiveness of therapy, which can only be evaluated by determining whether the drug is having the desired effect of reducing number of seizures. To determine the effect the drug is having on other body systems, it would be necessary to draw lab levels that measure functioning of that particular system. 28. The nursing instructor is discussing absence seizures and how to treat them in children. A student asks the difference between ethosuximide and methsuximide, the drugs used to control absence seizures. What is the instructors best response? A) Ethosuximide has more severe adverse effects than methsuximide. B) Seizures are more refractory to methsuximide. C) There is no real difference in the drugs. D) Methsuximide has more severe adverse effects than ethosuximide. Ans: D Feedback: Ethosuximide and methsuximide are indicated for the control of absence seizures. Ethosuximide should be tried first; methsuximide should be reserved for the treatment of seizures that are refractory to other agents because it is associated with more severe adverse effects. 29. A) A patient, newly diagnosed with a seizure disorder, has been prescribed valproic acid. What is one adverse effect of valproic acid that the nurse should include in the medication teaching plan? Liver toxicity Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) B) Esophageal irritation C) Cardiac insufficiency D) Muscle weakness Ans: A 384 Feedback: Valproic acid is associated with liver toxicity. Esophageal irritation, cardiac insufficiency, and muscle weakness are not associated with valproic acid therapy. 30. While writing a care plan for a patient newly diagnosed with generalized seizures, the nurse might appropriately choose what nursing diagnosis? A) Risk for injury related to gastrointestinal (GI) effects B) Disturbed thought processes related to central nervous system effects C) Monitor complete blood count (CBC) before and periodically during therapy. D) Offer support and encouragement. Ans: B Feedback: Disturbed thought processes related to central nervous system (CNS) effects is a nursing diagnosis for a patient receiving any antiepileptic medication for generalized seizures. Monitoring CBC and offering support and encouragement are implementations rather than diagnosis. Risk for injury is incorrect because the risk for injury to this patient is from the CNS effects and not GI effects. 31. The patient, newly diagnosed with epilepsy, asks the nurse to explain the meaning of the diagnosis. What is the nurse’s best response? A) Epilepsy is a single disease that causes seizures. B) Epilepsy is a convulsive disorder caused by electrical discharge in the muscle. C) Epilepsy is characterized by sudden discharge of excessive electrical energy. D) Epilepsy is the tonicclonic muscle contractions with potential to cause injury. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) Ans: 385 B Feedback: The most prevalent of the neurological disorders, epilepsy is not a single disease but a collection of different syndromes characterized by the same feature: sudden discharge of excessive electrical energy from nerve cells located within the brain, which leads to a seizure. In some cases, this release stimulates motor nerves, resulting in convulsions, with tonicclonic muscle contractions that have the potential to cause injury, tics, and spasms. Other discharges may stimulate autonomic or sensory nerves and cause very different effects, such as a barely perceptible, temporary lapse in consciousness or a sympathetic reaction. 32. The nurse is providing patient teaching with a patient who is newly diagnosed with epilepsy. The patient asks, Can I still drive to work? What is the nurse’s best response? A) Not until your seizures are controlled by medication B) Yes, as long as you take your medications regularly. C) You can drive as soon as therapeutic drug levels are obtained. D) Epileptics need to use public transportation because a seizure could occur anytime. Ans: A Feedback: Patients newly diagnosed with epilepsy will not be able to drive. However, after the patient’s seizures are controlled (usually for 6 months to 2 years depending on state law), the patient may be able to regain the ability to drive. 33. The nurse is caring for an 84-year-old patient in the acute care facility who was newly diagnosed with a seizure disorder. Before starting the patient on an antiepileptic medication that will be continued after discharge, what laboratory studies would the nurse want to assess? (Select all that apply.) A) Serum drug levels B) Liver function studies C) Renal function studies D) Cardiovascular function studies E) Central nervous system function studies Ans: B, C Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 386 Feedback: Baseline kidney and liver function tests should be done and results will guide dosing of the antiepileptic medication because patients with liver or kidney disease will require lower dosages of medication. Serum drug levels will not be drawn until after specific medications are started. Cardiovascular and central nervous system function studies are not indicated. 34. The patient has a seizure that causes rhythmic twitching of the left hand for 90 seconds with no loss of consciousness and then stops. The nurse notes this same action repeated many times throughout the day and documents this as what type of seizure? A) Myoclonic seizure B) Jacksonian seizure C) Psychomotor seizure D) Simple partial seizure Ans: D Feedback: This patient is having simple partial seizures, which occur in a single area of the brain and may involve a single muscle movement or sensory alteration. Myoclonic seizures involve short, sporadic periods of muscle contractions that last for several minutes. Jacksonian seizures begin in one area of the brain and involve one part of the body and then progressively spread to other parts of the body; they can develop into generalized tonicclonic seizures. Psychomotor seizures are complex seizures that involve sensory, motor, and psychic components. 35. What antiepileptic classification of drugs works by stabilizing nerve membranes by influencing ionic channels in the cell membrane, thereby decreasing excitability and hyperexcitability to stimulation? A) Hydantoins B) Benzodiazepines C) Valproic acid D) Carbamazepine Ans: A Feedback: Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 387 The hydantoins stabilize nerve membranes throughout the central nervous system directly by influencing ionic channels in the cell membrane, thereby decreasing excitability and hyperexcitability to stimulation. By decreasing conduction through nerve pathways, they reduce the tonicclonic, muscular, and emotional responses to stimulation. Valproic acid and benzodiazepines increase gammaaminobutyric acid (GABA) effects and decrease electrical activity. Carbamazepine increases GABA activity and blocks sodium and calcium channels to stop action potentials. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 388 Chapter 24 - Antiparkinsonism Agents 1. Degeneration in neurons that release a neurotransmitter leads to Parkinson’s disease. What neurotransmitter is involved? A) Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) B) Acetylcholine C) Dopamine D) Serotonin Ans: C Feedback: Degeneration of dopamine-releasing neurons in the substantia nigra leads to Parkinson’s disease. When dopamine is decreased in the area of the corpus striatum, a chemical imbalance allows the cholinergic or excitatory cells to dominate. This affects the functioning of the basal ganglia and cortical and cerebellar components of the extrapyramidal motor system. This system provides coordination for unconscious muscle movements, including those that control position, posture, and movement. The result of the imbalance produces the signs and symptoms of Parkinson’s disease. The corpus striatum in the brain is connected to the substantia nigra by a series of neurons that use the inhibitory neurotransmitter GABA. Higher neurons from the cerebral cortex secrete acetylcholine in the area of the corpus striatum as an excitatory neurotransmitter to coordinate movements of the body. Serotonin is not involved in these functions. 2. A 10-year-old boy has been prescribed an antiparkinsonian drug. Which drug would the nurse expect as the first choice for this child? A) Benztropine (Cogentin) B) Diphenhydramine (Benadryl) C) Trihexyphenidyl (Artane) D) Procyclidine (Kemadrin) Ans: B Feedback: Parkinson’s disease is rare in children. However, if a child needs an antiparkinsonian drug, Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 389 diphenhydramine is the drug of choice. Benztropine, trihexyphenidyl, and procyclidine are not recommended for use in children. 3. A patient is newly diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease. An anticholinergic drug is ordered for the patient. When reviewing the patient’s medical history, the nurse realizes an anticholinergic drug is contraindicated for this patient because of what secondary diagnosis? (Select all that apply.) A) Benign prostatic hypertrophy B) Narrow-angle glaucoma C) Myasthenia gravis D) Dysrhythmias E) Hepatic dysfunction Ans: A, B, C Feedback: Anticholinergics are contraindicated in the presence of narrow-angle glaucoma, GI obstruction, genitourinary (GU) obstruction, and prostatic hypertrophy, all of which could be exacerbated by the peripheral anticholinergic effects of these drugs, and in myasthenia gravis, which could be exacerbated by the blocking of acetylcholine-receptor sites at the neuromuscular synapses. These agents should be administered cautiously, but they are not contraindicated in therapy for the following conditions: tachycardia and other dysrhythmias and hypertension or hypotension because the blocking of the parasympathetic system may cause a dominance of sympathetic stimulatory activity, and in hepatic dysfunction, which could interfere with the metabolism of the drugs and lead to toxic levels. 4. A patient is newly diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease and levodopa (Dopar) has been prescribed. What patient teaching information should be considered a high priority for this patient? A) Avoid vitamin B6 intake. B) Avoid hot environments. C) Many adverse effects will subside when the body adjusts to the drug. D) Allow rest periods. Ans: A Feedback: The priority information would be to avoid vitamin B6 intake, which would include grains and bran. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 390 Vitamin B6 speeds the conversion of levodopa to dopamine before it can cross the bloodbrain barrier. This leads to Parkinson’s symptoms. The other options are all important and should be discussed with the patient. However, sweating, headaches, difficulty sleeping, fatigue, weakness, and dizziness are expected adverse effects, which will eventually subside or decrease. 5. A patient with Parkinsonism has been told that the levodopa prescribed is no longer controlling the disease. What drug would the nurse question if ordered as adjunctive therapy? A) Diphenhydramine (Benadryl) B) Pramipexole (Mirapex) C) Trihexyphenidyl (Artane) D) Vitamin B6 Ans: D Feedback: Vitamin B6 would further decrease the therapeutic effects of levodopa and is contraindicated with levodopa, so the nurse would question this order. Pramipexole, diphenhydramine, and trihexyphenidyl are all useful adjunctive drugs when Parkinson’s disease is no longer controlled with levodopa therapy alone. 6. The nurse provides patient teaching about use of levodopa for treatment of Parkinson’s disease. What statement by the patient would indicate a good understanding of levodopa? A) I will take the medication for about a year and then stop. B) I should avoid exercising while taking this drug. C) I should take this drug with meals to avoid GI upset. D) I will take megavitamins to ensure that I have good nutrition. Ans: C Feedback: The patient should be instructed to take levodopa with meals if GI upset occurs. Patients being treated for Parkinson’s disease should be taught that drug treatment will be needed for life and cannot be stopped in a year. The patient should continue to be as active as possible. Multivitamins will contain vitamin B6, which should be avoided when taking levodopa. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 7. 391 What drug does the nurse administer to treat Parkinson’s disease that is also classified as an antiviral? A) Amantadine (Symmetrel) B) Entacapone (Comtan) C) Diphenhydramine (Benadryl) D) Ropinirole (Requip) Ans: A Feedback: Amantadine is an antiviral drug that increases the release of dopamine and is effective in Parkinson’s disease so long as there is a possibility of more dopamine release. Ropinirole is a dopaminergic antiparkinsonism drugs. Entacapone is used as adjunctive treatment of idiopathic Parkinson’s disease with levodopacarbidopa for patients who are experiencing wearing off of drug effects. Diphenhydramine is used, particularly in children, to treat parkinsonism and is also classified as an antihistamine. 8. A patient has Parkinson’s disease. Apomorphine (Apokyn), a dopamine agonist, has been prescribed for periods of hypomobility. What will the nurse teach the patient regarding administration of the drug? A) The drug will be injected intramuscularly three times a day in a range of 1.0 to 1.5 mL. B) The drug will be given intravenously, 50 mg every third day. C) The drug will be administered subcutaneously three times a day with a dosage range of 2 to 6 mg. D) The drug is taken orally, 20 mg three times a day. Ans: C Feedback: The drug is administered subcutaneously three times a day in a range of 2 to 6 mg per dose. A dosing pen is available for patient use. The other options are inappropriate for this drug. 9. An order is written for a drug that is an adjunctive therapy for Parkinson’s disease. The nurse reviews the order before administering the drug. What medication orders should the nurse question? A) Levodopa 0.5 to 1 g/d orally in 2 divided doses B) Amantadine (Symmetrel) 200 mg orally b.i.d. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) C) Tolcapone (Tasmar) 400 mg orally t.i.d. D) Selegiline (Carbex) 10 mg/d orally Ans: C 392 Feedback: The order for tolcapone should be questioned. The maximum dose is 600 mg daily. The order is a total of 1,200 mg a day (400 times 3 equals 1,200 mg). The other options are correct dosages. 10. The expected outcome for a patient taking benztropine as drug therapy for Parkinson’s disease would be what? A) Decrease in rigidity B) Decrease in light-headedness C) Decrease in disorientation D) Decrease in flushing Ans: A Feedback: Benztropine should cause a decrease in rigidity. Light-headedness, disorientation, and flushing are all adverse effects of benztropine and can be expected with a patient taking this drug. 11. A patient is newly diagnosed with parkinsonism. Parkinsonism, which may occur in association with long-term use of antipsychotics, can be treated with what drug type? A) Anticholinergic agents B) Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) C) Synthetic antiviral agents D) Dopaminergic drugs Ans: A Feedback: Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 393 Anticholinergic drugs that are centrally active are useful in treating parkinsonism. MAOIs, synthetic antiviral agents, and dopaminergic agents are incorrect. 12. The nurse is presenting an educational event to a local community group on Parkinson’s disease. What will the nurse tell the attendees causes the classic Parkinson’s disease symptoms? A) Decreased enzyme aromatic l-amino acid decarboxylase (AADC) B) Increased gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) C) Brain lesions D) Degeneration of dopamine-producing nerve cells Ans: D Feedback: Classic Parkinson’s disease results from destruction or degenerative changes in dopamine-producing nerve cells in an area of the brain that controls movement. 13. The nurse has a patient who is receiving selegiline (Carbex, Eldepryl). What is the nurse’s priority assessment? A) Irregular heart rate B) Elevated blood pressure C) Decreased urinary output D) Gingival hyperplasia Ans: B Feedback: The excessive stimulation of the sympathetic nervous system can cause severe hypertension and stroke so it is important for the nurse to assess blood pressure. Gingival hyperplasia is an adverse effect of phenytoin (Dilantin). Irregular heart rate and decreased urinary output are not adverse effects of selegiline. 14. The nurse is speaking to a group at the senior citizen’s center about Parkinson’s disease and explains the importance of avoiding what when taking an anticholinergic medication? Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) A) Strenuous exercise in high environmental temperatures B) Fluids high in potassium C) Foods high in vitamin K D) Anything containing red dye Ans: A 394 Feedback: Anticholinergic drugs decrease sweating. As a result, the body is not as effective at reducing internal temperature as this could result in fever and heatstroke. Elderly people taking anticholinergic drugs do not need to avoid fluids high in potassium, foods high in vitamin K, or anything containing red dye. 15. When providing patient teaching for older adults, the nurse employs what priority strategy to improve patient understanding? A) Repetition B) Meticulous detail C) Extensive written teaching D) Family involvement Ans: C Feedback: The drugs that are used to manage Parkinson’s disease are associated with many adverse effects in older people with long-term problems. In many cases, other pharmacotherapeutic agents are given to counteract the adverse effects of these drugs. So patients then have complicated drug regimens with many associated adverse effects and problems. Consequently, it is essential for these patients to have extensive written drug-teaching protocols. Repetition, attention to detail, and family involvement can further improve effectiveness of teaching, but providing written instructions is the highest priority strategy. 16. A patient, newly diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease, has been prescribed an anticholinergic drug. What common adverse effect of anticholinergic agents used for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease will the nurse share with the patient? A) Blood dyscrasias B) Diaphoresis Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) C) Memory loss D) Diarrhea Ans: C 395 Feedback: Most people diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease are older adult men so it is important for the nurse to warn the patient that memory loss may occur to reduce anxiety the patient may experience with this adverse effect. Blood dyscrasias are not associated with these drugs. Constipation is more likely than diarrhea and lack of sweating rather than diaphoresis is associated with anticholinergics. 17. The nurse often gives another drug with levodopa (L-dopa) to decrease the amount of levodopa needed to reach a therapeutic level in the brain, thereby reducing adverse effects? What is the name of this drug? A) Bromocriptine B) Carbidopa C) Amantadine D) Trihexyphenidyl Ans: B Feedback: Carbidopa is frequently given with levodopa in a fixed-dose combination product called Sinemet or Sinemet CR. When used with carbidopa, the enzyme dopa decarboxylase is inhibited in the periphery, diminishing the metabolism of levodopa in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract and in peripheral tissues, thereby leading to higher levels crossing the bloodbrain barrier. Because carbidopa decreases the amount of levodopa needed to reach a therapeutic level in the brain, the dosage of levodopa can be decreased, which reduces the incidence of adverse effects. Bromocriptine, amantadine, and trihexyphenidyl may be effective longer than levodopa but are not usually prescribed together. 18. When the nurse develops a plan of care for a patient newly diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease, the nurse includes what appropriate goal for this patient? A) Deficient knowledge related to the disease process B) Increase compliance with drug regimen as evidenced by no missed dosages within 1 week of discharge Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) C) Risk for injuries related to the disease process D) Symptom improvement as demonstrated by ability to ambulate the length of the hall within 24 hours of starting medication Ans: D 396 Feedback: One goal of drug therapy is to reduce symptoms to allow for more normal movement involving muscles. Goals should be specific and measurable, so the ability to ambulate the length of the hall is a valid assessment. The patient cannot increase compliance when he or she has not been lacking in compliance because this is a new diagnosis. Deficient knowledge and risk for injury are nursing diagnoses and not goals. 19. The nurse is teaching a new patient about levodopa (L-dopa). What is important to instruct the patient to avoid using concurrently with L-dopa? A) Aspirin compounds B) Multivitamin-mineral preparations C) Alcohol D) Antianginal agents Ans: B Feedback: Iron preparations and multivitaminmineral preparations containing iron should not be given with Ldopa. Aspirin compounds, alcohol, and antianginal agents are not contraindicated in concurrent therapy with L-dopa. 20. When carbidopa is given with levodopa (L-dopa), the dosage of L-dopa must be reduced. What would the reduction of L-dopa cause? A) Heightened levels of sedation B) Prolonged effect of medications C) Decreased adverse effects D) Decreased effectiveness of symptom control Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) Ans: 397 C Feedback: Because carbidopa decreases the amount of L-dopa needed to reach a therapeutic level in the brain, the dosage of L-dopa can be decreased, which reduces the incidence of adverse effects. Other options are incorrect. 21. What is the main purpose of the drugs used to treat Parkinson’s disease? A) Adjust the balance of neurotransmitters. B) Make the catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) inhibitors work better. C) Substitute monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) for dopamine agonists. D) Increase the actions of acetylcholine in the brain. Ans: A Feedback: Drugs used in Parkinson’s disease increase levels of dopamine (levodopa, dopamine agonists, monoamine oxidase [MAO] inhibitors, COMT inhibitors) or inhibit the actions of acetylcholine (i.e., anticholinergic agents) in the brain. Thus, the drugs help adjust the balance of neurotransmitters. 22. The nurse is teaching a group of student nurses about Parkinson’s disease. The nurse would determine teaching was successful if the students identified what neurotransmitters as imbalanced in Parkinson’s disease? A) Cholinergic and anticholinergic neurotransmitters B) Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and dopamine C) GABA and anticholinergic neurotransmitters D) Dopamine and acetylcholine Ans: D Feedback: The correct balance of dopamine and acetylcholine is important in regulating posture, muscle tone, and voluntary movement. People with Parkinson’s disease have an imbalance in these neurotransmitters, resulting in a decrease in inhibitory brain dopamine and a relative increase in excitatory acetylcholine. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 23. 398 The nurse is caring for a patient diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease who has been prescribed an anticholinergic drug. When are anticholinergic drugs usually added to the therapeutic regimen? A) When symptoms increase B) Sporadically to reduce development of toleration to levodopa C) When levodopa does not elicit a therapeutic response D) During the end stage of the disease process Ans: C Feedback: Although anticholinergics are not as effective as levodopa in the treatment of advancing cases of the disease, they may be useful as adjunctive therapies and for patients who no longer respond to levodopa. They are not withheld until symptoms advance or end-stage symptoms occur and they are not given sporadically. 24. 2 Drugs in Focus Anticholinergic Agents A) Combines with anticholinergic receptors to increase the action of levodopa B) Stimulates postsynaptic dopamine receptors directly C) Combines with anticholinergic receptors to increase dopamine action D) Inhibits postsynaptic dopamine receptors directly Ans: B Feedback: Ropinirole is a newer drug that directly stimulates dopamine receptors. It is also used to treat restless legs syndrome. The other options are incorrect because ropinirole only works as a dopamine receptor stimulant. 25. A home health nurse is visiting an elderly patient with Parkinson’s disease. What would the nurse assess this man for related to common adverse effects? A) Blood dyscrasias B) Increased dopamine activity Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) C) Pliability D) Urinary retention Ans: D 399 Feedback: The nurse would assess the patient for urinary retention because this reaction is caused by loss of muscle tone in the bladder and is most likely to occur in elderly men who have enlarged prostate glands. Parkinson’s does not generally cause blood dyscrasias. The nurse cannot assess for increased dopamine activity except to assess for reduced symptoms caused by medication therapy. Pliability is a distracter for this question. 26. What patient is most likely to be diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease? A) A 45-year-old woman B) A 35-year-old man C) A 55-year-old person of either gender D) A 60-year-old man Ans: D Feedback: Although Parkinson’s disease may affect people of any age, gender, or nationality, the frequency of the disease increases with age. This debilitating condition, which affects men more often than women, may be one of many chronic problems associated with aging. 27. The nurse is teaching a patient about antiparkinson drugs. What drug would the nurse expect to be prescribed for the patient experiencing wearing off of drug effects? A) Pramipexole B) Entacapone C) Ropinirole D) Amantadine Ans: B Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 400 Feedback: Entacapone is an adjunctive drug that is prescribed when a patient with Parkinson’s disease has a wearing off effect of his or her other Parkinson’s medications, meaning the drugs previously prescribed are having less of an effect. Therefore, options A, C, and D are incorrect. 28. While providing patient education for a patient newly diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease and his or her family, the nurse will explain that Parkinson’s disease is characterized by what? A) Reduced cognitive function B) Abnormalities in stature C) Postural instability D) Reduced nerve transmission Ans: C Feedback: Parkinson’s disease is a chronic, progressive, and degenerative disorder of the central nervous system (CNS) characterized by abnormalities in movement and posture (e.g., tremor, bradykinesia, joint and muscular rigidity, postural instability). 29. The nurse is assessing a patient who was prescribed levodopa 1 week earlier. How might the nurse evaluate the effectiveness of drug therapy? A) Stable mood B) Psoriasis C) Drugdrug interactions with dopaminergic agents D) Improvement in handwriting Ans: D Feedback: The nurse would evaluate the patient for improvement in function and reduction in symptoms. With preparations containing levodopa and with dopaminergic agents, assess for improvement in mobility, balance, posture, gait, speech, handwriting, and ability to provide self-care. Drooling and seborrhea may be abolished, and mood may be elevated. Stable mood and psoriasis are not findings associated Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 401 with Parkinson’s disease. Assessing for drugdrug interactions is an important nursing assessment but it is not related to evaluating effectiveness of the drug. 30. When describing Parkinson’s disease to a patient with a new diagnosis, what statement made by the nurse would be accurate? A) Parkinson’s disease can be cured if medication is taken regularly as prescribed. B) Degeneration of the neurons is arrested by medication. C) Surgical procedures involving the basal ganglia have had varying degrees of success. D) Diet-related therapy is the primary treatment for managing Parkinson’s disease. Ans: C Feedback: Surgical procedures involving the basal ganglia have been tried with varying success at prolonging the physical degeneration caused by this disease. Drug therapy remains the primary treatment. At this time, no available treatment arrests the neuron degeneration of Parkinson’s disease and the eventual decline in patient function. 31. What is the primary reason a nurse might administer an antiparkinsonism drug to a child? A) New-onset Parkinson’s disease B) Drug abuse C) Fibromyalgia D) Parkinsonian symptoms Ans: D Feedback: The incidence of Parkinson’s disease in children is very low. Children do, however, experience parkinsonian symptoms as a result of drug adverse effects, not of drug abuse. Fibromyalgia is not usually diagnosed in children either. 32. A) The nurse is caring for a patient who is unable to swallow properly. What drug would the nurse expect to be prescribed? Apomorphine (Apokyn) Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) B) Bromocriptine (Parlodel) C) Levodopa (Dopar) D) Ropinirole (Requip) Ans: A 402 Feedback: Only apomorphine can be given parenterally so this would be an appropriate drug to give to a patient with difficulty swallowing. Bromocriptine, levodopa, and ropinirole are only given in oral formulations. 33. How does the drug levodopa contrast with dopamine? (Select all that apply.) A) Levodopa is a precursor of dopamine. B) Levodopa crosses the bloodbrain barrier. C) Levodopa is converted to dopamine. D) Levodopa is effective for 8 to 10 years. E) Dopamine returns to levodopa for metabolism. Ans: A, B, C Feedback: Levodopa is a precursor of dopamine, which is deficient in parkinsonism; it crosses the bloodbrain barrier, where it is converted to dopamine and acts as a replacement neurotransmitter; it is effective for 2 to 5 years in relieving the symptoms of Parkinson’s disease. 34. The nurse is preparing to administer the patient’s first dosage of trihexyphenidyl (Artane). What will the nurse tell the patient about the dosage? A) Initial dose is 1 to 2 mg and then dosage is titrated up to manage symptoms of disease. B) Initial dose is 6 mg to establish serum levels and then 1 mg is taken daily. C) A 5-mg dose is taken orally twice a day starting with first dose. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) D) Take 1 to 2 mg orally every day starting with first dosage. Ans: A 403 Feedback: Trihexyphenidyl (Artane) is given 1 to 2 mg orally daily initially and then titrated up to 6 to 10 mg/d with a maximum of up to 15 mg/d to control symptoms. Trihexyphenidyl is an adjunctive therapy to levodopa in treatment of parkinsonism but it can be used alone for the control of drug-induced extrapyramidal disorders. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 404 Chapter 25 - Muscle Relaxants 1. The nurse is teaching a class on muscular coordination and explains it is the movement of what electrolyte that contributes to the process of muscle contraction and relaxation? A) Calcium B) Chloride C) Magnesium D) Hydrogen Ans: A Feedback: Calcium is released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum, which leads to the binding of calcium with troponintropomyosin. This leads to contraction of the muscle fiber. The calcium pump then moves calcium back into the sarcoplasmic reticulum, which leads to relaxation of muscle fiber. Chloride, magnesium, and hydrogen are not involved in this process. 2. A mother brings her 9-year-old son to the clinic for a routine check up. The 9-year-old boy has cerebral palsy and is very spastic. The mother asks the nurse what causes the spasticity in her son. What is the nurse’s best response? A) Your son’s spasticity is caused by injury to the muscle tissue. B) Your son’s spasticity is caused by deficiency of a neurotransmitter called serotonin. C) Your son’s spasticity is caused by damaged sensory neurons. D) Your son’s spasticity is caused by damaged motor neurons. Ans: D Feedback: Muscle spasticity is the result of damage to neurons within the central nervous system (CNS) rather than injury to peripheral structures such as the musculoskeletal system. Serotonin is not involved in the process of muscle contraction and relaxation. Although acetylcholine is released and increases muscle cell membrane permeability to sodium, which eventually leads to the release of calcium, this process does play a vital part in muscle contraction and relaxation. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 3. 405 A nurse is providing discharge teaching for a patient who will be going home on cyclobenzaprine (Flexeril) prescribed for his acute musculoskeletal pain. The nurse will stress that the patient should avoid what? A) Drinking alcohol B) Taking antiemetics C) Taking antihistamines D) Taking antibiotics Ans: A Feedback: Taking cyclobenzaprine with alcohol can cause an increase in central nervous system depression. The nurse should stress that this combination should be avoided due to possible injury or severe body system depression that could lead to coma or death. No significant concerns exist with the use of antiemetics, antihistamines, or antibiotics with this drug. 4. The nurse provides patient teaching about chlorzoxazone (Paraflex) in preparation for the patient’s discharge to home. The nurse evaluates the patient understands potential adverse effects when the patient makes what statement? A) This drug can cause diarrhea. B) My urine may turn orange to purple red while taking this drug. C) My skin may turn yellow but that will go away when I stop taking the drug. D) After I take a pill it will take 2 to 3 hours before I feel the effects. Ans: B Feedback: The patient indicates an understanding of adverse effects of this drug by stating that his urine may be discolored while using the drug. Chlorzoxazone may discolor the urine, which will turn orange to purple-red when metabolized and excreted. Patients should be warned about this effect to prevent any fears of blood in the urine. Chlorzoxazone usually causes constipation, not diarrhea. The onset of action is usually within an hour after the drug has been taken. Yellow discoloration of the skin would indicate liver damage or dysfunction, which should be reported immediately. 5. The nurse admits a child diagnosed with tetanus. What medication will the nurse expect to administer? Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) A) Methocarbamol (Robaxin) B) Baclofen (Lioresal) C) Dantrolene (Dantrium) D) Diphenhydramine (Benadryl) Ans: A 406 Feedback: Methocarbamol is the drug of choice if a child needs to be treated for tetanus. Baclofen and dantrolene are not recommended for use with children. Diphenhydramine is not indicated for treatment of tetanus. 6. A 20-year-old female patient has been diagnosed with multiple sclerosis. What drug will most likely be prescribed? A) Baclofen (Lioresal) B) Cyclobenzaprine (Flexeril) C) Metaxalone (Skelaxin) D) Orphenadrine (Banflex) Ans: A Feedback: Baclofen is used for treatment of muscle spasticity associated with neuromuscular diseases such as multiple sclerosis. Cyclobenzaprine, metaxalone, and orphenadrine are used for relief of discomfort associated with painful, acute musculoskeletal conditions. 7. The nurse is caring for four patients. Which patient would have the highest risk for hepatotoxicity from dantrolene (Dantrium)? A) An 87-year-old man who is taking a cardiac glycosideh B) A 32-year-old man who is taking an antipsychotic drug C) A 65-year-old woman who is on hormone replacement therapy D) A 48-year-old woman who is taking an antihypertensive agent Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) Ans: 407 C Feedback: If dantrolene is combined with estrogen, the incidence of hepatocellular toxicity is increased. This combination should be avoided. Nothing indicates that patients taking a cardiac glycoside, an antipsychotic drug, and an antihypertensive would have serious adverse effects when combined with dantrolene therapy. 8. The nurse alerts the patient to what adverse effect of tizanidine (Zanaflex) that could cause injury? A) Constipation B) Dry mouth C) Fatigue D) Hypotension Ans: D Feedback: Tizanidine has been associated with hypotension, which could be a safety risk especially if the patient is also taking an antihypertensive drug. Constipation, dry mouth, and fatigue are common adverse effects that do not pose a safety risk. 9. A young woman attends a Botox Party and is injected with botulinum toxin type A to decrease frown lines between her eyebrows. Later that evening the patient is admitted to the emergency department and is hysterical, because she cannot move her eyebrows. The nurse explains that that toxin causes what? A) The toxin causes muscle death, which smoothes wrinkles in the area. B) The toxin causes muscle paralysis, preventing movement and relieving wrinkles. C) The drug is a toxin to nerves in the area. D) The drug is a permanent muscle relaxant and the muscles will never move again. Ans: B Feedback: Botulinum toxin types A and B bind directly to the receptor sites of motor nerve terminals and inhibit Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 408 the release of acetylcholine, leading to local muscle paralysis. These two drugs are injected locally and used to paralyze or prevent the contractions of specific muscle groups. The action smoothes wrinkles in the area, but does not cause muscle death. The effect is temporary and does not cause nerve death. The other options are false statements. 10. A patient has stepped on a rusty nail and is exhibiting signs of muscle rigidity and contractions. The patient’s wife called the emergency department (ED) and the triage nurse told her to bring him in. The ED nurse will have which drug available for administration when the patient arrives? A) Carisoprodol (Soma) B) Cyclobenzaprine (Flexeril) C) Metaxalone (Skelaxin) D) Methocarbamol (Robaxin) Ans: D Feedback: The patient is exhibiting signs of tetanus and methocarbamol (Robaxin) is indicated for treatment. Carisoprodol, cyclobenzaprine, and metaxalone are not used to treat tetanus. 11. The nurse assesses a newly admitted patient and finds the muscle tone in his left leg has sustained muscle contraction. How will the nurse document this finding? A) Tonus B) Flaccid C) Atonic D) Spastic Ans: D Feedback: Muscle spasticity is defined as a sustained muscle contraction. Soft and flabby muscle tone is defined as atonic. A limp muscle without tone is described as flaccid. The state of readiness, known as muscle tone (tonus), is produced by the maintenance of some of the muscle fibers in a contracted state. 12. A patient comes to the clinic to receive a Botox injection in her forehead. The patient has adult acne across her forehead. What is the nurse’s priority action? Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) A) Hold the injection and consult the health care provider. B) Cleanse the area well with an antibacterial soap. C) Apply a topical antibiotic after administering the Botox. D) Provide patient information about post-Botox injection care. Ans: A 409 Feedback: Botulinum toxins should not be injected into any area with an active infection because of the risk of exacerbation of the infection. As a result, the nurse would hold the injection and consult with the physician, with the expectation the medication would be held until the acne resolved. Cleansing the area well, applying a topical antibiotic, and providing information about postinjection care would not resolve the problem and are not indicated. 13. The patient presents to the emergency department with muscle spasms in the back. What types of injury would the nurse recognize can result in muscle spasm? (Select all that apply.) A) Overstretching a muscle B) Wrenching a joint C) Tearing a tendon or ligament D) Breaking a bone E) Exercising too vigorously. Ans: A, B, C Feedback: Muscle spasms often result from injury to the musculoskeletal system (e.g., overstretching a muscle, wrenching a joint, tearing a tendon or ligament). These injuries can cause violent and painful involuntary muscle contractions. Breaking a bone or exercising would not cause muscle spasms unless one of the other options was involved. 14. A) The nurse is giving discharge instructions to a patient who just had Botox A injections around her eyes. What adverse effects would the nurse include in her discharge instructions? (Select all that apply.) Respiratory infections Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) B) Flu-like syndrome C) Droopy eyelids D) Cough E) Diarrhea Ans: A, B, C 410 Feedback: Adverse effects associated with use of botulinum toxin type A for cosmetic purposes include headache, respiratory infections, flu-like syndrome, and droopy eyelids in severe cases. Adverse effects do not include cough or diarrhea. 15. A patient with severe spasticity sees his physician. The physician orders dantrolene. In what circumstances is the drug dantrolene contraindicated? A) Spasticity that contributes to upright position B) Spasticity that involves both legs C) Spasticity that involves the arm and the leg on the same side D) Spasticity that contributes to mobility Ans: A Feedback: Dantrolene is contraindicated in the presence of any known allergy to the drug. It is also contraindicated in the following conditions: spasticity that contributes to locomotion, upright position, or increased function, which would be lost if that spasticity was blocked; active hepatic disease, which might interfere with metabolism of the drug and because of known liver toxicity; and lactation because the drug may cross into breast milk and cause adverse effects in the infant. The other options would not contraindicate the medication. 16. Which muscle relaxant was found to be embryotoxic in animal studies? A) Carisoprodol (Soma) B) Botulinum toxin A (Botox) C) Cyclobenzaprine (Flexeril) Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) D) Dantrolene (Dantrium) Ans: D 411 Feedback: Dantrolene crosses the placenta and was found to be embryotoxic in animal studies. Botulinum toxin A, carisoprodol, and cyclobenzaprine are not known to be embryotoxic. 17. When spinal reflexes involve synapses with interneurons within the spinal cord, what physiological adjustments are made? A) Coordinate movement and position B) Adjust response and recovery C) Adjust to upright position D) Coordinate balance Ans: A Feedback: Other spinal reflexes may involve synapses with interneurons within the spinal cord, which adjust movement and response based on information from higher brain centers to coordinate movement and position. Spinal reflexes do not adjust response and recovery, adjust the body to the upright position, or coordinate balance. 18. What are the simplest nerve pathways in the body? A) Arc reflexes B) Spinal reflexes C) Afferent nerve reflexes D) Spindle gamma loop Ans: B Feedback: Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 412 The spinal reflexes are the simplest nerve pathways that monitor movement and posture. Arc reflexes and afferent nerve reflexes are distracters for this question. Spindle gamma loops respond to stretch receptors. 19. The anatomy and physiology instructor is discussing reflex systems with the prenursing class. What system would the instructor say causes a muscle fiber contraction that relieves the stretch? A) Arch reflex system B) Spinal reflex system C) Spindle gamma loop system D) Stretch receptor system Ans: C Feedback: A spindle gamma loop system responds to stretch receptors or spindles on muscle fibers to cause a muscle fiber contraction that relieves the stretch. In this system, nerves from stretch receptors form a synapse with gamma nerves in the spinal cord, which send an impulse to the stretched muscle fibers to stimulate their contraction. These reflexes are responsible for maintaining muscle tone and keeping an upright position against the pull of gravity and are important in helping venous return when the contracting muscle fibers massage veins to help move the blood toward the heart. The arch reflex system and the stretch receptor system are distracters for this question. The spinal reflex system is not the reflex systems that respond to stretch receptors in the body. 20. A 3-year-old girl with a diagnosis of spasticity caused by cerebral palsy has been admitted to the unit. The physician has ordered dantrolene to see if it relieves the spasticity in the child’s arms and hands. The nurse would schedule this child for what routine screenings? A) Central nervous system and gastrointestinal (GI) function B) Respiratory and cardiovascular (CV) function C) Growth and development D) Renal and hepatic function Ans: A Feedback: Children prescribed dantrolene should be routinely and regularly screened for central nervous system and gastrointestinal (including hepatic) toxicity. Growth and development should be routinely screened in all children. Renal, respiratory, and CV screening is not indicated. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 21. 413 A patient is admitted to the unit with central spasticity after a terrible motor vehicle accident. The doctor places an intrathecal delivery pump. What medication can be administered via this route to treat the central spasticity? A) Baclofen (Lioresal) B) Cyclobenzaprine (Flexeril) C) Dantrolene (Dantrium) D) Carisoprodol (Soma) Ans: A Feedback: Baclofen is available in oral and intrathecal forms and can be administered via a delivery pump for the treatment of central spasticity. Flexeril, dantrolene, and Soma are not administered intrathecally. 22. Baclofen is a prototype drug for the centrally acting skeletal muscle relaxants. What adverse effects do drugs in this class have? (Select all that apply.) A) Coronary artery disease B) Hypotension C) Urinary frequency D) Dizziness E) Bone marrow suppression Ans: B, C, D Feedback: Adverse effects include transient drowsiness, dizziness, weakness, fatigue, constipation, headache, insomnia, hypotension, nausea, and urinary frequency. Bone marrow suppression and coronary artery disease are not associated with therapy involving these drugs. 23. When caring for a patient taking dantrolene, what adverse effects would the nurse monitor for? (Select all that apply.) Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) A) Bradycardia B) Hepatitis C) Urinary retention D) Fatigue E) Rash Ans: B, D, E 414 Feedback: Adverse effects of dantrolene include drowsiness, dizziness, weakness, fatigue, diarrhea, hepatitis, myalgia, tachycardia, transient blood pressure changes, rash, and urinary frequency. Adverse effects of dantrolene do not include bradycardia or urinary retention. 24. The nurse is caring for a patient who is having a pump placed to deliver intrathecal baclofen and another patient who will receive dantrolene as a muscle relaxant. What nursing diagnosis would be appropriate for both care plans? (Select all that apply.) A) Acute pain related to GI effects of drug B) Risk for injury related to central nervous system (CNS) effects C) Disturbed body image related to muscle pain D) Disturbed thought processes related to CNS effects E) Deficient knowledge related to procedure Ans: A, B, D Feedback: Acute pain related to GI effects of drug, risk for injury related to CNS effects, and disturbed thought processes related to CNS effects all apply to both patients. Disturbed body image may apply to the patient having the pump placed, but this is not related to muscle pain. Only the patient having the pump placed would need information related to the procedure. 25. The nurse is caring for a patient who is being discharged home from the rehabilitation unit. Baclofen will be discontinued and the patient will begin taking carisoprodol as an outpatient. What is the nurse’s primary consideration about discontinuing administration of baclofen? Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) A) Taper drug over 72 hours to reduce dependence on the drug. B) Alternate doses of baclofen and soma over 10 days to prevent drug withdrawal. C) Taper drug slowly over 1 to 2 weeks to prevent psychoses and hallucinations. D) Start carisoprodol immediately while continuing baclofen at full dose to establish carisoprodol level. Ans: C 415 Feedback: If using baclofen, taper drug slowly over 1 to 2 weeks to prevent the development of psychoses and hallucinations. Giving both drugs at once would risk toxicity and serious adverse effects and would never be done. 26. The nurse is caring for a patient receiving intrathecal baclofen via pump while participating in rigorous rehabilitation therapy. What is the nurse’s priority to monitor related to adverse effects of this drug? A) Blood pressure B) Pulse pressure C) Spasticity D) Respiratory status Ans: D Feedback: The priority to monitor is respiratory status. One of the primary adverse effects of this drug is central nervous system (CNS) depression. If the patient receives too much medication, or reaches toxic levels, respiratory rate will decline as the result of excessive CNS depression and the drug dosage will either be adjusted downward or the drug may be held until the patient’s respirations improve. Monitoring other vital signs including blood pressure and pulse is indicated but is not the priority. 27. A patient has been diagnosed with multiple sclerosis and experiences spasticity in several muscle groups. What drug would the nurse anticipate will be ordered as the drug of choice to manage spasticity associated with neuromuscular diseases? A) Dantrolene (Dantrium) B) Baclofen (Lioresal) Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) C) Carisoprodol (Soma) D) Botulinum toxin type B (Myobloc) Ans: A 416 Feedback: Dantrolene directly affects peripheral muscle contraction, and has become important in the management of spasticity associated with neuromuscular diseases. Baclofen, carisoprodol, and botulinum toxin type B are not the drugs of choice for management of spasticity in neuromuscular disease. 28. The nurse is caring for a patient taking dantrolene. How would the nurse assess the therapeutic effects of this drug? A) Observe the patient when emotionally stressed to assess for exacerbation of spasticity. B) Discontinue the drug for 2 to 4 days and assess for exacerbation of spasticity. C) Measure the amount of spasticity before and after administration of medication. D) Collect a thorough history to ask the patient any improvement has been noticed. Ans: B Feedback: Periodically discontinue drug for 2 to 4 days to monitor therapeutic effectiveness. A clinical impression of exacerbation of spasticity indicates a positive therapeutic effect and justifies continued use of the drug. It would not be ethical to stress the patient, there is no known measurement of spasticity, and the patient may not be able to relate how much improvement was felt because it is unlikely all spasticity will be eliminated. 29. What drug would the nurse expect to administer to the patient experiencing malignant hyperthermia? A) Orphenadrine B) Metaxalone C) Chlorzoxazone D) Dantrolene Ans: D Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 417 Feedback: Indications for dantrolene include control of clinical spasticity resulting from upper motor neuron disorders; preoperatively to prevent or attenuate the development of malignant hyperthermia in susceptible patients; IV for management of fulminant malignant hyperthermia. The other drugs are not indicated for treatment of malignant hyperthermia. 30. What part of the brain does the nurse recognize the patient is using when making precise, intentional movements? A) Pyramidal tract B) Substantia nigra C) Broca’s area D) Extrapyramidal tract Ans: A Feedback: Upper-level controls of muscle activity include the pyramidal tract in the cerebellum, which regulates precise intentional muscle movement, and the extrapyramidal tract in the cerebellum and basal ganglia, which coordinates crude movements related to unconscious muscle activity. Broca’s area has to do with speech, not movement. The substantia nigra does not control muscle movement. 31. The patient reports pain caused by muscle spasms in his back. The nurse assesses the patient as being very anxious and notes how the anxiety results in tensing of muscles. What medication would be most effective in treating this patient? A) Baclofen (Lioresal) B) Botulinum toxin type B (Myobloc) C) Dantrolene (Dantrium) D) Diazepam (Valium) Ans: D Feedback: Adults complaining of muscle spasm pain that may be related to anxiety often respond very effectively to diazepam, which is a muscle relaxant and anxiolytic. Although many drugs, including baclofen, will Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 418 treat the muscle spasm, diazepam also reduces anxiety. Dantrolene would be better indicated for spasticity than for spasm and botulinum toxin type B is not prescribed for either anxiety or muscle spasm. 32. What is the drug of choice for an older adult or a patient with hepatic or renal impairment? A) Baclofen B) Carisoprodol C) Chlorzoxazone D) Cyclobenzaprine Ans: B Feedback: Carisoprodol is the centrally acting skeletal muscle relaxant of choice for older patients and for those with hepatic or renal impairment. Although the other options may be prescribed, older adults are more likely to experience the adverse effects associated with the drug. 33. After administering a centrally acting skeletal muscle relaxant, what other independent nursing measures might the nurse implement to relieve pain and reduce spasm? A) Rest of the affected muscle B) Application of cold C) Physical therapy D) Order of a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug Ans: A Feedback: Other measures in addition to drugs should be used to alleviate muscle spasm and pain. The nurse can independently encourage rest of the affected muscle and provide heat applications to increase blood flow to the area to remove the pain-causing chemicals. 34. A) The nurse is caring for a patient with an infusing IV who is allowed noting by mouth due to a paralytic ileus. What centrally acting medication could the nurse administer to this patient? Chlorzoxazone (Paraflex) Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) B) Carisoprodol (Soma) C) Cyclobenzaprine (Flexeril) D) Orphenadrine (Banflex) Ans: D 419 Feedback: Only orphenadrine (Banflex) of these options can be given parenterally, either IV or intramuscularly. The other options are available for oral use only. 35. What is the maximum daily dose of cyclobenzaprine (Flexeril) the nurse can administer? A) 20 mg B) 30 mg C) 40 mg D) 60 mg Ans: D Feedback: The normal daily dosage of cyclobenzaprine is 10 mg taken orally t.i.d., and it can be increased to a maximum of 60 mg per day. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 420 Chapter 26 - Narcotics, Narcotic Antagonists, and Antimigraine Agents 1. A geriatric patient received a narcotic analgesic before leaving the post-anesthesia care unit to return to the regular unit. What is the priority nursing action for the nurse receiving the patient on the regular unit? A) Administer a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug. B) Encourage fluids. C) Create a restful, dark, quiet environment. D) Put side rails up and place bed in low position. Ans: D Feedback: Older patients are more susceptible to the central nervous system effects of narcotics; it is important to ensure their safety by using side rails and placing the bed in the low position in case the patient tries to get up unaided. Postoperative patients are allowed nothing by mouth until bowel function returns so an oral medication or encouraging fluids would not be appropriate. This patient will require careful observation for respiratory depression, so a dark room would be unsafe. 2. A patient who is experiencing severe pain is administered a narcotic. What would the nurse write in the plan of care as a desirable and measurable outcome for this patient? A) A shorter period of time between requests for medication B) Reduced complaints about limited movement C) Lack of restlessness and ability to sustain one position D) Increased autonomy in providing AM care Ans: D Feedback: Monitor patient response to the drug (e.g., relief of pain, sedation).When pain is being adequately managed with opioid therapy, a desirable and measurable outcome would be that the patient is able to be more autonomous in providing care in the morning. Shorter periods between requests for medication would not be a desirable outcome because it is not an indicator of pain control given that some patients are reluctant to ask for medicine even though they are in pain. Patients in pain tend not to move for fear Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 421 of exacerbating the pain, so lack of movement can be an indication the patient is in pain. Just because the patient does not complain of pain doesn’t mean he isn’t experiencing pain. 3. The health care provider orders oral (PO) codeine as an adjunctive therapy to pain control medication. What order would be appropriate for the nurse to administer? A) Codeine 5 mg PO every 6 hour B) Codeine 10 mg PO every 4 hour C) Codeine 15 mg PO every 2 hour D) Codeine 20 mg PO every 4 hour Ans: D Feedback: The correct dosage for codeine administered for pain by mouth is 15 to 60 mg q 4 to 6 hour. The other options are incorrect oral dosages because they are too low a dose or give an incorrect dosing frequency. 4. A patient with migraine headaches is changed from an ergot to a prescription for a triptan. The nurse has completed teaching related to the drug. What statement would indicate she has a clear understanding of the new drug? A) My life is over. I can’t function not knowing when I’m going to have a headache. B) I will not have to avoid driving because this medication isn’t sedating. C) I should not experience as many adverse effects from my new medication. D) I take my medication every hour when I have a headache. Ans: C Feedback: Triptans are a new class of selective serotonin receptor blockers that cause vasoconstriction; they are not associated with as many systemic adverse effects experienced in ergot therapy. Triptan therapy will enable her to live a near normal life even during headaches. Although adverse effects are fewer than those associated with ergot therapy, triptans can still cause dizziness, feelings of strangeness, and vertigo, so the patient should not drive while taking the drug. Medications are often only taken once due to prolonged half-lives, but some may be repeated in 2 to 4 hours if the headache does not subside. 5. The nurse receives an order for a triptan for a patient diagnosed with cluster headaches. What drug Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 422 would be indicated for this purpose? A) Almotriptan (Axert) B) Frovatriptan (Frova) C) Naratriptan (Amerge) D) Sumatriptan (Imitrex) Ans: D Feedback: Sumatriptan, the first drug of this class, is used for the treatment of acute migraine attacks and for the treatment of cluster headaches in adults. No other triptans are approved for treatment of cluster headaches. 6. Before administering an ergot drug to the patient for the first time, the nurse would assess the patient’s currently prescribed medications for what drug? A) Antidiabetic agents B) Beta adrenergic blockers C) Oral contraceptives D) Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) Ans: B Feedback: The concurrent use of beta blockers and ergot preparations increases the patient’s risk for peripheral ischemia and gangrene. This combination should be avoided. There is no indication for concern with the use of antidiabetic agents, SSRIs, and oral contraceptives with these drugs. 7. The anatomy and physiology instructor is talking about pain sensations. What produces pain sensations when stimulated by generating nerve impulses? (Select all that apply) A) A-delta fibers B) D-delta sensory nerves Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) C) Mu receptors D) Sigma-receptors E) C fibers Ans: A, E 423 Feedback: Two small-diameter sensory nerves, A-delta and C fibers, respond to stimulation by generating nerve impulses that produce pain sensations. Large-diameter sensory nerves (i.e., A fibers) transmit sensations associated with touch and temperature. Mu-receptors are primarily pain-blocking receptors; sigma-receptors cause papillary dilation and may be responsible for the hallucinations, dysphoria, and psychoses that can occur with narcotic use. 8. A nurse is caring for a 6-year-old patient after surgery. The child has an order for meperidine (Demerol) 1.8 mg/kg IM every 3 to 4 hour as needed for pain. The child weighs 30 kg and the meperidine is available as 50 mg/mL. How many mL will the nurse administer per dose? A) 1 mL B) 1.8 mL C) 0.8 mL D) 1.08 mL Ans: D Feedback: To calculate the correct amount to be administered, first multiply 1.8 mg times 30 kg (54 mg). Next determine the volume in mL that 54 mg is equal to (50 mg: 1 mL as 54 mg: × mL). Solve forx (50x is equal to 54 mg; 54 divided by 50 is equal to 1.08 mL). 9. A patient with a migraine took a dose of a prescribed triptan, eletriptan (Relpax), and 1 hour later the headache is still intense. The patient’s husband calls the clinic and asks the nurse what they should do. What is an appropriate nursing response? A) Tell her to lie down in a quiet cool room and just wait it out. It will subside. B) She can take another dose of the drug 2 hours after the initial dose if the headache continues. C) Give her a dose of an ergot drug if you have it. It will decrease the intensity of the pain. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) D) Ibuprofen may increase the action of the triptan. Ans: B 424 Feedback: A patient taking eletriptan to relieve a migraine can take another dose in 2 hours if the headache is not relieved. The combination of ergot drugs with triptans is not indicated because of the vasoconstriction caused by both. The patient will not get relief by waiting it out. Ibuprofen is an anti-inflammatory that does not affect the mechanism associated with migraines. 10. The nurse is caring for a patient who is receiving an opioid analgesic. What are the nurse’s priority assessments? A) Pain intensity and blood glucose level B) Level of consciousness and respiratory rate C) Respiratory rate and electrolytes D) Urine output and pain intensity Ans: B Feedback: The nurse should assess respiratory rate and level of consciousness because respiratory depression and sedation are adverse effects of opioid analgesics. Blood glucose levels, electrolytes, and urine output are not priority assessments with opioid ingestion. 11. The nurse is caring for a patient experiencing postoperative pain. The physician orders 2.5 mg of morphine IV every two hours. Morphine is supplied in 10 mg/mL vials. How many mL will the nurse administer? A) 0.25 mL B) 0.5 mL C) 1 mL D) 2 mL Ans: A Feedback: Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 425 10 mg = 1 mL and a dose of 2.5 mg is ordered. 10 mg/1 mL: 2.5 mg/x Cross-multiply to yield 2.5 mg = 10x. Divide each side by 10 to learn the nurse should administer 0.25 mL 12. A 72-year-old patient is admitted to the hospital for surgery. After the patient returns to the floor, the patient’s daughter tells the nurse she is concerned that her mother will overdose on morphine because she keeps pressing the button on her patient-controlled anesthesia (PCA) pump. What is the nurse’s best response? A) You should control how often she presses the button. B) If she will follow the directions she was given, that will not happen. C) The PCA device always provides the correct amount, so pressing the button is just for placebo effect. D) The device is preset, so your mother cannot get more than a specific amount. Ans: D Feedback: A PCA system using morphine provides a baseline, constant infusion of morphine and gives the patient control of the system to add bolus doses of morphine if the patient believes that pain is not being controlled. The system prevents overdose by locking out extra doses until a specific period of time has elapsed. The PCA is for the patient to control the analgesia, not for a family member to control it because the patient will fall asleep when adequate pain control is reached. If the family keeps pushing the button while the patient’s level of consciousness continues to decline, serious overdosage could occur. Not following directions could result in inadequate pain management but not overdosage. The button delivers small bolus dosages so it is not a placebo effect. 13. What drug might the nurse administer for both analgesic and antitussive effects? A) Codeine B) Aspirin C) Ibuprofen D) Acetaminophen Ans: A Feedback: Codeine is a narcotic drug used for its analgesic and antitussive effects. Aspirin, ibuprofen, and Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 426 acetaminophen do not have antitussive effects. 14. As the nurse settles the patient into his room after returning from the post-anesthesia care unit (PACU), the patient says he is in severe pain. The nurse checks the medical record and sees the patient has an order for morphine 4 to 8 mg every 1 to 2 hour IV as needed for pain. The nurse sees this medication has not been administered yet so the nurse administers 4 mg. After administering the drug, the PACU nurse calls to say a dose of morphine was given and not documented. What drug will the nurse be prepared to administer if the patient’s respiratory rate is depressed? A) Naloxone hydrochloride tartrate (Narcan) B) Butorphanol C) Buprenorphine (Buprenex) D) Nalbuphine hydrochloride (Nubain) Ans: A Feedback: Naloxone is the drug of choice for treatment of opioid overdose. Butorphanol (INN) is amorphinantype synthetic opioid analgesic that would not reverse the effects of an opioid. Buprenex (buprenorphine hydrochloride) is a narcotic-agonist-antagonist and would suppress respirations further. Nalbuphine is a synthetic opioid used commercially as an analgesic that would also depress respirations. 15. The nurse is providing patient teaching about a prescribed opioid analgesic. What is an important teaching point related to a possible adverse effect of this drug? A) Ataxia B) Blurred vision C) Hypotension D) Dysrhythmias Ans: C Feedback: Orthostatic hypotension is commonly seen in association with some narcotics. Ataxia, blurred vision, and dysrhythmias are not commonly seen adverse effects of an opioid analgesic. 16. The nurse receives an order for morphine sulfate 8 mg IV every 1 hour as needed for pain. For which Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 427 patient would the nurse need to question this order? A) A 78-year-old with osteoarthritis B) A 45-year-old, 1-day postoperative mastectomy C) A 28-year-old with a fractured tibia D) A 17-year-old, 1-day postoperative appendectomy Ans: A Feedback: Older patients are more likely to experience the adverse effects associated with narcotics, including central nervous system, gastrointestinal, and cardiovascular effects. Furthermore, a strong narcotic analgesic would not be indicated for chronic osteoarthritis pain. For both of these reasons, the nurse would question the large dosage of a narcotic. The other patients could appropriately receive morphine 8 mg unless they were smaller than average adults. 17. The nurse is administering morphine to a trauma patient for acute pain. Before administering the morphine, what common adverse effect should the nurse inform the patient about? A) Paresthesia in lower extremities B) Occipital headache C) Increased intracranial pressure D) Drowsiness Ans: D Feedback: Common adverse effects include dizziness, drowsiness, and visual changes. Morphine does not commonly cause paresthesia in the lower extremities, an occipital headache, or increased intracranial pressure. 18. The nurse administers a narcotic analgesic to the postoperative patient. What is the best way for the nurse to evaluate response to the medication? A) Observe the patient without her awareness. B) Use a pain assessment tool before and 30 minutes after administration. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) C) Assess vital signs. D) Measure oxygen saturation. Ans: B 428 Feedback: A standard pain assessment tool should be used both pre- and post-analgesia. Observing the patient when she is not aware you are watching, assessing vital signs, and measuring oxygen saturation may all contribute useful data but it would not be the best means of determining pain response following analgesic administration. 19. A patient, 6 days postoperative, is being weaned off an opioid analgesic. The patient reports he is getting no relief from the pain with the new non-opioid medication he is receiving. What might the nurse suspect is causing this patient’s pain? A) The patient needs a higher dose of the opioid analgesic. B) The patient has become addicted to the opioid medication. C) The patient has developed withdrawal syndrome. D) The patient has developed a cross-hypersensitive reaction. Ans: C Feedback: Caution should be used in cases of physical dependence on a narcotic because a withdrawal syndrome may be precipitated, the narcotic antagonistic properties can block the analgesic effect, and so intensify the pain. It is important to differentiate between addiction and dependence because addiction generally does not occur in patients receiving narcotics for medical reasons. There is no indication of a hypersensitivity reaction. Giving a higher dose of the opioid would eliminate the progress made to date on weaning the patient from the narcotic, so attempts should be made to avoid this intervention. 20. Which narcotic analgesics can the nurse administer to a child because she has an established pediatric dose? (Select all that apply.) A) Transdermal fentanyl B) Methadone C) Morphine Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) D) Meperidine E) Hydrocodone Ans: C, D, E Feedback: Narcotics that have an established pediatric dose include codeine, fentanyl (but not the transdermal form), hydrocodone, meperidine, and morphine. Methadone is not recommended as an analgesic in children. 21. The home care nurse administers oral morphine to the patient with cancer pain. When will the nurse expect this medication to reach peak activity? A) 10 minutes B) 30 minutes C) 45 minutes D) 60 minutes Ans: D Feedback: With oral administration, peak activity occurs in about 60 minutes. The duration of action is 5 to 7 hours. 22. Before administering an opiate medication, what will the nurse assess? A) The patient’s weight B) The patient’s heart rate C) The patient’s respiratory rate D) The patient’s drug tolerance Ans: C Feedback: 429 Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 430 Check the rate, depth, and rhythm of respirations before each dose. If the patient’s heart rate is slower than 12 beats per minute, delay or omit the dose and report to the physician. Weight would be assessed before determining dosage. Heart rate would not be an essential assessment before administration. Drug tolerance is assessed by monitoring patient’s response to the medication and could not be assessed before administration. 23. The nursing instructor asks the student nurse to explain the action of sumatriptan. What is the student’s best response? A) Vasoconstrictive on cranial blood vessels B) Depresses pain response in the central nervous system C) Vasodilation of peripheral blood vessels D) Binds to acetylcholine receptors to prevent nerve transmission Ans: A Feedback: Sumatriptan binds to serotonin receptors to cause vasoconstrictive effects on cranial blood vessels. The other options are incorrect. 24. The nurse administers pentazocine cautiously to what population? A) Patients with known GI disease B) Patients with known heart disease C) Patients with known urinary disease D) Patients with known respiratory disease Ans: B Feedback: Pentazocine must be administered cautiously to patients with known heart disease because the drug may cause cardiac stimulation including arrhythmias, hypertension, and increased myocardial oxygen consumption, which could lead to angina, myocardial infarction, or congestive heart failure. No indication exists that it must be given cautiously to patients with gastrointestinal, urinary, or respiratory diseases. 25. Narcotic agonists-antagonists have what function? (Select all that apply.) Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) A) Relief of moderate-to-severe pain B) Adjunctive therapies to nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) C) Relief of pain during labor and delivery D) Relief of orthopedic pain E) Adjuncts to general anesthesia Ans: A, C, E 431 Feedback: These drugs have three functions: (1) relief of moderate-to-severe pain, (2) adjuncts to general anesthesia, and (3) relief of pain during labor and delivery. Adjunctive therapies to NSAIDs or specificity for orthopedic pain are not functions of this classification of medication. 26. You are caring for a patient taking pentazocine (Talwin). What would be an appropriate nursing diagnosis for this patients care plan? A) Fluid volume deficit related to diarrhea caused by medication B) Risk for pain related to administration of medication C) Monitor timing of analgesic doses. D) Impaired gas exchange related to respiratory depression Ans: D Feedback: Nursing diagnosis may include impaired gas exchange related to respiratory depression. The drug is more likely to cause constipation due to slowing of the GI tract instead of diarrhea, so that fluid volume deficit would not be appropriate. Monitoring timing of analgesic doses is an intervention and not a nursing diagnosis. If the patient is receiving pentazocine that would indicate he is experiencing pain and is not just at risk for pain, and that the pain is not caused by the drug. The drug is given to reduce the pain so this diagnosis is incorrect. 27. A) When evaluating the effects of narcotic agonist-antagonists on a patient, what adverse effects would the nurse monitor for? Hypertension Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) B) Bleeding C) Suppressed bone marrow function D) Increased pulse pressure Ans: A 432 Feedback: Monitor for adverse effects (e.g., central nervous system changes, gastrointestinal (GI) depression, respiratory depression, arrhythmias, hypertension). Bleeding, bone marrow suppression, and increased pulse pressure are not normally seen with these drugs. 28. What is the nurse’s priority assessment when administering narcotics to older adults? (Select all that apply.) A) Central nervous system (CNS) effects B) Gastrointestinal effects C) Cardiovascular effects D) Urinary effects E) Developmental effects Ans: A, B, C Feedback: Older patients are more likely to experience the adverse effects associated with these drugs, including central nervous system, gastrointestinal (GI), and cardiovascular effects. Urinary and developmental effects are not areas of high concern. 29. By what route will the nurse administer methylnaltrexone (Relistor)? A) IV B) Subcutaneously C) Intranasally D) Orally Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) Ans: 433 B Feedback: Relistor is only given by subcutaneous injection once each day. 30. According to the Gate Control Theory, what interventions by the nurse could help to block pain impulses? A) Administration of opioid medications B) Administration of narcotic agonist-antagonists C) Back massage D) Acupuncture Ans: C Feedback: According to the gate control theory, the transmission of these impulses can be modulated or adjusted all along these tracts. All along the spinal cord, interneurons can act as gates by blocking the ascending transmission of pain impulses. It is thought that the gates can be closed by stimulation of the larger A fibers and by descending impulses coming down the spinal cord from higher levels in such areas as the cerebral cortex, the limbic system, and the reticular activating system. Administration of medications does not use the Gate Control Theory. Acupuncture uses the Gate Control Theory but is not performed by the nurse. 31. The patient in labor receives morphine every 2 hours to manage labor pain. After 22 hours of labor the woman delivers a baby boy. What is the nurse’s priority action related to the newborn? A) Monitor for opioid effects. B) Administer naloxone. C) Monitor for withdrawal syndrome. D) Assess for congenital anomaly. Ans: A Feedback: Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 434 Morphine, meperidine, and oxymorphone are often used for analgesia during labor. The mother should be monitored closely for adverse reactions, and, if the drug is used during a prolonged labor, the newborn infant should be monitored for opioid effects. Naloxone would only be given if the newborn displays opioid effects. Withdrawal syndrome would not be seen with less than 24 hours of use. Every newborn is assessed for congenital anomalies but this would not be related to administration of morphine to the mother and so would not be the highest priority. 32. What medication would the nurse administer to the patient in severe pain? A) Codeine B) Hydrocodone C) Hydromorphone D) Opium Ans: C Feedback: Hydromorphone is indicated for moderate-to-severe pain. Codeine is indicated for mild-to-moderate pain, hydrocodone is indicated for moderate pain, and opium is indicated for treatment of diarrhea and relief of moderate pain. 33. The patient is brought to the emergency department in respiratory arrest after overdosing on heroin. The person accompanying the patient says he has been using heroin for years. After being administered one dose of a narcotic antagonist, the patient begins to breathe spontaneously but remains nonresponsive to stimuli so another dose of narcotic antagonist is ordered. What symptoms would indicate the patient is experiencing acute narcotic abstinence syndrome? (Select all that apply.) A) Tachycardia B) Hypertension C) Vomiting D) Confusion E) Sedation Ans: A, B, C Feedback: The most common adverse effect is an acute narcotic abstinence syndrome that is characterized by Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 435 nausea, vomiting, sweating, tachycardia, hypertension, tremulousness, and feelings of anxiety. Confusion and sedation are not associated with acute narcotic abstinence syndrome. 34. What order for naloxone would be appropriate for the nurse to administer for reversal of opioid effects? A) 1 mg IV repeat every 2 to 3 minutes B) 5 mg IV repeat every 5 minutes C) 0.1 mg IV repeat every 2 to 3 minutes D) 0.4 mg IV repeat every 3 minutes Ans: C Feedback: 0.1 to 0.2 mg is given IV and then repeated every 2 to 3 minutes for reversal of opioid effects. If the patient has overdosed on opioids the dose would be 0.4 to 2 mg every 2 to 3 minutes. The other options are incorrect. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 436 Chapter 27 - General and Local Anesthetic Agents 1. To decrease sympathetic stimulation in balanced anesthesia type of what agent would be used? A) Antihistamines B) Antiemetics C) Narcotics D) Sedative-hypnotics Ans: D Feedback: Sedative-hypnotics relax the patient, facilitate amnesia, and decrease sympathetic stimulation. Antihistamines decrease the chance of allergic reaction and help dry secretions. Antiemetics decrease the nausea and vomiting associated with gastrointestinal (GI) depression. Narcotics aid in the analgesic and sedative effects. 2. During what stage of anesthesia would the nurse see the patient’s skeletal muscles relax and return of regular respirations? A) Stage 1: Analgesia stage B) Stage 2: Excitement stage C) Stage 3: Surgical anesthesia stage D) Stage 4: Medullary paralysis Ans: C Feedback: Stage 3 is surgical anesthesia, which involves relaxation of skeletal muscles and return of regular respirations. During this stage, eye reflexes and pupil dilation are progressively lost. Surgery can be safely performed in this stage. Stage 1 refers to the loss of pain sensation; stage 2 involves a period of excitement with sympathetic stimulation (e.g., tachycardia, increased respirations, blood pressure changes); and stage 4 involves deep central nervous system depression with loss of respiratory and vasomotor center stimuli. Death can occur rapidly at this stage if adequate support is not supplied. 3. The nurse is developing a plan of care for the patient undergoing general anesthesia. What is a priority Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 437 of care for this patient? A) Encourage clear fluids. B) Increase oxygen. C) Reassure the patient that about safety. D) Maintain regular repositioning. Ans: D Feedback: The patient would need to be moved or turned periodically to prevent skin breakdown and the formation of decubitus ulcers if the surgery lasted longer than an hour. Muscle paralysis resulting from the medications used in general anesthesia would prevent the patient from shifting himself or herself to relieve increase pressure. A patient receiving a general anesthetic would be unconscious, require respiratory support, and be connected to a mechanical ventilator to maintain respirations. Increased oxygen would not be indicated unless oxygen levels were less than adequate, and the patient would not receive anything by mouth eliminating option A. Reassurance would not be necessary for the unconscious patient. 4. A plan of care formulated by an operating room (OR) nurse includes four nursing diagnoses. Which diagnoses will the nurse include that is directly related to safety? A) Deficient knowledge regarding drug therapy B) Disturbed sensory perception (kinesthetic, tactile) related to anesthesia C) Risk for impaired skin integrity related to immobility D) Risk for injury related to central nervous system (CNS) depressive effects of drugs Ans: D Feedback: The nursing diagnosis, which directly relates to safety, is high risk for injury. The other three options are only indirectly related to safety. While in the OR, the patient under general anesthetic is unable to express safety concerns and must rely completely on the surgeon and OR staff for protection. 5. A) What nursing interventions would help minimize the risk of a headache in a patient recovering from spinal anesthesia? Administer a triptan intramuscularly. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) B) Administer morphine intravenously. C) Maintain patient in recumbent position. D) Place patient in Trendelenburg position. Ans: C 438 Feedback: Patients receiving spinal anesthesia should remain in a recumbent position for as long as 12 hours. Triptan would not be effective because it is indicated for treatment of migraine headaches. Morphine would treat the headache but would not prevent it. 6. An extremely anxious patient is beginning to awaken in the postanesthesia care unit. He or she states that his or her arms and legs feel like tree trunks and that they are hard to move. He or she also complains that his or her head feels fuzzy and that the right words will not come to his or her. What is the priority nursing intervention for this patient? A) Provide analgesic medication for the discomfort. B) Stay with patient as much as possible and provide reassurance. C) Provide fluids to increase his or her wakefulness. D) Encourage the patient to turn from side to side periodically. Ans: B Feedback: Most patients are disoriented and confused when awaking from anesthesia. It would be most important for the nurse to be with the patient as much as possible and reassure the patient that everything is as expected. Providing pain medication is important and may be needed during recovery if the patient reports pain, but would not be useful in treating the reported symptoms. The nurse would not provide fluids to patients immediately after surgery until ensuring the swallow reflex has returned and bowel motility has resumed. The nurse will help the patient turn from side to side, but this is not the priority nursing action at this time. However, the most effective nursing action for anxious postoperative patients is for the nurse to stay with them as much as possible. 7. A) The patient appears awake but is unconscious and has no response to painful stimuli. What medication does the nurse suspect this patient has received? Thiopental (Pentothal) Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) B) Midazolam (Generic) C) Ketamine (Ketalar) D) Propofol (Diprivan) Ans: C 439 Feedback: Ketamine has been associated with a bizarre state of unconsciousness in which the patient appears to be awake but is unconscious and cannot feel pain. This drug, which causes sympathetic stimulation with increase in blood pressure and heart rate, may be helpful in situations when cardiac depression is dangerous. Thiopental is a barbiturate anesthetic. Midazolam and propofol are nonbarbiturate anesthetics. None of these medications have this type of effect. 8. Which nonbarbiturate anesthetic when used with halothane (Fluothane) can cause severe cardiac depression? A) Droperidol (Inapsine) B) Etomidate (Amidate) C) Ketamine (Ketalar) D) Propofol (Diprivan) Ans: C Feedback: If ketamine and halothane are used in combination, severe cardiac depression with hypotension and bradycardia may occur. Use of droperidol, etomidate, and propofol with halothane should not be a concern. 9. The operating room nurse is developing the care plan for a 10-year-old child with asthma who is scheduled for a tonsillectomy and who will receive halothane as the anesthetic agent. Why is this an appropriate drug for this patient? A) Halothane is metabolized in the liver. B) Halothane dilates the bronchi. C) Halothane is excreted unchanged in the urine. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) D) Halothane causes an accumulation of secretions. Ans: B 440 Feedback: Halothane is of particular benefit to a child with asthma because it dilates bronchi. Halothane is inhaled drug so it is not metabolized in the liver or excreted in the urine. It does not cause an accumulation of secretions. 10. The nurse should recognize what drug is classified as an amide local anesthetic? A) Lidocaine (Xylocaine) B) Benzocaine (Dermoplast) C) Chloroprocaine (Nesacaine) D) Tetracaine (Pontocaine) Ans: A Feedback: Lidocaine is an example of an amide anesthetic. Benzocaine, chloroprocaine, and tetracaine are ester anesthetics. 11. A 21-year-old patient is positioned on the operating room table in preparation for knee surgery. After the anesthesiologist induces the patient, what is the next phase of anesthesia? A) Induction B) Maintenance C) Recovery D) Medullary paralysis Ans: D Feedback: Induction is the period from the beginning of anesthesia until stage 3, or surgical anesthesia, is reached. After induction comes the maintenance phase from stage 3 until the surgical procedure is complete. A Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 441 slower, more predictable anesthetic, such as a gas anesthetic, may be used to maintain the anesthesia after the patient is in stage 3. This is followed by the recovery period that begins with the discontinuation of anesthesia. Medullary paralysis is the depth of anesthesia known as stage 4. Option C is a distracter. 12. The nurse is collecting a nursing history from a preoperative patient who is to receive local anesthesia. While taking the admission history, the patient says she is allergic to lidocaine. What is the nurse’s priority action? A) Notify the anesthesiologist. B) Cancel the surgery. C) Notify the surgeon. D) Tell the perioperative nurse. Ans: A Feedback: The priority action is to inform the anesthesiologist who will administer the anesthetic because local anesthesia often involves use of lidocaine. It is not within the nurse’s scope of practice to cancel surgery. Notifying the surgeon and the perioperative nurse is appropriate but is not the priority of care. 13. The nurse is caring for a patient in stage 2 of general anesthesia. What is the care priority for this patient? A) Rub the patient’s back. B) Monitor vital signs. C) Provide eye care. D) Reposition the patient. Ans: B Feedback: Stage 2, the excitement stage, is a period of excitement and often combative behavior, with many signs of sympathetic stimulation (e.g., tachycardia, increased respirations, blood pressure changes). Monitoring vital signs can be lifesaving at this stage. Eye care is important in stages 3 and 4. Rubbing the patient’s back and repositioning the patient are not indicated in this stage of anesthesia. 14. The patient received midazolam in combination with an inhaled anesthetic and a narcotic during Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 442 surgery. The postanesthesia care unit (PACU) nurse anticipates this combination of drugs will have what impact on the patient’s stay in the unit? A) Increased use of medications to offset adverse effects B) Extended time needed in the unit C) Decreased nursing support needed D) Increased analgesics needed Ans: B Feedback: Midazolam is associated with increased toxicity and length of recovery when used in combination with inhaled anesthetics, other central nervous system depressants, narcotics, propofol, or thiopental. Because this patient received both narcotics and inhaled anesthetics, the nurse will anticipate this patient’s time in the PACU will be extended. The patient is likely to need fewer analgesics because it will take longer for the patient to wake from anesthesia, which will also mean fewer medications will be used. Until the patient is awake, he or she will need continuous nursing support. 15. The nurse is caring for a patient in the emergency department with a 2-inch laceration to the left arm caused by broken glass. The nurse suspects the local anesthetic will be administered by what method? A) Topical Administration B) Infiltration C) Field block D) Nerve block Ans: B Feedback: Infiltration local anesthesia involves injecting the anesthetic directly into the tissues to be treated (e.g., sutured, drilled, cut). This injection brings the anesthetic into contact with the nerve endings in the area and prevents them from transmitting nerve impulses to the brain. Topical administration would not be absorbed deeply enough to prevent pain. Field block would be used in a larger area (e.g., the entire area required surgical repair). Nerve block would anesthetize a far larger area than is required for 2-inch laceration. 16. A nurse is caring for a patient who received thiopental as an anesthetic agent during surgery. What adverse effects would the nurse attribute to the medication? Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) A) Tachycardia B) Urinary retention C) Tachypnea D) Headache Ans: D 443 Feedback: Adverse effects of thiopental include emergence delirium, headache, restlessness, anxiety, cardiovascular depression, respiratory depression, apnea, salivation, hiccups, and rashes. Tachycardia, tachypnea, and urinary retention are not usually associated with this drug. 17. The nurse is caring for a patient who will receive an epidural block. What procedure is this patient likely to be having? A) Rhinoplasty B) Inguinal hernia repair C) Removal of a brain tumor D) Closed reduction of the right humerus Ans: B Feedback: Nerve block is a method of administering local anesthesia by injecting the anesthetic at some point along the nerve or nerves that run to and from the region in which the loss of pain sensation or muscle paralysis is desired. Several types of nerve blocks are possible. Epidural anesthesia is an injection of the drug into the epidural space where the nerves emerge from the spinal cord. As a result, only an inguinal hernia repair would be an appropriate procedure for administering an epidural. Surgery performed about the spinal cord, such as surgery on the nose or brain, could not be anesthetized by injection of medication into the spinal cord. Closed reduction of the right humerus would not be performed using a local anesthetic. 18. A) The operating room nurse is taking the patient into the operating room when the patient says his grandmother almost died from a high fever in surgery 15 years ago. The nurse shares this information with the surgical team, recognizing this information indicates the patient is at risk for what? An allergic reaction to anesthesia Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) B) Malignant hyperthermia C) Anxiety D) Hypothermia Ans: B 444 Feedback: The nurse assesses for a personal or family history of malignant hyperthermia, which may be triggered by the use of general anesthetics. Identifying patients at risk is imperative because the mortality rate is very high. All of these drugs have the potential to trigger malignant hyperthermia and should be used with caution in any patient at high risk. The patient’s anxiety is to be expected, all patients are at risk for hypothermia because they are often uncovered in a cold room. Allergy to anesthesia must always be considered a possibility but there is no indication of a higher than normal risk in this patient. 19. The circulating nurse in the day surgery center is caring for a patient who is to receive a local anesthetic. What potential complications will the nurse monitor for? (Select all that apply.) A) Malignant hypothermia B) Pain C) Blurred vision D) Peripheral vasodilation E) Nausea Ans: C, D, E Feedback: Adverse effects of local anesthetics are associated with the route of administration and the amount of drug that is absorbed systemically. These effects are related to the blockade of nerve depolarization throughout the system. Effects that may occur include central nervous system effects such as headache (especially with epidural and spinal anesthesia), restlessness, anxiety, dizziness, tremors, blurred vision, and backache; gastrointestinal (GI) effects such as nausea and vomiting; cardiovascular effects such as peripheral vasodilation, myocardial depression, arrhythmias, and blood pressure changes, all of which may lead to fatal cardiac arrest; and respiratory arrest. There is no such problem as malignant hypothermia (the condition is malignant hyperthermia) and pain may be caused by the procedure but not the anesthetic. 20. What nursing diagnosis would a circulating nurse use on his or her intraoperative patients who receive general anesthesia? (Select all that apply.) Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) A) Disturbed sensory perception B) Risk for hypovolemia C) Risk for latex allergy response D) Disturbed body image E) Anxiety Ans: A, C, E 445 Feedback: Nursing care of patients receiving general or local anesthetics should include safety precautions to prevent injury and skin breakdown, support and reassurance to deal with the loss of sensation and mobility, and patient teaching regarding what to expect to decrease stress and anxiety. Risk for hypovolemia and disturbed body image would be applicable to some surgical procedures but would not be related to general anesthesia. 21. The patient receives lidocaine as a local anesthetic before insertion of a chest tube. After the procedure the patient tells the nurse, The area is still numb. How long will this last? What is the nurse’s best response? A) 15 minutes B) 1 hour C) 2 hours D) 4 hours Ans: C Feedback: The onset of intramuscular lidocaine is 5 to 10 minutes, peaks within 5 to 15 minutes, and the duration of action is 2 hours. Options A, B, and D are distracters. 22. A) The pharmacology instructor is explaining balanced anesthesia to the students. What agents would the instructor say are involved in balanced anesthesia? (Select all that apply.) Neuromuscular junction blockers Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) B) Narcotics C) Anticholinergics D) 446 Salicylates E) Nonsteriodal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) Ans: A, B, C Feedback: Balanced anesthesia involves giving a variety of drugs with specific effects to achieve analgesia, relax muscles, and invoke unconsciousness and amnesia. Classification of drugs administered includes anticholinergics, rapid intravenous anesthetics, inhaled anesthetics, neuromuscular junction blockers, and narcotics. Balanced anesthesia does not include use of salicylates or nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs. 23. The nurse is caring for a patient who received halothane as an anesthetic agent. The patient will require additional surgery. When can halothane be used again without risk of halothane’s recovery syndrome? A) 1 week B) 2 weeks C) 3 weeks D) 4 weeks Ans: C Feedback: Halothane’s recovery syndrome is characterized by fever, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, and eventual hepatitis, which can progress to fatal hepatic necrosis. Although this syndrome is rare, halothane is not used more frequently than every 3 weeks to reduce patient risk. Other options are incorrect. 24. A 54-year-old patient with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease is admitted for emergency surgery. What anesthetic agent would be dangerous to use on this patient? A) Enflurane B) Desflurane C) Sevoflurane Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) D) Isoflurane Ans: B 447 Feedback: Desflurane is associated with a collection of respiratory reactions, including cough, increased secretions, and laryngospasm. The other options have far fewer respiratory adverse effects and would be safer for use in this patient. 25. The nurse is admitting a 35-year-old patient to the preoperative unit in preparation for an elective inguinal hernia repair procedure to be performed under general anesthesia. What is the nurse’s initial priority nursing assessment? A) Assess the patient’s anxiety. B) Start an IV. C) Show the family the waiting area. D) Weigh the patient. Ans: D Feedback: Weighing the patient is an initial priority because his or her weight will be used to determine appropriate dosing of all medications and will establish a baseline used for evaluation of any potential adverse effects. Other options are all actions the nurse will need to perform, but none are of higher priority than weighing the patient. 26. A very anxious patient asks the nurse what type of anesthesia they will have for a scheduled tooth extraction. The nurse would describe what type of local anesthetic in laymen’s terms? A) Topical B) Infiltration C) Field block D) Nerve block Ans: C Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 448 Feedback: Field block local anesthesia involves injecting the anesthetic all around the area that will be affected by the procedure or surgery. This is more intense than infiltration anesthesia because the anesthetic agent comes in contact with all of the nerve endings surrounding the area. This type of block is often used for tooth extractions. Topical would not be appropriate because it would not absorb deeply enough to block pain impulses in the root of the tooth. Nerve block would not be possible for oral surgery. 27. The nurse receives a patient into the postanaesthesia care unit who has had surgery using the anesthetic agent methohexital. The nurse anticipates the patient’s need for what in the postoperative period? A) Assistance in maintaining respirations B) Assistance in moving lower extremities C) Positioning in Semi-Fowler’s position D) Analgesia to control the patient’s pain Ans: D Feedback: Methohexital lacks analgesic properties so the patient may require postoperative analgesics to control pain. The patient who has surgery under methohexital does not generally require assistance in maintaining respirations or assistance in moving their lower extremities. They also do not generally require positioning in a semi-Fowler’s position. 28. The emergency room nurse is teaching a class for newly hired graduate nurses on the different types of local anesthetic agents. How would the nurse differentiate lidocaine and procaine as a local anesthetic agent? A) Lidocaine is an amide that is broken down slowly and this can lead to toxicity. B) Lidocaine is an ester that cannot become toxic in the system because of rapid metabolism. C) Procaine is an amide that is broken down immediately in the tissues. D) Procaine is metabolized by the liver with risk of toxicity and is classified as an ester. Ans: A Feedback: The ester local anesthetics are broken down immediately in the plasma by enzymes known as plasma esterases. The amide local anesthetics are metabolized more slowly in the liver. Serum levels of these Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 449 drugs can become elevated and lead to toxicity. Lidocaine is an amide and procaine is an ester. 29. A nursing student in a pharmacology class asks the instructor why nitrous oxide is used for dental surgery. What is the instructor’s most accurate response? A) Nitrous oxide stays in the body for a long time. B) Nitrous oxide does not cause pressure in body compartments. C) Nitrous oxide does not cause muscle relaxation. D) Nitrous oxide does not need to be administered with oxygen. Ans: C Feedback: Nitrous oxide is a potent analgesic; it is used frequently for dental surgery because it does not cause muscle relaxation. It moves quickly in and out of the body so duration of action is short and recovery after dental work is quick. Nitrous oxide does need to be given in combination with oxygen to avoid hypoxia in the patient. 30. The nurse is admitting a patient to the postanesthesia care unit (PACU) who received halothane and ketamine as anesthesia. What is the nurse’s priority assessment? A) Blood pressure and pulse B) Respirations and airway C) Pain and respirations D) Temperature and airway Ans: A Feedback: If halothane and ketamine are used in combination, severe cardiac depression with hypotension and bradycardia may occur. If these agents must be used together, the patient should be monitored closely. Pain, respirations, airway, and temperature are all assessments the nurse will collect on any patient in the PACU, but they are not priority assessments associated with combining ketamine and halothane. 31. The nurse is assisting while the physician is suturing a wound in the urgent care clinic. The physician asks for lidocaine with epinephrine. The nurse identifies the primary reason for adding epinephrine to the lidocaine is what effect? Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) A) It will sting more when it is injected into the tissue. B) Risk of systemic absorption is increased. C) Local effect is increased. D) Bleeding at the wound site is increased. Ans: C 450 Feedback: There is less risk of systemic absorption and increased local effects if these drugs are combined with epinephrine. Epinephrine causes vasoconstriction, which reduces bleeding, slows absorption, and makes the duration of effect longer. It does sting more when injected, but that is not a reason to use it. 32. The nurse is caring for a patient scheduled for surgery who is to receive a barbiturate as part of the planned balanced anesthesia. What drugs, if taken by the patient, could result in a clinically important drugdrug interaction with the barbiturate? (Select all that apply.) A) Thyroid hormone B) Ibuprofen C) Oral contraceptive D) Theophylline E) Anticoagulant Ans: C, D, E Feedback: Caution must be used when these drugs are used with any other central nervous system suppressants. Barbiturates can cause decreased effectiveness of theophylline, oral anticoagulants, beta-blockers, corticosteroids, hormonal contraceptives, phenylbutazones, metronidazole, quinidine, and carbamazepine. Combinations of barbiturate anesthetics and narcotics may produce apnea more commonly than occurs with other analgesics. Thyroid hormone and ibuprofen have no known drug interactions with barbiturates. 33. A) The nurse is caring for a patient experiencing malignant hyperthermia. What medication will be administered to treat this condition? Midazolam Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) B) Dantrolene C) Halothane D) Thiopental Ans: B 451 Feedback: Dantrolene is the preferred treatment for malignant hyperthermia and should always be readily available whenever anesthetics are used that could trigger the syndrome. Midazolam and thiopental are barbiturates whereas halothane is a volatile gas that can trigger malignant hyperthermia. 34. The nurse is caring for a patient who will undergo cardioversion in the patient’s room this morning. The patient will receive propofol as anesthetic during the procedure. What are the benefits of using propofol for this procedure? (Select all that apply.) A) It has a very rapid clearance. B) It produces less of a hangover effect. C) It allows for quick recovery from anesthesia. D) Its onset of action is 5 minutes. E) It is painless to inject IV. Ans: A, B, C Feedback: Propofol often is used for short procedures because it has a very rapid clearance and produces much less of a hangover effect and allows for quick recovery. It is a very short-acting anesthetic with a rapid onset of action of 30 to 60 seconds. Propofol often causes local burning on injection. 35. The nurse applies a topical anesthetic to reduce sensation at the site while starting an IV. What age group is at greatest risk for systemic absorption of the topical anesthetic? A) Older adult B) Infant C) Toddler Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) D) Adolescent Ans: B Feedback: When topically applying a local anesthetic, it is important to remember that there is greater risk of systemic absorption and toxicity with infants. Therefore, the other options are incorrect. 452 Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 453 Chapter 28 - Neuromuscular Junction Blocking Agents 1. According to the sliding filament theory, what is the initial action in a muscle contraction? A) Troponin is freed and prevents actin and myosin from reacting with each other. B) Calcium binds to troponin, which causes the release of actin and myosin binding sites. C) Actin and myosin molecules react with each other sliding along the filament and making it shorter. D) Muscle filament relaxes or slides back to the resting position. Ans: C Feedback: Actin and myosin molecules react with each other again and again, sliding along the filament and making it shorter. This is a contraction of the muscle fiber according to the sliding filament theory. As the calcium is removed from the cell during repolarization of the muscle membrane, the troponin is freed and once again prevents the actin and myosin from reacting with each other. The muscle filament then relaxes or slides back to the resting position. Muscle tone results from a dynamic balance between excitatory and inhibitory impulses to the muscle. 2. When causing depolarization of the muscle membranes, what neurotransmitter interacts with the nicotinic cholinergic receptors leading to the release of calcium ions? A) Acetylcholine B) Serotonin C) D-gluconamidoethyl methacrylate (GAMA) D) Epinephrine Ans: A Feedback: At the acetylcholine receptor site on the effector’s side of the synapse, the acetylcholine interacts with the nicotinic cholinergic receptors causing the depolarization. Serotonin, GAMA, and epinephrine are not part of muscle contraction and relaxation. 3. The nurse, working in the preoperative holding area, is caring for a 70-year-old patient who is scheduled to receive succinylcholine as part of general anesthesia. When collecting the nursing history, Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 454 what condition would require the nurse to notify the anesthesiologist of the need for caution? A) Bone fracture B) Malnutrition C) Fluid volume overload D) Narrow-angle glaucoma E) Pregnancy Ans: A, B, D Feedback: Succinylcholine should be used with caution in patients with fractures because the muscle contractions it causes might lead to additional trauma; in patients with narrow-angle glaucoma or penetrating eye injuries because intraocular pressure increases. Extreme caution is necessary in the presence of genetic or disease-related conditions causing low plasma cholinesterase levels (e.g., cirrhosis, metabolic disorders, carcinoma, burns, dehydration, malnutrition, hyperpyrexia, thyroid toxicosis, collagen diseases, exposure to neurotoxic insecticides). 4. The nurse is caring for a patient who received succinylcholine during surgery. The nurse would expect the patient to spend more time in the postanesthesia care unit due to prolonged paralysis and inability to breathe if the patient was from what ethnic group? A) American Japanese B) Alaskan Eskimos C) Native Americans D) Hawaiian natives Ans: B Feedback: Alaskan Eskimos belong to a genetic group that is predisposed to low plasma cholinesterase levels, making them susceptible to prolonged paralysis after succinylcholine use. The other ethnic groups do not have this genetic predisposition. 5. A patient scheduled for surgery is to have a nondepolarizing neuromuscular junction (NMJ) blocker as adjunctive anesthesia. The nurse will have cause for concern about prolonged paralysis if the patient has been taking what medication? Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) A) An aminoglycoside B) Aminophylline C) A barbiturate anesthetic D) A cephalosporin Ans: A 455 Feedback: Combining nondepolarizing NMJ blockers with aminoglycosides can result in prolonged paralysis, and this combination should be avoided. This interaction does not occur with barbiturate anesthetics, cephalosporins, or aminophylline. 6. A patient is having outpatient surgery that should last only 45 minutes. The patient is planning to go home immediately after the surgery is complete. What nondepolarizing neuromuscular junction blocker will most likely be used as an adjunct therapy to general anesthesia for this patient? A) Atracurium (Tracrium) B) Cisatracurium (Nimbex) C) Pancuronium (Pavulon) D) Rocuronium (Zemuron) Ans: D Feedback: Rocuronium has a rapid onset of action and a short duration, making it a drug of choice for outpatient surgical procedures when the patient will be leaving to go home and will need to be awake, alert, and mobile. Atracurium, cisatracurium, and pancuronium are associated with longer paralysis and recovery. 7. A patient is taking aminophylline for their chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. The patient is about to undergo emergency surgery and will receive an neuromuscular junction (NMJ) blocker as part of the procedure. It is important for the nurse to take what action? A) Make sure the patient receives the aminophylline on a regular schedule to maintain therapeutic levels. B) Monitor the patient very closely for signs of early arousal and return of muscle function. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) C) Carefully explain all that is going on because the patient will be unable to talk. D) Switch the patient to theophyllines before the procedure begins. Ans: B 456 Feedback: Aminophylline can cause a decreased effectiveness of NMJ blockers, leading to reduced paralysis and early return of movement. If a patient has emergency surgery and has been taking aminophylline, the patient should be carefully monitored for early arousal and return of movement. The patient will not be awake during surgery using an NMJ blocker and will be intubated to ensure respirations. Aminophylline and other xanthine derivatives like the theophyllines will have the same effect. 8. The nurse is caring for a patient who is being maintained on mechanical ventilation. Atracurium is administered to limit the resistance to mechanical ventilation. What is the nurse’s priority assessment? A) Hypotension B) Tachycardia C) Bradycardia D) Increased secretions Ans: C Feedback: Bradycardia is a common adverse effect associated with atracurium. The nurse should monitor the patient regularly to avoid serious adverse effects. Increased secretions and hypotension are common with tubocurarine. Option B is a distracter. 9. The nurse is preparing a patient for surgery who will receive a neuromuscular junction blocker during the procedure. It is important for the nurse to review the patient’s medication history for concurrent use of what? A) Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors B) Beta blockers C) Calcium channel blockers D) Montelukast Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) Ans: 457 C Feedback: When calcium channel blockers are used concurrently with neuromuscular junction blockers, the patient is at increased risk of prolonged paralysis. The dose of the neuromuscular junction blocker should be lowered if this combination cannot be avoided and the patient should be monitored closely. There is no anticipated drugdrug interaction with ACE inhibitors, beta blockers, or montelukast. 10. An elderly patient has received a neuromuscular junction blocker during surgery. What would be an appropriate nursing diagnosis for this patient? A) Excess fluid volume B) Risk for impaired skin integrity C) Deficient fluid volume D) Chronic confusion Ans: B Feedback: An elderly or frail patient will need extra nursing care to prevent skin breakdown during the period of paralysis because skin tends to be thinner and more susceptible to breakdown. Therefore, risk of impaired skin integrity would be an appropriate nursing diagnosis. Fluid excess or deficit should not be a concern and the patient may be acutely confused when awakening, but there is no reason to think he or she would remain chronically confused if he was not before surgery. 11. What are the primary uses of neuromuscular junction blockers (NMJ) blockers? (Select all that apply.) A) To facilitate endotracheal intubation B) To sedate patient for general anesthesia C) To prevent injury during electroconvulsive therapy D) To provide greater ease in extubating patient E) To facilitate mechanical ventilation Ans: A, C, E Feedback: Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 458 NMJ blockers are primarily used as adjuncts to general anesthesia, to facilitate endotracheal intubation, to facilitate mechanical ventilation, and to prevent injury during electroconvulsive therapy. NMJ blockers do not sedate the patient who will be paralyzed after administration but will remain alert unless another medication is given. These medications would not be given before extubation because respiratory muscles would be paralyzed, resulting in the inability to breathe. 12. The pharmacology instructor is discussing nondepolarizing neuromuscular junction blockers (NMJ) blockers with the nursing class. How would the instructor explain the action of nondepolarizing NMJ blockers? A) Blocks acetylcholine (ACh) from acting B) Acts like ACh then prevents repolarization C) Takes the place of ACh in the depolarizing/repolarizing process D) Stops depolarization in the axion Ans: B Feedback: Depolarizing NMJ blockers cause muscle paralysis by acting like ACh. They excite (depolarize) the muscle and prevent repolarization and further stimulation. Options A, C, and D are incorrect. 13. A patient is to have surgery and it is planned that atracurium (Tracrium) is to be used as an adjunct to general anesthesia. How will the atracurium work? A) Act as agonist to acetylcholine B) Stops depolarization in the axion C) Act as antagonist to acetylcholine D) Stops repolarization in the axion Ans: C Feedback: Nondepolarizing neuromuscular junction blockers compete with acetylcholine (ACh) for the ACh receptor site and after they occupy the site, stimulation cannot occur. This results in paralysis because the muscle cannot respond. Other options are incorrect. 14. The nurse is caring for a patient who is receiving pancuronium (Pavulon) to facilitate mechanical Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 459 ventilation. The patient is also receiving a barbiturate. How will the nurse administer these two medications? A) They can be mixed and given in the same syringe. B) Administer IM quickly after mixing the two drugs. C) Shake vigorously when mixed in one syringe. D) If given together, a precipitate may form. Ans: D Feedback: Do not mix this drug with any alkaline solutions such as barbiturates because a precipitate may form, making it inappropriate for use. Pancuronium is only given IV. Shaking does not prevent precipitation. 15. The nurse is caring for a patient who is scheduled for abdominal surgery in the morning and is scheduled to receive rocuronium (Zemuron). The patient asks the nurse to describe the adverse effects of rocuronium. What would the nurse describe for the patient? A) This drug is associated with pulmonary hypertension. B) This drug contains benzyl alcohol. C) This drug is associated with bradycardia. D) This drug is associated with an increased heart rate. Ans: A Feedback: Rocuronium may be associated with pulmonary hypertension. Cisatracurium (Nimbex) contains benzyl alcohol; Atracurium (Tracrium) is associated with bradycardia; and Pancuronium (Pavulon) is associated with an increased heart rate. 16. The postanesthesia care unit (PACU) nurse is caring for a patient that had succinylcholine (Anectine) as an adjunct to anesthesia. What is the nurse’s priority assessment while caring for this patient? A) Movement B) Temperature Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) C) Mental status D) Heart rate Ans: B 460 Feedback: Succinylcholine is more likely to cause malignant hyperthermia than other drugs so it is very important that the nurse carefully monitor the patient’s temperature while in the PACU. Movement, mental status, and heart rate monitoring are all routine components of PACU care, but after receiving this medication, temperature monitoring becomes the priority. 17. The nurse is caring for a patient scheduled for abdominal surgery in the morning. The patient confides that he or she watched a movie last week about someone who had surgery and the anesthetic did not work, but no one knew because that patient could not move. What nursing diagnosis will the nurse include in this patient’s plan of care? A) Alteration in fluid volume B) Deficient knowledge regarding drug therapy C) Fear related to paralysis D) Risk for skin impairment Ans: C Feedback: Nursing diagnoses related to drug therapy may include Fear related to paralysis. This care plan would not include alteration in fluid volume; deficient knowledge regarding drug therapy; or risk for skin impairment. 18. The nurse is caring for a patient in the intensive care unit who has been receiving neuromuscular junction (NMJ) blockers, sedatives, and analgesics for the past 2 weeks. The NMJ blocker therapy has been discontinued and the other medications are being reduced gradually. The patient is now alert and awake, communicating with his or her family by using paper and pencil. The family asks why the patient cannot sustain normal respirations. What is the nurse’s best response? (Select all that apply.) A) His or her muscles need to get their strength back again. B) This is a common occurrence in situations like this. C) He or she is likely to breathe better each day. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) D) The drugs created temporary muscle damage. E) He or she will not be taken off the mechanical ventilator until he is ready. Ans: A, B, C, E 461 Feedback: After 2 weeks of muscle paralysis, the muscles are weak and will take time to strengthen as the patient begins using them again. Profound and prolonged muscle paralysis is always possible; patients must be supported until they are able to resume voluntary and involuntary muscle movement. When the respiratory muscles are paralyzed, depressed respiration, bronchospasm, and apnea are anticipated adverse effects so the patient will remain ventilated until he or she can demonstrate adequate respiratory effort. The drugs did not damage the muscle, but lack of use has weakened them. 19. The nurse is caring for a very anxious 33-year-old female patient scheduled for abdominal surgery today. The patient says the anesthesiologist said she would receive succinylcholine (Anectine) during surgery and asks the nurse how long it will take before the medicine starts to work. What is the nurse’s best response? A) 1 to 2 minutes B) 30 to 60 seconds C) 5 to 10 minutes D) 30 minutes Ans: B Feedback: Succinylcholine has an onset of action of 30 to 60 seconds. The other options are incorrect. 20. The patient returns from surgery complaining about muscle pain after receiving succinylcholine during the procedure. After reviewing the postoperative orders, which of these ordered analgesics will the nurse administer to treat this pain? A) Aspirin B) Acetaminophen (Tylenol) C) Ketorolac (Toradol) D) Morphine Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) Ans: 462 A Feedback: Succinylcholine is associated with muscle pain, related to the initial muscle contraction reaction. A nondepolarizing neuromuscular junction blocker may be given first to prevent some of these contractions and the associated discomfort. Aspirin also alleviates much of this pain after the procedure. Tylenol is not an antiinflammatory medication and would not be appropriate. Toradol and morphine provide stronger pain relief than what is indicated for this discomfort. 21. A student asks the pharmacology instructor how succinylcholine differs from acetylcholine (ACh). What should the instructor respond? A) Succinylcholine is not broken down instantly. B) It results in a prolonged contraction of the muscle. C) The muscle becomes hyper stimulated by succinylcholine. D) Succinylcholine’s duration of action is about 2 hours. Ans: A Feedback: Unlike endogenous ACh, succinylcholine is not broken down instantly. Succinylcholine, a depolarizing NMJ blocker, attaches to the ACh-receptor site on the muscle cell, causing a prolonged depolarization of the muscle. This depolarization causes stimulation of the muscle and muscle contraction (seen as twitching) and then as flaccid paralysis, so the contraction of the muscle is not prolonged and the muscle is incapable of being stimulated. The duration of effects of succinylcholine is 4 to 6 minutes and not 2 hours. 22. The certified registered nurse anesthetist documents the anesthesia plan as using a depolarizing neuromuscular junction (NMJ) blocker as adjunct to other anesthetics on the patient when they go to surgery. The nurse would understand from this note that the patient will receive what drug? A) Rocuronium (Zemuron) B) Pancuronium (Pavulon) C) Succinylcholine (Anectine, Quelicin) D) Cisatracurium (Nimbex) Ans: C Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 463 Feedback: Currently the only agent classified as a depolarizing NMJ blocker is succinylcholine. rocuronium, pancuronium, and cisatracurium are all nondepolarizing NMJ blockers. 23. The nurse administers pancuronium to the mechanically ventilated patient in the pediatric intensive care unit. What assessment finding would the nurse suspect is an adverse effect resulting from the drug? A) Bradycardia B) Bronchospasm C) Should not be used in neonates D) Associated with pulmonary hypertension Ans: B Feedback: Adverse effects of pancuronium include respiratory depression, apnea, bronchospasm, and cardiac arrhythmias. Rocuronium is associated with pulmonary hypertension, cisatracurium should not be used in neonates, and atracurium is associated with bradycardia. 24. The nursing student asks the mental health nurse why pancuronium was administered to the patient before electroconvulsive therapy was performed. What is the mental health nurse’s best response? A) To prevent aspiration of vomitus B) To reduce the pain of the procedure C) To put the patient to sleep D) To reduce the intensity of muscle contractions Ans: D Feedback: Pancuronium is used, in this case, to induce skeletal muscle relaxation and to reduce the intensity of muscle contractions in electroconvulsive therapy. Pancuronium has no analgesic or amnesic effects. It would not reduce the risk of aspiration unless an endotracheal tube was placed with the cuff inflated and then it would not be the drug that was preventing aspiration. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 25. 464 When a nondepolarizing neuromuscular junction blocker is used as an adjunct to surgery, what classification of medications could reverse the neuromuscular blockage leading to early arousal and return of muscle function? A) Xanthines B) Barbiturates C) Opiates D) Antihypertensives Ans: A Feedback: Administering xanthines (e.g., theophylline, aminophylline) could result in reversal of the neuromuscular blockage. Patients receiving this combination of drugs should be monitored very closely during the procedure for the potential of early arousal and return of muscle function. Barbiturates, opiates, and antihypertensives do not reverse neuromuscular blockage. 26. The nursing instructor asks the student nurse what causes the respiratory obstruction that can occur with many of the depolarizing neuromuscular junction (NMJ) blockers. What is the student’s most accurate response? A) Acetylcholine (ACh) B) Histamine release C) Serotonin D) Hyperkalemia Ans: B Feedback: The histamine release associated with many of the depolarizing NMJ blockers can cause respiratory obstruction with wheezing and bronchospasm. Hyperkalemia is an adverse effect of the depolarizing NMJ blockers, ACh is what is acted on by the NMJ blockers, and serotonin is a distracter for this question. 27. The nurse is assisting the nurse practitioner who is preparing to intubate the patient. The nurse practitioner has ordered atracurium and midazolam (Versed), a short acting benzodiazepine used to sedate the patient. In what order will the nurse administer these medications? Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) A) It does not matter; they can be given in any order. B) Give the midazolam first and then atracurium a few moments later. C) Give atracurium and then give midazolam a few moments later. D) Benzodiazepines are contraindicated with atracurium. Ans: B 465 Feedback: Atracurium induces muscular paralysis resulting in the inability to breath due to paralysis of respiratory muscles but it has no impact on perception of consciousness. Receiving this drug before being sedated would be frightening and extremely anxiety provoking for the patient, so the sedative should be given first to reduce perception and consciousness before administering atracurium. There is no contraindication of benzodiazepines and the order they are given does matter. 28. When a normal muscle functions, several actions take place. In what order do these actions occur? 1. Acetylcholine (ACh) is broken down by acetylcholinesterase. 2. ACh interacts with the nicotinic cholinergic receptors. 3. ACh is released by the motor nerve. 4. ACh crosses the synaptic cleft. 5. The muscle membrane is depolarized. 6. The muscle membrane is repolarized. Put these actions in the correct order. A) 1, 3, 5, 2, 4, 6 B) 2, 4, 6, 5, 3, 1 C) 6, 5, 4, 1, 2, 3 D) 3, 4, 2, 5, 1, 6 Ans: D Feedback: Normal muscle function involves the arrival of a nerve impulse at the motor nerve terminal, followed by the release of the neurotransmitter, ACh into the synaptic cleft. At the acetylcholine receptor site on the effector side of the synapse, ACh interacts with the nicotinic cholinergic receptors, causing Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 466 depolarization of the muscle membrane. ACh is then broken down by acetylcholinesterase (an enzyme), freeing the receptor for further stimulation. 29. The patient has been mechanically ventilated for the past week and is receiving a neuromuscular junction (NMJ) blocker, an analgesic, and a sedative. The goal is to extubate the patient. What medication will the nurse stop administering first? A) NMJ blocker B) Sedative C) Analgesic D) All three medications will be stopped at the same time. Ans: A Feedback: NMJ blockers have no effect on pain perception or consciousness and should not be used without sedation so the NMJ blocker should be removed first. Because the patient has been receiving analgesics for a week, he or she will have to be weaned off them to overcome dependence. Sedatives can be removed more quickly after the NMJ blocker’s effects are gone. 30. The student asks the physiology instructor where the motor neuron communicates with a skeletal muscle fiber. What would the instructor respond? A) Synapse B) Neuromuscular junction C) Synaptic cleft D) Afferent junction Ans: B Feedback: The neuromuscular junction (NMJ) simply is the point at which a motor neuron communicates with a skeletal muscle fiber. The synapse and synaptic cleft are part of the NMJ. The afferent junction is a distracter for this question. 31. What drug will the nurse administer to reverse the actions of neuromuscular junction (NMJ) blocker? Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) A) Cholinesterase inhibitor B) Xanthine C) Halothane D) Aminoglycoside Ans: A 467 Feedback: Ensure that a cholinesterase inhibitor is readily available to overcome excessive neuromuscular blockade caused by nondepolarizing NMJ blockers. Although xanthines reverse NMJ blocking effects, they would not be administered for that purpose because their effects are not predictable. Halothane and aminoglycosides enhance paralytic effects of NMJ blockers. 32. How can the nurse assess the degree of neuromuscular blockage the patient is experiencing? A) Peripheral nerve stimulator B) Measure vital signs C) Assess response to painful stimuli D) Test reflexes Ans: A Feedback: Have a peripheral nerve stimulator on standby to assess the degree of neuromuscular blockade, if appropriate. Vital signs can indicate degree of sedation and assess pain sensation, but they are not an indicator of the degree of neuromuscular blockade. Response to painful stimuli would be more of an indication of effects of sedation and/or analgesic than degree of muscular blockade. Any neuromuscular junction blockage would reduce or eliminate reflexes so it would not be a means of assessing degree of blockage. 33. Why will the nurse administer a small dose of nondepolarizing neuromuscular junction (NMJ) blocker before administering succinylcholine? A) To reduce discomfort of depolarization of muscles B) To reduce the risk of malignant hyperthermia Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) C) To reduce negative effects of dantrolene D) To increase the duration of effect for succinylcholine Ans: A 468 Feedback: Succinylcholine is associated with muscle pain related to the initial muscle contraction reaction. A nondepolarizing NMJ blocker may be given first to prevent some of these contractions and the associated discomfort. Administering a small dose of nondepolarizing NMJ blocker will not reduce the risk of malignant hyperthermia or increase the duration of effects. Dantrolene is a drug given to treat malignant hyperthermia. 34. The nurse administers a sedative followed by a neuromuscular junction (NMJ) blocker after which the neonatologist attempts to intubate the patient without success. While waiting for the anesthesiologist to come to the unit to establish an artificial airway, what is the nurse’s priority of care? A) Reposition the patient frequently. B) Monitor oxygen saturation. C) Monitor respirations and pulse rate. D) Use a bag-valve-mask to ventilate the patient. Ans: D Feedback: Following administration of an NMJ blocker, the patient will be unable to breathe independently so maintaining an airway and breathing for the patient using a bag-valve mask is the nurse’s number-one priority. The patient will not be repositioned until after the artificial airway is placed (endotracheal tube or tracheostomy). Monitoring oxygen saturation and pulse will be second in priority after providing breathing for the patient. The patient will have no independent respirations until the NMJ is metabolized. 35. The nurse is caring for the intensive care unit patient who is mechanically ventilated and receiving a neuromuscular junction (NMJ) blocker, a sedative, and an analgesic. What are priorities of nursing care for this patient? (Select all that apply.) A) Reposition patient frequently. B) Ensure care of the patient’s eyes. C) Monitor temperature. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) D) Provide a means for patient communication. E) Increase ventilator breaths per minute as needed. Ans: A, B, C 469 Feedback: Frequent repositioning is important because the patient is unable to move and protect skin integrity independently. The loss of blink reflex due to muscle paralysis from NMJ blockers can result in conjunctival damage so eye care is very important. Monitor patient temperature for prompt detection and treatment of malignant hyperthermia. The patient cannot communicate while receiving NMJ blocker. Ventilator changes are made by physician order in most facilities and are usually based on arterial blood gas results. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 470 Chapter 29 - Introduction to the Autonomic Nervous System 1. The central nervous system (CNS) cells, where the impulses for the sympathetic nervous system (SNS) originate, are located where? A) Cranium and sacral area of the spinal cord B) Hypothalamus and the medulla C) Nerve membranes D) Thoracic and lumbar sections of the spinal cord Ans: D Feedback: The SNS is also called the thoracolumbar system because the CNS cells, where the impulses for the SNS originate, are located in the thoracic and lumbar sections of the spinal cord. The parasympathetic nervous system (PNS) is called the craniosacral system because the CNS neurons, where the impulses for the PNS originate, are found in the cranium and the sacral area of the spinal cord. Alpha2-receptors are located on nerve membranes and the hypothalamus and medulla are located where the main nerve centers for the autonomic nervous system (ANS) are located. 2. The nurse assesses that the patient is having a sympathetic response when noting what manifestations? A) Decrease in sweating, decrease in respirations, and pupil constriction B) Decrease in heart rate and perfusion, and an increase in inflammatory reactions C) Increase in blood pressure, bronchodilation, and decreased bowel sounds D) Increased motility and secretions in the GI tract, and constriction of bronchi and pupils Ans: C Feedback: When stimulated, the sympathetic nervous system prepares the body to flee or to turn and fight (Figure 29.3). Cardiovascular activity increases, as do blood pressure, heart rate, and blood flow to the skeletal muscles. Respiratory efficiency also increases; bronchi dilate to allow more air to enter with each breath, and the respiratory rate increases. Pupils dilate to permit more light to enter the eye, to improve vision in darkened areas (which helps a person to see to fight or flee). Sweating increases to dissipate heat generated by the increased metabolic activity. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 3. 471 An anatomy and physiology instructor scratches chalk across the blackboard causing a screeching sound. Several students get a feeling like their hair is standing on end. This response is part of the sympathetic stress reaction and is called what? A) Diaphoresis B) Diuresis C) Piloerection D) Vasoconstriction Ans: C Feedback: The goose flesh or hair standing on end reaction that occurs as part of the stress response is called piloerection. Diaphoresis refers to sweating. Diuresis is the loss of water through the kidneys. Vasoconstriction is a muscle contraction in the blood vessel leading to blood vessel narrowing. 4. The nurse administers a drug to the patient whose heart rate is bradycardic aimed at increasing heart rate and myocardial activity. What adrenergic receptor is this drug stimulating? A) Alpha1 B) Alpha2 C) Beta1 D) Beta2 Ans: C Feedback: Beta1-receptors are found in cardiac tissue where they can stimulate increased myocardial activity and increased heart rate. Alpha1-receptors are found in blood vessels, in the iris, and in the urinary bladder. Alpha2-receptors are located on nerve membranes and act as modulators of norepinephrine release. Beta1-receptors are found in smooth muscle in blood vessels, in the bronchi, in the periphery, and in uterine muscle. 5. The nurse administers a drug that stimulates the parasympathetic nervous system. What physiological response would indicate the drug is working? Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) A) Vasoconstriction B) Increased gastrointestinal (GI) motility C) Increased heart rate D) Pupil dilation Ans: B 472 Feedback: When the parasympathetic nervous system is stimulated, the result is increased GI motility, decreased GI secretions, decreased heart rate, and pupillary constriction, which all result from stimulation of the sympathetic nervous system. 6. When the nurse administers a drug that stimulates the nicotinic receptors, what manifestation would indicate the drug is working? A) Increased gastrointestinal (GI) motility B) Decrease in heart rate C) Muscle contraction D) Pupil constriction Ans: C Feedback: Nicotinic receptors are located in the central nervous system (CNS), the adrenal medulla, the autonomic ganglia, and the neuromuscular junction. Stimulation of nicotinic receptors causes muscle contractions, autonomic responses, and release of norepinephrine from the adrenal medulla. Increased GI motility, decreased heart rate, and pupil constriction are the result of stimulation of the muscarinic receptors. 7. A young woman who lives alone comes home at night to find a man in her apartment. What body responses would be expected for the young woman? A) Increased blood pressure (BP), increased heart rate, and pupil dilation B) Decrease sweating, decreased BP, and increased heart rate C) Pupil constriction, increased respiratory rate, and decreased heart rate Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) D) Increased sweating, decreased respiratory rate, and increased BP Ans: A 473 Feedback: When stimulated by a stressful or fearful situation, the sympathetic nervous system (SNS) prepares the body to flee or to turn and fight. Cardiovascular activity increases as do blood pressure, heart rate, and blood flow to skeletal muscles. Respiratory rate increases, pupils dilate, and sweating increases. Decrease in sweating, BP, heart rate, respiratory rate, and pupil constriction indicate stimulation of the parasympathetic nervous system, which would not be stimulated by fear. 8. When there is stimulation of the sympathetic nervous system (SNS), blood is diverted away from the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. What might the nurse assess that would indicate this diversion of blood flow to the GI tract? A) Increased blood glucose levels B) Decreased bowel sounds C) Increased blood pressure D) Decreased immune reactions Ans: B Feedback: When blood is diverted away from the GI tract, bowel sounds decrease and digestion slows dramatically, sphincters are constricted, and bowel evacuation cannot occur. Increased blood glucose levels, elevated blood pressure, and decreased immune reaction are due to SNS stimulation but are not concerned with the GI tract. 9. A patient is being admitted to the floor following a motor vehicle accident. Because of the stressful nature of the event, the nurse anticipates the patient will continue to have a sympathetic stress reaction during the postoperative period. When monitoring the patient’s serum electrolytes, what will the nurse closely monitor? A) Increased calcium B) Decreased potassium C) Increased chloride D) Decreased sodium Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) Ans: 474 B Feedback: Aldosterone, also released with adrenal stimulation, retains sodium and water and causes the excretion of potassium in the urine. As water is retained, sodium is also retained, therefore increasing serum levels. Chloride levels are unlikely to change significantly. Calcium is not involved. 10. What does the body require in order to produce acetylcholine? A) Tyramine B) Tyrosine from the diet C) Choline from the diet D) Bilirubin from the liver Ans: C Feedback: Acetylcholine (ACh) is an ester of acetic acid and an organic alcohol called choline. Cholinergic nerves use choline, obtained in the diet, to produce ACh. Tyramine and tyrosine are associated with norepinephrine production. Bilirubin is not a neurotransmitter. 11. Which of these is a neurotransmitter? A) Calcium B) Cholinesterase C) Acetylcholine (ACh) D) Monoamine oxidase Ans: C Feedback: The last step in the production of the neurotransmitter involves choline acetyltransferase, an enzyme that is also produced within cholinergic nerves. Just like norepinephrine, the ACh is produced in the nerve and travels to the end of the axons, where it is packaged into vesicles. Calcium is an electrolyte and not a neurotransmitter. Cholinesterase breaks down acetylcholine and is an enzyme, not a neurotransmitter. Monoamine oxidase is an enzyme that breaks down norepinephrine. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 12. 475 Neurons that use acetylcholine as its neurotransmitter are what type of neurons? A) Cholinergic B) Dopaminergic C) GABA-ergic D) Serotonergic Ans: A Feedback: Neurons that use ACh as their neurotransmitter are called cholinergic neurons. Other options are incorrect. 13. The nursing student learns that the hypothalamus serves what purpose? A) Causes the secretion of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) B) Controls voluntary movement C) Secretes norepinephrine D) Helps maintain red blood cell production Ans: A Feedback: The hypothalamus causes the secretion of ACTH, leading to a release of the adrenal hormones including cortisol, which suppresses the immune and inflammatory reactions to preserve energy that otherwise, might be used by these activities. The hypothalamus does not have a role in controlling voluntary movement. The adrenal glands secrete norepinephrine. Red blood cells are produced in the bone marrow and are stimulated to produce the cells by epoetin secreted by the kidney. 14. Central nervous system drugs bind to receptors embedded in the cell membranes of neurons. Cholinergic receptors have been classified as what? A) Muscarinic B) Hormones Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) C) Enzymes D) Proteins Ans: A 476 Feedback: Cholinergic receptors or acetylcholine receptors are found on organs and muscles. They have been classified as muscarinic receptors and nicotinic receptors. Cholinergic receptors are not classified as hormones, enzymes, or proteins. 15. What helps to prevent overstimulation of effector sites on nerve membranes? A) Alpha1-receptors B) Alpha2-receptors C) Beta1-receptors D) Beta2-receptors Ans: C Feedback: Alpha2-receptors are located on nerve membranes and act as modulators of norepinephrine release. When norepinephrine is released from a nerve ending, it crosses the synaptic cleft to react with its specific receptor site. Some of it also flows back to react with the alpha-receptor on the nerve membrane. This causes a reflex decrease in norepinephrine release. In this way, the Alpha2-receptor helps to prevent overstimulation of effector sites. 16. The sympathetic nervous system (SNS) is associated with a fight-or-flight reaction. What reaction is the parasympathetic nervous system is associated? A) Recover and repair B) Respond and return C) Rest and digest D) Calm and peace Ans: C Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 477 Feedback: Although the SNS is associated with the stress reaction and expenditure of energy, the parasympathetic nervous system is associated with activities that help the body to store or conserve energy, a rest-anddigest response. 17. The control systems of the body act in many ways to maintain homeostasis. These homeostatic control systems regulate the functions of the cell, integrate the functions of different organ systems, and do what else? A) Control vital functions B) Feed cells under stress C) Act on invading organisms D) Shut down the body at death Ans: A Feedback: In many areas, the parasympathetic nervous system works in opposition to the sympathetic nervous system. This allows the autonomic system to maintain a fine control over vital functions. This is a homeostatic control system. Homeostatic control systems do not feed cells when they are under stress, they do not act on invading organisms, and do they shut down the body at death. 18. The nurse administers a medication that stimulates the parasympathetic nervous system (PNS). What manifestations would indicate the medication is working? (Select all that apply.) A) Hyperactive bowel sounds B) Increased saliva production C) Elevated heart rate D) Urinary incontinence E) Constricted pupils Ans: A, B, E Feedback: Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 478 PNS stimulation results in increased motility and secretions in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract to promote digestion and absorption of nutrients: decreased heart rate and contractility to conserve energy and provide rest for the heart; constriction of the bronchi, with increased secretions; relaxation of the GI and urinary bladder sphincters, allowing evacuation of waste products; pupillary constriction, which decreases the light entering the eye and decreases stimulation of the retina. While urinary sphincters relax, they do not lose control so incontinence would not be an expected manifestation. 19. The nurse administers a parasympathetic stimulator that only stimulates nicotinic receptors. What effects would the nurse expect to assess? (Select all that apply.) A) Muscle contraction B) Slowing heart rate C) Increased bladder contraction D) Signs and symptoms of a stress reaction E) Release of epinephrine from adrenal medulla Ans: A, D, E Feedback: Stimulation of nicotinic receptors causes muscle contractions, autonomic responses such as signs and symptoms of a stress reaction, and release of norepinephrine and epinephrine from the adrenal medulla. Stimulation of muscarinic receptors causes pupil constriction, increased gastrointestinal (GI) motility and secretions (including saliva), increased urinary bladder contraction, and a slowing of the heart rate. 20. Neurotransmitters are small molecules that exert their actions through specific proteins, called receptors, embedded in the postsynaptic membrane. Where are neurotransmitters synthesized? A) In the dendrite terminal B) In the presynaptic junction C) In the postsynaptic junction D) In the axon terminal Ans: D Feedback: Norepinephrine is made by the nerve cells using tyrosine, obtained in the diet. Dihydroxyphenylalanine (dopa) is produced by a nerve, using tyrosine from the diet and other chemicals. With the help of the Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 479 enzyme dopa decarboxylase, the dopa is converted to dopamine, which in turn is converted to norepinephrine in the axon terminals of adrenergic cells. The norepinephrine then is stored in granules or storage vesicles within the cell. 21. The patient is undergoing chronic stress and has a prolonged sympathetic response. What type of drug could this patient receive to reduce the sympathetic response? (Select all that apply.) A) A drug that reduces sympathetic response B) A drug that increases sympathetic response C) A drug that reduces parasympathetic response D) A drug that increases parasympathetic response E) A drug that reduces central nervous system (CNS) response Ans: A, D, E Feedback: Decreasing sympathetic response would reduce the stress response, whereas increasing parasympathetic response would have the same effect. Although not optional, a medication that slowed down the entire nervous system would also work. In many areas, the parasympathetic nervous system works in opposition to the sympathetic nervous system (SNS). This allows the autonomic system to maintain a fine control over internal homeostasis. For example, the SNS increases heart rate, whereas the parasympathetic nervous system decreases it. Thus, the autonomic nervous system can influence heart rate by increasing or decreasing sympathetic activity or by increasing or decreasing parasympathetic activity. 22. Where are Alpha1-receptors found? (Select all that apply.) A) Blood vessels B) The iris C) Nerve membranes D) Urinary bladder E) Stomach sphincters Ans: A, B, D Feedback: Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 480 Alpha1-receptors are found in blood vessels, in the iris, and in the urinary bladder. Alpha2-receptors are located on nerve membranes. Option E is a distracter. 23. The nurse administers a drug to treat hypertension that causes vasodilation of blood vessels. What is the drug stimulating? A) Alpha1-receptors B) Alpha2-receptors C) Beta1-receptors D) Beta2-receptors Ans: C Feedback: In blood vessels, beta2 stimulation leads to vasodilation. Stimulation of Alpha1-receptors causes vasoconstriction. Beta1 and Alpha2-receptors are not involved with blood vessels 24. The nurse administers a drug that stimulates beta2 receptors. What type of health condition would this drug treat? A) Heart disease B) High lipid levels C) Diabetes D) Respiratory disease Ans: D Feedback: Beta2-receptors are found in the smooth muscle in blood vessels, in the bronchi, in the periphery, and in uterine muscle. Beta2-receptors also cause dilation in the bronchi. Beta1-receptor stimulation would improve some heart disease and are responsible for increased lipolysis. Because beta2-receptors increase release of glucagon and the breakdown of glycogen, increasing serum glucose levels, stimulation of these receptors would exacerbate diabetes. 25. What is another name for the parasympathetic nervous system? Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) A) Craniosacral system B) Cephalocaudal system C) Preganglionic system D) Thoracolumbar system Ans: A 481 Feedback: The parasympathetic system is sometimes called the craniosacral system because the central nervous system neurons that originate parasympathetic impulses are found in the cranium (one of the most important being the vagus or tenth cranial nerve) and in the sacral area of the spinal cord. The thoracolumbar system is the sympathetic nervous system. The other options are distractors. 26. The nurse administers a medication that stimulates the muscarinic receptors. What types of manifestations will the nurse assess in this patient that indicate the drug is working? A) Pupil dilation B) Increased activity of bowel sounds C) Increased heart rate D) Muscle contractions Ans: B Feedback: Stimulation of muscarinic receptors increases gastrointestinal (GI) motility which would cause increased activity of bowel sounds. Other effects include pupil constriction, increased urinary bladder contraction, and a slowing of the heart rate. Stimulation of nicotinic receptors cause muscle contractions. 27. When muscarinic receptors are stimulated, what happens physiologically in the body? (Select all that apply.) A) Pupil constriction B) Pupil dilation C) Increased secretions Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) D) Increased bladder contraction E) Increased heart rate Ans: A, C, D 482 Feedback: Stimulation of muscarinic receptors causes pupil constriction, increased gastrointestinal (GI) motility and secretions (including saliva), increased urinary bladder contraction, and a slowing of the heart rate. Pupils are constricted, not dilated and heart rate slows, it does not increase. 28. The nurse administers a drug that stimulates the nicotinic receptors. What assessment findings would indicate effectiveness of the drug? (Select all that apply.) A) Muscle contractions B) Release of norepinephrine from the adrenal medulla C) Signs and symptoms of a stress reaction D) Urinary incontinence E) Hyperactive bowel sounds Ans: A, B, C Feedback: Stimulation of nicotinic receptors causes muscle contractions, autonomic responses such as signs and symptoms of a stress reaction, and release of norepinephrine and epinephrine from the adrenal medulla. Urinary incontinence would not be associated with stimulation of the nicotinic receptors and increased bowel activity would result from muscarinic receptors. 29. The body makes norepinephrine by using what from the diet? A) Tyrosine B) Thiamine C) Tryptophan D) Trichonosis Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) Ans: 483 A Feedback: Norepinephrine is made by adrenergic nerves using tyrosine from the diet. Therefore the other options are incorrect. 30. The nurse administers a drug that causes vasoconstriction, contracted piloerection muscles, pupil dilation, closure of salivary sphincter, and male sexual emission. What receptor is this drug stimulating? A) Alpha1-receptors B) Alpha2-receptors C) Beta1-receptors D) Beta2-receptors Ans: A Feedback: Stimulation of Alpha1-receptors results in vasoconstriction of blood vessels, increased peripheral resistance with increased blood pressure, contracted piloerection muscles, pupil dilation, thickened salivary secretions, closure of the urinary bladder sphincter, and male sexual emission. None of the other receptors, when stimulated, would have this effect. 31. The nurse accompanies the physician into the patient’s room and remains after the patient is told he has cancer and it is likely to be terminal. The patient’s respirations become rapid and deep, pupils dilate, and measurement of vital signs indicates the patient’s heart rate and blood pressure are elevated. What type of response is the nurse assessing? A) Sympathetic nervous system (SNS) response B) Parasympathetic nervous system (PNS) response C) Muscarinic receptor stimulation response D) Nicotinic receptor stimulation response Ans: A Feedback: Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 484 When stimulated, the SNS prepares the body to flee or to turn and fight. Cardiovascular activity increases, as do blood pressure, heart rate, and blood flow to the skeletal muscles. Respiratory efficiency also increases; bronchi dilate to allow more air to enter with each breath, and the respiratory rate increases. Pupils dilate to permit more light to enter the eye to improve vision in darkened areas. PNS would lower heart rate and blood pressure and would constrict pupils. Stimulation of muscarinic receptors cause pupil constriction, increased gastrointestinal (GI) motility and secretions (including saliva), increased urinary bladder contraction, and a slowing of the heart rate. Stimulation of nicotinic receptors causes muscle contractions, autonomic responses such as signs and symptoms of a stress reaction, and release of norepinephrine and epinephrine from the adrenal medulla. 32. Muscarinic and nicotinic receptors are part of what system? A) The limbic system B) The reticular activating system C) The sympathetic nervous system D) The parasympathetic nervous system Ans: D Feedback: Cholinergic receptors or acetylcholine receptors of the parasympathetic nervous system are found on organs and muscles. They have been classified as muscarinic receptors and nicotinic receptors. Because these receptors are part of the parasympathetic nervous system, all other options are incorrect. 33. After the effector cell has been stimulated by acetylcholine (ACh), what enzyme stops this stimulation and allows the effector membrane to repolarize? A) Decarboxylase B) Norepinephrine C) Acetylcholinesterase D) Catecholamine Ans: C Feedback: After the effector cell has been stimulated by ACh, stimulation of the receptor site must be terminated and destruction of any ACh must occur. The destruction of ACh is carried out by the enzyme acetylcholinesterase. This enzyme reacts with the ACh to form a chemically inactive compound. The breakdown of the released ACh is accomplished in 1/1,000 second, and the receptor is vacated, Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 485 allowing the effector membrane to repolarize and be ready for the next stimulation. Dopa decarboxylase is an enzyme that converts dopa to dopamine. Norepinephrine is a catecholamine as are dopamine, serotonin, and epinephrine. 34. The nurse is teaching a class about the autonomic nervous system for critical care nurses. What statements, if made by the nurse during the class, are accurate? (Select all that apply.) A) Adrenergic receptors respond to norepinephrine. B) Adrenergic receptors are part of the sympathetic nervous system. C) Cholinergic receptors are part of the parasympathetic nervous system. D) Cholinergic receptors include alpha- and beta- receptors. E) Cholinergic and adrenergic receptors are part of the autonomic nervous system. Ans: A, B, C, E Feedback: The sympathetic nervous system contains the adrenergic receptors that respond to norepinephrine and include alpha- and beta-receptors. The parasympathetic nervous system contains the cholinergic receptors including the muscarinic and nicotinic receptors that respond to acetylcholine. Together the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems, including cholinergic and adrenergic receptors, make up the autonomic nervous system. Option D is incorrect. 35. What statement correctly explains the nerve impulse transmission? A) The impulse travels from the central nervous system (CNS) to the preganglionic neuron to the ganglia to the postganglionic neuron to the neuroeffector cells. B) The impulse travels from the preganglionic neuron to the CNS to the ganglia to the postganglionic neuron to the neuroeffector cells. C) The impulse travels from the preganglionic neuron to the ganglia to the postganglionic neuron to the CNS to the neuroeffector cell. D) The impulse travels from the CNS, to the neuroeffector cells, to the preganglionic neuron to the ganglia to the postganglionic neuron. Ans: A Feedback: The autonomic nervous system does not send impulses directly to the periphery. Instead, axons from Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 486 CNS neurons end in ganglia, or groups of nerve bodies that are packed together, located outside of the CNS. These ganglia receive information from the preganglionic neuron that started in the CNS and relay that information along postganglionic neurons. The postganglionic neurons transmit impulses to the neuroeffector cellsmuscles, glands, and organs. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 487 Chapter 30 - Adrenergic Agonists 1. A patient is admitted to the emergency department in shock. Isoproterenol (Isuprel) is administered. What would the nurse expect the effect of the isoproterenol to be? A) Increased blood pressure B) Decreased blood pressure C) Increased body temperature D) Decreased heart rate Ans: A Feedback: Isoproterenol stimulates beta-adrenergic receptors. Blood pressure is increased and heart rate is increased. Body temperature should not be affected. 2. What action do sympathomimetic drugs have in the body? A) Decreased heart rate B) Decreased blood pressure C) Increased respirations D) Increased intraocular pressure Ans: C Feedback: Sympathomimetic drugs increase respirations. Heart rate and blood pressure are also increased and intraocular pressure is decreased. 3. A) An 80-year-old patient has been brought to the emergency department in shock. The patient is receiving dopamine (Intropin). What potentially serious adverse effect will the nurse monitor for? Blood dyscrasia Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) B) Cardiac arrhythmia C) Hepatic toxicity D) Renal insufficiency Ans: B 488 Feedback: Dopamine therapy can result in cardiac arrhythmias, which can be life threatening. Older patients are more likely to experience the adverse effects associated with adrenergic agonists and should be started on lower doses and monitored closely for arrhythmias and blood pressure changes. Blood dyscrasias, hepatic toxicity, and renal insufficiency are not commonly associated with dopamine use. In fact, at lower doses, dopamine increases renal perfusion. 4. A patient comes to the clinic complaining of seasonal rhinitis. What adrenergic agonist would be prescribed for treatment of seasonal rhinitis? A) Dobutamine (Dobutrex) B) Ephedrine (generic) C) Dopamine (Intropin) D) Norepinephrine (Levophed) Ans: B Feedback: Ephedrine has been used to treat seasonal rhinitis by stimulating the release of norepinephrine from nerve endings and directly acting on adrenergic receptor sites. Although ephedrine was formerly used for situations ranging from the treatment of shock to chronic management of asthma and allergic rhinitis, its use in many areas is declining because of the availability of less toxic drugs with more predictable onset and action. Dobutamine is used to treat congestive heart failure. Dopamine and norepinephrine are used to treat shock. 5. The patient is taking midodrine (ProAmatine). What is the most important nursing action to include in the plan of care for this patient? A) Monitor urine output. B) Monitor blood pressure. C) Monitor heart rate. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) D) Monitor respirations. Ans: B 489 Feedback: Midodrine is an oral drug used to treat orthostatic hypotension in patients who do not respond to traditional therapy. It activates alpha-adrenergic receptors, leading to peripheral vasoconstriction and an increase in vascular tone and blood pressure. This effect can cause serious supine hypertension. Patients should be monitored in the standing, sitting, and supine positions to determine whether this will be a problem. It is also important to monitor heart rate, respirations, and urine output in this patient. However, assessing for supine hypertension would pose the greatest threat to the patient and would take priority. 6. The nurse is planning discharge teaching for a patient who is taking clonidine (Catapres). What would be most important for the nurse to include when teaching about adverse effects? A) Pupil constriction B) Strange dreams C) Increased urine output D) Increased appetite Ans: B Feedback: Central nervous system effects from clonidine therapy include feelings of anxiety, restlessness, depression, fatigue, strange dreams, and personality changes. However, bad dreams would be the most upsetting and stressful effect for the patient. Pupil dilation, decreased urine output, and anorexia are all adverse effects of clonidine. 7. What drug would the nurse expect to administer if beta-specific adrenergic agonist effects are desired to prevent bronchospasm during anesthesia? A) Dobutamine (Dobutrex) B) Ephedrine (generic) C) Isoproterenol (Isuprel) D) Phenylephrine (Neo-Synephrine) Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) Ans: 490 C Feedback: Isoproterenol is a beta-specific adrenergic agonist used to prevent bronchospasm during anesthesia. Phenylephrine is an alpha-specific adrenergic agonist. Both dobutamine and ephedrine are alpha- and beta-adrenergic agonists. 8. The nurse is preparing discharge teaching for four patients. Which patient should be advised by the nurse that over-the-counter cold and allergy preparations contain phenylephrine and should be avoided? A) A 47-year-old woman with hypertension B) A 52-year-old man with adult onset diabetes C) A 17-year-old girl with symptoms of an upper respiratory infection D) A 62-year-old man with gout Ans: A Feedback: Phenylephrine, a potent vasoconstrictor and alpha1-agonist with little or no effect on the heart or bronchi, is used in many combination cold and allergy products. Patients with hypertension should avoid these drugs because serious increases in blood pressure could occur. Use of this drug in patients with diabetes and gout are not contraindicated. An upper respiratory infection may be an indication for the drug. 9. The nurse is writing a plan of care for a patient receiving an alpha-specific adrenergic agonist. What should this plan of care include? A) Monitoring the patient for diarrhea B) Monitoring blood pressure and heart rate every 2 to 4 hours C) Assessing skin turgor for dehydration D) Assessing for fatigue and lethargy Ans: B Feedback: Sympathetic stimulation will cause hypertension and increased heart rate so it is important these be Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 491 monitored. Sympathetic stimulation will also result in increased sweating, decreased gastrointestinal activity, and a sense of anxiety and heightened awareness. Diarrhea, dehydration, fatigue, and lethargy would not be expected. 10. A nurse receives an order for clonidine (Catapres) for a 25-year-old pregnant woman. What is the nurse’s priority action? A) Weigh the patient to obtain correct dose/kg/day. B) Have a second nurse check the dose before administering the drug. C) Consult with the physician about the order. D) Make sure the patient is wearing a fetal monitor. Ans: C Feedback: The nurse would consult with the physician to ensure awareness of the pregnancy and desire to administer this drug. There are no adequate studies about use during pregnancy and lactation, so use should be reserved for situations in which the benefit to the mother outweighs any potential risk to the fetus or neonate. The nurse should question the prescriber regarding this order. It would not be necessary to implement the other options. 11. The nursing students are studying sympathomimetic drugs. How do these drugs act on the body? A) Stimulate beta receptors and block alpha-receptors B) Stimulate alpha-receptors and block beta-receptors C) Block adrenergic receptors D) Stimulate both alpha and beta-receptors Ans: D Feedback: Drugs that are generally sympathomimetic are called alpha-agonists (stimulate alpha-receptors) and beta-agonists (stimulate beta-receptors). These agonists stimulate all of the adrenergic receptors; that is they affect both alpha and beta-receptors. 12. How does ephedrine act on the body? Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) A) Stimulates the release of norepinephrine B) Acts indirectly on beta-adrenergic receptor sites C) Stimulates the release of dopamine D) Acts indirectly on alpha-adrenergic receptor sites Ans: A 492 Feedback: Ephedrine stimulates the release of norepinephrine from nerve endings and acts directly on adrenergic receptor sites. Therefore, the other options are incorrect. 13. In what age group are adrenergic agonists contraindicated? A) Older adults B) Adolescents C) Children D) No age group Ans: D Feedback: The use of adrenergic agonists varies from ophthalmic preparations for dilating pupils to systemic preparations used to support patients experiencing shock. They are used in patients of all ages. Therefore, the other options are incorrect responses. 14. A patient in shock is receiving an infusion of dopamine when it is discovered that an extravasation has occurred. What drug should be on standby for this occurrence? A) Phenylephrine B) Propranolol C) Phenylalanine D) Phentolamine Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) Ans: 493 D Feedback: Maintain phentolamine on standby in case extravasation occurs; infiltration of the site with 10 mL of saline containing 5 to 10 mg of phentolamine is usually effective in saving the area. Phenylephrine, propranolol, and phenylalanine are not indicated for use when extravasation occurs. 15. The pharmacology instructor is discussing adrenergic agonists with the nursing class. Which drugs would the instructor tell the nursing students are generally indicated for the treatment of shock, bronchospasm, and some types of asthma? A) Sympathomimetic drugs B) Beta-blocking drugs C) Parasympathetic stimulating drugs D) Anticatecholamine drugs Ans: A Feedback: These drugs generally are indicated for the treatment of hypotensive states or shock, bronchospasm, and some types of asthma. Beta-blocking drugs, parasympathetic stimulating drugs, and anticatecholamine drugs are not the drugs of choice in these situations. 16. When studying for a pharmacology exam, a student asks her peers which agents affect both alpha- and beta-receptor sites. What would be an appropriate response to this student? (Select all that apply.) A) Dobutamine (Dobutrex) B) Epinephrine (Adrenalin, Sus-Phrine) C) Dopamine (Intropin) D) Clonidine (Catapres) E) Albuterol (Proventil) Ans: A, B, C Feedback: Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 494 Agents that affect both alpha- and beta-receptor sites include dobutamine, dopamine, ephedrine, epinephrine, and norepinephrine. Clonidine is an alpha-specific adrenergic agonist; albuterol is a betaspecific adrenergic agonist. 17. The nurse is admitting a mental health patient and collects the medication history. The patient says he takes Haldol, midodrine, hydrochlorothiazide, acetaminophen, and Cymbalta. The nurse will call the provider to discuss what dangerous drug combination? A) Haldol and midodrine B) Hydrochlorothiazide and midodrine C) Cymbalta and midodrine D) Acetaminophen and midodrine Ans: A Feedback: Midodrine can precipitate increased drug effects of digoxin, beta-blockers, and many antipsychotics. Such combinations should be avoided. The other drug combinations do not pose any immediate concerns. 18. A 4-year-old is admitted to the emergency department in shock after a motor vehicle accident. The patient weighs 12.5 kg. What would be the minimum safe dose of adrenalin if the pediatric dose is 0.005 to 0.01 mg/kg IV? A) 0.0625 mg B) 0.075 mg C) 0.08 mg D) 0.085 mg Ans: A Feedback: To calculate the minimum dosage, multiply the child’s weight in kg by the lower dosage range; 12.5 × 0.005 = 0.0625 mg. 19. When giving beta-specific adrenergic agonists, at what age is an adult dose given? Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) A) 10 years B) 11 years C) 12 years D) 13 years Ans: C 495 Feedback: Adult doses are given to children who are 12 years and older (see dosages in Table 30.3, page 497.) Therefore, the other options are incorrect. 20. The home health nurse is caring for a 77-year-old male patient who has just been discharged from the hospital. The patient is receiving an infusion of dobutamine (Dobutrex) to treat congestive heart failure. What is the priority nursing assessment? A) Capillary refill time and vital signs B) Effectiveness of comfort measures C) Dietary intake and hydration D) Compliance with treatment plan Ans: A Feedback: Dobutamine, although it acts at both receptor sites, has a slight preference for beta1-receptor sites. It is used in the treatment of heart failure because it can increase myocardial contractility without much change in rate and does not increase the oxygen demand of the cardiac muscle, an advantage over all of the other sympathomimetic drugs. Assessing capillary refill time and vital signs will allow the nurse to assess perfusion as an indicator of the effectiveness of the infusing drug. Dietary intake, compliance with treatment plan, and effectiveness of comfort measures are all important assessments but the priority assessment is perfusion. 21. What is the nurse’s rationale for administering clonidine to treat hypertension? A) Clonidine stimulates alpha2-receptors. B) Clonidine stimulates alpha1-receptors. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) C) Clonidine stimulates beta2-receptors. D) Clonidine stimulates beta1-receptors. Ans: A 496 Feedback: Clonidine specifically stimulates alpha2-receptors and is used to treat hypertension because its action blocks release of norepinephrine from nerve axons. Therefore, the other options are incorrect answers. 22. Isoproterenol is reserved for use in emergency situations. What is the rationale for this? A) Its onset of action B) Its duration of action C) Its adverse effects D) Its peak plasma concentration Ans: C Feedback: Because of its many adverse effects, isoproterenol is reserved for use in emergency situations that do not respond to other, safer therapies. It is not reserved for emergency use because of its onset of action, its duration of action, or its peak plasma concentration. 23. The nurse is preparing to give isoproterenol parenterally. Before starting to administer the drug, what does the nurse ensure is on hand in case a severe reaction occurs? A) An alpha-adrenergic blocker B) An alpha-adrenergic stimulant C) A beta-adrenergic stimulant D) A beta-adrenergic blocker Ans: D Feedback: Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 497 Ensure that a beta-adrenergic blocker is readily available when giving parenteral isoproterenol in case severe reaction occurs. This makes other options incorrect. 24. The nursing instructor is quizzing a student who is preparing to administer an alpha-specific adrenergic agonist to a patient. The instructor asks the student what the student will assess in this patient after administering the drug. What is the student’s best response? A) Blood pressure B) Respirations C) Mental status D) Vision Ans: A Feedback: Monitor blood pressure, pulse, rhythm, and cardiac output regularly, even with ophthalmic preparations, to adjust dosage or discontinue the drug if cardiovascular effects are severe. Respirations, mental status, or vision may also need to be monitored but they are not impacted significantly by the drug being given. 25. When assessing a patient who has been prescribed midodrine, what would the nurse assess for? A) Pancreatic disease B) Renal failure C) Open-angle glaucoma D) Hypothyroidism Ans: B Feedback: Assess for contraindications or cautions: any known allergies to the drug to avoid hypersensitivity reactions; presence of any cardiovascular diseases, which could be exacerbated by the vascular effects of these drugs; thyrotoxicosis, or diabetes, which would lead to an increase in thyroid stimulation or glucose elevation; chronic renal failure, which could be exacerbated by drug use; renal or hepatic impairment, which could interfere with drug excretion or metabolism; and current status of pregnancy and lactation. Options A, C, and D are incorrect. 26. The patient has been taking clonidine and is now being changed to another antihypertensive drug. How Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 498 will the nurse instruct the patient regarding discontinuing the clonidine? A) Check your blood pressure and pulse every 2 to 4 hours. B) Inform your family the drug is being changed. C) Reduce clonidine gradually over 2 to 4 days. D) Keep an over-the-counter analgesic available to treat headaches. Ans: C Feedback: Do not discontinue clonidine abruptly because sudden withdrawal can result in rebound hypertension, arrhythmias, flushing, and even hypertensive encephalopathy and death; taper drug over 2 to 4 days. It is not necessary to teach the patient to check blood pressure and pulse every 2 to 4 hours, discuss plans for changing medications with the family, or prepare the patient for severe headaches. 27. The clinic nurse is teaching a patient about transdermal clonidine (Catapres). What information would be included in the nurse’s teaching plan? (Select all that apply.) A) Change the patch in the morning. B) Rotate the site where the patch is placed. C) Monitor blood pressure daily. D) Stop the drug immediately if adverse effects occur. E) Keep the physician informed of any new diagnoses or medications. Ans: B, C, E Feedback: Transdermal patches should not be placed in the same site repeatedly so it is important to instruct the patient to rotate sites to improve absorption of drug. Blood pressure should be monitored daily and the patient should be provided with acceptable ranges versus when to notify the physician because severe hypertension can occur. Due to drugdrug interactions, contraindications, and cautions related to specific diagnosis (cardiovascular disease, vasomotor spasm, thyrotoxicosis, diabetes, renal or hepatic impaiment), it is important for the patient to inform the physician if another physician prescribes a medication or a new diagnosis for decisions to be made about whether to continue the drug or change the dosage. The patch is changed weekly and not every morning. The patient should be taught not to stop the drug abruptly because it could lead to tachycardia, hypertension, arrhythmias, flushing, and even death. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 28. 499 The nurse needs to be aware, before administering, that what drug has a duration of action of only 1 to 2 minutes? A) Isoproterenol B) Dopamine C) Phenylephrine D) Ephedrine Ans: A Feedback: Isoproterenol has a duration of action lasting 1 to 2 minutes with immediate onset of action. Dopamine acts as long as the drug is infusing with peak action 10 minutes after initiating the infusion. Phenylephrine’s duration of action is 15 to 20 minutes. Ephedrine’s duration of action will depend on how the drug is administered as it could be given intramuscularly, subcutaneously, IV, or orally, but no matter by what route it is administered, the duration of action is longer than 1 to 2 minutes. 29. A 4-year-old girl is prescribed an albuterol (Proventil) inhaler for her asthma. What is the recommended safe dosage for this patient? A) 1.25 to 2.5 mg q.i.d B) 1.25 to 2.5 mg b.i.d C) 2 mg q.i.d D) 0.5 to 1 mg b.i.d Ans: B Feedback: The recommended dosage for albuterol when given via inhaler is 1.25 to 2.5 mg b.i.d. When taken orally, the dosage is 2 mg t.i.d. or q.i.d. The other options are incorrect because they are outside the acceptable dosage range. 30. A) The nurse is caring for a male patient who is taking a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI). The patient complains of seasonal rhinitis and the intern for his service orders phenylephrine nasal spray. What is the nurse’s priority action? Verify patency of the nares. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) B) Review the patient’s medication history. C) Question the order with the prescriber. D) Position the patient to give the drug as ordered. Ans: C 500 Feedback: Phenylephrine, combined with MAOIs, can cause severe hypertension, headache, and hyperpyrexia. This combination should be avoided. As a result, the priority action is to remind the intern the patient is taking an MAOI and obtain an order for a different drug. Until the new order is received, no other actions would be taken. 31. The nurse receives an order to begin a dopamine (Intropin) infusion at 5 mcg/kg/min. The patient weighs 50 kg. Each milliliter of solution contains 3 mg of dopamine. How many mL/h will the nurse set the pump to deliver? A) 3 mL/h B) 5 mL/h C) 3,000 mL/h D) 83.3 mL/h Ans: B Feedback: To calculate this dosage, multiply the ordered mcg by the weight (5 ×50 kg) to yield mcg/min (250 mcg/min) and then multiply this times 60 to get mcg/h (250 ×60 = 15,000 mcg/h). Convert mcg/h to mg/h (15,000/1,000 = 15 mg/h). Set up ratio (3 mg/1 mL = 15 mg/X mL) and cross multiply (3X = 15 mg). Divide both sides by 3 to yield 5 mL/h to deliver 5 mg/kg/min. 32. The nurse calculates the infusion rate for administering dopamine to a premature infant in the neonatal intensive care unit who is in cardiogenic shock secondary to a cardiac anomaly. What is the nurse’s next priority action? A) Insert an intravenous catheter B) Obtain permission from parents C) Ask another nurse to perform independent calculation Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) D) Show the nurse’s calculations to the physician Ans: C 501 Feedback: It is good practice to have a second person check the dosage calculation before administering the drug to avoid potential toxic effects. When having calculations double-checked, it is best to let the other person work out separate calculations rather than just looking at the nurse’s calculation first because this will be more likely to catch an error. The nurse would have another nurse perform calculations rather than the doctor. Only after calculations are correct would the drug be administered, usually through a central line or the nurse may establish a peripheral line. Permission from parents is not required above general permission needed to care for the neonate. 33. The student nurse is administering an ophthalmic adrenergic agonist. What action would reflect the need for further education about how to administer a medication ophthalmically? A) Rests the tip of the dropper against the lower eyelid B) Grasps the lower eyelid and pulls it away to form a pocket C) Applies gentle pressure to the inside corner of the eye for 3 to 5 minutes D) Instructs the patient to close his or her eyes and look downward Ans: A Feedback: First, wash hands thoroughly. Do not touch the dropper to the eye or to any other surfaces. Have the patient tilt his or her head back or lie down and stare upward. Gently grasp the lower eyelid and pull the eyelid away from the eyeball. Instill the prescribed number of drops into the lower conjunctival sac and then release the lid slowly (Fig. 30.1). Have the patient close the eye and look downward. Apply gentle pressure to the inside corner of the eye for 3 to 5 minutes. Do not rub the eyeball and do not rinse the dropper. If more than one type of eyedrop is being used, wait 5 minutes before administering the next one. 34. When transcribing new orders for sympathomimetic medications prescribed for a geriatric patient, the nurse expects the dosage will be what? A) The average adult dosage B) Slightly higher than adult dosages C) The lowest possible effective dosage Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) D) Approximately half the normal adult dosage Ans: C 502 Feedback: Older patients should be started on lower doses of the drugs and should be monitored very closely for potentially serious arrhythmias or blood pressure changes. Other options are incorrect. 35. The nurse is serving a breakfast tray to the patient receiving an alpha- and beta-adrenergic agonist medication. The nurse notifies dietary of the error with the patient’s diet when finding what on the tray? A) Eggs B) Bacon C) Coffee D) Milk Ans: C Feedback: Patients being treated with any adrenergic agonists who are also taking ma huang, guarana, or caffeine are at increased risk for overstimulation, including increased blood pressure, stroke, and death. The nurse should counsel patients to avoid these ingredients. There would be no reason to prevent the patient from ingesting eggs, bacon, or milk. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 503 Chapter 31 - Adrenergic Antagonists 1. The nurse administers an adrenergic blocking agent in order to prevent release of what neurotransmitter? A) Epinephrine B) Norepinephrine C) Serotonin D) Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) Ans: B Feedback: Adrenergic blocking agents prevent norepinephrine from being released from the adrenal medulla or from the nerve terminal from activating the receptor, which blocks sympathetic nervous system effects. Epinephrine, serotonin, and GABA are not associated with this process. 2. What medication, if ordered for an 8-year-old patient, should the nurse question? (Select all that apply.) A) Amiodarone (Cordarone) 400 mg orally per 24 hours B) Labetalol (Normodyne) 100 mg orally b.i.d. C) Phentolamine (Regitine) 1 mg intramuscularly 1 to 2 hours before surgery D) Prazosin (Minipress) 3 mg orally t.i.d. E) Carvedilol (Coreg) 6.25 mg orally b.i.d. Ans: A, B, E Feedback: Amiodarone, labetalol, and carvedilol are not indicated for pediatric use and do not have established pediatric dosages. Phentolamine and prazosin have established pediatric dosages and would not need to be questioned. 3. A nurse is working with a patient who is taking an adrenergic blocking agent. While assessing the patient’s medication history, the nurse discovers that the patient takes several alternative therapies. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 504 What herb is the nurse concerned may interact with the adrenergic blocking agent and affect the patient’s blood glucose level? A) Ginseng B) Nightshade C) Di huang D) Saw Palmetto Ans: C Feedback: Di huang is an alternative therapy that can lower blood glucose when used in combination with adrenergic blocking agents. Ginseng increases antihypertensive effects; nightshade slows the heart rate; and saw palmetto increases the risk of urinary tract complications when used in combination with adrenergic blocking agents. 4. A priority nursing assessment for a patient who is to receive an alpha- or beta-adrenergic blocking agent would be what? A) Monitoring respiratory rate B) Checking blood glucose level C) Measuring urine output D) Assessing heart rate Ans: D Feedback: The most serious adverse effect would be severe bradycardia, so the nurse’s priority would be assessing the heart rate. If the patient were identified as having diabetes, then monitoring blood glucose levels would become important because these drugs can aggravate diabetes by blocking sympathetic response including masking the usual signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia. Respiratory rate could be impacted if the patient was identified as having a condition causing bronchospasm and diabetes because the combination could worsen both conditions. Measuring urine output should be part of the patient’s care, but it is not the priority assessment. 5. A) Bisoprolol (Zebeta) would be the drug of choice for which patient with a diagnosis of hypertension? A 7-year-old patient Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) B) A 15-year-old patient C) A 37-year-old patient D) A 69-year-old patient Ans: D 505 Feedback: Bisoprolol is the drug of choice for older adults. It is not associated with as many adverse effects in the elderly and regular dosing profiles can be used. This drug does not have an established pediatric dosage. Although the 37-year-old patient is an adult, there are additional choices for this patient, with a more favorable adverse effect profile. 6. What would be the teaching priority for a diabetic patient being treated with a nonselective betablocker? A) To take his own pulse B) To weigh himself once a week at the same time of day C) To avoid smoke-filled rooms D) To understand signs and symptoms of hypo- or hyperglycemic reaction Ans: D Feedback: Because the beta-blockers stop the signs and symptoms of a sympathetic stress reaction, the signs and symptoms associated with hypo- or hyperglycemia, the diabetic patient taking a beta-blocker will need to understand this and learn new indicators of these reactions. Taking his pulse, weekly weighing, and avoiding smoke-filled rooms are good health practices and should be done, but not specifically needed by a diabetic patient taking a beta-blocker. 7. The nurse is caring for a patient who is receiving an adrenergic blocking agent. While writing the care plan for this patient what nursing diagnoses would be most appropriate concerning comfort? A) Acute pain related to cardiovascular and systemic effects B) Decreased cardiac output related to cardiovascular effects C) Ineffective airway clearance related to lack of bronchodilating effects Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) D) Deficient knowledge regarding drug therapy Ans: A 506 Feedback: All four options would be appropriate nursing diagnoses for a patient receiving an adrenergic blocking agent. However, acute pain would be the only nursing diagnosis related to the patient’s comfort level. 8. A nurse is providing discharge instructions to a patient who is taking atenolol (Tenormin) to treat hypertension. What would the nurse teach the patient regarding a possible drugdrug interaction? A) Antibiotics B) Oral contraceptives C) Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) D) Antifungal agents Ans: C Feedback: A decreased hypertensive effect can occur if a beta-selective adrenergic blocking agent is used in combination with NSAIDs. If this combination is used, the patient should be monitored closely and dosage adjustments made. Antibiotics, oral contraceptives, and antifungal agents are not known to have a drugdrug interaction. 9. A busy patient with many responsibilities is to have a medication ordered to treat her hypertension. To increase compliance with drug therapy, what drug would be a good choice for this patient? A) Acebutolol (Sectral) B) Atenolol (Tenormin) C) Bisoprolol (Zebeta) D) Metoprolol (Lopressor) Ans: D Feedback: Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 507 Metoprolol would be the best choice because it has an extended release form that only needs to be taken once a day, which should increase patient compliance. Acebutolol, atenolol, and bisoprolol do not come in extended release forms. 10. The nurse provides patient teaching for a patient who has a new order for nadolol (Corgard) to treat hypertension. What statement by the patient concerning nadolol (Corgard) would indicate that the teaching has been effective? A) I should cover my head at all times while I am outdoors. B) Since I am taking this drug, I no longer need to worry about diet and exercise. C) I will not stop taking this drug abruptly and will talk to my doctor before discontinuing. D) I may have a very dry mouth while taking this drug. Ans: C Feedback: A patient receiving an adrenergic blocker must be aware that abruptly stopping the medication may result in a serious reaction. When changing medications or discontinuing their use, these drugs need to be tapered off gradually. This drug is not associated with photophobia or the anticholinergic effect of dry mouth. If the teaching were effective, the patient would be aware that he would need to continue lifestyle modifications, including diet and exercise. 11. The nurse frequently administers propranolol (Inderal) as treatment for what condition? A) Hypotension B) Angina C) Prevent first myocardial infarction (MI) D) Cluster headaches Ans: B Feedback: The beta-adrenergic blocking agents are used to treat cardiovascular problems (hypertension, angina, migraine headaches) and to prevent reinfarction after MI. The prototype drug, propranolol, was in fact the most prescribed drug in the country in the 1980s and is still considered a first-line drug. Propranolol does not prevent first MIs and it is not used for hypotension or cluster headaches. 12. A patient with benign prostatic hypertrophy (BPH) has been prescribed prazosin (Minipress) and asks Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 508 the nurse what this is going to do for him. The nurse’s response will include what action to explain the purpose of taking this medication? A) Decreasing vascular tone and vasodilation B) Reducing the size of the prostate to reduce pressure on the urethra C) Relaxing the bladder and prostate and improving urine flow D) Lowering blood pressure Ans: C Feedback: Alpha1-selective adrenergic blocking agents block smooth muscle receptors in the prostate, prostatic capsule, prostatic urethra, and urinary bladder neck, which leads to a relaxation of the bladder and prostate and improved flow of urine in male patients. Although they also block the postsynaptic alpha1receptor sites, causing a decrease in vascular tone and vasodilation that leads to a fall in blood pressure without the reflex tachycardia that occurs when the presynaptic alpha2-receptor sites are blocked, this is not the purpose for administering the drug to a patient with BPH. They do not reduce the size of the prostate. 13. The nurse is caring for a 55-year-old patient receiving metoprolol (Lopressor). What statement by the patient would lead the nurse to believe that he needs additional instruction? A) If I have side effects from the medication, I will contact my physician before I stop taking it. B) I can take over-the-counter (OTC) cold medication while on metoprolol. C) I will take the medication on an empty stomach. D) I will report a weight gain of 2 pounds or more in 1 week. Ans: B Feedback: OTC medications can interact to increase or decrease the effects of antiadrenergic drugs. Antacids decrease the effects of beta-adrenergic blocking drugs. Decreased antihypertensive effects result when taken with ibuprofen. Other options reflect correct statements and would not indicate that the patient would need further instruction. 14. Nonselective adrenergic blocking agents have a variety of therapeutic uses. Which agent is used for the treatment of heart failure? Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) A) Carvedilol (Coreg) B) Sotalol (Betapace) C) Propranolol (Inderal) D) Tamsulosin (Flomax) Ans: A 509 Feedback: available orally and is used to treat hypertension as well as congestive heart failure and left ventricular dysfunction after a myocardial infarction. Sotalol is a nonselective beta-adrenergic blocking agent used to treat potentially life-threatening ventricular arrhythmias and to maintain normal sinus rhythm in patients with atrial fibrillation or flutter. Propranolol is a nonselective beta-adrenergic blocking agent used for treatment of hypertension, angina, idiopathic hypertrophic subaortic stenosis (IHSS)induced palpitations, angina and syncope, some cardiac arrhythmias induced by catecholamines or digoxin, pheochromocytoma; prevention of reinfarction after myocardial infarction; prophylaxis for migraine headache (which may be caused by vasodilation and is relieved by vasoconstriction, although the exact action is not clearly understood); prevention of stage fright (which is a sympathetic stress reaction to a particular situation); and treatment of essential tremors. Tamsulosin is used to treat benign prostatic hyperplasia and is analpha1-selective adrenergic blocking agent. 15. Before administering a nonselective adrenergic blocker, what should the nurse assess? A) Pulse and blood pressure B) Bowel sounds and appetite C) Serum albumin level D) Serum sodium and potassium levels Ans: A Feedback: Monitor vital signs and assess cardiovascular status including pulse, blood pressure, and cardiac output to evaluate for possible cardiac effects. Although assessment of bowel sounds, appetite, serum albumin level, or serum sodium and potassium levels may be important to patient care, they are not related to administration of a nonselective adrenergic blocking agent. 16. A 75-year-old male patient was admitted to the unit with angina. He was started on nadolol (Corgard). The patient asks why he is taking this medication because he does not have high blood pressure. What is the nurse’s best response? Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) A) Some beta-blockers have been approved as antianginal agents. B) This medication will prevent blood pressure problems later on. C) This drug will prevent you from developing an arrhythmia. D) This medication will reduce benign prostatic hypertrophy (BPH) as well as treat heart failure. Ans: A 510 Feedback: Decreased heart rate, contractility, and excitability, as well as a membrane-stabilizing effect, lead to a decrease in arrhythmias, a decreased cardiac workload, and decreased oxygen consumption. The juxtaglomerular cells are not stimulated to release renin, which further decreases the blood pressure. These effects are useful in treating hypertension and chronic angina and can help to prevent reinfarction after a myocardial infarction by decreasing cardiac workload and oxygen consumption. Corgard will not prevent blood pressure problems, arrhythmias, or glaucoma in the future. Corgard is not used to treat BPH. 17. In what patient is propranolol (Inderal) contraindicated? A) 26-year-old man with viral myocarditis B) 45-year-old woman with heart failure who suffered a myocardial infarction C) 42-year-old man with hypertension D) 65-year-old woman with persistent migraines Ans: B Feedback: Beta-adrenergic blocking agents are contraindicated in patients with bradycardia, heart failure, and heart block. The drug would not be contraindicated in the other patients. 18. What assessment finding indicates to the nurse that timolol (Timoptic) has been effective? A) The patient’s blood pressure increases. B) The patient’s intraocular pressure is reduced. C) The patient’s pulse is reduced. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) D) The patient’s angina is reduced. Ans: B 511 Feedback: Timolol and carteolol are available in an ophthalmic form of the drug for reduction of intraocular pressure in patients with open-angle glaucoma. A decrease in intraocular pressure would indicate it has been effective. Timolol can also be used to treat hypertension but an increase in blood pressure would indicate the drug was not effective. Reduced pulse rate and reduced angina would not be related to this drug, especially if it was given in ophthalmic form when very little of the drug is absorbed systemically. 19. The student nurse is studying for a pharmacology exam and notices that many of the adrenergic blocking antagonists drugs studied in class have what suffix? A) -aine B) -lol C) -azole D) -triptan Ans: B Feedback: The suffix -lol is seen in many of the drug names for adrenergic blocking antagonists. The suffix -aine would indicate a topical anesthetic, whereas -azole indicates an antifungal, and the suffix -triptan relates to the triptans. 20. A 23-year-old female patient presents at the clinic with a migraine headache. What beta-adrenergic blocking agent might the physician prescribe for the prophylactic prevention of future migraine headaches? A) Propranolol (Inderal) B) Nadolol (Corgard) C) Timolol (Blocadren) D) Sotalol (Betapace) Ans: A Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 512 Feedback: Propranolol is indicated for the treatment of hypertension, angina pectoris, idiopathic hypertrophic subaortic stenosis, supraventricular tachycardia, tremor; prevention of reinfarction after myocardial infarction; adjunctive therapy in pheochromocytoma; prophylaxis of migraine headache; and management of situational anxiety. The other options do not treat or prevent migraine headaches. 21. A 5-year-old African American patient has been admitted to the pediatric intensive care unit with pheochromocytoma. The physician has ordered phentolamine. The nurse knows that the other indication for phentolamine is what? A) Migraine headaches B) Extravasation of IV norepinephrine or dopamine C) Life-threatening arrhythmias D) Heart failure Ans: B Feedback: Phentolamine (Regitine) is used for the prevention of cell death and tissue sloughing after extravasation of intravenous norepinephrine or dopamine, and severe hypertension reactions caused by manipulation of the pheochromocytoma before and during surgery; diagnosis of pheochromocytoma. Phentolamine would not be indicated for treatment of migraine headaches, life-threatening arrhythmias, or heart failure. 22. The nurse is caring for a well-known stage actor who has suddenly developed severe stage fright that is preventing him from working. What drug does the nurse suspect will be prescribed for this patient? A) Carteolol (Cartrol) B) Nebivolol (Bystolic) C) Nadolol (Corgard) D) Propranolol (Inderal) Ans: D Feedback: One of the indications for use of propranolol is prevention of stage fright, which is a sympathetic stress reaction to a particular situation. None of the other options are indicated for this use. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 23. 513 The nurse assesses the patient receiving phentolamine (Regitine) and suspects what finding is an adverse effect of the medication? A) Hypertension B) Wheezing C) Tachycardia D) Depressed respirations Ans: C Feedback: Patients receiving phentolamine often experience extensions of the therapeutic effects, including hypotension, orthostatic hypotension, angina, myocardial infarction, cerebrovascular accident, flushing, tachycardia, and arrhythmiaall of which are related to vasodilation and decreased blood pressure. Headache, weakness, and dizziness often occur in response to hypotension. Nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea may also occur. Hypertension, wheezing, and depressed respiration would not be associated with phentolamine. 24. The home care nurse is caring for a patient newly prescribed a nonselective beta-blocking agent. What would the nurse include in the teaching plan related to this drug? (Select all that apply.) A) Take with meals. B) Change position slowly. C) Avoid driving or operating hazardous machinery. D) Warn of possible increase in libido. E) Increase activity levels as much as possible. Ans: A, B, C Feedback: Patients should be taught to change position slowly, avoid driving or operating hazardous machinery, and to pace activities as a result of potential dizziness from orthostatic hypotension in order to avoid injury. Patients should take medicine with meals when possible. Drug is more likely to decrease libido than increase it. Activity levels should be paced and care should be taken not to overdo. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 25. 514 The nurse is discharging a 35-year-old patient with diabetes who has been prescribed an adrenergic blocking agent. What is the priority teaching point for the nurse to discuss with this patient? A) Monitor blood glucose levels closely and report any instability B) Document signs and symptoms of hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia C) Reduce carbohydrate intake more than usual while taking the new drug D) Increase insulin dosage to compensate for the drug’s effect in increasing blood sugar Ans: A Feedback: It is important for the patient to be instructed to monitor blood sugar levels more frequently because adrenergic blocking agents mask the normal hypo- and hyperglycemic manifestations that normally alert patients such as sweating, feeling tense, increased heart rate, and rapid breathing. There is no need to change the diet or the diabetic medications. There may be no signs and symptoms to record because they are blocked by the adrenergic blocker. 26. The home care nurse is providing teaching for a 59-year-old patient taking a nonselective beta-blocker. The nurse teaches the patient the importance of notifying the prescribing physician when what occurs related to this medication? A) If the patient’s pulse stays above 100 bpm for 3 or more days B) If the patient has a sudden onset of a cough C) If the patient falls D) If the patient’s pulse falls below 60 bpm for 3 or more days Ans: B Feedback: Bronchospasm, cough, rhinitis, and bronchial obstruction are related to loss of bronchodilation of the respiratory tract and vasodilation of mucous membrane vessels so a sudden onset of a cough or difficulty breathing should be immediately reported to the health care provider. Other options may need to be reported but not in relation to the nonselective beta-blocking medication. 27. A) A 31-year-old male patient has been prescribed propranolol to reduce and prevent angina. What will the nurse assess this patient for related to the medication? (Select all that apply.) Sleep disturbance Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) B) Impotence C) Bronchospasm D) Gastric pain E) Tachycardia Ans: B, C, D 515 Feedback: Adverse effects of propranolol that the nurse would assess for include allergic reaction, bradycardia, heart failure, cardiac arrhythmias, cerebrovascular accident, pulmonary edema, gastric pain, flatulence, impotence, decreased exercise tolerance, and bronchospasm. 28. Which nonselective alpha-adrenergic blocking agent is still used? A) Metoprolol B) Propranolol C) Timolol D) Phentolamine Ans: D Feedback: Of the nonselective alpha-adrenergic blocking agents, only phentolamine is still used today. Metoprolol is a beta1-selective adrenergic blocking agent. Timolol and propranolol are nonselective betaadrenergic blocking agents. 29. The labor and delivery nurse assists with the delivery of a newborn to a woman taking an adrenergic blocker for a congenital heart defect. What organ systems may be affected in the newborn by these drugs? (Select all that apply.) A) Cardiovascular B) Respiratory C) Central nervous system (CNS) Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) D) Gastrointestinal (GI) E) Genitourinary (GU) Ans: A, B, C 516 Feedback: Adrenergic blockers can affect labor, and babies born to mothers taking these drugs may exhibit adverse cardiovascular, respiratory, and CNS effects. Problems with the GI and GU systems have not been reported. 30. Beta-adrenergic blocking drugs are used in children for disorders similar to those in adults. What adrenergic blocking agent is used during surgery for pheochromocytoma? A) Propranolol B) Prazosin C) Phentolamine D) Guanethidine Ans: C Feedback: Phentolamine is used during surgery for pheochromocytoma in children. Prazosin is used to treat hypertension in children. Propranolol and guanethidine are not indicated for use in children with a pheochromocytoma. 31. What are the therapeutic and adverse effects associated with the adrenergic blocking agents related to? A) Receptor-site specificity B) Sympathetic nervous system manifestations C) Norepinephrine release D) Function of the nerve terminal Ans: A Feedback: Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 517 The therapeutic and adverse effects associated with these drugs are related to their adrenergic-receptorsite specificity; that is, the ability to react with specific adrenergic receptor sites without activating them, thus preventing the typical manifestations of sympathetic nervous system (SNS) activation. By occupying the adrenergic receptor site, they prevent norepinephrine released from the nerve terminal or from the adrenal medulla from activating the receptor, thus blocking the SNS effects. 32. The specificity of the adrenergic blocking agents allows the clinician to select a drug to do what? A) Have the desired effect B) Multiply undesired effects C) Increase specificity with higher serum blood levels D) Improving concentration in the body Ans: A Feedback: This specificity allows the clinician to select a drug that will have the desired therapeutic effects without the undesired effects that occur when the entire sympathetic nervous system is blocked. In general, however, the specificity of adrenergic blocking agents depends on the concentration of drug in the body. Most specificity is lost with higher serum drug levels. 33. What agents are used primarily to treat cardiac-related conditions? (Select all that apply.) A) Nonselective adrenergic blocking agents B) Nonselective alpha-adrenergic blocking agents C) Alpha1-selective adrenergic blocking agents D) Nonselective beta-adrenergic blocking agents E) Beta1-selective adrenergic blocking agents Ans: A, D, E Feedback: Drugs that block both alpha- and beta-adrenergic receptors are primarily used to treat cardiac-related conditions. Phentolamine, a nonselective alpha-adrenergic blocking agent, is used to treat extravasation of IV norepinephrine or dopamine and hypertension related to a pheochromocytoma. Alpha1-selective Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 518 adrenergic blocking agents are used for treatment of hypertension and benign prostatic hyperplasia. The beta-adrenergic blocking agents are used to treat cardiovascular problems (hypertension, angina, migraine headaches) and to prevent reinfarction after myocardial infarction. Beta1-selective adrenergic blocking agents are used for treating hypertension, angina, and some cardiac arrhythmias. 34. The patient takes labetalol and is scheduled for surgery. The anesthesiologist plans to use halothane as one of the anesthetic agents. The nurse consults with the anesthesiologist to ensure awareness the patient’s medication history knowing that the combination of labetalol and halothane will have what effect? A) Excessive hypotension B) Hypoglycemia C) Conduction system disturbances D) Vomiting Ans: A Feedback: There is increased risk of excessive hypotension if any of these drugs is combined with volatile liquid general anesthetics such as enflurane, halothane, or isoflurane. The effectiveness of diabetic agents is increased, leading to hypoglycemia when such agents are used with these drugs. Carvedilol has been associated with potentially dangerous conduction system disturbances when combined with verapamil or diltiazem. Vomiting is not associated with this combination of drugs. 35. The 64-year-old patient has smoked since age 15 and has been diagnosed with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. What classification of adrenergic blocking antagonist would be safest for this patient to treat angina? A) Nonselective adrenergic blocking agents B) Nonselective alpha-adrenergic blocking agents C) Alpha1-selective adrenergic blocking agents D) Beta1-selective adrenergic blocking agents Ans: D Feedback: Beta1-selective adrenergic blocking agents have an advantage over the nonselective beta-blockers in some cases. Because they do not usually block beta2-receptor sites, they do not block the sympathetic Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 519 bronchodilation that is so important for patients with lung diseases or allergic rhinitis. Consequently, these drugs are preferred for patients who smoke or who have asthma, any other obstructive pulmonary disease, or seasonal or allergic rhinitis. Nonselective adrenergic blocking agents block both alpha- and beta-adrenergic receptors exacerbating respiratory conditions by the loss of norepinephrine’s effect of bronchodilation. Nonselective alpha-adrenergic blocking agents are not used to treat angina. Alpha1selective adrenergic blocking agents are not used to treat angina. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 520 Chapter 32 - Cholinergic Agonists 1. The patient has had cevimeline (Evoxac) prescribed. What would be an appropriate dosing schedule for the nurse to administer this drug? A) Once a day B) Twice a day C) Three times a day D) Every 4 hours Ans: C Feedback: Cevimeline should be given three times a day with meals. Once or twice a day dosing would cause a decrease in therapeutic effects of the drug and every 4 hours could lead to toxicity. 2. A student asks the pharmacology instructor to describe the function of a cholinergic agonist. What would the instructor reply? A) Cholinergic agonists increase the activity of dopamine receptor sites throughout the brain and spinal cord. B) Cholinergic agonists decrease the activity of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptor sites throughout the body. C) Cholinergic agonists increase the activity of acetylcholine receptor sites throughout the body. D) Cholinergic agonists decrease the activity of norepinephrine receptor sites throughout the brain and spinal cord. Ans: C Feedback: Cholinergic agonists are drugs that increase the activity of acetylcholine receptor sites throughout the body. Dopamine, GABA, and norepinephrine are not associated with cholinergic agonist function. 3. A 10-year-old child with spina bifida is receiving bethanechol (Urecholine) for treatment of neurogenic bladder. What adverse effect will the nurse assess for? Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) A) Constipation B) Loss of bowel and bladder control C) Decrease salivation D) Increased appetite Ans: B 521 Feedback: Loss of bowel and bladder control is an adverse effect of cholinergic agents that would cause stress in a child. Diarrhea and increased salivation are also adverse effects. Increased appetite is not associated with these drugs. Children are more likely to have gastrointestinal (GI) upset that could result in a decrease in appetite. 4. A nurse is writing a plan of care for a patient who is taking bethanechol (Urecholine). What would be an appropriate outcome for this patient? A) Pupillary dilation B) Increased blood pressure C) Improved bladder function D) Decreased secretions Ans: C Feedback: Bethanechol is prescribed for nonobstructive urinary retention and neurogenic bladder. The appropriate outcome for this patient would be improved bladder function. This drug causes pupillary constriction and increased secretions. This drug would not increase blood pressure. However, it could cause hypotension in the older patient. 5. What drug is the nurse likely to administer to diagnose myasthenia gravis in a child? A) Atropine (generic) B) Bethanechol (Urecholine) C) Edrophonium (Enlon, Reversol) Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) D) Neostigmine (Prostigmine) Ans: C 522 Feedback: Edrophonium is the drug of choice for diagnosing myasthenia gravis. Bethanechol is used to treat neurogenic bladder. Neostigmine is used for treatment of myasthenia gravis and could be used for diagnosis if edrophonium could not be used. Atropine is an anticholinergic drug and would not be used to test for myasthenia gravis. 6. A patient is brought to the emergency department having a cholinergic reaction, which includes a severe drop in blood pressure. What drug will the nurse expect to administer? A) Atropine (generic) B) Edrophonium (Enlon, Reversol) C) Propranolol (Inderal) D) Succinylcholine (Anectine) Ans: A Feedback: The antidote for a cholinergic reaction is atropine. This drug will block the cholinergic sites. Edrophonium would cause an accumulation of acetylcholine and worsen the situation. Propranolol blocks beta-receptors in the sympathetic system. Succinylcholine is a neuromuscular junction drug and would not affect other sites. 7. Memantine hydrochloride (Namenda) has been prescribed for a 63-year-old patient who has a confirmed diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. What would be the target dose for this patient? A) 5 mg/d B) 10 mg b.i.d. C) 15 mg/d D) 20 mg b.i.d. Ans: B Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 523 Feedback: The drug is started at 5 mg/d PO, increasing by 5 mg/d at weekly intervals. The target dose is 20 mg/d given as 10 mg b.i.d. 8. An Alzheimer’s patient taking donepezil (Aricept) has a complete blood count that indicates he or she is anemic. What drug taken in combination with donepezil could be the cause of the anemia? A) Cimetidine (Tagamet) B) Ibuprofen (Advil) C) Diltiazem (Cardizem) D) Furosemide (Lasix) Ans: B Feedback: There could be an increased risk of gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding if donepezil is taken with a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) because of the combination of increased GI secretions and the GI mucosal erosion associated with the use of NSAIDs. Cimetidine, diltiazem, and furosemide would not affect GI bleeding. 9. The Air Force nurse is treating a patient who was exposed to a particular nerve gas. What drug has been approved to treat this patient? A) Neostigmine (Prostigmin) B) Pyridostigmine (Mestinon) C) Ambenonium (Mytelase) D) Edrophonium (Enlon, Reversol) Ans: B Feedback: Pyridostigmine has been approved for use by military personnel who have been exposed to particular nerve gases. Neostigmine, ambenonium, and edrophonium are not approved for this use. 10. The nurse administers a direct-acting cholinergic agonist to the patient. When assessing this patient for drug effects, the nurse would expect to see effects arising from stimulation of what receptors? Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) A) Nicotinic B) Alpha C) Beta D) Muscarinic Ans: D 524 Feedback: The direct-acting cholinergic agonists are similar to acetylcholine (ACh) and react directly with receptor sites to cause the same reaction as if Ach had stimulated the receptor sites. These drugs usually stimulate muscarinic receptors within the parasympathetic system. They are used as systemic agents to increase bladder tone, urinary excretion, and gastrointestinal (GI) secretions. One drug is used as an ophthalmic agent to induce miosis to relieve the increased intraocular pressure of glaucoma. They have no effect on alpha and beta receptors in the sympathetic nervous system and little impact on nicotinic receptors. 11. The nurse is caring for a 49-year-old patient, who has been receiving bethanechol (Duvoid) for 1 week. The patient develops progressive muscle weakness and respiratory difficulty. Edrophonium is ordered and injected and the patient’s symptoms worsen. How would the nurse interpret this response? A) Myasthenic crisis B) Cholinergic crisis C) Anaphylactic reaction D) Pulmonary edema Ans: B Feedback: The patient with a cholinergic crisis presents with progressive muscle weakness and respiratory difficulty because the accumulation of acetylcholine at the cholinergic receptor site leads to reduced impulse transmission and muscle weakness. This is a crisis when the respiratory muscles are involved. Myasthenic crisis and cholinergic crisis display similar clinical pictures. The drug edrophonium can be used as a diagnostic agent to distinguish the two conditions. If the patient improves immediately after the edrophonium injection, the problem is a myasthenic crisis, which is improved by administration of the cholinergic drug. If the patient gets worse, the problem is probably a cholinergic crisis, so withdrawal of the patient’s cholinergic drug along with intense medical support is indicated. The situation does not depict an anaphylactic reaction or pulmonary edema. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 12. 525 A 70-year-old female patient has just been diagnosed with Alzheimer’s disease. What cholinergic drug is used for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease? A) Bethanechol (Duvoid) B) Neostigmine (Prostigmin) C) Donepezil (Aricept) D) Edrophonium (Enlon, Reversol) Ans: C Feedback: Currently, there are four reversible indirect-acting cholinergic agonists available to slow the progression of this disease. These include tacrine (Cognex), galantamine (Razadyne), rivastigmine (Exelon), and donepezil (Aricept). Edrophonium (Enlon, Reversol) is used to diagnose myasthenia gravis; neostigmine is used for the diagnosis and management of myasthenia gravis; and bethanechol is used to treat neurogenic bladder. 13. The 38-year-old patient has just been administered edrophonium (Enlon, Reversol). The nurse will know whether this patient has myasthenia gravis if the patient exhibits what within 30 minutes after receiving the medication? A) Increased muscle strength B) Decreased adventitious breath sounds C) Decreased muscle spasms D) Increased urinary output Ans: A Feedback: Edrophonium is administered to diagnose myasthenia gravis because administration of this drug will cause a marked increase in muscle strength within 30 minutes of administration if the patient has this disease. Edrophonium does not produce decreased adventitious breath sounds, decreased muscle spasms, or increased urinary output. 14. A) When the nurse administers a cholinergic agonist to the patient, the nurse’s expectation is that what system will be stimulated? Sympathetic nervous system Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) B) Parasympathetic nervous system C) Central nervous system D) Voluntary nervous system Ans: B 526 Feedback: Cholinergic agonists act at the same site as the neurotransmitter acetylcholine (ACh) and increase the activity of the ACh receptor sites throughout the body. Because these sites are found extensively throughout the parasympathetic nervous system, their stimulation produces a response similar to what is seen when the parasympathetic system is activated. These drugs do not stimulate the sympathetic, central, or voluntary nervous systems. 15. A 78-year-old patient is admitted to the emergency department and is diagnosed with bradycardia. The patient tells the nurse he or she is taking donepezil (Aricept), a cholinergic agent, for Alzheimer’s disease. The nurse will anticipate what drug will be ordered to treat the patient’s bradycardia? A) Atropine B) Pseudoephedrine C) Propranolol D) Bethanechol Ans: A Feedback: Maintain a cholinergic blocking drug on standby, such as atropine, to use as an antidote for excessive doses of cholinergic drugs to reverse overdose or counteract severe reactions arising from use of cholinergic agonists. Atropine will block cholinergic effects that are causing this patient’s heart rate to decline. Bethanechol will slow the heart rate further whereas propranolol and pseudoephedrine will not reverse the cholinergic stimulation. 16. The nurse administers bethanechol (Duvoid, Urecholine) to treat what condition? A) Hypertension B) Urinary retention Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) C) Bradycardia D) Asthma Ans: B 527 Feedback: Bethanechol is used for the treatment of nonobstructive postoperative and postpartum urinary retention, neurogenic bladder atony in adults and children older than 8 years; diagnosis and treatment of reflux esophagitis in adults, and orally in infants and children for treatment of esophageal reflux. It would be ineffective in treating hypertension, bradycardia, and asthma. 17. The nurse is caring for a patient who has indirect-acting cholinergic agonists prescribed to treat myasthenia gravis. When administering this classification of drug, the nurse should assess the patient for toxic effects of the drugs including what? A) Paralytic ileus B) Abdominal distension C) Hypertension D) Muscle weakness Ans: D Feedback: The patient with a cholinergic crisis presents with progressive muscle weakness and respiratory difficulty because the accumulation of acetylcholine at the cholinergic receptor site leads to reduced impulse transmission and muscle weakness. This is a crisis when the respiratory muscles are involved. Toxic effects of the drug would not include paralytic ileus, abdominal distention, or hypertension. 18. Which indirect-acting anticholinesterase medication will the nurse administer as an antidote to neuromuscular junction blockers? A) Pyridostigmine (Mestinon) B) Donepezil (Aricept) C) Rivastigmine (Exelon) D) Ambenonium (Mytelase) Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) Ans: 528 A Feedback: Pyridostigmine is indicated for management of myasthenia gravis; antidote to neuromuscular junction blockers; increased survival after exposure to nerve gas. Donepezil and rivastigmine are used to treat Alzheimer’s disease. Ambenonium is used to treat myasthenia gravis. 19. A patient is brought to the emergency department after a motor vehicle accident. The patient is diagnosed with multiple injuries including a bladder injury. The patient is taken to surgery and develops a nonobstructive postoperative urinary retention. What drug would the nurse expect to be ordered for this patient? A) Neostigmine B) Bethanechol C) Ambenonium D) Pyridostigmine Ans: B Feedback: The agent bethanechol, which has an affinity for the cholinergic receptors in the urinary bladder, is available for use orally and subcutaneously to treat nonobstructive postoperative and postpartum urinary retention and to treat neurogenic bladder atony. The other options are not indicated for this purpose. 20. A patient is taking memantine for Alzheimer’s disease. This drug does not affect what? A) Nicotinic receptor sites B) Glucagon receptor sites C) Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptor sites D) Muscarinic receptor sites Ans: C Feedback: The drug, memantine hydrochloride (Namenda) has a low-to-moderate affinity for N-methyl-D- Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 529 aspartate (NMDA) receptors with no effects on dopamine, GABA, histamine, glycine, or adrenergic receptor sites. It is believed that persistent activation of the central nervous system NMDA receptors contributes to the symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease. By blocking these sites, it is thought that the symptoms are reduced or delayed. Other options are incorrect. 21. A patient is brought to the emergency department and is found to have cholinergic toxicity. What is the drug of choice to treat this condition? A) Atropine B) Epinephrine C) Lidocaine D) Edrophonium (injectable) Ans: A Feedback: Maintain atropine sulfate on standby as an antidote in case of overdose or severe cholinergic reaction. Epinephrine, lidocaine, and edrophonium would not be used for this purpose. 22. A 47-year-old man is suspected of having been exposed to nerve gas. Atropine is given to temporarily block cholinergic activity and to activate acetylcholine sites in the central nervous system. What drug does the nurse give with the atropine to free up the acetylcholinesterase to start breaking down acetylcholine? A) Pyridostigmine B) Pralidoxime C) Neostigmine D) Rivastigmine Ans: B Feedback: If nerve gas exposure is expected, patients who may have been exposed are given intramuscular injections of atropine (to temporarily block cholinergic activity and to activate acetylcholine sites in the central nervous system) and pralidoxime (to free up the acetylcholinesterase to start breaking down acetylcholine). An auto-injection is provided to military personnel who may be at risk. The injector is used to give atropine and then pralidoxime. The injections are repeated in 15 minutes. If symptoms of nerve gas exposure exist after an additional 15 minutes, the injections are repeated. If symptoms still persist after a third set of injections, medical help should be sought. Pyridostigmine, neostigmine, and Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 530 rivastigmine are not used in nerve gas exposure. 23. A 77-year-old man is brought to the emergency department with a cholinergic overdose. The nurse knows that older adults are likely to have a greater number of adverse drug effects for what reason? A) They are more likely to take the medications inconsistently. B) All older adults have some type of chronic health problem. C) Older adults have a number of different physiological changes. D) Older adults have a poor memory and are more likely to overdose. Ans: C Feedback: Older patients are more likely to experience the adverse effects associated with these drugs (e.g., central nervous system, cardiovascular, gastrointestinal, respiratory, and urinary) because of normal physiological changes associated with aging. Those patients with known renal or hepatic impairment would receive a lower dosage to avoid overdose. Older people are not more likely to take medications inconsistently or to take too much medication. Not all older adults have chronic health problems. 24. The nurse is caring for a 45-year-old female patient who is in chronic renal failure. What cholinergic drug is contraindicated for this patient? A) Neostigmine B) Pyridostigmine C) Edrophonium D) Galantamine Ans: D Feedback: Drugs used to treat Alzheimer’s disease are metabolized in the liver and excreted in the urine, so caution should be used in the presence of hepatic or renal dysfunction, which could interfere with the metabolism and excretion of the drugs. Dosage adjustments may be needed for neostigmine, edrophonium, and pyridostigmine if the patient has renal disease but they are not contraindicated. 25. A 72-year-old man is newly diagnosed with Alzheimer’s disease. The patient’s daughter asks the nurse how her father’s medication is going to help him. What will the nurse explain in layman’s terms? Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 531 A) The drugs work by increasing acetylcholine (ACh) levels in the brain and slowing the progression of the disease. B) The drugs work by crossing the bloodbrain barrier and cure the disease in the brain. C) The drugs work by increasing ACh levels in the brain and reverse the progression of the disease. D) The drugs work by crossing the bloodbrain barrier and decreasing ACh levels in the neuromuscular junctions. Ans: A Feedback: Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors that cross the bloodbrain barrier are used to manage Alzheimer’s disease by increasing ACh levels in the brain and slowing the progression of the disease. Decreasing ACh levels in the brain does not slow the progression, reverse the progression, or cure the disease. Decreasing ACh levels at the neuromuscular junctions has no effect on Alzheimer’s disease. 26. A patient has been newly diagnosed with myasthenia gravis. What important teaching will the nurse provide the family? A) If one dose of medication is missed double the next dose B) The warning signs of drug overdose C) How to encourage activity when the patient is tired D) Importance of monitoring level of consciousness Ans: B Feedback: The patient who is being treated for myasthenia gravis and his or her significant other should both receive instruction in drug administration, warning signs of drug overdose, and signs and symptoms to report immediately to enhance patient knowledge about drug therapy and to promote compliance. Missed doses should not be doubled with next dose because this will lead to overdosage. Patients with myasthenia gravis will experience muscle weakness and should not be pushed to do more than they can tolerate. Level of consciousness is not a concern in patients with myasthenia gravis. 27. A) A new patient has come to the clinic. The patient tells the nurse he or she takes donepezil (Aricept). What is the priority nursing assessment related to the medication? (Select all that apply.) Nutritional status Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) B) Blood pressure C) History of incontinence D) Breath sounds E) Muscle strength Ans: A, B, C 532 Feedback: Gastrointestinal (GI) adverse effects can include nausea, vomiting, cramps, diarrhea, increased salivation, and involuntary defecation, so it is important for the nurse to assess nutritional status. This is made all the more important by the condition the drug is treating that often results in patients forgetting to eat healthfully. Blood pressure should be monitored because adverse effects of donepezil include hypotension, bradycardia, and heart block. Involuntary defecation and relaxation of bladder sphincter can result in incontinence so the nurse should assess for both incontinence and, if it occurred, skin integrity. Respiratory adverse effects are not associated with donepezil and muscle strength should not be impacted either. 28. What family of drugs is used in the treatment of myasthenia gravis? A) Direct-acting cholinergic agonists B) Muscarinic inhibitors C) Indirect-acting cholinergic agonists D) Nicotinic agonists Ans: C Feedback: The drugs used to treat patients with myasthenia gravis include several indirect-acting cholinergic agonists that do not cross the bloodbrain barrier and do not effect acetylcholine transmission in the brain. These drugs include ambenonium (Mytelase), edrophonium (Enlon, Reversol), neostigmine (Prostigmin), and pyridostigmine (Mestinon). Other options are incorrect. 29. For what purpose would the nurse in the critical care unit administer pyridostigmine? A) To reverse neuromuscular junction blockers B) To reverse smooth muscle blockade Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) C) To reverse cholinergic crisis D) To prevent myasthenic crisis Ans: A 533 Feedback: Pyridostigmine is approved for management of myasthenia gravis, as an antidote to neuromuscular junction blockers, and to increase survival after exposure to nerve gas. Other options are not indications for use of this drug. 30. A patient diagnosed with myasthenia gravis is having trouble swallowing. What anticholinesterase inhibitor would be the drug of choice for this patient? A) Galantamine B) Pyridostigmine C) Donepezil D) Bethanechol Ans: B Feedback: Pyridostigmine is preferred in some cases for the management of myasthenia gravis because it does not need to be taken as frequently and can be given parenterally for patients who are having difficulty swallowing. Galantamine and bethanechol cannot be given parenterally to the patient having difficulty swallowing. Donepezil is not indicated for the treatment of myasthenia gravis but is used to manage Alzheimer dementia, including severe dementia. 31. The nurse is treating a patient who has been exposed to nerve gas. The provider ordered pyridostigmine (Mestinon) 0.25 mg/kg. The patient weighs 96 kg. What dosage will the nurse administer to this patient? A) 24 mg B) 384 mg C) 11 mg D) 31.7 mg Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) Ans: 534 A Feedback: Multiply the patient’s weight times the ordered dose per kilogram: 0.25 × 96 = 24 mg. Other options are incorrect. 32. The nurse is caring for a patient diagnosed with Sjögren’s syndrome. What medication will the nurse anticipate administering to treat this condition? A) Bethanechol B) Carbachol C) Ambenonium D) Pilocarpine Ans: D Feedback: Only pilocarpine is indicated for treatment of Sjögren’s syndrome. None of the other medications are indicated for this purpose. 33. The nurse administers bethanechol to the patient on an empty stomach for what purpose? A) To promote rapid absorption B) To prevent destruction of the drug C) To reduce irritation of stomach lining D) To decrease nausea and vomiting Ans: D Feedback: Administer bethanechol and all oral forms of direct-acting cholinergic agonists on an empty stomach to decrease nausea and vomiting. The other options do not correctly explain the rationale for administering bethanechol on an empty stomach. 34. The nurse in the pediatric intensive care unit is caring for an infant with severe gastroesophageal reflux. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 535 What medication, if ordered, would the nurse administer to treat this condition? A) Bethanechol B) Carbachol C) Cevimeline D) Pilocarpine Ans: B Feedback: Only bethanechol is indicated for the treatment of esophageal reflux in infants and children. The other drugs treat intraocular pressure, dry mouth, or to allow surgeons to perform certain surgical procedures. 35. The nurse is caring for a patient receiving carbachol to treat glaucoma. The patient says he or she has stopped driving at night because he or she just does not see well in the dark. What is the best nursing diagnosis for this patient? A) Anxiety related to poor vision B) Grief related to loss of driving privileges C) Risk for injury related to visual changes D) Pain related to altered vision Ans: C Feedback: This patient is at risk for injury related to visual changes and requires safety teaching to make the home as safe as possible. Nothing indicates the patient is experiencing anxiety, grief, or pain. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 536 Chapter 33 - Anticholinergic Agents 1. A student asks the pharmacology instructor to explain the action of anticholinergic agents. What would be the instructor’s best response? A) They block nicotinic receptors. B) They compete with serotonin for muscarinic acetylcholine receptor sites. C) They act to block the effects of the parasympathetic nervous system. D) They increase norepinephrine at the neuromuscular junction. Ans: C Feedback: Drugs that are used to block the effects of acetylcholine are called anticholinergic drugs. Because this action lyses, or blocks, the effects of the parasympathetic nervous system, they are also called parasympatholytic agents. The drug works by blocking only the muscarinic effectors in the parasympathetic nervous system. They compete with acetylcholine for the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor sites. They do not block the nicotinic receptors and have little or no effect at the neuromuscular junction. 2. A patient calls the clinic and talks to the nurse. The patient tells the nurse he or she is going on a cruise and is concerned about motion sickness. The patient says that a friend has recommended that he or she see his or her primary care physician to get a prescription for scopolamine. What adverse effect would the nurse inform the patient that using scopolamine may result in? A) Pupil constriction B) Tachycardia C) Diarrhea D) Urinary incontinence Ans: B Feedback: Scopolamine blocks the parasympathetic nervous system, which may result in dilated pupils and increased heart rate (i.e., tachycardia). Blocking the parasympathetic system also results in decreased GI activity and urinary bladder tone causing constipation and urinary retention. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 3. 537 A 29-year-old man is going on a company-sponsored deep-sea fishing trip in 2 weeks. He comes to the clinic requesting a scopolamine patch because he is afraid that he will get seasick. The medication is prescribed for him and the nurse’s instructions concerning use of the patch will include what? A) Shave the area before applying the patch. B) The patch’s effectiveness will last about 72 hours. C) When replacing the patch, apply the new patch in the same area. D) Do not clean the application area before applying the patch. Ans: B Feedback: The scopolamine patch is replaced every 3 days (i.e., 72 hours). The scopolamine patch should be applied to a clean, dry, intact, and hairless area of the body. The area should not be shaved because abrasion of the skin could occur and lead to increased absorption. Patches should be placed at new sites each time to avoid skin irritation. The old patch should be removed and the area cleaned. 4. The nurse is taking a health history on a new patient who has been prescribed propantheline(generic) as adjunctive therapy for peptic ulcers. While collecting the health history, what will the nurse specifically assess for? A) Diabetes mellitus B) Obsessive-compulsive disorder C) Insomnia D) Glaucoma Ans: D Feedback: Propantheline is contraindicated for a patient with glaucoma because the drug could result in increased intraocular pressure due to pupil dilation. Diabetes mellitus, obsessive-compulsive disorder, and insomnia are not recognized as being adversely affected by this drug. 5. A nurse is admitting a patient for outpatient eye surgery. The nurse routinely administers preoperative medications for eye surgery and is aware that an increased dosage of a mydriatic is likely when given to a member of what ethnic group? Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) A) African Americans B) German Americans C) Irish Americans D) Scandinavian Americans Ans: A 538 Feedback: African Americans with dark eyes usually require an increased dosage and may have a prolonged time to peak effect. The need for an increased dose appears to be related to the amount of pigment in the person’s eyes because people with darker-pigmented eyes require a higher dose. German, Irish, and Scandinavian Americans generally have less pigmentation in their eyes and are therefore less likely to need a greater dose. 6. A patient has been newly diagnosed with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). The nurse knows that the most likely choice of anticholinergic drug to be prescribed for this patient is what? A) Atropine (generic) B) Dicyclomine (generic) C) Glycopyrrolate (Robinul) D) Methscopolamine (Pamine) Ans: B Feedback: Dicyclomine is the most likely choice of anticholinergic drug for IBS. It relaxes the GI tract and is a frequent choice in the treatment of hyperactive bowel and IBS. Atropine is used to decrease secretions, for bradycardia, pylorospasm, ureteral colic, relaxing the bladder, pupil dilation, and as an antidote for cholinergic drugs. Glycopyrrolate is used to decrease secretions and as an antidote for neuromuscular blockers. Methscopolamine is used as adjunctive therapy for ulcers. 7. A patient has come to the clinic for a follow-up visit. He or she has been taking glycopyrrolate (Robinul) for adjunctive management of his or her peptic ulcer disease for 1 year. What would the nurse question this patient about? A) Diarrhea B) Oral discomfort Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) C) Headaches D) Dyspnea Ans: B 539 Feedback: Patients taking anticholinergic drugs will have dry mucous membranes. Oral hygiene will be extremely important during glycopyrrolate therapy to avoid gum disease. The nurse should encourage the patient to suck on sugarless lozenges and perform frequent oral care. Diarrhea, headaches, or dyspnea should not be a concern with this drug. 8. A 73-year-old male with Parkinson’s disease comes to the clinic for routine care. The man has a comorbidity of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). An anticholinergic drug is prescribed for the patient. What is the priority teaching point the nurse must give to the patient in regard to his medication? A) Avoid excessively hot environments. B) Avoid driving his car while taking the drug. C) Call his doctor if he cannot urinate. D) Take the drug with food to avoid gastrointestinal (GI) upset. Ans: C Feedback: Due to the patient’s diagnosis and drug therapy, calling the doctor if he cannot urinate would be the most important instruction. Older men with BPH have difficulty urinating and if an anticholinergic drug is taken, this can lead to urinary retention and bladder sphincter spasm. The patient should be encouraged to empty his bladder before taking the drug. Because this is an anticholinergic drug, avoiding hot environmental temperatures (reduced ability to perspire) and driving or operating machinery (possible central nervous system effects) should also be encouraged as well as taking the medication with food to help with GI upsets. However, the highest priority is addressing urinary retention issues. 9. A patient has been given atropine to cause mydriasis and cycloplegia. What is the expected outcome for this patient? A) Constricted pupils and blurred vision B) Dilated pupils and improved vision Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) C) Dilated pupils and blurred vision D) Dry eyes and constricted pupils Ans: C 540 Feedback: Atropine can be used to cause dilated pupils, which is mydriasis resulting in cycloplegia, which is the inability of the lens of the eye to accommodate leading to blurred vision. 10. Because the effects of atropine are dose related, at what dose of atropine would the nurse expect to see a patient having difficulty speaking? A) 0.5 mg B) 1.0 mg C) 2.0 mg D) 5.0 mg Ans: D Feedback: Toxicity of atropine is dose related. With 5.0-mg dosage, the nurse would expect marked speech disturbances, difficulty swallowing, restlessness, fatigue, headache, dry and hot skin, difficulty voiding, and reduced intestinal peristalsis. With 0.5-mg dosage of atropine, slight cardiac slowing, dryness of the mouth, and inhibition of sweating would be noticed. Definite dryness of the mouth and throat, thirst, rapid heart rate, and pupil dilation would be evident with 1.0-mg dosage. With 2.0-mg dosage, the nurse would note rapid heart rate, palpitations, marked mouth dryness, dilated pupils, and some blurring of vision. 11. A 66-year-old woman presents at the clinic complaining of motion sickness. The physician orders a scopolamine patch. Which statement by the patient leads you to believe she knows how to use the patch? A) I will place it on my chest each morning after I shower. B) I will use it only if I feel sick to my stomach. C) I will change the patch every 4 hours. I can use the patches for 1 week. D) I will change the patch every 3 days. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) Ans: 541 D Feedback: The scopolamine patch should be applied to a clean, dry, intact, and hairless area of the body. The area should not be shaved because abrasion of the skin could occur and lead to increased absorption. Patches should be placed at new sites each time to avoid skin irritation. The old patch should be removed and the area where it had been should be cleaned. 12. A patient is scheduled for surgery in 2 hours. The physician orders preoperative medications glycopyrrolate (Robinul) 1 mg and meperidine (Demerol) 50 mg intramuscularly. The nurse would hold the medication and consult the provider if the patient had what disorder? A) Tachycardia B) Paralytic ileus C) Hypertension D) Diabetes mellitus Ans: B Feedback: These drugs are also contraindicated with any condition that could be exacerbated by blockade of the parasympathetic nervous system. These conditions include stenosing peptic ulcer, intestinal atony, paralytic ileus, gastrointestinal (GI) obstruction, severe ulcerative colitis, and toxic megacolon, all of which could be exacerbated with a further slowing of GI activity. Tachycardia, hypertension, and diabetes would not be contraindications to administration of glycopyrrolate. 13. The nurse is caring for a patient with atropine poisoning. What drug will the nurse administer to reverse these effects? A) Bethanechol B) Neostigmine C) Edrophonium D) Physostigmine Ans: D Feedback: Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 542 Physostigmine can be used as an antidote for atropine poisoning. A slow intravenous injection of 0.5 to 4 mg (depending on the weight of the patient and the severity of the symptoms) usually reverses the delirium and coma of atropine toxicity. Physostigmine is metabolized rapidly, so the injection may need to be repeated every 1 to 2 hours until the atropine has been cleared from the system. 14. Because of the systemic effects of anticholinergic drugs, the nurse understands that older adults using these drugs are susceptible to what? A) Heat stroke B) Diarrhea C) Urinary frequency D) Hypotension Ans: A Feedback: Because older patients are more susceptible to heat intolerance owing to decreased body fluid and decreased sweating, extreme caution should be used when an anticholinergic drug is given that reduces sweating still further and can result in heat stroke. Older adults are not more susceptible to diarrhea, urinary frequency, and hypotension. 15. A 50-year-old female patient received atropine and meperidine (Demerol) preoperatively. After surgery, the patient complains of mouth dryness. What is the nurse’s best response? A) Preoperative medications decrease saliva production but it is temporary and will improve. B) This is the result of all of the blood and fluid you lost during surgery. C) You are probably dehydrated. The IV fluids you are receiving will correct the problem. D) The preoperative medication causes an electrolyte imbalance making your mouth feel dry. Ans: A Feedback: Patients receiving anticholinergic drugs must be monitored for dry mouth, difficulty swallowing, constipation, urinary retention, tachycardia, pupil dilation and photophobia, cycloplegia and blurring of vision, and heat intolerance caused by a decrease in sweating. 16. Anticholinergics have varied effects on the body. What is one of those effects? Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) A) Preventing vagal stimulation B) Stimulating the release of acetylcholine C) Increasing respiratory tract secretions D) Increasing secretion of sweat glands Ans: A 543 Feedback: Adjunctive therapy to treat peptic ulcer, overactive gastrointestinal (GI) disorders; neurogenic bladder or cystitis; parkinsonism; biliary or renal colic; to decrease secretions pre-operatively; treatment of partial heart block associated with vagal activity; treatment of rhinitis or anticholinesterase poisoning. 17. Anticholinergic drugs are used in ophthalmology because they produce what effect? A) Sedation B) Pupil dilation C) Pupil constriction D) Decreased lacrimal secretions Ans: B Feedback: Patients receiving anticholinergic drugs must be monitored for dry mouth, difficulty swallowing, constipation, urinary retention, tachycardia, pupil dilation and photophobia, cycloplegia and blurring of vision, and heat intolerance caused by a decrease in sweating. 18. A male patient, age 75, is started on flavoxate (Urispas). What adverse effects should the patient be made aware of? A) Rash B) Headache C) Weight gain D) Blurred vision Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) Ans: 544 D Feedback: The patient should be warned of possible blurring of vision when taking this drug, which could put the patient at risk for injury if precautions are not taken. Adverse effects could include central nervous system adverse effects, such as blurred vision, pupil dilation and resultant photophobia, cycloplegia, and increased intraocular pressure, all of which are related to the blocking of the parasympathetic effects in the eye. 19. The nurse administers atropine preoperatively for what purpose? A) Providing sedation B) Dilating the pupils C) Relaxing bladder muscles D) Decreasing secretions Ans: D Feedback: Atropine is administered preoperatively to reduce secretions, but added indications include gastrointestinal (GI) effects that reduce GI activity. Atropine has no sedating effects, and is not given preoperatively for its pupil dilation effects, or for its bladder muscle relaxation effects. 20. What is the recommended dosage for atropine for a patient with a bradycardia? A) 0.2 to 0.4 mg B) 0.3 to 0.5 mg C) 0.4 to 0.6 mg D) 0.5 to 0.7 mg Ans: C Feedback: The usual dosage for atropine is 0.4 to 0.6 mg intramuscularly, subcutaneously, or IV; use caution with older patients. The other options are incorrect dosages and therefore wrong. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 21. 545 When the nurse administers an anticholinergic drug to a child, the nurse would carefully assess for what effect that is more likely to occur in children than in adults? A) Rashes B) Pupil dilation C) Heat intolerance D) Tachycardia Ans: C Feedback: Children are often more sensitive to the adverse effects of the drugs, including constipation, urinary retention, heat intolerance, and confusion. Similar effects are seen in children related to pupil dilation. Tachycardia and rashes would not be associated with these drugs in children. 22. The nurse is writing a plan of care for an older adult patient taking flavoxate. What is an appropriate goal for this patient’s plan of care? A) The patient will have adequate pupil dilation within 24 hours. B) The patient will experience fewer bronchospasms within 8 hours. C) The patient will experience fewer symptoms of prostatitis within 24 hours. D) The patient will show resolution of peptic ulcer within 2 weeks. Ans: C Feedback: Flavoxate is used to relieve symptoms of dysuria, urgency, nocturia, suprapubic pain, frequency, and incontinence associated with cystitis, prostatitis, urethritis, urethrocystitis, and urethrotrigonitis. As a result, the nurse would know the drug was working when the patient experienced fewer symptoms related to any one of these conditions. Because the drug is not indicated for pupil dilation, bronchospasm, or treatment of a peptic ulcer, the nurse’s outcomes would not be related to these conditions. 23. A) What drug would the nurse administer to treat a patient diagnosed with bronchospasm associated with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)? Atropine Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) B) Flavoxate C) Glycopyrrolate D) Ipratropium Ans: D 546 Feedback: Ipratropium is indicated for the treatment of bronchospasm associated with COPD. Atropine is indicated for use to decrease secretions, bradycardia, pylorospasm, ureteral colic, relaxing of bladder, emotional liability with head injuries, antidote for cholinergic drugs, and pupil dilation. Flavoxate is used for the symptomatic relief of dysuria, urgency, nocturia, suprapubic pain, frequency, and incontinence associated with cystitis, prostatitis, urethritis, urethrocystitis, and urethrotrigonitis. Glycopyrrolate is indicated to decrease secretions before anesthesia or intubation, used orally as an adjunct for treatment of ulcers, to protect the patient from the peripheral effects of cholinergic drugs and to reverse neuromuscular blockade 24. A 72-year-old female patient is being discharged home from the hospital on newly prescribed anticholinergic drugs. A referral to the home health nurse has been made. What priority teaching point will the home health nurse emphasize when discussing the patient’s drugs? A) Do not drive or use machinery. B) Take lots of hot baths or showers. C) Keep the house warm to avoid a chill. D) Limit intake of fluids. Ans: A Feedback: Safety precautions may be needed if blurred vision and dizziness occur. The patient should be urged not to drive or perform tasks that require concentration and coordination. The home care nurse would not teach the patient to take hot baths or showers. The patient would be cautioned about inability to perspire in hot environments and to avoid them. Fluid intake should not be limited. 25. A) The nurse is caring for a new mother who received atropine before undergoing a laparoscopic tubal ligation. The patient tells the nurse that she is breast-feeding her baby and asks whether she can breastfeed when she gets home. What is the nurse’s best response? You can breast-feed when you get home because the drugs given before surgery will be out of your system. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 547 B) You can breast-feed as soon as you get home because atropine will not cross into the breast milk. C) Discard all breast milk for the next week and feed the baby formula before returning to breastfeeding. D) Discard all breast milk for the next 24 hours and feed formula until tomorrow when you can nurse your baby. Ans: D Feedback: Lactating mothers should not breast-feed after receiving atropine until the drug has been fully excreted. Because atropine crosses into breast milk and the duration of action is 4 hours, it is safest to have the mother wait 24 hours to breast-feed, continuing to pump and discard the milk while feeding the infant formula. After 24 hours, she can return to breast-feeding because any atropine in breast milk will be eliminated. There is no need to wait a week and although the drug may be out of the bloodstream, the milk in her breast will still contain atropine. 26. The patient, who takes an anticholinergic medication, tells the nurse how much he or she enjoys experimenting with different herbal teas. What herbs will the nurse caution the patient to avoid? (Select all that apply.) A) Burdock B) Thyme C) Rosemary D) Parsley E) Tumeric Ans: A, C, E Feedback: The risk of anticholinergic effects can be exacerbated if anticholinergic agents are combined with burdock, rosemary, or turmeric and used as herbal therapy. Advise patients who use herbal therapies to avoid these combinations. Nothing indicates that thyme or parsley is contraindicated with anticholinergic medications. 27. A 27-year-old male patient is taking an anticholinergic drug as adjunctive therapy to treat his peptic ulcer disease. The patient comes to the clinic and tells the nurse that he feels his heart beating. What adverse effect is the patient experiencing from the anticholinergic medication? Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) A) Tachypnea B) Tachycardia C) Hypotension D) Urinary frequency Ans: B 548 Feedback: Tachycardia and palpitations are possible adverse effects related to blocking of the parasympathetic effects on the heart; this would give the sensation of a heart beating. Tachypnea, hypotension, and urinary frequency are not generally adverse effects of anticholinergic medications and they would not be evident the way the patient described. 28. The 10-year-old child is brought to the respiratory clinic and is prescribed ipratropium (Atrovent). Prior to administering the medication, what would the nurse assess for? A) Cardiac disorders B) Hypertension C) Recent injuries D) Breath sounds Ans: D Feedback: The nurse would assess breath sounds because ipratropium is indicated for treatment of bronchospasm so it is important to get a baseline assessment to determine whether the drug improves the patient’s condition after administration. Cardiac disorders, hypertension, and recent injuries are all valid assessments but are likely to have been assessed during admission history taking and are not related to the purpose of administering the drug. 29. The nurse is caring for a patient who has just been started on hyoscyamine (Symax and others) as adjunctive therapy for his or her peptic ulcers. When developing this patient’s plan of care, what nursing diagnosis would the nurse establish related to the purpose of administering this drug? A) Chronic pain related to peptic ulcer disease B) Impaired urinary elimination related to bladder relaxation Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) C) Risk for hyperthermia related to decreased ability to perspire D) Decreased cardiac output related to cardiovascular effects Ans: A 549 Feedback: All these nursing diagnoses could be used for the patient receiving an anticholinergic drug, but only chronic pain is related to the drug this patient is receiving and the purpose for which it is being administered. 30. What does parasympathetic nervous system blockade cause? (Select all that apply.) A) Decrease in heart rate B) Decrease in urinary bladder tone C) Increase in heart rate D) Pupil constriction E) Decrease in gastrointestinal (GI) activity Ans: B, C, E Feedback: Parasympathetic nervous system blockade causes an increase in heart rate, decrease in GI activity, decrease in urinary bladder tone and function, and pupil dilation and cycloplegia. 31. The patient was involved in a motor vehicle accident and experienced a severe closed head injury resulting in increased intracranial pressure. While intubating the patient, his or her heart rate dropped and did not return to acceptable levels after the tube was in place so the nurse received an order to administer atropine. The physician is performing an exam to determine whether brain death has occurred. What assessment for brain death will be postponed until all atropine is excreted and no longer exerting an effect. A) Pupil response B) Electroencephalogram C) Brainstem reflexes D) Computed tomographic scan of the brain Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) Ans: 550 A Feedback: One test for neurological function is to shine a light in the patient’s eyes to test pupil reaction to light. Because this patient has received atropine, pupils will be dilated and will not react normally to light. This could be mistaken as an indication of brain death if the nurse did not know atropine had been administered. This test will be postponed until the pupils are no longer dilated by the medication. The other tests would not have to be postponed because of atropine. 32. The nurse is caring for a patient who is unconscious and requires an anticholinergic drug to treat bradycardia. What drug can the nurse administer IV for this purpose? A) Ipratropium (Atrovent) B) Dicyclomine (generic) C) Methscopolamine (Pamine) D) Atropine (generic) Ans: D Feedback: Atropine can be given intramuscularly (IM), subcutaneously, or IV for the treatment of bradycardia. Ipratropium is administered by inhalation to treat bronchospasm. Dicyclomine is used to treat irritable or hyperactive bowel and can be given orally or IM. Methscopolamine is administered orally to treat peptic ulcers. 33. What is the proper dosage of scopolamine administered by the nurse transdermally to reduce nausea and vomiting associated with motion sickness? A) 0.32 to 0.65 mg B) 1.5 mg C) 3 mg D) 3.5 mg Ans: B Feedback: Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 551 The scopolamine transdermal patch is 1.5 mg. If administered subcutaneously (SC) or intamuscularly (IM), the dosage would be 0.32 to 0.65 mg. Pediatric dosage is 0.006 mg/kg subcutaneous, IM, or IV. 34. The nurse receives an order to administer glycopyrrolate 0.002 mg/kg to the pediatric patient preoperatively. The patient weighs 14 lbs. If 1 pound = 2.2 kg, how many kilograms would the nurse administer to this patient? A) 0.013 mg B) 0.13 mg C) 0.028 mg D) 0.28 mg Ans: A Feedback: Begin by calculating the child’s weight in kilogram 14 lbs/2.2 kg = 6.36 kg. Multiply child’s weight in kg by dosage in kg 6.36 × 0.002 = 0.01272 rounded to 0.013 mg. 35. A mother calls the pediatric clinic and tells the nurse the family is planning a cross-country trip to visit some attractions the children will enjoy. Her 2-year-old child gets motion sickness soon after starting the car and she would like some scopolamine patches to use. What is the nurse’s best response? A) One patch lasts for 3 days. How long will you be driving? B) Children cannot receive scopolamine orally or by patch. C) It might be better to use the oral form of the drug only on days it is needed. D) Scopolamine loses effectiveness if it is used for several days. Ans: B Feedback: Scopolamine does not come in a pediatric oral or patch formulation. Scopolamine can only be given subcutaneously, or IV. Because children cannot use the patch, asking how many days they will be traveling or suggesting oral prescription when that form is not available is incorrect. Scopolamine does not lose effectiveness. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 552 Chapter 34 - Introduction to the Endocrine System 1. The nurse is discussing the endocrine system with a class of nursing students. What substance would the nurse label as a hormone? A) Acetylcholine B) Norepinephrine C) Nucleic acid D) Serotonin Ans: B Feedback: A hormone is secreted directly into the bloodstream and travels from the site of production to react with specific receptor sites to cause an action. Norepinephrine, which is a neurotransmitter, is a hormone when it is produced in the adrenal medulla, secreted into circulation, and travels to norepinephrine receptor sites to cause an effect. Acetylcholine and serotonin are neurotransmitters, but are not hormones. Nucleic acid is used to build deoxyribonucleic acid and ribonucleic acid. 2. What organ should the nurse recognize as the coordinating center for the nervous and endocrine responses to internal and external stimuli? A) Hypothalamus B) Pituitary gland C) Thyroid gland D) Parathyroid gland Ans: A Feedback: The hypothalamus is the coordinating center for the nervous and endocrine responses to internal and external stimuli. The pituitary, thyroid, and parathyroid glands all play an important role in maintaining homeostasis, but they do not connect the nervous and endocrine systems. 3. What criteria can the nurse use to describe all hormones? Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) A) They are produced in very large amounts. B) They circulate until they are used by receptor cells. C) They are secreted directly into the tissue where they react. D) They travel in the blood to specific receptor sites. Ans: D 553 Feedback: Hormones are chemicals that are produced in the body and meet specific criteria. All hormones are produced in very small amounts and are secreted directly into the bloodstream. They travel in the blood to specific receptor sites throughout the body and are immediately broken down. 4. The nurse is caring for a patient with abnormal calcium levels. What thyroid hormone does the nurse expect this will impact? A) Aldosterone B) Calcitonin C) Erythropoietin D) Insulin Ans: B Feedback: Calcitonin is produced and secreted by the thyroid gland in direct response to serum calcium levels. Aldosterone is an adrenocorticoid hormone that is released in response to adrenocorticotropic hormone. Erythropoietin is released by the juxtaglomerular cells in the kidney in response to decreased pressure or decreased oxygenation of the blood flowing into the glomerulus. Insulin is produced by the pancreas in response to varying blood glucose levels. 5. The nurse explains the end result of the hypothalamus in regulating the central nervous system (CNS), autonomic nervous system (ANS), and endocrine system is what? A) Regulation of the negative feedback system B) Creation of a diurnal rhythm Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) C) Maintenance of homeostasis D) Production of prolactin-inhibiting factor (PIF) Ans: C 554 Feedback: The hypothalamus maintains internal homeostasis by sensing blood chemistries and by stimulating or suppressing endocrine, autonomic, and CNS activity. In essence, it can turn the ANS and its effects on or off. The negative feedback system is one way homeostasis is maintained. When the hypothalamus senses a need for a particular hormone, it secretes a releasing factor directly into an area such as the anterior pituitary. This causes the area to produce a hormone. When the hypothalamus senses a rising level of the hormone it stops secreting the releasing factor, which decreases the hormone production. When this occurs the hypothalamus senses the falling hormone level and the releasing factor is secreted again. This process is how the hormone level is maintained. Diurnal rhythm refers to the release of hormones at various times of the day. PIF, produced by the hypothalamus, acts as a regulator to shut off production of hormones when levels become too high. 6. While caring for a diabetic patient, the nurse explains that normally insulin is produced by the pancreas and does what when reacting with the human cell? A) Metabolizes glucose B) Allows water to enter the cell C) Alters cellular messenger ribonucleic acid (RNA) D) Changes the cell permeability to glucose Ans: D Feedback: Insulin reacts with specific receptor sites on the cell membrane to change the cell’s permeability to glucose to allow glucose to enter the cell. It does not affect water transport or messenger RNA. Insulin does not metabolize glucose but rather helps it move into the cell where it supplies energy for cellular activity. 7. What hormone enters the cell and reacts with a receptor inside the cell to change messenger ribonucleic acid and affect the cell’s function? A) Estrogen B) Insulin C) Calcitonin Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) D) Thyroid-stimulating hormone Ans: A 555 Feedback: Estrogen enters the cell and reacts with a receptor site inside of the cell to make changes and produce an action. This does not happen quickly, and it may take months to years to produce the changes. Estrogen, calcitonin, and thyroid-stimulating hormone react with specific receptor sites on the cell membrane to stimulate change and action within the cell. 8. The patient’s body modulates pain perception as a result of the production of what in the intermediate lobe of the pituitary gland? A) Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) B) Endorphins C) Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) D) Oxytocin Ans: B Feedback: Endorphins and enkephalins are produced by the intermediate lobe of the pituitary gland. Oxytocin and ADH are produced by the posterior pituitary gland, and ACTH is produced by the anterior pituitary gland. 9. The nurse explains the purpose of the negative feedback system used by the endocrine system is what? A) To change the environment of the pituitary gland B) To regulate hormone release C) To maintain hormone concentration at a certain level D) To control the action of hormones Ans: C Feedback: Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 556 The negative feedback system is a control system in which increasing levels of a hormone lead to decreased levels of releasing and stimulating hormones, leading to decreased hormone levels, which stimulates the release of releasing and stimulating hormones; it allows tight control of the endocrine system. It does not involve changing the environment or control the action of hormones. 10. Melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH) released from the anterior pituitary is important in humans because of its suspected ability to do what? A) Block the perception of pain B) Change the color of skin in some environments C) Stimulate fat mobilization D) Stimulate nerve growth and development Ans: D Feedback: MSH might be important for nerve growth and development in humans. Animals use MSH to change skin color as part of protective camouflage, but it does not have this effect in humans. Lipotropins stimulate fat mobilization. Endorphins and enkephalins are hormones that block the perception of pain. 11. The nurse is caring for a patient diagnosed with a condition resulting in inadequate production of cholecystokinin. What would the nurse expect to find when assessing this patient? A) Elevated serum sodium and reduced serum potassium levels B) Decreased bowel sounds C) Increased numbers of red blood cells D) Increased serum calcium levels Ans: B Feedback: Cholecystokinin is secreted by the intestine and decreases gastric movement resulting in diminished bowel sounds as well as stimulation of bile and pancreatic juice secretion. Aldosterone causes sodium retention and potassium excretion. Erythropoietin increases red blood cell production. Parathyroid hormone causes an increase in serum calcium levels. 12. A group of nursing students are developing a presentation on hormones. What hormone will the Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 557 students’ presentation identify as regulating the metabolic rate and influencing the growth and development of the body? A) Parathyroid hormone or parathormone B) Thyroid hormone C) Cortisol D) Insulin Ans: B Feedback: Thyroid hormone regulates the metabolic rate of the body and greatly influence growth and development. Parathormone, cortisol, and insulin do not regulate the metabolic rate or influence growth and development. 13. The patient’s anterior pituitary hormone secretion is impacted by time of day and activity level, which the nurse assesses as what? A) Diurnal rhythm B) Physiological rhythm C) Circadian rhythm D) Biannual rhythm Ans: A Feedback: The anterior pituitary hormones are released in a rhythmic manner into the bloodstream. Their secretion varies with time of day (often referred to as diurnal rhythm) or with physiological conditions, such as exercise or sleep. A biannual rhythm would be twice a year. Circadian rhythm is indicated by when the patient prefers to sleep or wake, such as those who describe themselves as morning people. There is no such thing as a physiological rhythm. 14. Some hormones react with specific receptor sites on a cell membrane and stimulate what? A) Meiosis B) Cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) C) Increase in hormonal inactivity D) Decrease in hormonal activity Ans: B 558 Feedback: Some hormones react with specific receptor sites on a cell membrane to stimulate the nucleotide cAMP within the cell to elicit an effect. Hormones that react with specific receptor sites do not stimulate miosis, or a change in amount of hormonal activity, either an increase or decrease, which would be regulated by a negative feedback mechanism. 15. Estrogen enters the cell and reacts with a receptor site. What is the final result of this reaction? A) Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is affected. B) Ribonucleic acid enters the cell nucleus. C) Alteration in cellular function D) Changes messenger RNA Ans: C Feedback: Estrogen enters the cell and reacts with a receptor site inside the cell to change messenger RNA, which enters the cell nucleus to affect cellular DNA, and the final result is an alteration in the cell’s function. 16. The nurse is preparing a class on the endocrine system for students. What benefit is served by the positioning of the hypothalamus in the brain? (Select all that apply.) A) Close to other important areas of the brain B) Able to influence and be influenced by emotions and thoughts C) Poorly protected by the bloodbrain barrier D) Floats within ventricles of the brain E) Protected from the limbic system Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) Ans: 559 A, B, C Feedback: Situated at the base of the forebrain, the hypothalamus receives input from virtually all other areas of the brain, including the limbic system, cerebral cortex and the special senses that are controlled by the cranial nerves: smell, sight, touch, taste, hearing. Because of its positioning, the hypothalamus is able to influence, and be influenced by, emotions and thoughts. The hypothalamus also is located in an area of the brain that is poorly protected by the bloodbrain barrier, so it is able to act as a sensor to various electrolytes, chemicals, and hormones that are in circulation and do not affect other areas of the brain. It does not float within the ventricles of the brain, and it is located to allow input from the limbic system. 17. The nurse is caring for a pregnant patient. What hormone must be secreted to cause uterine contractions? A) Oxytocin B) ADHD C) Estrogen D) Enkephalins Ans: A Feedback: The pituitary is made up of three lobes: anterior, intermediate, and posterior. The posterior lobe stores two hormones produced by the hypothalamus, ADH and oxytocin. Oxytocin stimulates uterine smooth muscle contraction in late phases of pregnancy and also causes milk release or let down reflex in lactating women. The posterior lobe does not store estrogen or enkephalins. ADHD (i.e., attention deficit hyperactivity disorder is a disease process, not a hormone. 18. What receptors in the body stimulate the hypothalamus to release antidiuretic hormone (ADH)? A) Diuretic receptors B) Osmoreceptors C) Alpha receptors D) Nicotinic receptors Ans: B Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 560 Feedback: The osmoreceptors in the hypothalamus stimulate the release of ADH. There is no such thing as a diuretic receptor. Alpha receptors are associated with the sympathetic nervous system and nicotinic receptors are associated with the parasympathetic nervous system. 19. What are the areas of the hypothalamus called that are specifically sensitive to certain stimuli to regulate body functions? A) Nodes B) Lobes C) Neurocenters D) Epicenters Ans: C Feedback: The hypothalamus has various neurocentersareas specifically sensitive to certain stimulithat regulate various body functions, including body temperature, thirst, hunger, water retention, blood pressure, respiration, reproduction, and emotional reactions. Areas of special sensitivity in the hypothalamus are not called depots, lobes, or epicenters. 20. The hypothalamus receives input from virtually all other areas of the brain. Where is the hypothalamus located? A) Behind the frontal lobe B) In the substantia nigra C) At the base of the pons D) At the base of the forebrain Ans: D Feedback: Situated at the base of the forebrain, the hypothalamus receives input from virtually all other areas of the brain, including the limbic system and the cerebral cortex. Therefore, the other options are incorrect. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 21. 561 The hypothalamus fine-tunes and regulates the release of hormones using what process? A) Negative feedback systems B) Indirect feedback systems C) Direct local input D) Direct release of hormones into bloodstream Ans: A Feedback: The fine-tuning and regulation of hormone release through the hypothalamus is often regulated by a series of negative feedback systems. Other options are incorrect answers as they are distracters for this question. 22. To better understand the negative feedback system, what might the nurse compare it with? A) The actions of use and disuse B) The law of supply and demand C) The concept of need and use D) The contract of give and take Ans: B Feedback: A negative feedback system works much like the law of supply and demand in business. In business, when the supply of a product is adequate, production of that product will be cut back because demand is not there. Other options are distracters for this question. 23. When the hypothalamus senses a need for thyroid hormone, where does it secrete the releasing factor thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH)? A) Directly into the posterior pituitary B) Directly into the bloodstream C) Directly into the anterior pituitary Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) D) Directly into the thyroid gland Ans: C 562 Feedback: When the hypothalamus senses a need for a particular hormone, it secretes TRH directly into the anterior pituitary. Other options, therefore, are incorrect. 24. What hormones does the pancreas produce and release that aids in the body’s varying blood glucose levels? (Select all that apply.) A) Insulin B) Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) C) Glucagon D) Somatostatin E) Amylase Ans: A, C, D Feedback: Hormones other than stimulating hormones are also released in response to stimuli. For example, the endocrine pancreas produces and releases insulin, glucagon, and somatostatin from different cells in response to varying blood glucose levels. ADH does not respond to blood glucose levels but controls sodium and potassium levels. Amylase is an enzyme released by the pancreas. 25. The hypothalamicpituitary axis (HPA) functions through one of two processes to regulate hormone production. One of these processes is the negative feedback system. What is the other process? A) Direct use of inhibiting factors B) Indirect use of feedback loop C) Direct use of releasing factors D) Indirect use of stimulating factors Ans: A Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 563 Feedback: The HPA functions through negative feedback loops or the direct use of inhibiting factors to constantly keep particular hormones regulated. Other options are incorrect because hormones are not regulated by feedback loops, releasing factors, or stimulating factors. 26. The nurse administers an exogenous hormone to the patient. How does the nurse’s action impact the endocrine system? (Select all that apply.) A) May decrease exogenous hormone levels B) May increase hormone levels in the body C) May stop production of releasing and stimulating hormones D) May lead to a decrease in the normal production of the hormone E) May increase the endogenous hormone levels Ans: B, C, D Feedback: Supplying an exogenous hormone may increase the hormone levels in the body, but then might affect the hypothalamicpituitary axis (HPA) to stop production of releasing and stimulating hormones, leading to a decrease in the body’s normal production of the hormone. Supplying exogenous hormone will not cause a decrease in exogenous hormone levels nor will it cause an increase in endogenous hormone levels. 27. The nursing instructor is talking with her clinical group about the hypothalamicpituitary axis (HPA) and what happens when a need arises to interact with the total system. The instructor explains that this can create what? A) A negative feedback system B) Homeostasis C) Complications D) Maximum efficiency Ans: C Feedback: Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 564 This system (i.e., the HPA) also can create complications, especially when a need exists to override or interact with the total system, as is the case with replacement therapy or treatment of endocrine disorders. Interactions with the total system cannot create a negative feedback system, homeostasis, or maximum efficiency. The other options are incorrect. 28. What is the connecting link between the nervous system and the endocrine system? A) Hypothalamus B) Thalamus C) Medulla oblongata D) Posterior pituitary Ans: A Feedback: The main connecting link between the nervous system and the endocrine system is the hypothalamus, which responds to nervous system stimulation by producing hormones. The thalamus and medulla oblongata are part of the nervous system and the posterior pituitary is part of the endocrine system but none of these represents a link between the two systems. 29. When the student develops a poster of the endocrine system, what gland will be excluded because it is not classified as a major organ of the endocrine system? A) Hypothalamus B) Pituitary C) Thyroid D) Gallbladder Ans: D Feedback: The gallbladder is not part of the endocrine system and does not secrete hormones. All other options are organs of the endocrine system. 30. A) What is a releasing hormone? Chemical that interacts with a hormone to activate it Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) B) Chemical released by the body to stimulate the hypothalamus C) Chemical released by the body organs to stimulate the pituitary D) Chemical released by the hypothalamus into the anterior pituitary Ans: B 565 Feedback: Releasing hormones or factors are chemicals released by the hypothalamus into the anterior pituitary to stimulate the release of anterior pituitary hormones. The releasing hormone does not activate a hormone but stimulates its production. It does not stimulate the glands (hypothalamus or pituitary) but rather stimulates release of an anterior pituitary hormone. 31. The nurse overhears a physician talking about the master gland. What gland does the nurse recognize is being discussed? A) The pituitary gland B) The hypothalamus gland C) The thyroid gland D) The parathyroid gland Ans: B Feedback: Scientists now designate the hypothalamus as the master gland because it has even greater direct regulatory effects over the neuroendocrine system, including stimulation of the pituitary gland to produce its hormones. The pituitary gland was formerly considered the master gland, but new research has helped scientists realize it is the hypothalamus that is the master gland. 32. The nurse administers a thyroid hormone replacement pill to the patient. What effect will this action have on the patient’s production of thyroid hormones? A) Stimulates the gland that normally produces that hormone B) Stops production of releasing and stimulating hormones C) Initiates the negative feedback system Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) D) Stimulates the hypothalamicpituitary axis Ans: B 566 Feedback: Supplying an exogenous hormone may increase the hormone levels in the body, but it then may affect the hypothalamicpituitary axis (HPA) to stop production of releasing and stimulating hormones, leading to a decrease in the body’s normal production of the hormone. It does not stimulate the gland or the HPA. It also does not trigger a negative feedback response. 33. What hormones do not have a target organ to produce hormones and cannot be regulated by the same feedback as other hormones? A) Growth hormone and prolactin B) Estrogen and progesterone C) Erythropoietin and renin D) Insulin and glucagon Ans: A Feedback: Two of the anterior pituitary hormones (i.e., growth hormone and prolactin) do not have a target organ to produce hormones and so cannot be regulated by the same type of feedback mechanism. Estrogen and progesterone have the uterus, ovaries, and breast, as their target organs. The target organs for erythropoietin is the bone marrow, for renin it is the arteries, and insulin and glucagon come from the pancreas to stimulate cells to metabolize glucose and regulate serum glucose levels 34. What qualifies the hypothalamus to be called the master gland? A) It regulates the nervous and endocrine responses to stimuli. B) It stimulates the pituitary gland to control the endocrine system. C) It combines the nervous and endocrine system to work together. D) It produces all of the releasing hormones in the body. Ans: B Feedback: Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 567 The hypothalamus gland is called the master gland of the neuroendocrine system because it regulates both nervous and endocrine responses to internal and external stimuli. There is more to the hypothalamus than just its stimulation of the pituitary gland or its production of releasing hormones that leads it to be considered the master gland. The neuroendocrine system combines the nervous and endocrine systems to work closely together to maintain regulatory control and homeostasis in the body. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 568 Chapter 35 - Hypothalamic and Pituitary Agents 1. A patient suspected of having Cushing’s disease comes to the clinic. What drug might the nurse administer to test for adrenal function and responsiveness? A) Corticotropin B) Menotropins C) Thyrotropin alfa D) Chorionic gonadotropin Ans: A Feedback: Corticotropin (ACTH) and cosyntropin are used for diagnostic purposes to test adrenal function and responsiveness. Menotropin is a purified preparation of gonadotropins and is used as a fertility drug. Thyrotropin alfa is used as adjunctive treatment for radioiodine ablation of thyroid tissue remnants in patients who have undergone a near-total to total thyroidectomy for well-differentiated thyroid cancer and who do not have evidence of metastatic thyroid cancer. Chorionic gonadotropin acts like luteinizing hormone and stimulates the production of testosterone and progesterone. 2. A nurse is working at a fertility clinic. Today she is administering ganirelix acetate (Antagon) to a woman participating in a fertility research program. By what route is this drug administered? A) Orally B) Subcutaneously C) Intramuscularly D) IV Ans: B Feedback: Ganirelix acetate (Antagon) is administered subcutaneously and cannot be administered orally, intramuscularly, or intravenously. 3. A patient is taking leuprolide (Lupron) to treat prostatic cancer. The nurse caring for this patient is careful to monitor for what? Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) A) Diarrhea B) Urinary retention C) Peripheral edema D) Increased appetite Ans: C 569 Feedback: Peripheral edema is an identified adverse effect of leuprolide therapy. Constipation not diarrhea; urinary frequency not urinary retention; and anorexia not increased appetite are also identified adverse effects. 4. After administering somatropin (Saizen) to an 11-year-old patient with growth failure, what outcome would indicate that the drug should be stopped? A) Early sexual development B) Thyroid overactivity C) Closure of the epiphyses in long bones D) Gynecomastia Ans: C Feedback: Closure of the epiphyses is a sign that the drug should be stopped. Early sexual development, thyroid overactivity, and gynecomastia would not be associated with this drug. 5. The nurse administers desmopressin (DDAVP) to the patient to treat diabetes insipidus. What assessment finding would indicate to the nurse that the desmopressin is producing a therapeutic effect? A) Decreased urine output B) Decreased water reabsorption C) Increased plasma osmolarity Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) D) Decreased blood volume Ans: A 570 Feedback: Desmopressin produces its antidiuretic activity in the kidneys, causing the cortical and medullary parts of the collecting duct to become permeable to water, thereby increasing water reabsorption and decreasing urine formation. These activities reduce plasma osmolarity and increase blood volume. 6. A patient with diabetes insipidus is taking desmopressin (DDAVP). He or she is complaining of drowsiness, lightheadedness, and headache. What does the nurse suspect that he is experiencing? A) An allergic reaction B) Dehydration C) Depression D) Water intoxication Ans: D Feedback: The adverse effects associated with the use of desmopressin include water intoxication (drowsiness, light-headedness, headache, coma, convulsions) related to the shift to water retention and resulting electrolyte imbalance. An allergic reaction, dehydration, or depression would not be associated with these symptoms and desmopressin. 7. What drug would the nurse expect to administer to an AIDS patient with cachexia? A) Bromocriptine (Parlodel) B) Somatropin (Saizen) C) Desmopressin (DDAVP) D) Leuprolide (Lupron) Ans: B Feedback: Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 571 Indications for somatropin therapy include cachexia, long-term treatment of children with growth failure associated with various deficiencies, girls with Turner’s syndrome, AIDS-related wasting, growth hormone deficiency in adults, and treatment of growth failure in children of small gestational age who do not achieve catch-up growth by 2 years of age. Bromocriptine mesylate is indicated for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease, hyperprolactinemia associated with pituitary adenomas, female infertility associated with hyperprolactinemia, and acromegaly; and short-term treatment of amenorrhea or galactorrhea. Desmopressin is indicated for the treatment of neurogenic diabetes insipidus and hemophilia A. Leuprolide is used as an antineoplastic agent for treatment of specific cancers. 8. What symptoms will the nurse instruct the patient taking octreotide (Sandostatin) to report to the health care provider? A) Abdominal pain B) Alteration in consciousness C) Changes in vision D) Muscle cramps Ans: A Feedback: Octreotide and lanreotide have commonly been associated with the development of acute cholecystitis, cholestatic jaundice, biliary tract obstruction, and pancreatitis, which would present with abdominal pain, so patients should be taught to report this symptom. The drug is not associated with alteration in consciousness, changes in vision, or muscle cramps. 9. The nurse has been caring for a child who has been receiving growth hormone therapy for several years. When the child returns for evaluation following a sudden growth spurt, what nursing diagnosis will the nurse add to the plan of care? A) Disturbed body image B) Deficient knowledge regarding drug therapy C) Imbalanced nutrition: Less than body requirements related to metabolic changes D) Risk for disproportionate growth Ans: C Feedback: A child who is taking growth hormone may experience sudden growth, which will require increased nutritional intake, so it is important to include nutritional needs in the plan of care. More than likely an Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 572 increase in caloric intake and nutrients will be necessary. Most children who are small for their age see growth as a positive thing and not a disturbed body image. After taking the drug for several years, the patient should have received adequate teaching from the nurse ot make deficient knowledge unlikely. The child should not be at risk for, but have a diagnosis of, disproportionate growth as the reason for taking the medication. 10. The nurse receives an order to administer leuprolide 5 mcg/kg subcutaneously to a child with precocious puberty. The child weighs 30 kg. What is the correct dosage for this child? A) 150 mcg B) 6 mcg C) 68 mcg D) 330 mcg Ans: A Feedback: Multiply the child’s weight times the mg/kg: 30 × 5 = 150 mcg/dose. 11. The nurse is caring for a patient with infertility related to hyperprolactinemia. What drug would the nurse recognize was ordered to treat this problem? A) Bromocriptine mesylate B) Somatropin C) Leuprolide D) Desmopressin Ans: A Feedback: Bromocriptine mesylate is indicated for the treatment of female infertility associated with hyperprolactinemia. Somatropin is indicated for the treatment of growth failure, Turners syndrome, AIDS wasting and cachexia, and growth hormone deficiency in adults. Leuprolide is used as antineoplastic agent for treatment of specific cancers and for treatment of endometriosis and precocious puberty that results from hypothalamic activity. Desmopressin is used for the treatment of neurogenic diabetes insipidus, von Willebrand’s disease, hemophilia; and is currently being studied for the treatment of chronic autonomic failure. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 12. 573 A child weighing 14.5 kg has von Willebrand’s disease. How much desmopressin (DDAVP) should be administered? A) 4.4 mcg B) 9.6 mcg C) 10.3 mcg D) 21.1 mcg Ans: A Feedback: The normal dosage of desmopressin used to treat von Willebrand’s disease is 0.3 mcg/kg. Multiply this dosage times the child’s weight: 14.5 kg × 0.3 g = 4.4 g. 13. What is the purpose of releasing hormones secreted by the hypothalamus? A) Stimulating or inhibiting release of hormones from the pituitary B) Stimulating organs within the body to secrete hormones C) Allowing the secretion of hormones from the hypothalamus D) Stimulating other glands to release hormones Ans: A Feedback: The hypothalamus uses various hormones or factors to either stimulate or inhibit the release of hormones from the anterior pituitary. These do not stimulate other organs, the hypothalamus, or other glands to release hormones. 14. A 48-year-old patient with acromegaly is not a candidate for other therapy. What medication, administered subcutaneously, would the nurse caring for the patient expect the physician to order? A) Gonadorelin hydrochloride (Factrel) B) Octreotide (Sandostatin) C) Nafarelin (Synarel) Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) D) Gonadorelin acetate (Lutrepulse) Ans: B 574 Feedback: Octreotide (Sandostatin) is a treatment for acromegaly in adults who are not candidates for, or cannot tolerate, other therapy. Gonadorelin hydrochloride, nafarelin, and gonadorelin acetate are not indicated for treating acromegaly. 15. A patient is brought to the emergency department after a motor vehicle accident. The patient is hemorrhaging, indicating that which hormone is being secreted to restore blood volume? A) Growth hormone (GH) B) Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) C) Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) D) Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) Ans: C Feedback: ADH possesses antidiuretic, hemostatic, and vasopressor properties. During hemorrhage, GH, FSH and ACTH are not involved in blood volume restoration. 16. The nurse administers somatropin to a child with impaired growth due to a deficiency of endogenous growth hormone during what period of growth and development? A) Before the start of elementary school B) Any time before age 18 C) Before the child reaches 5 feet in height D) Before epiphyses close Ans: D Feedback: Somatropin is contraindicated in the presence of closed epiphyses so the drug can be given at any time Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 575 before closure of the epiphyses. Age and height are not an indication impacting when the drug is given so long as the epiphyses remain open. 17. The nurse would teach a patient receiving octreotide for acromegaly of the importance of baseline and periodic what? A) Ultrasound evaluation of the gallbladder B) Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain C) Serum glucose levels D) Complete blood counts Ans: A Feedback: Arrange for baseline and periodic ultrasound evaluation of the gallbladder for patients receiving octreotide because common adverse effects of the drug are acute cholecystitis, cholestatic jaundice, biliary tract obstruction, and pancreatitis. A patient taking octreotide does not need baseline and periodic MRIs of the brain, serum glucose levels, or complete blood counts. 18. The nurse is caring for a patient with neurogenic diabetes insipidus and administers what drug to treat the condition? A) Dexamethasone (Decadron) B) Desmopressin (DDAVP, Stimate) C) Methylprednisolone (Solu-Medrol) D) Physostigmine (Antilirium) Ans: B Feedback: Synthetic preparations of antidiuretic hormone (ADH), which are purer and have fewer adverse effects, are used to treat diabetes insipidus. Only one ADH preparation is currently available, desmopressin. Dexamethasone, methylprednisolone, and physostigmine would not be indicated for treatment of this disorder. 19. The nurse transcribes an order for menotropin (Pergonal), which will be administered to have what effect? Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) A) Promote development of secondary sex characteristics B) Induce ovulation C) Promote bone growth D) Treat diabetes insipidus Ans: B 576 Feedback: Menotropin (Pergonal) is used as fertility drug to stimulate ovulation and spermatogenesis. Pergonal is not used to promote the development of secondary sex hormones, to promote bone growth, or to treat diabetes insipidus. 20. The nurse administers desmopressin to treat a patient with diabetes insipidus. Assessment of what laboratory studies would indicate the drug is working? A) Increased serum sodium levels B) Increased red blood cell count C) Decreased urine specific gravity D) Reduced urine glucose levels Ans: A Feedback: Patients with diabetes insipidus (DI) produce large amounts of dilute urine with a decrease in serum sodium levels. Administering desmopressin would reduce urine output and allow sodium levels to rise. Urine specific gravity would increase as the urine production slows and urine becomes more concentrated. There is no impact on red blood cell production with diabetes insipidus or its treatment. The urine of a patient with DI does not contain glucose. 21. The nurse would administer desmopressin (DDAVP) cautiously, with careful monitoring, to the patient with what co-morbidity? (Select all that apply.) A) Hyponatremia B) Asthma C) Severe renal dysfunction Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) D) Gastrointestinal (GI) disease E) Epilepsy Ans: A, B, E 577 Feedback: Caution should be used with any known vascular disease because of its effects on vascular smooth muscle, epilepsy, asthma, and with hyponatremia, which could be exacerbated by the effects of the drug. The drug is contraindicated and should not be used in patients with severe renal dysfunction. GI disease is not a caution or contraindication. 22. The nurse is caring for a 25-year-old female patient who is receiving chorionic gonadotropin alfa. What would be an appropriate nursing diagnosis for this patient? A) Anxiety related to injection of medication B) Acute pain related to need for injections C) Imbalanced nutrition: More than body requirements D) Evaluate effectiveness of the teaching plan Ans: B Feedback: Nursing diagnoses related to drug therapy might include acute pain related to need for injections. Not all patients are anxious at the thought of an injection so more information would be needed. The patient is more likely to have reduced nutritional intake because of gastrointestinal (GI) adverse effects. Evaluating the effectiveness of the teaching plan is not a nursing diagnosis. 23. When providing patient teaching to the family of a 12-year-old child receiving Somatropin, the nurse stresses the need to notify prescriber if what manifestation occurs? A) Severe hip or knee pain B) Development of a bruise C) Severe hypertension D) Tachycardia Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) Ans: 578 A Feedback: The adverse effects that most often occur when using a growth hormone (GH) include the development of antibodies to GH and subsequent signs of inflammation and autoimmune-type reactions, such as swelling and joint pain, and the endocrine reactions of hypothyroidism and insulin resistance. It would not be necessary to notify the physician for development of a bruise. The health care provider should always be notified if a patient develops severe hypertension or tachycardia but this would not be related to administration of somatropin so it would not be included in drug teaching. 24. What medication would the nurse expect the physician to prescribe as palliative treatment for advanced prostate cancer? A) Histrelin (Vantas) B) Ganirelix (Antagon) C) Nafarelin (Synarel) D) Somatropin (Nutropin) Ans: A Feedback: Histrelin (Vantas) is used to provide palliative treatment for advanced prostate cancer. Nafarelin (Synarel) is used for treatment of endometriosis and precocious puberty; Ganirelix (Antagon) is used for inhibition of premature luteinizing hormone surge in women undergoing controlled ovarian stimulation as part of a fertility program; Somatropin (Nutropin) is used for treatment of children with growth failure due to lack of growth hormone or to chronic renal failure. 25. A 4-year-old is tested and found to have deficient growth hormone (GH). What does this condition cause? A) Gigantism B) Acromegaly C) Syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone (SIADH) D) Dwarfism Ans: D Feedback: Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) GH deficiency in children results in short stature (dwarfism). Excess production of GH results in gigantism and acromegaly. SIADH is caused by excessive production of antidiuretic hormone. 26. What hormone does the posterior pituitary gland store and release? A) Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) B) Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) C) Growth hormone (GH) D) Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) Ans: A Feedback: The posterior pituitary stores two hormones produced in the hypothalamus: ADH, also known as vasopressin and oxytocin. The posterior pituitary does not store FSH, GH, or TSH. 27. For what purposes might the nurse administer a hypothalamic hormone? (Select all that apply.) A) Diagnostic testing B) Synthesis of growth factors C) Prevent aging D) Treating some forms of cancer E) Adjuncts in fertility programs Ans: A, D, E Feedback: The hypothalamic hormones are not all available for pharmacological purposes. Those available are used mostly for diagnostic testing, for treating some forms of cancer, or as adjunctive therapies in fertility programs. They would not be used to prevent aging or for the synthesis of growth factor. 28. The nurse is caring for a patient diagnosed with syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone (SIADH) which the nurse recognizes is caused by what? 579 Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) A) Excessive secretion of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) B) Insufficient secretion of ADH C) Excessive secretion of androgens D) Insufficient secretion of antidepressants Ans: A 580 Feedback: SIADH occurs with excessive secretion of ADH. Insufficient secretion of ADH causes diabetes insipidus. ADH is not related to androgenic or antidepressant actions. 29. The nurse explains the role of the posterior pituitary gland is to do what? A) It synthesizes different hormones. B) It makes two hormones. C) It stores hormones. D) It controls most of the metabolic functions of the body. Ans: C Feedback: The posterior pituitary stores two hormones produced in the hypothalamus: antidiuretic hormone (ADH, also known as vasopressin) and oxytocin. The posterior pituitary is anatomically an extension of the hypothalamus and is composed mainly of nerve fibers. Although it does not manufacture any hormones itself, it stores and releases hormones synthesized in the hypothalamus. The hypothalamus of the brain and the pituitary gland interact together to control most metabolic functions of the body and to maintain homeostasis. 30. The nurse is caring for a patient receiving tolvaptan and digoxin. What drugdrug interaction will the nurse assess for when reviewing this patient’s laboratory results? A) Elevated serum sodium levels B) Reduced digoxin levels C) Elevated serum potassium levels Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) D) Tolvaptan toxicity Ans: C 581 Feedback: Tolvaptan should be used with care with digoxin, which could cause hyperkalemia, so the nurse must carefully monitor serum potassium levels. The combination of drugs would not cause reduced digoxin levels or tolvaptan toxicity. The indication for administering tolvaptan would be to treat hyponatremia, so an elevation in serum sodium levels to normal range would be an indication the drug was working but would not be a result of a drug-drug interaction. 31. The nurse is caring for a patient who has been receiving long-term growth hormone treatment to stimulate growth. What diagnostic testing would the nurse expect to see ordered as a standard part of the treatment plan? (Select all that apply.) A) Blood sugar level B) Serum electrolytes C) X-ray of the long-bones D) Nasal examination E) Bone density studies Ans: A, B, C Feedback: Periodic radiography of the long bones, as well as monitoring of blood sugar levels and electrolytes, should be a standard part of the treatment plan for children who receive any of the hypothalamic or pituitary agents. There would be no indication for nasal assessment because growth hormone is not administered nasally. Bone density would not be impacted by these drugs. 32. What is the nurse’s priority assessment when administering hypothalamic or pituitary agents to older adults? A) Hydration and nutrition B) Balance and fall risk C) Cognitive function D) Urinary incontinence Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) Ans: 582 A Feedback: Older adults may be more susceptible to the imbalances associated with alterations in the endocrine system. They should be evaluated periodically during treatment for hydration and nutrition, as well as for electrolyte balance. These drugs would not be expected to impact balance, cognitive function, or to cause incontinence so these would not be the priority assessment. 33. The mother of a child awaiting a renal transplant asks the nurse whether growth hormone could be effective for her child. What is the nurse’s best response? A) Growth hormone is only used to treat short stature in children who do not produce enough growth hormone naturally. B) Growth hormone has been used successfully in children with renal failure but there is a lot to consider and you should talk to the doctor about it. C) Administration of growth hormone requires frequent injections so it would be cruel for a child with existing medical problems. D) You do not want to use growth hormone if you do not have to. What would make you even think of something like that? Ans: B Feedback: Growth hormone therapy is used with children with renal failure but the decision carries risks as well as benefits so it is important for the mother to talk to the child’s primary physician and nephrologist to get recommendations for its safety. It is not just used in children with inadequate growth hormone secretion. It is never correct for the nurse to castigate the mother for a question so telling her it would be cruel or that she should not use it if it is not essential would destroy the patient/nurse relationship. 34. The nurse is asked to explain how to administer somatropin (Saizen) to the mother of a 6-year-old. How would the nurse explain how this drug is administered? A) It requires only a very small needle and doesn’t hurt much at all. B) There will no longer be any need to rotate sites because it uses a needleless system. C) This system will be used until your son gets older and is more tolerant of needles. D) This delivers a fine mist through the skin without needles and far less discomfort. Ans: D Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 583 Feedback: Saizen uses the cool.click delivery system, which is a neon-colored, needle-free system that delivers the drug through the skin using a fine mist. Tests have shown a bioequivalency of this method with standard injection techniques, and the young patients who must use this drug are much less resistant to the dosing. There are no needles but site of injection still require rotation to avoid skin damage. The child does not have to go back to a needle system when he gets older. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 584 Chapter 36 - Adrenocortical Agents 1. The nurse administers fludrocortisone (Florinef) to a patient diagnosed with salt-losing adrenogenital syndrome and then assesses for what therapeutic action? A) Development of hypokalemia and elevated serum glucose level B) An increase in sodium and water reabsorption and potassium excretion C) Headache, edema, weakness, arrhythmias, and hypertension D) Sodium and water depletion along with potassium retention Ans: B Feedback: Fludrocortisone’s therapeutic effects include an increase in sodium and water reabsorption with potassium excretion. Headache, edema, weakness, arrhythmias, and hypertension are adverse, and not therapeutic, effects. Hypokalemia is possible but glucose levels should not be impacted. 2. When developing a plan of care for the patient receiving a glucocorticoid, what nursing diagnosis would be of highest priority? A) Deficient fluid volume related to water retention B) Risk for injury related to muscle weakness C) Imbalanced nutrition: less than body requirements D) Risk for infection related to immunosuppression Ans: D Feedback: Risk for infection related to immunosuppression would be the appropriate nursing diagnosis because steroids suppress the immune system, which puts the patient at risk for infection. Nutritional imbalance is more likely to be more than body requirements than less than body requirements. Excess fluid volume is more appropriate than deficient fluid volume. Glucocorticoids are not associated with muscle weakness. 3. What glucocorticoids could the nurse only administer orally? Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) A) Cortisone (Cortone Acetate) B) Hydrocortisone (Cortef) C) Prednisone (Deltasone) D) Triamcinolone (Aristocort) Ans: C 585 Feedback: Prednisone is available in oral form only and is used for replacement therapy for adrenal insufficiency, and treatment of allergic and inflammatory disorders. Cortisone can be administered orally or intramuscularly and is used for replacement therapy. Hydrocortisone, used for replacement therapy, is administered by the oral, IV, intramuscular, topical, ophthalmic, rectal, and intra-articular routes. Triamcinolone is administered by the oral, intramuscular, inhalant, intra-articular, and topical routes and is used for treatment of allergic and inflammatory disorders and in the management of asthma. 4. The mother asks the nurse for a steroid cream to put on her infant’s diaper rash. What teaching will the nurse provide the mother? (Select all that apply.) A) Topical corticosteroids are very effective treatment for diaper rash. B) Topical corticosteroid application should not be occluded with a diaper. C) Topical corticosteroids should not be applied to open lesions. D) Use of topical corticosteroids should be limited in children. E) Topical corticosteroids should be applied in a thick coat to the rash. Ans: B, C, D Feedback: Topical use of corticosteroids should be limited in children because their body surface area is comparatively large and the amount of the drug absorbed in relation to weight is greater than in an adult. When the medication is used in children, it should be applied sparingly and the area should not be occluded with a diaper. The nurse should not make a judgment nor should he or she allow a patient or family member to dictate a treatment just because he or she wants it. More effective treatments for diaper rash than corticosteroids are available. 5. An older adult patient taking high-dose corticosteroids to treat arthritis requests a pneumonia vaccine. What is the nurse’s best response? Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) A) Pneumonia vaccines are only given if you are at risk for serious pulmonary problems. B) Live virus vaccines cannot be given to people who are significantly immunosuppressed. C) Patients taking corticosteroids are well protected from viruses and do not need vaccines. D) Corticosteroids interact with the pneumococcal vaccine to create serious adverse effects. Ans: B 586 Feedback: Corticosteroids block the inflammatory response and are very helpful in conditions such as arthritis. However, they also block the immune response, making a person immunosuppressed. The vaccine would not be given to this patient because of the increased risk for infection. An older adult would be considered at high risk for pneumonia so getting the vaccine would be encouraged if not for taking corticosteroids. Corticosteroids do not protect against viruses. The vaccine is contraindicated because of risk for infection and not because of a potential drugdrug interaction. 6. A patient who is steroid dependent due to adrenocortical insufficiency calls the clinic and is very upset, telling the nurse of the extreme stress he or she is experiencing right now. What does the nurse expect the health care provider will order concerning his or her medication? A) The dosage may continue as ordered. B) The medication may be discontinued until stress declines. C) The dosage of the medication may be increased. D) The dosage of the medication may be decreased. Ans: C Feedback: The patient’s body will initiate a stress reaction. Normally, activation of the stress reaction can cause release of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) and secretion of the adrenocortical hormones. A patient with adrenocortical insufficiency may not be able to supplement the increased need for ACTH. The stress reaction may block the immune and inflammatory systems, making the body more susceptible to pathogens. Therefore, an increase in medication may be necessary to prevent further adrenal insufficiency and to meet the increased demands for corticosteroids in the body under stress. 7. A) A nurse is providing patient education to a patient who has had corticosteroids prescribed. What drug will the nurse teach the patient to avoid while taking the corticosteroids? Aspirin Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) B) Dimenhydrinate (Dramamine) C) Ibuprofen (Advil) D) Famotidine (Pepcid) Ans: A 587 Feedback: Serum levels and effectiveness may decrease if corticosteroids are combined with salicylates. Dimenhydrinate, ibuprofen, and famotidine have not been found to produce drugdrug interaction. 8. The nurse is caring for a patient with a heightened stress response following a fearful experience. When assessing this patient, what findings will the nurse attribute to this response? (Select all that apply.) A) Elevated serum blood glucose B) Reduced inflammatory response C) Heightened immune response D) Increased blood volume E) Extreme hunger Ans: A, B, D Feedback: The stress response causes an increase in blood volume and a release of glucose for energy. It also slows the rate of protein production and blocks the activities of the inflammatory and immune systems, which reserves energy. This patient is unlikely to be hungry. 9. The nurse is providing patient education to a patient taking a glucocorticoid and advises the patient to take his or her medication at what time of the day? A) At bedtime B) With the noon meal C) At 3:00 PM D) Immediately on awakening in the morning Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) Ans: 588 D Feedback: Glucocorticoids should be taken immediately on awaking in the morning to mimic the normal diurnal pattern. The peak levels of cortisol usually come between 6:00 and 8:00 AM. The levels then fall off slowly and reach a low in the late evening with the lowest levels around midnight. For those patients who work night shifts, the schedule would be changed to accommodate their sleep pattern. Waiting until later in the day could result in sleeplessness. 10. An 8-year-old with asthma has been prescribed triamcinolone (Aristocort). What dosage of medication would the nurse appropriately deliver? A) One inhalation per day B) One inhalation b.i.d. C) Two inhalations every 3 hours D) Two inhalations t.i.d. Ans: D Feedback: Pediatric dosage is individualized based on severity and response. However, children between 6 and 12 years of age are prescribed one to two inhalations t.i.d. or q.i.d. The other options are incorrect based on the recommended dosage. 11. The nurse, caring for a patient experiencing stress, knows that activation of the stress reaction will cause the release of what? A) Glucose B) Aldosterone C) Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) D) Oxytocin Ans: C Feedback: Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 589 Activation of the stress reaction through the sympathetic nervous system bypasses the usual diurnal rhythm and causes release of ACTH and secretion of the adrenocortical hormonesan important aspect of the stress (fight-or-flight) response. Glucose will eventually be released to supply energy, but first ACTH and adrenocortical hormones must stimulate this response. Aldosterone can be released without ACTH stimulation when the blood surrounding the adrenal gland is high in potassium. This is a direct stimulus for aldosterone release. Oxytocin is released to promote the let-down reflex in the lactating woman and to stimulate uterine contractions but is not involved in the stress response. 12. The nurse is developing a plan of care for an 84-year-old diabetic patient who is receiving oral hydrocortisone 40 mg daily for treatment of arthritis. What is this patient’s priority nursing intervention? A) Increasing sodium in diet B) Restricting protein in diet C) Increasing fluids to 2,000 mL/d D) Monitoring blood glucose levels frequently Ans: D Feedback: Caution should be used in patients with diabetes because the glucose-elevating effects disrupt glucose control. More frequent blood sugar monitoring is this patient’s priority intervention. Sodium, protein, and fluid intake do not need to be altered. 13. A patient with adrenal insufficiency has been admitted to the intensive care unit in adrenal crisis. What assessment findings support this diagnosis? (Select all that apply.) A) Physiological exhaustion B) Hypertension C) Fluid shift D) Shock E) Septicemia Ans: A, C, D Feedback: Symptoms of adrenal crisis include physiological exhaustion, hypotension, fluid shift, shock, and even Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 590 death. Hypotension rather than hypertension would be expected. Septicemia is a possible cause of adrenal crisis, not a symptom. 14. The nurse is providing discharge teaching for a patient prescribed prednisone to be taken on alternate days. The patient asks why he cannot take half a pill every day. What is the nurse’s best response? A) To eliminate adverse side effects B) To prolong therapeutic effects C) To prevent steroid tolerance D) To decrease adrenal suppression Ans: D Feedback: Alternate-day maintenance therapy is used with short-acting drugs whenever possible to decrease the risk of adrenal suppression. Alternate-day therapy would not eliminate adverse effects or prolong therapeutic effects. There is no such thing as steroid tolerance. 15. The clinic nurse receives a call from the mother of a 4-year-old child on long-term corticosteroid therapy saying the child woke up with a cold and is pulling on his ear. What instructions will the nurse provide? A) Encourage fluids, monitor his temperature, and he will be better in 3 days. B) Take him to the emergency room (ER) immediately. C) Bring him to the clinic to be seen today. D) Hang up and call 911. Ans: C Feedback: Children receiving long-term therapy should be protected from exposure to infection. Special precautions should be instituted to avoid injury. If injuries or infections do occur, the child should be seen by a primary care provider as soon as possible. There is no need to treat this as an emergency so the mother need not rush the child to the ER or call 911, but she should be encouraged to have the child seen today at the clinic. It would not be appropriate to give home care instructions until he has been seen at the clinic. 16. When doing a shift assessment on the patient, the nurse would report what symptoms as a possible Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 591 adverse effect of intranasal methylprednisolone? (Select all that apply.) A) Headache B) Impaired wound healing C) Epistaxis D) Hypotension E) Nasal irritation Ans: A, B, C, D, E Feedback: Intranasal administration of hydrocortisone can result in headache, nausea, nasal irritation, fungal infections, epistaxis, rebound congestion, perforation of the nasal septum, anosmia, and urticaria. Systemically administered hydrocortisone has many possible adverse effects including impaired wound healing and hypotension, but these would not be likely to be associated with intranasal administration of hydrocortisone. 17. The nurse is providing dietary teaching to the patient on long-term mineralocorticoid therapy and includes what teaching point? A) Decreasing sodium B) Increasing calcium C) Increasing vitamin D D) Increasing potassium Ans: D Feedback: Mineralocorticoids cause sodium and water retention and potassium excretion. These patients benefit from a diet with increased potassium. They would not decrease sodium intake as the drug is often administered for the purpose of increasing serum sodium levels. Calcium and vitamin D intake would be the same for this patient as any other patient of similar age and gender. 18. A) The nurse anticipates an order for a glucocorticoid when caring for a patient with what condition? Hypoglycemia Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) B) Appendicitis C) Arthritis D) Septicemia Ans: C 592 Feedback: Glucocorticoids are indicated for the short-term treatment of many inflammatory disorders, to relieve discomfort, and to give the body a chance to heal from the effects of inflammation. They block the actions of arachidonic acid, which leads to a decrease in the formation of prostaglandins and leukotrienes. Without these chemicals, the normal inflammatory reaction is blocked. Hypoglycemia would more safely be treated with glucose. Appendicitis and septicemia are infections that would contraindicate the use of glucocorticoids because of the immunosuppressant effects of the drugs. 19. The 2-year-old patient with asthma is placed on a short-term dose of prednisone. What important instruction will the nurse provide the patient about this drug? A) Increase intake of carbohydrates. B) The child may receive immunizations while on this drug. C) Do not stop this medication suddenly; you will have to taper dosage gradually. D) Reduce intake of protein until drug therapy is complete. Ans: C Feedback: Prednisone is usually ordered for short-term use with tapering dosage. It is important to instruct the parent to taper doses and to not just stop the drug suddenly when discontinuing from high doses so as to give the adrenal glands a chance to recover and produce adrenocorticoids. This is the priority instruction. Parents should also be told to wait to get the child immunizations until after drug therapy is completed. There is no need to alter carbohydrate or protein intake. 20. When caring for a patient receiving long-term therapy with corticosteroids, the nurse would plan care incorporating interventions aimed at preventing what? A) Allergies B) Inflammation Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) C) Infection D) Anemia Ans: C 593 Feedback: When planning care for a patient taking long-term corticosteroid therapy, the nurse needs to incorporate interventions aimed at reducing risk of infection because the patient’s immune system will be suppressed, which places the patient at increased risk. The nurse would not try to prevent the antiinflammatory effects of the drug. The drug is not associated with causing allergies or anemia. 21. A 66-year-old female patient is on long-term oral glucocorticoid therapy to treat chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. When providing drug teaching, the nurse will inform this patient that she is at particular risk for what? A) Hyponatremia B) Spontaneous fractures C) Respiratory depression D) Ineffective temperature regulation Ans: B Feedback: Only spontaneous fractures are considered an adverse effect of glucocorticoids; this patient would be at increased risk because her age and gender put her at higher risk for osteoporosis, which also has the adverse effect of spontaneous fractures. Long-term glucocorticoid therapy is not associated with hyponatremia, respiratory depression, or ineffective temperature regulation. 22. The nurse provides teaching to a patient with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease who has been prescribed budesonide (Pulmicort) two puffs and fluticasone (Flovent) three puffs t.i.d. The nurse evaluates that further teaching is needed when the patient makes what statement? A) Take all five puffs as quickly as possible. B) Replace the inhalers before they run out. C) Rinse the mouth after taking the medication. D) Continue medication even when symptoms start to subside. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) Ans: 594 A Feedback: The nurse needs to review how to administer the drug via inhalation because the patient must hold the medication in the airways as long as possible before exhaling and should not try to rush the treatment. The other statements are correct and would not require clarification. 23. The home health nurse provides patient teaching to his or her patient who is taking oral prednisolone. The nurse provides what instruction to reduce the occurrence of nausea? A) Take with a meal. B) Take 1 hour before meals. C) Take before bedtime. D) Split the dose into two equal doses. Ans: A Feedback: Steroids, taken on an empty stomach, would exacerbate the nausea. If the patient takes only one dose per day, it should be taken immediately after breakfast. If spaced throughout the day, eating something before taking the pill will reduce risk of nausea. Timing is dictated by frequency of administration, and if only taken once daily, the medication should be taken in the morning (so bedtime is inappropriate). Splitting the dose would decrease effectiveness and would be inappropriate for the nurse to suggest because it is outside the scope of nursing practice. Taking the medication before meals would mean it was being taken on an empty stomach. 24. What would be important for the nurse to teach the parents of a pediatric patient about the use of topical corticosteroids? A) Apply the medication sparingly. B) Apply directly to open lesions. C) After applying cover with a bandage. D) Reapply as often as needed to keep the rash coated with the medication. Ans: A Feedback: Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 595 Topical use of corticosteroids should be limited in children, because their body surface area is comparatively large, so that the amount of the drug absorbed in relation to weight is greater than in an adult. Apply sparingly and do not use in the presence of open lesions. Do not occlude treated areas with dressings or diapers, which may increase the risk of systemic absorption. 25. The nurse is teaching the patient who will require long-term corticosteroid therapy how to reduce the risk of infection. What suggestions will the nurse include? A) Avoid large crowds of people tightly packed together. B) Avoid working in areas with other people. C) Avoid exercising to reduce risk of injury. D) Avoid touching other people who may carry germs. Ans: A Feedback: With long-term therapy, the importance of avoiding exposure to infectioncrowded areas, people with colds or the flu, activities associated with injuryshould be stressed. If an injury or infection should occur, the patient should be encouraged to seek medical care. These patients do not need to avoid work, exercise, or touching others but they should use good hand hygiene to avoid infection from these sources. 26. The nurse is caring for an African American patient who received a kidney transplant and receives methylprednisolone for immunosuppression. What is the nurse’s priority assessment specific to this patient? A) Assessing capillary refill time B) Assessing cardiac rhythm C) Assessing white blood cell count D) Assessing blood glucose levels Ans: D Feedback: African Americans develop increased toxicity to the corticosteroid methylprednisoloneparticularly when it is used for immunosuppression after renal transplantation. This toxicity can include severe steroid-induced diabetes mellitus. A priority intervention with this patient is monitoring blood glucose levels. Assessment of capillary refill time and cardiac rhythm would not be indicated by the data supplied about this patient. White blood cell counts should be monitored on any patient receiving long- Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 596 term corticosteroids but is not specific to this patient. 27. The nurse is caring for a patient who is diagnosed with protein-deficient malnutrition. Why would an order to administer androgens to this patient be appropriate? A) Androgens reduce the body’s requirement for protein. B) Androgens increase the body’s absorption of protein from the bowel. C) Androgens stimulate protein production and decrease protein breakdown. D) Androgens reduce carbohydrate metabolism and promote lipid absorption. Ans: C Feedback: Androgens are a form of the male sex hormone called testosterone. They affect electrolytes, stimulate protein production, and decrease protein breakdown, which will help to reverse the patient’s protein malnutrition in addition to a high-protein diet. They do not reduce the body’s need for protein, increase protein absorption from the bowel, or impact carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. 28. The nurse is caring for a patient who works night shift from 2200 (10 pm) to 0600 (6 am) and normally sleeps from 0800 (8 am) until 1600 (4 pm) each day. The nurse would teach this patient to take his or her corticosteroid at what time of the day? A) 06:00 (6 am) B) 08:00 (8 am) C) 16:00 (4 pm) D) 22:00 (10 pm) Ans: C Feedback: If a person works all night and goes to bed at 8 am, arising at 4 pm to carry on the day’s activities before going to work at 10 pm, the hypothalamus will release corticotropin-releasing hormone at about 4 pm in accordance with the new sleepwake cycle. It usually takes 2 or 3 days for the hypothalamus to readjust. A patient on this schedule who is taking replacement corticosteroids would then need to take them at 4 pm, or on arising. All other options would not be optimal. 29. For what reason might a nurse administer androgen injections to a 9-year-old boy? Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) A) Ovarian atrophy B) Dwarfism C) Acromegaly D) Hypogonadism Ans: D 597 Feedback: Androgens are used pharmacologically to treat hypogonadism or to increase protein growth and red blood cell production. Androgens are not used in a male to treat ovarian atrophy. Androgens are not used to treat dwarfism or acromegaly. 30. A patient is taking low-dose corticosteroids on a long-term basis for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. The nurse assesses this patient knowing prolonged use of corticosteroids puts the patient at risk for what? A) Adrenal storm B) Adrenal atrophy C) Stunted growth D) Hypothalamic insufficiency Ans: B Feedback: Prolonged use of corticosteroids suppresses the normal hypothalamicpituitary axis and leads to adrenal atrophy from lack of stimulation. The other options are all distracters for this question with no connection to long-term use of corticosteroids. 31. The nurse administers prednisone orally at 8 am. When would the nurse expect the drug to reach peak effect? A) 9 to 10 am B) 12 to 1 pm C) 8:30 to 9:00 am Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) D) 4 to 6 pm Ans: A 598 Feedback: Prednisone’s peak effect occurs 1 to 2 hours after administering the drug. If given at 8 am, the expected peak would occur between 9 and 10 am. 32. Nursing care for the postoperative patient requiring long-term glucocorticoid therapy will be directed at overcoming what adverse effect of the drug? A) Poor wound healing B) Inflammation C) Autoimmune response D) Lack of mobility Ans: A Feedback: Patients taking long-term glucocorticoid therapy will have impaired wound healing so nursing care is directed toward promoting healing. The drug has an anti-inflammatory effect so that would not need to be overcome. There is no autoimmune response or lack of mobility so these do not have to be overcome. 33. The nurse is teaching a class for his or her peers about glucocorticoids. What will the nurse say is initially blocked, resulting in the drug’s anti-inflammatory action? A) Arachidonic acid B) Phagocytes C) Lymphocytes D) Antibodies Ans: A Feedback: Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 599 Glucocorticoids block the actions of arachidonic acid, which leads to a decrease in the formation of prostaglandins and leukotrienes. They also impair the ability of phagocytes to leave the bloodstream and move to injured tissues; they inhibit the ability of lymphocytes to act within the immune system, including blocking the production of antibodies. Blocking arachidonic acid is, however, the initial action. 34. What hormones does the adrenal medulla secrete? A) Renin and erythropoietin B) Norepinephrine and epinephrine C) Epinephrine and dopamine D) Dopamine and serotonin Ans: B Feedback: The adrenal medulla is actually part of the sympathetic nervous system (SNS). It is a ganglion of neurons that releases the neurotransmitters norepinephrine and epinephrine into circulation when the SNS is stimulated. 35. The adrenal cortex responds to adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), which responds to corticotropinreleasing hormone (CRH) from the hypothalamus in a daily pattern called what? A) Pituitary rhythm B) hypothalamicpituitary axis C) Diurnal rhythm D) Circadian rhythm Ans: C Feedback: The adrenal cortex responds to ACTH released from the anterior pituitary. ACTH, in turn, responds to CRH released from the hypothalamus. This happens regularly during a normal day in what is called diurnal rhythm. Pituitary rhythm is a distracter; the term does not exist. The hypothalamicpituitary axis involves the interaction between the two glands. Circadian rhythm involves when people prefer to be most active, such as people who say they are morning people. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 600 Chapter 37 - Thyroid and Parathyroid Agents 1. The nurse is teaching the patient, newly diagnosed with Graves’s disease, about the normal functioning of the thyroid gland. What hormone will the nurse tell the patient controls production and release of thyroid hormones? A) Thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) B) Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) C) Tetraiodothyronine D) Triiodothyronine Ans: B Feedback: Thyroid hormone production and release are regulated by the anterior pituitary hormone called thyroidstimulating hormone (TSH). The secretion of TSH is regulated by thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH), a hypothalamic regulating factor. Tetraiodothyronine and triiodothyronine are thyroid hormones produced by the thyroid gland because of TSH stimulation. 2. A child is diagnosed with hypothyroidism. The nurse anticipates an order for the drug of choice when treating children, which is what? A) Liothyronine (Cytomel) B) Liotrix (Thyrolar) C) Levothyroxine (Synthroid) D) Methimazole (Tapazole) Ans: C Feedback: Levothyroxine is the drug of choice in children because of its predictable bioavailability and reliability. Liothyronine and liotrix tend to have more adverse effects and, although they can be used in children, are not the drugs of choice. Methimazole is an antithyroid drug and is used to treat hyperthyroidism. 3. A patient is at risk for thrombosis formation and is taking an oral anticoagulant. The patient has been newly diagnosed with hypothyroidism and placed on levothyroxine (Synthroid). What will the nurse Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 601 monitor the patient for? A) Tachycardia B) Elevated body temperature C) Increased time spent sleeping D) Increased bruising and bleeding Ans: D Feedback: The effectiveness of an oral anticoagulant is increased if it is used in combination with a thyroid hormone. This may lead to increased bleeding and the need to decrease the dosage of the oral anticoagulant. Tachycardia would be found with hyperthyroidism and the effect of levothyroxine is not increased with the drug combination. Increased time spent sleeping would indicate lowering of thyroid function and the treatment should increase thyroid function. Increased body temperature is associated with hyperthyroidism. 4. The nurse is providing patient teaching regarding the administration of levothyroxine (Synthroid). What is the nurse’s priority teaching point? A) Take the medication after breakfast. B) Take the medication with a full glass of water. C) Remain in the upright position for 30 minutes after administering. D) Take the medication before going to bed at night. Ans: B Feedback: The patient should be instructed to take the medication with a full glass of water to help prevent difficulty swallowing and esophageal atresia. The medication should be taken on an empty stomach before breakfast. There is no need to maintain an upright position. The medication should be taken as a single daily dose before breakfast each day to ensure consistent therapeutic levels. 5. A) The nurse instructs the patient with a new prescription to treat hyperthyroidism and includes the importance of regular lab studies to monitor for bone marrow suppression, which can be an adverse effect of this drug. What drug is the nurse teaching the patient about? Methimazole (Tapazole) Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) B) Propylthiouracil (PTU) C) Sodium iodide I131 (Generic) D) Potassium iodide (Thyro-Block) Ans: A 602 Feedback: Methimazole is associated with bone marrow suppression, so the patient using this drug must have frequent blood tests to monitor for this effect. Propylthiouracil is associated with GI effects. The most common adverse effect of sodium iodide I131 and potassium iodide is hypothyroidism. Other effects of these two drugs include metallic taste and burning in the mouth, sore teeth and gums, diarrhea, cold symptoms, stomach upset, stained teeth, rash, and the development of goiter. 6. A patient is seen in the clinic and diagnosed with hyperthyroidism. Potassium iodide is prescribed. The nurse reviews the patient’s medical record before administering the drug. What assessment finding would cause the nurse to alter the plan of care? A) A daily walk of 3 miles a day B) A low fat, low sodium diet C) A bowel movement every 2 to 3 days D) Digoxin 0.125 mg daily Ans: D Feedback: Potassium iodide will cause the patient to move from hyperthyroidism to hypothyroidism, thus altering the patient’s metabolism. Digoxin has a small margin of safety that could be altered by a change in thyroid function. The patient will need to be monitored carefully for an alteration in digoxin effects that may include an increased heart rate, arrhythmia, or reduced cardiac output. A daily walk of 3 miles, a low fat, low sodium diet, and a bowel movement every 2 to 3 days are important for maintenance of a healthy lifestyle but would not alter the plan of care. 7. A) A patient with Paget’s disease calls the clinic and tells the nurse that she is experiencing flushing of the face and hands and a rash. The patient states that she is taking calcitonin, salmon (Calcimar) for her Paget’s disease. What is the nurse’s best response? We expected this to happen. Just ignore it and please do not worry about it. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) B) You will need to see the doctor immediately. Come in as soon as possible. C) This is a common adverse effect of your medication that will lessen with time. D) This is a serious adverse effect. Stop taking the drug and see the doctor today. Ans: C 603 Feedback: The most common adverse effects seen with this drug include flushing of the face and hands, rash, nausea and vomiting, urinary frequency, and local inflammation at the site of injection. Many of these adverse effects lessen with time, the duration varying with each individual patient. Although it is an expected adverse effect, the nurse needs to provide more teaching instead of simply telling the patient to ignore it and to not worry. The patient does not need to be seen and this is not a serious adverse effect. 8. The nurse is teaching the patient with a new prescription for ibandronate (Boniva) how to take the medication. Which instruction provided by the nurse is correct? A) Take 150 mg once a month on the same day of the month. B) Take 70 mg once a week on the same day of the week. C) Take 400 mg/d. D) Take 3 mg once per month on the same day of the month. Ans: A Feedback: Ibandronate can be taken daily, monthly, or every 3 months. Taking 150 mg orally once a month on the same day of the month would be correct. If given IV every 3 months, the dose is 3 mg and if taken daily, the dose is 2.5 mg/d. All other options are incorrect. 9. The nurse admits an elderly patient in thyroid crisis for whom surgery is not an option. What antithyroid drug would the nurse expect will be ordered? A) Methimazole (Tapazole) B) Radioactive iodine (Generic) C) Propylthiouracil (PTU) Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) D) Potassium iodide (Thyro-Block) Ans: B 604 Feedback: If antithyroid agents are needed in the older adult patient, sodium iodide I131 may be the drug of choice because it has fewer adverse effects than the other agents. The use of sodium iodide is reserved for those patients who are not candidates for surgery, women who cannot become pregnant, and elderly patients with such severe, complicating conditions that immediate thyroid destruction is needed. Radioactive iodine targets the thyroid cells and destroys them without many adverse effects. Methimazole and propylthiouracil are antithyroid drugs but have cardiovascular adverse effects that might be unacceptable in an elderly patient who is not a candidate for surgery. Effects of potassium iodide are short-lived and may precipitate further thyroid enlargement and dysfunction so they would not be used in a patient who is not a candidate for surgery because they would not provoke long-term effects. 10. The nurse is providing care for a man diagnosed with osteoporosis. What drug will the nurse administer that is the only drug approved for treatment in men? A) Etidronate (Didronel) B) Pamidronate (Aredia) C) Tiludronate (Skelid) D) Alendronate (Fosamax) Ans: D Feedback: Alendronate is the only bisphosphonate that has been approved for the treatment of osteoporosis in men. Etidronate is used to treat Paget’s disease, postmenopausal osteoporosis, and heterotopic ossification. Pamidronate is used to treat Paget’s disease, postmenopausal osteoporosis in women, hypercalcemia of malignancy, and osteolytic bone lesions in cancer patients. Tiludronate is used to treat Paget’s disease that is not responsive to other treatment. 11. What assessment findings would the nurse expect to see in a patient who overdosed on levothyroxine (Synthroid)? A) Nervousness, tachycardia, tremors B) Somnolence, bradycardia, paresthesia C) Hyperglycemia, hypertension, edema Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) D) Buffalo hump, constipation, sodium loss Ans: A 605 Feedback: More pronounced adverse effects of levothyroxine would be seen including tremors, headache, nervousness, palpitations, tachycardia, allergic skin reactions, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting. Somnolence, bradycardia, and paresthesia would be more likely with insufficient drug intake, which would cause hypothyroidism and other symptoms. Hyperglycemia, edema, buffalo hump, constipation, or sodium loss would not be associated with excess thyroid hormone. 12. After administering propylthiouracil (PTU), what effect would the nurse anticipate the drug will have in the patient’s body? A) To destroy part of the thyroid gland B) To inhibit production of thyroid hormone in the thyroid gland C) To suppress the anterior pituitary gland’s secretion of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) D) To suppress the hypothalamus’s production of thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) Ans: B Feedback: PTU is a thioamide that acts by lowering thyroid hormone levels by preventing the formation of thyroid hormone in the thyroid cells, which lowers the serum levels of thyroid hormone. They also partially inhibit the conversion of thyroxine to triiodothyronine at the cellular level. Iodine solutions oversaturate thyroid cells and top production of thyroid hormone. Radioactive iodine destroys part of the thyroid gland. PTU does not impact production or secretion of TSH or TRH. 13. The nurse provides teaching regarding levothyroxine to a 55-year-old patient diagnosed with Hashimoto’s disease. What statement made by the patient does the nurse interpret to mean that the drug teaching had been understood? A) I can take this medication at any time of day. B) I should take this medication on an empty stomach in the morning. C) I may take this with a sip of water in the morning. D) If I feel nauseated, I may take this drug with an antacid. Ans: B Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 606 Feedback: Adults who require thyroid replacement therapy need to understand that this will be a lifelong need. An established routine of taking the tablet first thing in the morning may help the patient comply with the drug regimen. The drug should be taken on an empty stomach with a full glass of water. Antacids would slow or prevent absorption of the hormone replacement, so the patient should be corrected. 14. The nurse, developing a care plan for a patient diagnosed with hypothyroidism, creates what appropriate nursing diagnosis? A) Imbalanced nutrition: Less than body requirements B) Ineffective thermoregulation: Excess or ineffective airway clearance C) Decreased cardiac output D) Ineffective airway clearance Ans: C Feedback: Decreased cardiac output is related to hypothyroidism. Hyperthyroidism results in increased caloric needs and the nursing diagnosis of Imbalanced nutrition: Less than body requirements. Thyroid dysfunction would not normally result in Ineffective thermoregulation: Excess or ineffective airway clearance. 15. The nurse is caring for a 5-year-old child diagnosed with hypothyroidism whose mother voices skepticism about giving the child drugs. In explaining the need for medication, what will the nurse tell this mother could result if her daughter’s condition remains untreated so she can make an informed decision? A) Mental retardation B) Renal dysfunction C) Immune deficiency D) Paralytic ileus Ans: A Feedback: Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 607 Children who are born without a thyroid gland or who have a nonfunctioning gland develop a condition called cretinism. If untreated, these children will have poor growth and development and mental retardation because of the lack of thyroid hormone stimulation. The child would not be at increased risk of renal dysfunction, immune deficiency, or paralytic ileus. 16. A patient is diagnosed with a simple goiter and asks the nurse what caused it. What is the nurse’s best response? A) A goiter is the result of too much thyroxine. B) A goiter is the result of a chloride deficiency. C) A goiter is the result of too much TSH. D) A goiter is the result of an iodine deficiency. Ans: C Feedback: Goiter (enlargement of the thyroid gland) is an effect of hyperthyroidism, which occurs when the thyroid is overstimulated by thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH). This can happen if the thyroid gland does not produce sufficient thyroid hormones to turn off the hypothalamus and anterior pituitary. In the body’s attempt to produce the needed amount of thyroid hormone, the thyroid is continually stimulated by increasing levels of TSH. There is a deficiency of thyroxine. It is not related to chloride or iodine deficiencies. 17. The patient with hypothyroidism takes levothyroxine daily and has triiodothyronine (T3), thyroxine (T4), and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) levels drawn in the laboratory to check appropriateness of prescribed dosage. What results would the nurse analyze as indicating the need for a higher dosage of medication? A) Elevated TSH, elevated T3, and reduced T4 levels B) Reduced TSH, elevated T3 and T4 levels C) Elevated TSH, reduced T3 and T4 levels D) Reduced TSH, T3, and T4 levels Ans: C Feedback: TSH levels would be elevated to stimulate increased thyroid hormone secretion whereas T4 and T3 will Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 608 be low, which indicates the need for a higher dosage of medication. If TSH level is low, it would indicate a reduction in dosage would be needed, particularly if T3 and T4 levels are elevated. 18. A patient presents at the clinic with complaints of weight loss despite an increased appetite. The nurse assesses this patient for what? A) Chronic thyroiditis B) Hypercalcemia C) Hypothyroidism D) Hyperthyroidism Ans: D Feedback: Hyperthyroidism is manifested by increased metabolism and energy usage. It is not manifested by chronic thyroiditis, hyperglycemia, or hypothyroidism. 19. What patient will the nurse assess most closely for secondary hyperparathyroidism? A) The 12-year-old patient with hypothyroidism B) The 68-year-old patient with chronic renal failure C) The 35-year-old patient with diabetes mellitus D) The 48-year-old patient with hyperthyroidism Ans: B Feedback: Secondary hyperparathyroidism occurs most frequently in patients with chronic renal failure. Primary hyperparathyroidism occurs more often in women between 60 and 70 years of age. Although hyperparathyroidism can occur at any age, the patient with diabetes or thyroid disorder would not be at higher risk for the disorder. 20. A) What drug would the nurse appropriately administer to the patient to treat hypothyroidism? Teriparatide Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) B) Methimazole C) Propylthiouracil D) Levothyroxine Ans: D 609 Feedback: Levothyroxine (Synthroid, Levoxyl, Levothroid), a synthetic salt of thyroxine, is the most frequently used replacement hormone to treat hypothyroidism because of its predictable bioavailability and reliability. Propylthiouracil and methimazole would be used to treat hyperthyroidism; teriparatide is an antihypocalcemic agent. 21. The nurse is caring for a patient with a history of myocardial infarction and heart failure. What thyroid replacement drug would the nurse question if ordered? A) Liothyronine B) Levothyroxine C) Thyroid desiccated D) Methimazole Ans: A Feedback: Liothyronine and liotrix have a greater incidence of cardiac adverse effects and are not recommended for use in patients with potential cardiac problems or patients who are prone to anxiety reactions. Levothyroxine would be the drug of choice and thyroid desiccated would not be contraindicated. Methimazole is a treatment for hyperthyroidism and would not be appropriate for the patient with hypothyroidism. 22. The nurse is caring for a patient newly diagnosed with hypothyroidism. The patient also takes theophylline to control asthma symptoms. What changes will need to be made to the patient’s theophylline dose? A) Decrease theophylline dosage immediately. B) Increase theophylline dosage immediately. C) Increase theophylline dose when normal thyroid function returns. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) D) Decrease theophylline dose when normal thyroid function returns. Ans: B 610 Feedback: Theophylline clearance is decreased in hypothyroid states. As the patient approaches normal thyroid function, theophylline dose may need to be adjusted frequently. As the drug is cleared more quickly, the dosage may need to be increased. 23. The nurse is caring for a 57-year-old woman who is complaining about gaining so much weight after menopause and suggests that thyroid hormone replacement would help her lose weight and speed up her metabolism. What is the nurse’s best response? A) Inducing a state of hyperthyroidism would result in weight loss. B) People who are not hypothyroid should not take thyroid hormones. C) People who take thyroid hormones without cause will end up damaging their heart. D) The body compensates for the extra hormone by reducing the amount secreted. Ans: D Feedback: Taking thyroid hormone with normal thyroid function results in disruption of the hypothalamicpituitarythyroid control resulting in decreased production of thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) as the hypothalamus and pituitary sensed the rising levels of thyroid hormone. Because the thyroid was no longer stimulated to produce and secrete thyroid hormone, thyroid levels would actually fall. This would put the patient at greater risk of gaining weight. There is no evidence it would cause heart damage. Because thyroid hormone production is reduced, a state of hyperthyroidism is not induced. Even though the statement that people who are not hypothyroid should not take thyroid hormones is correct, it does not provide enough information to dissuade this patient from a dangerous practice. 24. The patient is 8 weeks pregnant and requires an antithyroid medication. The nurse identifies what drug as the drug of choice for this patient? A) Propylthiouracil B) Radioactive iodine C) Alendronate D) Methimazole Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) Ans: 611 A Feedback: If an antithyroid drug is essential during pregnancy, propylthiouracil (PTU) is the drug of choice because it is less likely to cross the placenta and cause problems for the fetus. Radioactive agents should not be used. Bisphosphonates should be used during pregnancy only if the benefit to the mother clearly outweighs the potential risk to the fetus. Methimazole is an antithyroid medication but would not be the drug of choice for the pregnant woman. 25. The nurse is discharging a patient with a new prescription for levothyroxine. What would the nurse teach the patient to report to her health care provider? (Select all that apply.) A) Nervousness B) Insomnia C) Chest pain D) Loss of hair E) Nausea Ans: A, B, C Feedback: Report chest pain, heart palpitations, nervousness, or insomnia. These adverse effects result from excessive stimulation and may indicate that drug dosage or intake of other stimulants needs to be reduced. Loss of hair is usually only seen in the first few months of therapy in children; nausea need not be reported unless it is persistent or interferes with adequate caloric intake. 26. The nurse tells the patient his or her serum calcium level is elevated and the patient asks what controls calcium levels in the body. What is the nurse’s best response? A) Renin B) Parathyroid hormone (PTH) C) Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) D) Epoetin Ans: B Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 612 Feedback: PTH is the most important regulator of serum calcium levels in the body. Renin controls blood pressure, epoetin stimulates production of red blood cells, and TSH stimulates thyroid hormone secretion. 27. The nurse is caring for a patient diagnosed with hyperparathyroidism who asks the nurse why parathyroid hormone (PTH) is important. The nurse explains that PTH performs what actions in the body? (Select all that apply.) A) Stimulation of osteoclasts B) Increased intestinal absorption of calcium C) Stimulation of calcitriol production D) Increased excretion of calcium from kidneys E) Decreased retention of vitamin D Ans: A, B, C Feedback: PTH has many actions, including stimulation of osteoclasts or bone cells to release calcium from the bone, increased intestinal absorption of calcium, increased calcium reabsorption from the kidneys, and stimulation of cells in the kidney to produce calcitriol. PTH increases absorption of calcium from the kidney and increases retention of vitamin D. 28. The nurse is teaching the patient how to take his newly prescribed alendronate and includes what teaching points? (Select all that apply.) A) Take the drug in the morning. B) Wait 60 minutes before eating breakfast. C) Take the drug with a full glass of water. D) Remain upright for 30 minutes after taking the medication. E) Eat a breakfast high in calcium after taking the medication. Ans: A, C, D Feedback: Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 613 Alendronate, ibandronate, and risedronate need to be taken on arising in the morning, with a full glass of water, fully 30 minutes before any other food or beverage, and the patient must then remain upright for at least 30 minutes; taking the drug with a full glass of water and remaining upright for at least 30 minutes facilitates delivery of the drug to the stomach. These drugs should not be given to anyone who is unable to remain upright for 30 minutes after taking the drug because serious esophageal erosion can occur. There is no need to eat a high-calcium breakfast, although the patient should make certain of adequate calcium intake. 29. The nurse is caring for an asthmatic patient prescribed zoledronic acid. What important question should the nurse ask this patient? A) Can you take aspirin without experiencing any bad effects? B) Are you taking theophylline to treat your asthma? C) Do you have a history of diarrhea? D) Are you taking digoxin? Ans: A Feedback: Zoledronic acid should be used cautiously in aspirin-sensitive asthmatic patients. Gastrointestinal (GI) distress may increase if bisphosphonates are combined with aspirin; this combination should, therefore, be avoided if possible. There is no drug interaction between theophylline and zoledronic acid or between digoxin and zoledronic acid. A history of diarrhea would not impact the ability to administer zoledronic acid. 30. The nurse is caring for a pediatric patient with hypercalcemia. What condition would the nurse suspect is causing this altered serum calcium level? A) Radiation injury B) Malignancy C) Kidney failure D) Hypothyroidism Ans: B Feedback: Hypercalcemia is relatively rare in children, although it may be seen with certain malignancies. It Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 614 would not result from a radiation injury, which would be more likely to affect the thyroid gland and it would not be caused by kidney failure or hypothyroidism. 31. The nurse is caring for a patient who takes alendronate. What lab studies would the nurse assess regularly? A) Serum iodine B) Serum potassium C) Serum calcium D) Serum iron Ans: C Feedback: Alendronate and risedronate are commonly used drugs for osteoporosis and calcium lowering. Serum calcium levels need to be monitored carefully with any of the drugs that affect calcium levels. Administration of alendronate would not require monitoring of iodine, potassium, or iron levels. 32. The patient, newly prescribed cinacalcet hydrochloride (Sensipar), asks the nurse how this drug works. What is the nurse’s best response? A) It slows or blocks bone’s resorption of calcium. B) It promotes entry of calcium into bone. C) It balances the effects of parathyroid hormone to lower serum calcium levels. D) It increases the receptor’s sensitivity to extracellular calcium. Ans: B Feedback: Cinacalcet hydrochloride is a calcimimetic drug that increases the sensitivity of the calcium-sensing receptor to activation by extracellular calcium. In increasing the receptors’ sensitivity, cinacalcet lowers parathyroid hormone (PTH) levels, causing a concomitant decrease in serum calcium levels. Bisphosphonates act to slow or block bone resorption; by doing this, they help to lower serum calcium levels, but they do not inhibit normal bone formation and mineralization. Calcitonins balance the effects of PTH by reducing calcium levels. Cinacalcet does not promote entry of calcium into the bone. 33. The nurse reviews the patient’s laboratory results and sees that the serum calcium level is acceptable as long as it is within what range? Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) A) 1 and 3 mg/dL B) 4 and 6 mg/dL C) 6 and 8 mg/dL D) 9 and 11 mg/dL Ans: D 615 Feedback: Calcium is an electrolyte that is used in many of the body’s metabolic processes. These processes include membrane transport systems, conduction of nerve impulses, muscle contraction, and blood clotting. To achieve all of these effects, serum levels of calcium must be maintained between 9 and 11 mg/dL. Other options are incorrect. 34. What electrolyte affects parathyroid hormone (PTH) secretion other than calcium? A) Magnesium B) Sodium C) Potassium D) Zinc Ans: A Feedback: Another electrolytemagnesiumalso affects PTH secretion by mobilizing calcium and inhibiting the release of PTH when concentrations rise above or fall below normal. Sodium, potassium, and zinc do not affect PTH function. 35. The nurse administers teriparatide (Forteo) and evaluates the drug as effective in achieving desired effects when what is assessed? A) Increase in serum calcium and phosphorous B) Increase in serum calcium and decrease in serum phosphorous C) Decrease in serum calcium and phosphorous Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) D) Decrease in serum calcium and increase in serum phosphorous Ans: B 616 Feedback: With once-daily administration, teriparatide stimulates new bone formation, leading to an increase in skeletal mass. It increases serum calcium and decreases serum phosphorous. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 617 Chapter 38 - Agents to Control Blood Glucose Levels 1. An type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetic reports recurrent hypoglycemia late in the morning. After collecting his health history what finding would the nurse suspect is causing the late morning hypoglycemia? A) The patient likes to nap after work before his evening meal. B) The patient jogs 2 miles in the morning before he goes to work. C) The patient likes to have an early lunch with his girlfriend. D) The patient eats oatmeal early in the morning for breakfast. Ans: B Feedback: Physical exercise, such as jogging, changes insulin requirements and may result in a delayed hypoglycemic reaction. The fact that he likes to nap before dinner and has an early lunch is unrelated to his hypoglycemia. The patient eating oatmeal early in the morning would help stabilize his blood sugars until later in the morning, but the jogging would have a dramatic effect. 2. The nurse suspects the diabetic patient may be having a hypoglycemic reaction when what manifestation is assessed? A) Dry, flaky skin B) Diaphoresis C) Flushing of the face D) Fruity breath Ans: B Feedback: Diaphoresis and cool clammy skin are signs of hypoglycemia. A fruity breath is seen with ketoacidosis. Flushing of the face is associated with hyperglycemia. 3. The nurse is preparing patient teaching for a diabetic patient who is to begin pramlintide acetate (Symlin) therapy, which will be taken in addition to insulin. What is the priority nursing instruction to include in this teaching plan? Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) A) The drug is injected subcutaneously immediately before a major meal. B) The drug has a rapid onset of action. C) Inject the drug at least 2 inches away from any insulin injection site. D) Do not combine the drug with insulin in the same syringe. Ans: A 618 Feedback: Pramlintide works to modulate gastric emptying after a meal, so correct timing of administration of this drug is essential to its function. All options are appropriate instructions for this drug. However, making sure that the patient understands that injecting the medication immediately before eating a major meal is most important because it has a dramatic effect on the therapeutic action of the drug. If the medication is not given at the correct time, the other options would be insignificant. 4. What type of insulin would the nurse administer if the fastest therapeutic effects are needed? A) Lispro (Humalog) B) Aspart (NovoLog) C) Regular (Humulin R) D) Glulisine (Apidra) Ans: D Feedback: Glulisine has an onset of 2 to 5 minutes and peaks in 30 to 90 minutes so it has the fastest onset of action. Lispro has an onset in <15 minutes and also peaks at 30 to 90 minutes. Aspart takes 10 to 20 minutes for onset and peeks in 1 to 3 hours. Regular insulin has a 30 to 60 minute onset and peaks in 2 to 4 hours. 5. When the nurse administers an oral combination drug called Metaglip, what doses of the two medications are being administered? A) 2.5 mg glipizide, 500 mg metformin B) 1.25 mg glyburide, 250 mg metformin Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) C) 5 mg glipizide, 250 mg metformin D) 4 mg rosiglitazone, 500 mg metformin Ans: A 619 Feedback: Metaglip is a combination of 2.5 mg glipizide with 250 or 500 mg metformin or 5 mg glipizide and 500 mg metformin. Glucovance is a combination of 1.25 mg glyburide with 250 mg metformin, 2.5 mg glyburide with 500 mg metformin, and 5 mg glyburide with 500 mg of metformin. Avandamet is a combination of 1, 2, or 4 mg rosiglitazone with 500 mg metformin. 6. The patient, newly diagnosed with diabetic retinopathy, asks what caused this disorder. What is the nurse’s best response? A) Inability of cells in the eye to reproduce B) Increase of aqueous humor in the eye C) Decrease of nerve innervations throughout the eye D) Oxygen cannot diffuse rapidly across the membrane to tissues in the eye Ans: D Feedback: The body’s inability to effectively cope with carbohydrate, fat, and protein metabolism over a long period of time results in a thickening of the basement membrane in large and small blood vessels. This thickening leads to changes in oxygenation of the lining of the vessels causing damage and narrowing of the vessels. The decreased blood flow through the vessels results in the inability of oxygen to rapidly diffuse across the membrane to the tissues of the eye. The tiny vessels of the eye are narrowed and closed, which causes loss of vision. Increase of aqueous humor is seen in glaucoma. Inability of cell replication and decrease in nerve innervations throughout the eye is not associated with retinopathy. 7. A diabetic patient is taking regular and NPH insulin to manage his diabetes. What is the best evaluation tool to measure the overall patient response to the insulin therapy? A) Blood pressure B) Bilirubin level C) Glycosylated hemoglobin (HbAlc) levels D) Fasting blood glucose levels Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) Ans: 620 C Feedback: HbAlc levels provide a 3-month average of glucose levels, which provides the best evaluation tool to measure the overall patient response to the treatment plan. Blood pressure readings would be used to evaluate a patient’s response to an antihypertensive drug. Bilirubin could indicate liver function. Fasting blood glucose levels provide only a baseline blood sugar and no historical overview. Comparing fasting blood glucose levels with HbAlc is like comparing a picture to a video because the HbAlc looks back across a period of 3 months whereas a blood glucose test result only tells you about the exact moment the blood was drawn. 8. A patient is brought to the emergency department with severe hypoglycemia. What drug would the nurse prepare to administer intravenously? A) Diazole (Hyperstat) B) Glyburide (DiaBeta) C) Glucagon (GlucaGen) D) Insulin (Humulin R) Ans: C Feedback: This patient will need a glucose-elevating agent. Glucagon (GlucaGen) is given parenterally only and is the preferred agent for emergency situations. Diazole is also a glucose-elevating agent but is only administered so it would take longer to take effect. Insulin would be administered for hyperglycemia. Glyburide is an oral antidiabetic agent, which is a second-generation sulfonylurea, and is administered for hyperglycemia. 9. The nurse will question what medication order for a diabetic patient who takes insulin to control his blood sugar level? A) Propranolol (Inderal) 10 mg orally t.i.d. B) Furosemide (Lasix) 60 mg/d orally C) Cefaclor (Ceclor) 250 mg orally every 8 hour D) Metoclopramide (Reglan) 20 mg PO Ans: A Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 621 Feedback: Propranolol is a beta-blocker and should be avoided in combination with insulin. The blocking of the sympathetic nervous system also blocks many of the signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia, hindering the patient’s ability to recognize problems. If propranolol must be taken, the nurse will need to teach this patient other ways to recognize hypoglycemia. Furosemide, cefaclor, and metoclopramide do not cause drugdrug interactions with insulin. 10. A patient comes to the diabetes educator and asks about changing his insulin. The patient explains that his occupation takes him on long international flights and he does not want to administer insulin on the plane. What kind of insulin would the diabetic nurse educator seek an order for? A) Lispro (Humalog) B) Glulisine (Apidra) C) Ultralente (Humulin U Ultralente) D) Aspart (NovoLog) Ans: C Feedback: Ultralente has a duration of 20 to 36 hours and a peak time of 10 to 30 hours. This would prevent him having to administer insulin on the airplane. Lispro has a duration of 2 to 5 hours and a peak time of 30 to 90 minutes. Glulisine has a duration of 1 to 2.5 hours and a peak time of 30 to 90 minutes. Aspart has a duration of 3 to 5 hours and a peak time of 1 to 3 hours. The last three insulin types mentioned in this Rationale would likely require administration on long plane flights. 11. The diabetes nurse educator describes type 1 diabetes with what statement? A) Blood glucose level can be controlled with diet. B) Exogenous insulin is required for life. C) Oral agents can help to control blood glucose levels. D) It is always diagnosed in early childhood. Ans: B Feedback: Type 1 diabetes results from an autoimmune disorder that destroys pancreatic beta cells. Insulin is the Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 622 only effective treatment for type 1 diabetes because pancreatic beta cells are unable to secrete endogenous insulin and metabolism is severely impaired. In type 1 diabetes, blood glucose levels cannot be controlled with diet, oral agents cannot control the disease process because they stimulate insulin production, and the patient with type 1 diabetes does not produce insulin. It can be diagnosed at other stages of the life span than just in early childhood. 12. A patient is admitted to the emergency department in diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) with a blood glucose level of 485 mg/dL. The physician orders an initial dose of 25 U insulin IV. Which type of insulin will be administered? A) NPH insulin B) Humulin L insulin C) Humulin N insulin D) Regular insulin Ans: D Feedback: Regular insulin is a short-acting insulin that manages the hyperglycemia and hyperkalemia resulting from DKA, which is a life-threatening complication that occurs with severe insulin deficiency. Furthermore, only regular insulin can be given IV and is the drug of choice in emergency situations. Humulin N, Humulin L, and NPH are intermediate-acting forms. 13. What instructions would be important to give to a 50-year-old patient with type 2 diabetes who has been switched from glyburide (DiaBeta) to repaglinide? A) It is less potent, so you will need to take a larger dose. B) It stimulates insulin production, so you need to eat soon after taking the medication. C) It is more potent and longer lasting, so you should take it every other day. D) The two medications are virtually the same. Ans: B Feedback: Glyburide is a second-generation sulfonylurea that stimulates insulin release from the beta cells in the pancreas with a 2- to 4-hour onset of action. Repaglinide has an onset of action within 30 minutes with peak effect in 1 hour, and duration of action is approximately 3 to 4 hours. Because repaglinide has a much faster onset of action, it is important the patient eats within15 to 30 minutes after taking the drug to avoid hypoglycemia. Repaglinide is not less potent, it is not more potent, and the two medications Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 623 are not virtually the same. 14. The nurse is instructing a patient how to mix NPH insulin with regular insulin in one syringe. The nurse tells the patient the mixture must be administered within how long after it is prepared? A) 5 minutes B) 10 minutes C) 15 minutes D) 20 minutes Ans: C Feedback: Use caution when mixing types of insulin. Administer mixtures of regular and NPH or regular and lente insulins within 15 minutes after combining them to ensure appropriate suspension and therapeutic effect. 15. The nurse is caring for a 3-year-old child newly diagnosed with type 1 diabetes. When developing the plan of care for this child, the nurse incorporates challenges the child faces that the adult does not, which includes what? (Select all that apply.) A) Children have a faster metabolic rate. B) Growth must be balanced with diet and activity. C) Insulin dose may be so small it is hard to calibrate accurately. D) Increased resistance by child to dietary restrictions is common. E) Changing metabolism makes regulating insulin difficult. Ans: A, B, C Feedback: Treatment of diabetes in children is a difficult challenge of balancing diet, activity, growth, stressors, and insulin requirements. Children need to be carefully monitored for any sign of hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia and treated quickly because their fast metabolism and lack of body reserves can push them into a severe state quickly. Insulin dosage, especially in infants, may be so small that it is difficult to calibrate. Insulin often needs to be diluted to a volume that can be detected on the syringe. It is usually during adolescence when increased resistance to dietary restrictions and changing metabolism makes regulating insulin difficult so this would not be part of the plan of care for a 3-year-old. Test Bank - Focus on Nursing Pharmacology (8th Edition by Karch) 16. 624 With what patient would the nurse question the administration of human insulin? A) Gestational diabetes B) Type 2 diabetes controlled on oral antidiabetic agents with systemic infection C) Type 1 diabetes of many years D) Type 2 diabetes controlled by diet Ans: D Feedback: Insulin is recommended for treatment of type 2 diabetes in patients whose diabetes cannot be controlled by diet or other pharmacotherapeutic agents. If the diabetes can be controlled by diet, the pancreas is still functioning and releasing insulin. Human insulin can be used in gestational diabetes, patients with type 2 diabetes controlled on oral antidiabetic agents with systemic infection, or patients with type 1 diabetes of many years standing. 17. The nurse is teac



