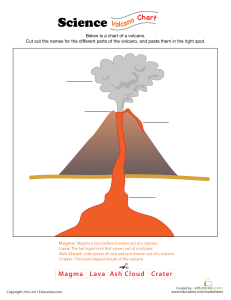
A DETAILED LESSON PLAN IN SCIENCE 6 I. LEARNING OBJECTIVES: Using a volcano model, the pupils would have: A. described the parts of a volcano; B. identified the parts of a volcano; C. applied preventive measures during a volcanic activity. II. SUBJECT MATTER Topic: Volcano Reference: Cyber Science 6 by: Villona, H. et.al pp. 267-269 Materials: LCD, laptop, model of a volcano, dishwashing paste, baking soda, water, vinegar, spoon, cup III. PROCEDURE Teacher’s Activity Pupils’ Activity A. Preparatory Activities 1. Setting of Standards a. You can show respect by listening to the teacher and to the one who is talking. b. There should be no cross-room conversations during work time. c. You can be responsible by completing the assigned task. 2. Motivation Have you seen a fountain? What are some of the fountains that you have seen? Will you name one? Can you describe it? Yes ma’am. Chocolate fountain, water fountain and firecracker fountain It is something that is sent up to the air and falls back. It is something that is forced up and falls back. Can you think of a landform that you can compare to a fountain? B. Presentation 1. Exploration Can you name some volcanoes that you know in the Philippines? Where can you find them? Have you seen them erupt? How does it look like when it erupts? I am holding something, what can you see? A fountain is compared to a volcano. Mount Mayon in Albay Taal Volcano in Batangas Mount Pinatubo in Zambales It emits gasses and smoke into the air. It has a mudflow of lava. A model volcano. How would you like to see this volcano erupts? May I ask somebody to pour a half-cup vinegar at the opening of a volcano? Observe what happens. 2. Comparison and Abstraction Describe the volcano Let us work on how to make a replica for magma. What do you think is found beneath the volcano? What do you call the hot liquid that exist beneath the Earths’ surface? Where do magma accumulate? What keeps them moving? What makes the magma move towards the surface of the Earth? Hot liquid rocks are found beneath the earth’s surface. The hot liquid is called magma. It accumulates at the center. The tremendous pressure and hot temperature make magma move. Where will it pass? What happens when magma reaches the surface? It becomes a lava Here are the parts of a volcano. What can be seen during eruption? During eruption, smoke and gasses are released. There is a mudflow of lava. If you were living in a place near an active volcano, what would you feel? What are the preventive measures that we can do in case of volcanic eruptions in the vicinity? IV. GENERALIZATION A volcano is a land form on the surface of the earth where molten rocks pass to reach the surface. Magma Chambers is a reservoir of magma A vent is a passage way of molten rocks. Crater is a depression at the tip of a volcano. C. Practice Identify what is being described in the flowing statements. Choose the letter of your answer and write it before the item number. a. b. c. d. e. Volcano Vent Magma chamber lava crater _____1. _____2. _____3. _____4. _____5. A land form on Earth’s surface. Hot molten rocks inside the earth. Molten rock that reach the earth’s surface. The opening of a volcano through which molten rocks erupts to the surface. The funnel-shaped pit at the top opening of the volcano. V. Assignment Draw a volcano and label its parts. Draw it in a short coupon bond. 1 Evacuate if necessary. Stay indoors. Prepare emergency materials like food, water and flashlights. Be alert. Republic of the Philippines NUEVA VIZCAYA STATE UNIVERSITY Bambang, Nueva Vizcaya COLLEGE OF TEACHER EDUCATION A Detailed Lesson Plan in Science VI Submitted by: Labaro, Christine Merel M. Pugayan, Robelita S. Bandioan, Jhouna Vi G. BEED III-B Submitted to: Ma. Corazon Francia Hongo Instructor