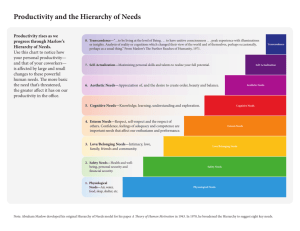
Social Need Presentation group (04) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. Sheuli Akter 17SOC84 Md.Apu Islam 17SOC37 Anamika Rani Paul 17SOC47 Md.Mehedi Hasan Molla 17SOC75 Sonia Khanam 17SOC38 Juwel Rana 17SOC09 Md.Annaf Sakil Tazwar 17SOC2 Md. Sahabur Rahman 17SOC19 Salah Uddin Kaysar 17SOC97 Md.Monirul Islam 17SOC27 Md.Ismail Hossain 17SOC81 Definition of Need : Presented by-- Sheuli Akter Malinowski suggested that individuals have physiological needs (reproduction, food, shelter) and that social institutions exist to meet these needs. (1884-1942) A lack of something requisite, desirable or useful, a building adequate for the company’s need, a physiological or psychological requirement for the well being of an organism, such as health and education needs. Definition of social need : In general, social needs are the basic needs of humans that prove that they are social beings. such as they may need for love, companionship, friendship etc. The social needs in Maslow's hierarchy include love, acceptance, and belonging. At this level, the need for emotional relationships drives human behavior. Some of the things that satisfy this need include: Friendships. Romantic attachments. The social needs in community settings cover at least one of the four bases and they are - Communicate Communicate means to share information with others by speaking, writing, moving your body, or using other signals. Create means bring (something) into existence. Contribute Example of social needs by Maslows love, intimacy, friendship, family, feedback, acceptance, and belonging Connect means to join or fasten together usually by something intervening. Contribute means to give something, such as money, goods, or time to help a person, group, cause, or organization. • Create means bring (something) into existence. Example of social needs by Maslows love, intimacy, friendship, family, feedback, acceptance, and belonging Types of need Presented by Md.Apu Islam According to Maslow, human needs are of five kinds 1. Physiological needs 2. Safety needs 3. Social needs 4. Esteem needs and 5. Self-actualization needs Physiological needs: The first of the id-driven lower needs on Maslow's hierarchy are physiological needs. These most basic human survival needs include food and water, sufficient rest, clothing and shelter, overall health, and reproduction. Maslow states that these basic physiological needs must be addressed before humans move on to the next level of fulfillment. Safety needs: Next among the lower-level needs is safety. Safety needs include protection from violence and theft, emotional stability and well-being, health security, and financial security. Love and belonging needs: The social needs on the third level of Maslow’s hierarchy relate to human interaction and are the last of the so-called lower needs. Among these needs are friendships and family bonds—both with biological family (parents, siblings, children) and chosen family (spouses and partners). Physical and emotional intimacy ranging from sexual relationships to intimate emotional bonds are important to achieving a feeling of elevated kinship. Additionally, membership in social groups contributes to meeting this need, from belonging to a team of co-workers’ to forging an identity in a union, club, or group of hobbyists. Esteem needs: The higher needs, beginning with esteem, are ego-driven needs. The primary elements of esteem are self-respect (the belief that you are valuable and deserving of dignity) and selfesteem (confidence in your potential for personal growth and accomplishments). Self-actualization needs: Self-actualization describes the fulfillment of your full potential as a person. Sometimes called self-fulfillment needs, self-actualization needs occupy the highest spot on Maslow's pyramid. Self-actualization needs include education, skill development—the refining talents in areas such as music, athletics, design, cooking, and gardening—caring for others, and broader goals like learning a new language, traveling to new places, and winning awards. CONCEPT OF SOCIAL NEEDS Presented by Anamika Rani Paul "The concept of social needs is inherent in the idea of social services " -Bradshaw J.R(1972) The taxonomy of social need, in melachlan G.(ed) 1.physiological needs 2.safty needs 3.love and belonging need 4.esteem needs 5.Self actualization needs PRIORITISE OF SOCIAL NEEDS Determining which social needs should receive attention and priority among the issues is challenging. social needs depends economical positions of countries "challenge is more daunting in the developing countries " -(Head of dept. psychology of awolowo University, Nigeria) 1.Health and education 2.women empowerment 3.establish day care service 4.psychological counselling 5.provided advanced training for social sector Presented by Md.Mehedi Hasan Molla Deprivation refers to removing or severely limiting any thing that an organism badly needs (C.Evans; 1978) > Deprivation include both lack as well as loss of factors considered necessary for the growth and the adaptation of the individual( G. Mishra & L.B.Tripathi; 1977) ➤ Prolonged Deprivation ➤ Relative Deprivation RELATIVE DEPRIVATION The feelings of discontent caused by the belief that one fares poorly compared to people groups.in other Absolute or Realistic Deprivation The belief that One's own resources are directly threatened by people in other groups. • Relative deprivation is formally defined as an actual or perceived lack of resources required to maintain the quality of life (e.g. diet, activities, material possessions) to which various socioeconomic groups or individuals within those groups have grown accustomed, or are considered to be the accepted norm within the group. Relative deprivation is the lack of resources (e.g. money, rights, social equality) necessary to maintain the quality of life considered typical within a given socioeconomic group. Relative deprivation often contributes to the rise of social change movements, such as the U.S. Civil Rights Movement. . Absolute deprivation or absolute poverty is a potentially life-threatening situation that occurs when income falls below a level adequate to maintain food and shelter. • Relative Deprivation Theory suggests that people who feel they are being deprived of something considered essential in their society (e.g. money, rights, political voice, status) will organize or join social movements dedicated to obtaining the things of which they feel deprived. •Relative Deprivation has been cited as a factor driving incidents of social disorder like rioting, looting, terrorism, and civil wars. In this nature, social movements and their associated disorderly acts can often be attributed to the grievances of people who feel they are being denied resources to which they are entitled. • In proposing one the first formal definitions of relative deprivation, British statesman and sociologist Walter Runciman listed four required conditions: . A person does not have something. . That person knows other people who have the thing. . That person wants to have the thing. . That person believes they have a reasonable chance of getting the thing. FAYE CROSBY'S MODEL OF RELATIVE DEPRIVATION (1976) • Relative deprivation has a counterpart: absolute deprivation. Both of these are measures of poverty in a given country. • Absolute deprivation describes a condition in which household income falls below a level needed to maintain the basic necessities of life, such as food and shelter. Maslow’s HierarcHy of Needs THeory Presented by Sonia Khanam Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs Theory Abraham Maslow's hierarchy of needs is one of the best known “A Theory of Human Motivation “. This hierarchy suggests that people are motivated to fulfill basic needs before moving on to other, more advanced needs. While some of the existing schools of thought at the time—such as psychoanalysis and behaviorism—tended to focus on problematic behaviors, Maslow was more interested in learning about what makes people happy and what they do to achieve that aim. As a humanist, Maslow believed that people have an inborn desire to be self-actualized, that is, to be all they can be. To achieve this ultimate goal, however, a number of more basic needs must be met. This includes the need for food, safety, love, and self-esteem.1 Maslow believed that these needs are similar to instincts and play a major role in motivating behavior.2 There are five different levels of Maslow’s hierarchy of needs, starting at the lowest level known as physiological needs. Maslow's hierarchy of needs is often displayed as a pyramid. The lowest levels of the pyramid of needs are made up of the most basic needs while the most complex needs are at the top. Once lower-level needs have been met, people can move on to the next level of needs. As people progress up the pyramid, needs become increasingly psychological and social. At the top of the pyramid, the need for personal esteem and feelings of accomplishment take priority. Like Carl Rogers, Maslow emphasized the importance of selfactualization, which is a process of growing and developing as a person in order to achieve individual potential. Demographic Facts: Presented by Juwel Rana There are some major demographic facts these directly impact on social needs.These are; 1.Age segmentation – Age is one of the most common demographic segmentation elements. Every age group has its peculiar characteristics and needs. Generally, teenagers might be more inclined towards the latest, good looking cars, but working professionals would require a vehicle that caters to his/her family and fits a particular budget. 2.Family segmentation – There is a lot of variation in this segmentation type. A lot of families have one or multiple children. . Child-free families will never purchase products related to children, such as baby lotion, toys, or diapers. A multinational organization that is into developing these products will conduct demographic examples based on the type of family 3.Gender segmentation – Gender is quite a primary category to conduct segmentation. Every gender has specific characteristics that are distinct and instrumental in decisionmaking. It is very natural for males, females, transgender people, to have different likes and dislikes. Men might not be as interested in makeup or fashion accessories in a manner that women will be. 4.Race and ethnicity segmentation – Race and ethnicity are sensitive categories. Promoting a product depends on that target race or ethnicity as it may be adapted differently by each of these races/ethnicities. Family income segmentation – One of the most straightforward segmentation types is based on income. An individual or a family’s income would govern their ability to purchase different cost categories’ products/services. Here are a few more demographic examples that researchers commonly use: Employment status: Business-owner, self-employed, unemployed, employed, retired. Living status: Home-owner, rented, lease. Education level: Graduate degree, undergrad, college degree, high school. Religion: Atheist, Muslim, Christian, Jew, Hindu, Buddhist Marital status: Single, married, separated, widow/ widower. Essentials of social needs: Social needs refer to the need to have relationships with others once the physiological and safety needs have been fulfilled. Maslow considered the social stage an important part of psychological development because our relationships with others help reduce emotional concerns such as depression or anxiety. Presented by Md.Annaf Sakil Tazwar Social needs are important basic human needs. When social needs are not satisfied it can also lead to mental and physical health problems Why Social Needs are Important? Human beings have social needs that are just as important as our biological need for food. Just as we may risk death by starvation if we stop eating, those whose social needs are not met may find themselves at risk of a form of extreme emotional pain that leads to thoughts of suicide. What Happens When Our Social Needs are Fulfilled? When our sense of significance is fulfilled, we experience a high degree of subjective well-being, feel a strong sense of identity, belonging, interpersonal connection, social support, and maintain the sense that our efforts are contributing to a cause beyond ourselves. Four basic social needs: Four basic social needs are achievement, power, intimacy and affiliation. Achievement: In humans, the need for achievement is to aspire to accomplish and seek "success in a competition with a standard of excellence" (McClelland, Atkinson, Clark & Lowell, 1953). Power: A high need for power stems from the desire to "impact, control, or influence... another person, group, or the world at large" (Winter, 1973), in which high-power individuals strive on dominance, reputation, status, and/or position (Reeve, 2009). Intimacy & Affiliation: The need for affiliation can be thought of as the need for approval, acceptance, and security in interpersonal relations, whilst more contemporary views focus on the need for approval and need for intimacy as two core facets that make up affiliation (Reeve, 2009). Intimacy & Old Age: Older and elderly people arguably prioritise their goals in terms of how emotionally meaningful and rewarding they are, a theory which is supported in research that has shown older people to focus their attention on close social partners (Carstensen, 1992). Presented by Md. Sahabur Rahman It is most obvious that we all have physical or Survival needs such as the need for sleep, food, water, comfort and warmth. In Choice Theory, the explanation of behaviour and motivation described by William Glasser, describes how these psychological needs fall into 4 main categories: 1.Love and Belonging We all need to feel cared for and be able to care for others. We need to be wanted and feel at ease with those around us. An example of this is the need to be accepted by those around us and the good feeling we get when others show they care for us, or we are able to help others. 2.Power / Self-Worth We are hard-wired to learn, appreciate feelings of competence, value and power. We feel good when we see the fruits of our effort, and a continual failure to succeed in turn leads to disempowerment. 3.Fun and Enjoyment All humans have a basic need to have fun, and seek enjoyment in what they do. Enjoyment can also be the reward of learning new things. We seek enjoyment through hobbies and leisure activities, but we are also driven by a need to enjoy our work. 4.Freedom This need can be viewed in 2 ways: freedom from pain, embarrassment, bullying, control of others; and freedom to make one’s own choices in life. Lackings of Social Needs Presented by Salah Uddin Kaysar Limitations of Maslow’s Social Needs Theory: 1. It is essential to note that not all employees are governed by same set of needs. Different individuals may be driven by different needs at same point of time. It is always the most powerful unsatisfied need that motivates an individual. 2. The theory is not empirically supported. 3. The theory is not applicable in case of starving artist as even if the artist’s basic needs are not satisfied, he will still strive for recognition and achievement. Maslow’s Theory and Criticism: Though Maslow’s hierarchy makes sense intuitively, little evidence supports its strict hierarchy. Actually, recent research challenges the order that the needs are imposed by Maslow’s pyramid. As an example, in some cultures, social needs are placed more fundamentally than any others. Further, Maslow’s hierarchy fails to explain the “starving artist” scenario, in which the aesthetic neglects their physical needs to pursuit of aesthetic or spiritual goals. Additionally, little evidence suggests that people satisfy exclusively one motivating need at a time, other than situations where needs conflict Conclusion Those who accept the consensus model of society where there are no fundamental structural conflicts of values and interests and where the powers of the state are not viewed as a menace to the individual, would believe that discretionary powers will be used to help those in need and disputes will be rare and resolved amicably within an accepted framework. Presented by Md.Monirul Islam Thank You All