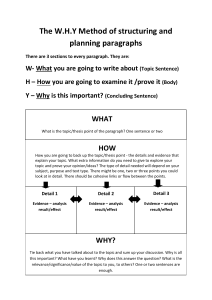
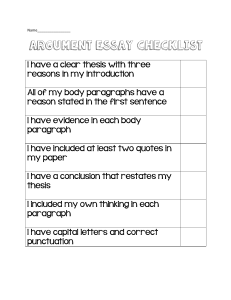
WRITING FUNDAMENTALS |Page1 How to write a proper introduction The introduction consists of 3 parts: 1. Topic sentence (Hook): Your first sentence sets the tone for the whole essay, make it interesting and catchy. Example - The internet is an extremely important invention. X - The invention of the internet is a big turning point in the history of human beings. 2. Background Information: Give a little information about your topic, DON’T give a lot of information and save it for the body of your writing. Example The whole world was depending on books and libraries to get a simple piece of information about any topic. It was really hard as it took a huge time for searching and making sure of the information. Until the scientists Vinton Cref and Bob Kahn invented the internet. 3. Thesis Statement: Now it’s time to show exactly what you want to say about the topic. This is your thesis statement—two or three statements that sum up your whole topic. Example As the first tool for communicating worldwide, the internet was a groundbreaking new technology. Not only it made people connecting easily with each other, but also helped in science development. |Page2 |Page3 Thesis Statement What is a Thesis Statement? It is often a point you want to argue or support in an essay. What does it tell? It is a sentence explains to the reader the main idea of the whole essay. How many sentences? It is usually one or two sentences. ?Where to write it It is often placed in the introductory paragraph of an essay. Things to avoid while writing a thesis statement • DO NOT USE the first person (I believe, In my opinion, etc.) • AVOID unclear language (It seems, etc.) • DO NOT attempt two topics at once (even if they seem related). Pick one and stick with it. |Page4 The Main Parts of an Essay Essay Outline Introduction Paragraphs • Start with a strong hook. • Give some bachground information. • State the main points you will write about in the thesis statement. Body • Topic sentence 1 based on the thesis statement. • Supporting Details. • Concluding sentence where you will restate the topic sentence in a simpler way. Body • Topic sentence 2 based on the thesis statement. • Supporting Details. • Concluding sentence where you will restate the topic sentence in a simpler way. Body • Topic sentence 3 based on the thesis statement. • Supporting Details. • Concluding sentence where you will restate the topic sentence in a simpler way. Conclusion • Restate the thesis statement and summerize your ideas. • DON'T give any new ideas in the conclusion. |Page5 Topic Sentences • It must tell the main idea or what the whole paragraph is about. Think of the strongest idea that you will present in your paragraph. Form the first sentence of the paragraph about it. Body Sentences • They talk about the topic sentence in more details. • They explain, describe, give reasons, or give examples. Closing Sentence for a Paragraph • It’s the last sentence of your paragraph. • It shows that you have finished all your thoughts. Writing Conclusions • Conclusions help to bring a text together, summarizing the main ideas and encouraging the reader to do some thinking for themselves. • There are 3 steps to write a strong conclusion: 1. Restate your 2. Summarize the 3. Draw to a close thesis statement main points Remind your reader with Restate the main points End up with a call of your points, but say that you want to stress action, quotation, etc… them differently that the on shortly. first paragraph. |Page6 Studying the writing process Brainstorming write down any words or ideas you can think of. Think about a topic. Cross out bad ideas and add details if you need to. Outlining Organize your ideas • Decide what goes in the topic, body and closing sentences. • You don't need to write complete sentences. Drafting Write the ideas from your outline into complete sentences. Don’t worry about making it perfect. Editing Make sure of the grammar, sentence structure, punctuation marks, and the spelling of each word. DON’T write a word you are not sure of its spelling and find a synonym. Revising Think about what to change in your writing to make it better. Publishing Write your final writing |Page7 1- Editing After revising your writing, correct any grammar, capitalization, punctuation, or spelling errors. Grammar -Subject – verb agreement. -The right tense. -The right form of sentences. Spelling Correct spelling by checking up the dictionary for the words you are not sure from. Capitalization -Beginning of a sentence. - Proper nouns. - Months, days of the week, holidays. Punctuation -Periods (.), question marks (?), exclamation points (!). - Commas (,) for words in a series and between the day and year. - Apostrophes (‘) to show possession and contractions |Page8 6+1 Writing Traits Ideas What is my message? Is my message clear? Organization Did I try hard enough to make it interesting? Do I have enough information? How does my paper begin? Voice Did I tell things in order? Does everything link to my message? How does my paper end? Do I really like this paper? Does this sound like me? How do I want my readers to feel? What is my favourite part? |Page9 Word Choice Have I used words I really love? Can my reader tell what my words mean? Have I used any new words? Did I repeat words too many times? Sentence Fluency Did I use sentences? Conventions Did my sentences begin in different ways? Did I use long and short sentences? Does my paper sound smooth as I listen? Did I use a title? Did I leave spaces? Did I use capitals? Did I use punctuation? Could another person read it easily? | 10