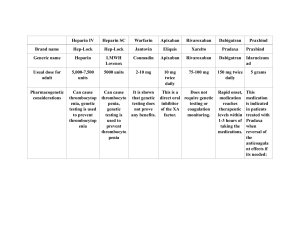
Anticoagulants: prevent formation of clots - Action: o - Prevents new clots from forming Use: o DVT o PE o MI o Artificial heart valves o Stroke Anticoag Heparin - - - - - - Action: o Bind with antithrombin III o Inhibit action of thrombin o Inhibit conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin o Inhibit clot formation Use: o Most commonly to prevent venous thrombosis o Acute PE Administration of heparin: o SQ o IV Heparin lab values: o PTT (1.5-2 times control value (control 60-70 seconds)) o aPTT (30-85 seconds (control 20 to 35 seconds)) o Xa Side effects: o Bleeding o Heparin induced thrombocytopenia Antidote: o Protamine sulfate Low Molecular Weight Heparin (Lovenox) - Action: o - - - Inactivates Xa factor Use: o Prevent DVT o Acute PE after surgery Why LMWH vs normal heparin? o Lower risk of bleeding o Frequent lab monitoring is not required Precautions: o Don’t take aspirin concurrently Oral Anticoags Warfarin (Coumadin) - Action: o Inhibits hepatic synthesis of vitamin K - Use: o - - - - Prevent thromboembolic conditions of thrombophlebitis, PE, and embolism formation Lab values: o INR (2-3) unless pt has a mechanical heart valve (2.5-3.5) o Frequent checks to maintain therapeutic range Side effects: o > 3 = bleeding o < 2 = clotting Interactions: o MANY food and drug interactions (EDUCATE) o Green, leafy vegetables Antidote: o Vitamin K for overdose o - Affects clotting factors II, VII, IX, and X Takes 24-48 hours to be effective For acute bleeding, fresh frozen plasma, or platelets GOOD TO KNOW!! o Long half-life o Still needs protection while they wait o Once INR is therapeutic, discontinue bridge therapy Nursing Process for Heparin and Warfarin - - Assessment: o Obtain a history of abnormal clotting or health problems affecting clotting o Gather a drug history including complementary and alternative therapy history Planning: o - The patient will not have excess bleeding Nursing interventions: o Monitor PT, INR for Warfarin, monitor aPTT for Heparin o Examine patient’s nose, urine, mouth, and skin for bleeding o Teach patient to inform dentist when taking an anticoag o Advise patient to use a soft toothbrush to prevent bleeding gums o Advise patient to avoid large amounts of green, leafy vegetables or be consistent with intake Direct Thrombin Inhibitors - Action: o - - Directly inhibit thrombin from converting fibrinogen to fibrin Use: o Prophylaxis and treatment of DVT and PE o Thrombus prophylaxis for HIT, unstable angina, A-FIB and stroke Administration: o IV o SQ Antiplatlets: suppress platelet aggregation - Used: o Prevent thrombosis in the arteries o Prevention of myocardial infarction or stroke for patients with familial history o Prevention of a repeat myocardial infarction or stroke o Prevention of a stroke for patients having transient ischemic attacks Antiplatelets Aspirin - Action: o - Inhibit cyclooxygenase, an enzyme needed by platelets to synthesize thromboxane A2 Use: o Prevention of MI, thromboembolism, prevention, and treatment of stroke - GOOD TO KNOW!! - Effective and inexpensive treatment for suppressing platelet aggression Thrombolytics: attack and dissolve clots that have already formed - - - Examples: o Aspirin (Bayer) o Clopidogrel (Plavix) - Adenosine diphosphate (ADP) antagonist Frequently used after MI or stroke Used with aspirin for more effective results Action: o Bind to fibrinogen promoting conversion of plasminogen to plasmin o Plasma digests fibrin in a clot and degrades fibrinogen, prothrombin, and other clotting factors Use: o - Prevention of MI or stroke Side effects: o Anaphylaxis o Dysrhythmias o Hemorrhage GOOD TO KNOW!! o Long action… stop 7 days before surgery o Avoid excessive foods that may cause bleeding (garlic)