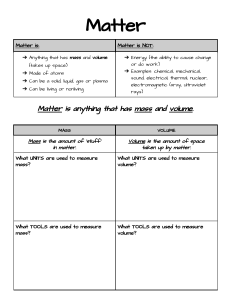
School: Date: January 16, 2023 Teacher: Grade & Subject: VIII-Physics Learning Competency: I. differentiate between heat and temperature at the molecular level (S8FE-Ig-29) OBJECTIVES At the end of the lesson, 80% of the students should be able to: a. Differentiate between heat and temperature in molecular level b. Discuss the properties of heat and temperature in molecular level; c. Compare the changes in the temperature of water to determine the relationship between the amount of heat transferred and the resulting temperature change. II. SUBJECT MATTER A. Topic: Heat and Temperature B. Materials: ICT resources C. Reference: Modules, TG III. LEARNING ACTIVITIES TEACHER’S ACTIVITY Preliminary Activity Prayer Attendance Classroom Management LEARNER’S ACTIVITY A. Elicit Review What is heat? What are the modes of heat transfer? Heat is a form of energy that transfers from a body of higher temperature to another body of lower temperature. - Conduction Convection Radiation B. Engage The teacher will ask the students a question to collect ideas and clear up confusion. Students’ answer may vary Are heat and temperature the same? C. Explore The teacher will let the students perform an activity. The students will be grouped into 5. D. Explain The students will answer the guide questions. 1. What similarities and differences did you observe when a drop of dye was added to each container? The students will do the activity. Activity 1 “Dye in Water” Explain the scattering of the dye in water at different temperatures. Students’ answer may vary. 1. After putting drops of dye into the water, the dye scattered throughout the water. But the rate of scattering of the dye differs in each container. 2. In which container did the dye scatter the fastest? In which did it scatter the slowest? 3. How do you relate the temperature of the water to the rate of scattering of the dye? 4. In which container are the particles of water moving fastest? In which container are the particles moving slowest? 5. How is temperature related to the speed of the particles? 6. In which container are the particles of water moving fastest? In which container are the particles moving slowest? Q13. How is temperature related to the speed of the particles? E. Elaborate The teacher will discuss the lesson about heat and temperature. Emphasize the concepts that are confusing. F. Extend - What are the applications of Enzyme Activity that you can observe in your daily life? IV. 2. Hot water. Cold water. 3. The higher the temperature of the water, the faster the scattering of the dye. 4. The particles are moving fastest in the container with hot water. The particles are moving slowest in the container with cold water. 5. The higher the temperature of the water, the greater the speed of the moving particles. The higher the temperature, the greater the kinetic energy of the particles. Students will answer various questions during discussion. Students may vary EVALUATION Class get ½ crosswise and answer the following questions. 1. Complete the table below with the proper information. Heat vs Temperature HEAT Definition Unit of Measurement Property TEMPERATURE Activity 1 Explaining hotness or coldness This first activity deals with one of the major effects of heat transfer, which is temperature change. You will describe the hotness or coldness of an object in terms of its temperature. You will also compare the changes in the temperature of water to determine the relationship between the amount of heat transferred and the resulting temperature change. Materials Needed: 3 identical containers thermometer hot water tap water (room temperature) cold water Procedure: 1. Half-fill the three containers with equal amount of cold water. Arrange them next to one another as shown in Figure 1 below. 2. Place your finger for a while into any of the containers. Try to recall your lesson on Heat Transfer in Grade 7 and answer the following questions: Q1. What actually transferred when you dipped your finger into the water? In what direction did it transfer? Q2. Was the water ‘hot’ or ‘cold’? Explain. Discuss your answers with the group. Try to estimate the temperature of the water in the containers. 3. Measure with a thermometer the temperature of the water in each container. Record your measurements in Table 1 below. (Note: The initial temperature of the water in each container should be the same as they come from the same source. Q3. How close is your estimated value to the measured temperature of the water? 4. Add the same amount of hot water to container 1, tap water to container 2 and the same cold water to container 3. Leave the containers for a while. 5. Dip your fingers again, this time into the three containers. Make sure that you do not dip the same finger into the containers. Q4. Which container feels ‘hottest’? Which container feels ‘coolest’? Q5. What do you think causes the difference in the hotness or coldness of the water inside the containers? 6. Measure and record the temperature of the water in all containers. Calculate the change in the temperature of water in each container. Q6. In which container(s) is heat transfer taking place? What evidence best supports your answer? Within this container, which absorbs heat? Which gives off heat? Q7. In which container was there the greatest amount of heat transferred? What is the basis of your answer? Q8. How are the amount of heat transferred and the change in temperature of water related? Activity 2 Dye in water At the end of this activity, you should be able to explain the scattering of the dye in water at different temperatures. Materials Needed: 3 transparent containers 1 thermometer 3 plastic droppers hot water tap water (room temperature) cold water dye (Food color) Procedure: 1. Fill the three containers separately with cold water, tap water, and hot water. 2. Measure the temperature of the water in each container. Record your measurements in Table 2 below. 3. With the dropper, place a drop of dye into the center of each container as shown in Figure 2. (Note: It is better if you place drops of dye into the three samples simultaneously.) 4. Carefully observe and compare the behavior of the dye in the three containers. Write down your observations in Table 2. Q1. What similarities and differences did you observe when a drop of dye was added to each container? Q2. In which container did the dye scatter the fastest? In which did it scatter the slowest? Q3. How do you relate the temperature of the water to the rate of scattering of the dye? You learned in Module 2 that moving objects possess kinetic energy. All the objects that you see around you that are moving possess kinetic energy. But do you know that even the very small things that you cannot see, like the particles of objects, are also moving and have kinetic energy? Take for example the water inside the containers in Activity 2. The scattering of the dye through the water indicates that the particles of water are moving. You will learn more about the movement of the particles of matter in the third quarter when you discuss about the Particle Theory of Matter. You also noticed that the rate of scattering of the dye throughout the water differs in each container. It can then be inferred that the speed of the particles of water varies in each container. Since kinetic energy depends on speed, the kinetic energies of the particles also vary. Q4. In which container are the particles of water moving fastest? In which container are the particles moving slowest? Q5. How is temperature related to the speed of the particles? Q6. How is temperature related to the kinetic energy of particles?