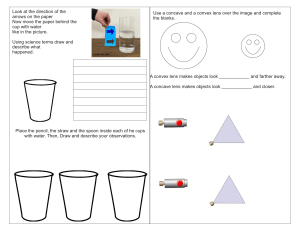
Light and Optics Study Guide 1. Vocabulary terms: refer to your vocab sheet, and make sure you are familiar with the vocabulary that we used this unit. 2. Light is Energy: it can be transformed into other forms of energy (electrical energy, thermal energy, etc.) a. What are some examples of light energy transforming to another form? b. What are some natural and man-made sources of light energy? 3. Reflection: the process of light bouncing off a surface. All surfaces reflect light. a. What is the difference between regular reflection and diffuse reflection? Can you draw a ray diagram to show the difference? b. What are some examples of surfaces that create a regular reflection? A diffuse reflection? c. How do we see things? How does light travel from its source to our eye? d. Why does a green shirt look green? How do we see colour? 4. Refraction: the process of light changing speed/bending through different substances. a. The more ________ the substance, the slower the light will travel. b. The change in speed results in the light bending, creating a distorted image. c. Can you draw a ray diagram of refraction? 5. Light Travels in Waves: Wavelengths a. Higher frequency waves are ________ together (smaller wavelength), and have more energy. b. What colour of visible light has the lowest frequency? What colour has the highest frequency? c. What happens to light when it moves through more dense mediums?Less Dense? d. Why does a green shirt appear green? 6. The Electromagnetic Spectrum: Visible light is the light we can see - ROYGBIV - and is only a small part of the electromagnetic spectrum. There are many types of light energy that our eyes cannot see. a. What are the 7 major types of light energy found on the electromagnetic spectrum? b. Which type of electromagnetic radiation has the least amount of energy? Can you explain why? c. Which type of electromagnetic radiation has the most amount of energy? Can you explain why? d. What are some real-life examples of ways we protect ourselves from high energy wavelengths? 7. The Human Eye: review the main parts of the eye and their function. a. Iris, Pupil, Lens, Cornea, Retina, Optic Nerve. b. What is hyperopia and Myopia and how are they corrected? 8. Lenses and Mirrors: Convex and Concave Lenses/Mirrors a. How do light rays act when they pass through a concave lens? A convex lens? b. How do light rays act when they bounce off a concave mirror? A convex mirror? c. Which type of lens focuses light to a focal point? What happens to an image if it is viewed from beyond the focal point? d. How do glasses or contact lenses help allow people to see clearly?