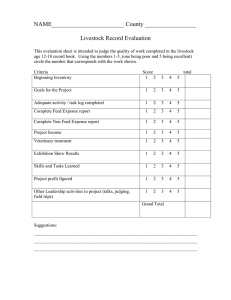
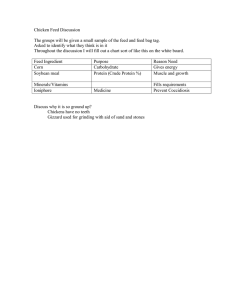
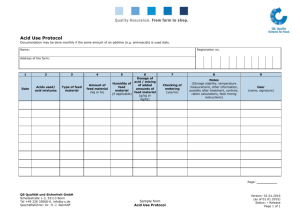
INTRODUCTION The course aims to equip students with knowledge on animal feeding requirements for optimum production, growth and health. Specifically the student will learn on feed classification, functions, resource base, composition and formulation. Definitions; classification of feeds; digestion, absorption, utilization, assimilation, requirement and functions of nutrients; deficiencies and toxicities; unidentified growth factors; feed additives; protein and energy evaluation for livestock and poultry; present status of feed industry, feed resources, feed formulation and mixing, feeding standards, composition of formulate feeds. LEARNING OBJECTIVES The course will provide opportunities for; a. Describing the range of livestock feeds using accepted industry terminology. b. Understanding energy foods, including the sources and functions of those foods, in animal diets. c. Understanding animal nutrients, functions and sources d. Understanding nutrient deficiencies and toxicity e. Understand the principle of feed formulation, feed ingredients, and standards of formulated feeds and feed additives f. Understand the current status of feed in Kenya EXPECTED LEARNING OUTCOMES By the end of the course, the learners will be able to: a. Describe the various terminologies applied in animal nutrition and feed industry b. Explain the role of water in animal nutrition. c. Describe various principles related to animal nutrition. d. Outline various nutrients requirements, their functions and sources e. Discuss the effects of nutrient deficiencies and toxicity to livestock f. Discuss common growth promoters and feed additives and their functions g. Explain carbohydrate and protein requirements of animals h. Give an overview of current feed industry and various feed ingredients i. Discuss the consideration for nutrient requirements during feed formulation and various methods for feed formulation j. Describe how basic formulation function works and Pearson’s square feed formulation method k. Describe the various fractions of formulate feed and feed ingredients classification l. Discuss various crop byproducts COURSE OUTLINE AND SCHEDULE WEEK LECTURE TOPIC LECTURE DETAILED OUTLINE 1 6 Introduction to course, expectations Terms and definitions Types of nutrients Water Principles related to Digestion (monogastric and ruminant) animal nutrition and Absorption and variety of mechanism of absorption feeding Utilization Assimilation Poultry digestive system Animal nutrient types Carbohydrates, their functions and sources and their function Proteins, their function and sources Fats , their function and sources Minerals, their functions and sources Vitamins, their functions and sources Other requirements Nutrition deficiencies Definition of deficiency and toxicity and toxicities General effects of nutrient deficiencies and toxicity to livestock Overview of carbohydrate, proteins, mineral and vitamin deficiencies and the effects Growth factors and feed Antibiotics additives Growth promoters Coccidiostats CONTINUOUS ASSESSMENT TEST 1 7 Practical 8 Current status of feed industry Livestock feed resources 2 3 4 5 Introduction 9 During this lesson, we will visit a farm where various types of livestock feeds and feeding strategies will be evaluated Production and supply, legislation, demand, trade, policy, taxes, quality concerns and regulation Roots and tubers, grains, concentrates, roughages, hay and silage. Additionally, anti-nutritive factors in animal feeds will be discussed. 10 CONTINUOUS ASSESSMENT TEST 2 11 Feed formulation Consideration for nutrient requirements Available methods for feed formulation How basic formulation function works Pearson’s square method Composition of feeds following feed analysis and the regulation of feed intake in farm animals 12 Feeding analysis 13 Feeding Standards/Systems Quality standards considered during feeding animals to ensure balanced diets Feed formulation simulation Formulate feed formulation using a mobile based application 14 15 & 16 END OF SEMESTER EXAMINATIONS EVALUATION INSTRUCTIONS Semester course assessments will include two continuous assessment tests. The distribution of Marks is as follows: CAT 1 – 30% Practical report -15% CAT 2 - 30% Average CAT = CAT 1 +Practical report + CAT 2 = 30% EXAM – 70 % TOTAL FINAL MARKS = 100% CORE READING MATERIALS 1. Chiba, L. I (2009) Animal Nutrition Handbook, Second revision 2. McDonald et al., (2010) Animal nutrition, 7th edition, @Pearson 3. Bels,.V. (2006) Feeding in Domestic Vertebrates, From Structure to Behaviour @ CAB International 4. International Livestock Research Institute (2007). Feeding dairy cattle A manual for smallholder dairy farmers and extension workers in East Africa Manuals and Guides No. 2; OTHER REFERENCE MATERIALS 1. FAO. 2012. Pig Sector Kenya. FAO Animal Production and Health Livestock Country Reviews. No. 3. Rome. 2. Dairy farmers training manual, Ministry of livestock development, 2012 3. ARC (1987). The nutrient requirements of farm livestock: Poultry Agricultural Research Council, Uk. 4. FAO and IFIF. 2010. Good practices for the feed industry – Implementing the Codex Alimentarius Code of Practice on Good Animal Feeding. FAO Animal Production and Health Manual No. 9. Rome