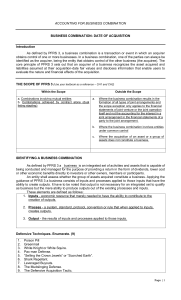
BUSINESS COMBINATION: FULL PFRS VS. 2015 PFRS FOR SMEs (SMALL MEDIUM ENTITIES) FULL PFRS Acquisition Method 1. Identify the acquirer 2. Determining the acquisition date 3. Recognize identifiable asset, acquire, liability and non-controlling interest 4. Recognize goodwill Note: Direct cost – expense (immaterial) Indirect cost – expense Stock cost – Share premium/ Retained Earnings Noncontrolling Interest Valuation a. Fair value b. Proportionate Goodwill – PAS 36 Not amortized but subject for impairment If the goodwill at the year-end is given, it must be compared to the goodwill computed. Any difference result to implied impairment. PFRS FOR SMEs Purchase Method 1. Identify the acquirer 2. Cost of business combination a. Consideration transfer + direct cost 3. Allocate the cost of your business combination to the Fair value Net Asset Acquired of acquiree Note: Direct cost – capitalize (material) Indirect cost – expense Stock cost – Share premium/ Retained Earnings Noncontrolling Interest Valuation a. Proportionate Goodwill Amortized: useful/maximum life of 10 years BUSINESS COMBINATION: FULL PFRS What is business? Integrated set of activities capable to conduct and manage to provide profit/ income in the form of shares or dividends. What are the element of IFRS 3? Input, process, and output What is the method to be used? Acquisition Method – Fair value What is the objective of business combination? 1. Identify the acquirer 2. Determining the acquisition date 3. Recognize identifiable asset, acquire, liability and non-controlling interest 4. Recognize goodwill What is the exception in PFRS 3? a. Formation of joint venture/joint arrangement – it questions your resource contribution or the asset you acquired b. Acquisition of group of assets that does not constitute a business c. Business under common control How do you identify business combinations? Definition: Must obtain CONTROL of another entity What is the forms of BusCom? Net asset acquisition a. Statutory merger – ABC Co. + DEF Co. = ABC or DEF Co. b. Statutory Combination – ABC Co. + DEF Co. = GHI Co. Stock Acquisition (parent -subsidiary) a. exchange of ownership to have power or control b. Acquirer own majority of outstanding share (more than 50%) for control to exist Explain the changes after stock acquisition. Parent Acquirer BusCom a. Continue to exist and operate separate legal entity (ex. Jollibee bought mang inasal and still they operate separately) Subsidiary Acquiree b. Continue /maintain separate books and unconsolidated FS c. Need CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL REPORTS of the parent and its subsidiaries at the end of accounting period What is the nature of BusCom in stock acquisition? Horizontal integration (similar/same business line) Vertical Integration – different operation but is in successive stages or industry or process integration Conglomerate – unrelated business/ dissimilar nature/ product and services What is measurement period? Why is it important? Date to measure their acquisition -fair value of asset and liabilities and the measurement of noncontrolling interest. Important to have correct data and adjust provisional amount of large entity. It cannot exceed one year from acquisition date or finalization whichever comes first and no adjustment are permitted after one year. How do you compute goodwill? Consideration NCI Prev. held interest in the acquiree Total Less: FVNAA GOODWILL (GAIN IN PURCHASE XXX XXX XXX XXX (XXX) XXX