EAQ NCLEX CC Quiz #2
advertisement
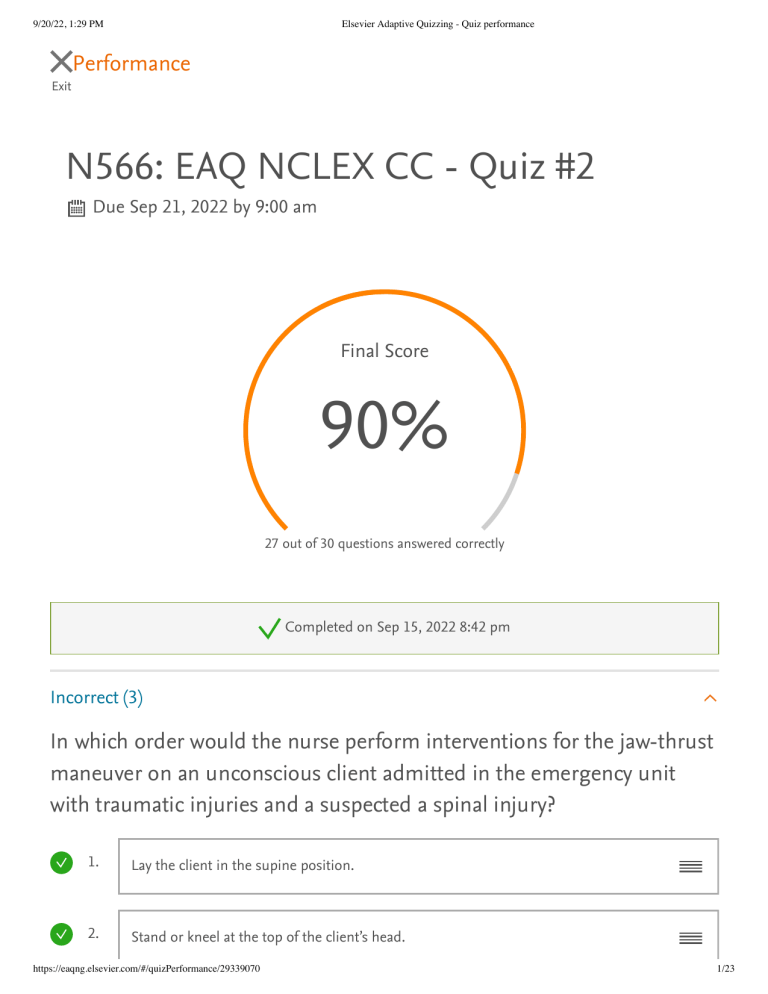
9/20/22, 1:29 PM Elsevier Adaptive Quizzing - Quiz performance Performance Exit N566: EAQ NCLEX CC - Quiz #2 Due Sep 21, 2022 by 9:00 am Final Score 90% 27 out of 30 questions answered correctly Completed on Sep 15, 2022 8:42 pm Incorrect (3) In which order would the nurse perform interventions for the jaw-thrust maneuver on an unconscious client admitted in the emergency unit with traumatic injuries and a suspected a spinal injury? 1. Lay the client in the supine position. 2. Stand or kneel at the top of the client’s head. https://eaqng.elsevier.com/#/quizPerformance/29339070 1/23 9/20/22, 1:29 PM Elsevier Adaptive Quizzing - Quiz performance 3. Grasp the client’s lower jaw and lift forward with both hands without tilting the head. 4. Place one hand on each side of the client’s head. 5. Rest elbows on the surface. Rationale Jaw-thrust maneuver is performed to open the airway of an unconscious client with possible spinal or neck injury. The client should be laid in supine position and the nurse would kneel at the top of the client’s head to initiate the procedure. This position allows access to the peritoneal, thoracic, and pericardial regions. This should be followed by resting the elbows on the surface and placing one hand on each side of the client’s head. Grasping the client’s lower jaw and lifting forward with both hands without tilting the head helps lift of the epiglottis and enlarge the laryngeal inlet and the pharynx, thereby resulting in improved ventilation. Test-Taking Tip: In this question type, you are asked to prioritize (put in order) the options presented. For example, you might be asked the steps of performing an action or skill such as those involved in medication administration. Which condition of a client with hemorrhagic stroke resulting from a motor bike accident requires immediate attention? Glasgow Coma score of 10 Body temperature of 81.2°F Oxygen (O 2) saturation of 90% Presence of carotid pulse with blood pressure (BP) of 80 mm Hg https://eaqng.elsevier.com/#/quizPerformance/29339070 2/23 9/20/22, 1:29 PM Elsevier Adaptive Quizzing - Quiz performance Rationale Severe hypothermia such as body temperature of 81.2°F must be immediately corrected by infusing warm fluids and blood. This helps prevent hypothermia-related complications. A Glasgow Coma score of 10 needs medium priority because it does indicate immediate danger to the client. O 2 saturation of 90% indicates a manageable status. Presence of carotid pulse with BP of 80 mm Hg is acceptable. Test-Taking Tip: Apply your critical thinking and identify the value of each observation to select the correct answer. Which are the priority emergency assessments the nurse will perform for a client with bomb blast injuries? Select all that apply. One, some, or all responses may be correct. Some correct answers were not selected Airway Breathing Circulation Giving comfort measures Facilitating family presence Exposure or environmental control Rationale The primary survey focuses on airway-breathing-circulation (ABC) and environmental control. These are surveyed during emergency assessments in a primary survey to identify life-threatening conditions and to analyze the appropriate interventions. Giving comfort measures and facilitating family presence are performed in a secondary survey of emergency assessment followed by a primary survey. Test-Taking Tip: Key words or phrases in the question stem such as first, primary, early, https://eaqng.elsevier.com/#/quizPerformance/29339070 3/23 9/20/22, 1:29 PM Elsevier Adaptive Quizzing - Quiz performance or best are important. Similarly, words such as only, always, never, and all in the alternatives are frequently evidence of a wrong response. No real absolutes exist in life; however, every rule has its exceptions, so answer with care. Correct (27) A client is diagnosed with a pituitary tumor. Before surgery for tumor removal, the probability of an aneurysm must be determined. The nurse anticipates that which diagnostic test will be prescribed? Skull x-ray Angiogram Computed tomography Magnetic resonance imaging Rationale A localized swelling or inflammation in an arterial wall is called an aneurysm. An angiogram is a diagnostic procedure used to visualize blood flow in arteries. Therefore, an angiogram should be prescribed to rule out the probability of an aneurysm before pituitary tumor removal surgery. A skull x-ray will reveal tumor-induced changes in the bony sella turcica, which houses the pituitary gland. Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging are useful to obtain distinct images of bony and softtissue lesions. When the emergency department nurse is caring for a client with acute coronary syndrome who reports severe crushing chest pressure, which prescribed medication is best for the nurse to administer? Ibuprofen 650 mg orally Acetaminophen 650 mg orally https://eaqng.elsevier.com/#/quizPerformance/29339070 4/23 9/20/22, 1:29 PM Elsevier Adaptive Quizzing - Quiz performance Nitroglycerin 0.4 mg sublingually Morphine sulfate 4 mg intravenously Rationale Morphine will relieve pain and decrease sympathetic nervous system stimulation associated with pain. Ibuprofen will not work quickly to reduce pain. Acetaminophen also will not be rapidly effective. Nitroglycerin is ineffective in relieving ischemic pain with myocardial infarction. A client is admitted to the hospital with partial- and full-thickness burns of the chest and face sustained while trying to extinguish a brush fire. Which concern is the nurse’s priority? Loss of skin integrity caused by the burns Potential infection as a result of the burn injury Inadequate gas exchange caused by smoke inhalation Decreased fluid volume because of the depth of the burns Rationale Maintaining a patent airway is the priority; because of the proximity of the chest and face to the nose and mouth, inhalation burns also may have occurred. Although loss of skin integrity caused by the burns is important, it is not the priority at this time. Although potential for infection as a result of the burn injury is important, it is not the priority. Although fluid needs are important, the gas exchange is priority. When the nurse is caring for a client who has cardiogenic shock, which clinical manifestations will be expected? Select all that apply. One, some, or all responses may be correct. Rapid pulse https://eaqng.elsevier.com/#/quizPerformance/29339070 5/23 9/20/22, 1:29 PM Elsevier Adaptive Quizzing - Quiz performance Deep respirations Warm, flushed skin Increased blood pressure Decreased urinary output Rationale The heart rate increases (tachycardia) to meet the body’s oxygen demands and circulate blood to vital organs; the pulse is weak and thready because of peripheral vasoconstriction. The urinary output decreases because increased catecholamines and activation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system increase fluid reabsorption in the kidneys. The respirations are rapid and shallow, not deep. The skin is cold and clammy because of vasoconstriction caused by the shunting of blood to vital organs. The blood pressure is decreased, not increased, because of continued hypoperfusion and multiorgan failure. Test-Taking Tip: Pace yourself when taking practice quizzes. Because most nursing exams have specified time limits, you should pace yourself during the practice testing period accordingly. It is helpful to estimate the time that can be spent on each item and still complete the examination in the allotted time. You can obtain this figure by dividing the testing time by the number of items on the test. For example, a 1-hour (60-minute) testing period with 50 items averages 1.2 minutes per question. The NCLEX exam is not a timed test. Both the number of questions and the time to complete the test varies according to each candidate's performance. However, if the test taker uses the maximum of 5 hours to answer the maximum of 265 questions, each question equals 1.3 minutes. The nurse is caring for a client whose mechanical ventilator settings include the use of positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP). This treatment improves oxygenation primarily through which mechanism of action? Providing more oxygen to lung tissue https://eaqng.elsevier.com/#/quizPerformance/29339070 6/23 9/20/22, 1:29 PM Elsevier Adaptive Quizzing - Quiz performance Forcing pressure into lung tissue, which improves gas exchange Opening collapsed alveoli and keeping them open Opening collapsed bronchioles, which allows more oxygen to reach lung tissue Rationale The primary mechanism of PEEP is to deliver positive pressure to the lung at the end of expiration. This helps open collapsed alveoli and keeps them open. With the primary mechanism of PEEP to open the alveoli and maintain them open, exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen can take place more efficiently, thus improving oxygenation by providing more oxygen to the lung tissue and improving gas exchange. PEEP does not force pressure into lung tissue. PEEP may have an indirect effect on opening bronchioles. STUDY TIP: Laughter is a great stress reliever. Watching a short program that makes you laugh, reading something funny, or sharing humor with friends helps decrease stress. Which is the priority focus of nursing care for a client with a spinal cord injury during the immediate postinjury period? Inhibiting urinary tract infections Preventing contractures and atrophy Avoiding flexion or hyperextension of the spine Preparing the client for vocational rehabilitation Rationale The priority of care at this time is to protect the spine from additional damage to the traumatized area while it heals. Infection can result from prolonged immobility; https://eaqng.elsevier.com/#/quizPerformance/29339070 7/23 9/20/22, 1:29 PM Elsevier Adaptive Quizzing - Quiz performance although important, it is not the immediate priority. Although important, preventing contractures and atrophy is not the priority in the immediate postinjury period. Vocational rehabilitation will assume greater importance after the client’s condition stabilizes. After an anterior fossa craniotomy, a client is placed on controlled mechanical ventilation. Which action would the nurse take to promote adequate cerebral blood flow? Clear the ear of draining fluid. Discontinue anticonvulsant therapy. Position the client’s head turned to the left. Monitor serum carbon dioxide levels. Rationale Carbon dioxide levels must be maintained because carbon dioxide can cause vasodilation, increasing intracranial pressure and decreasing blood flow. The fluid may be cerebrospinal fluid; clearing the ear may cause further damage. Because of manipulation during a craniotomy, anticonvulsants are given prophylactically to prevent seizures. Turning the neck impairs venous drainage from the head and may increase intracranial pressure, thus decreasing cerebral blood flow. Which intervention would the nurse implement for a 5-year-old child admitted to the burn unit with severe burns? Giving ice chips as desired Permitting milk if it has been iced Maintaining nothing-by-mouth (NPO) status for 24 to 48 hours Limiting oral fluid to 15 mL every 4 hours https://eaqng.elsevier.com/#/quizPerformance/29339070 8/23 9/20/22, 1:29 PM Elsevier Adaptive Quizzing - Quiz performance Rationale NPO status is maintained during the early emergency/resuscitative phase because of the probability of paralytic ileus. It is unsafe to offer ice chips because the fluid that is ingested interferes with monitoring and control of the child’s fluid and electrolyte status. It is unsafe to offer oral fluids, not only because of the danger of paralytic ileus, but also because they interfere with monitoring and control of the child’s fluid and electrolyte status. Test-Taking Tip: Pace yourself when taking practice quizzes. Because most nursing exams have specified time limits, you should pace yourself during the practice testing period accordingly. It is helpful to estimate the time that can be spent on each item and still complete the examination in the allotted time. You can obtain this figure by dividing the testing time by the number of items on the test. For example, a 1-hour (60-minute) testing period with 50 items averages 1.2 minutes per question. The NCLEX exam is not a timed test. Both the number of questions and the time to complete the test vary according to each candidate’s performance. However, if the test taker uses the maximum of 5 hours to answer the maximum of 265 questions, each question equals 1.3 minutes. Which emergency staff member would monitor vital signs, perform basic wound care, and ensure spinal immobilization for a client admitted to the emergency department after a train derailment? Paramedics Prehospital care providers Emergency medicine physician Emergency medical technicians Rationale Emergency medical technicians are the appropriate emergency staff members who would monitor vital signs, perform basic wound care, and ensure spinal https://eaqng.elsevier.com/#/quizPerformance/29339070 9/23 9/20/22, 1:29 PM Elsevier Adaptive Quizzing - Quiz performance immobilization, because these are basic life support (BLS) interventions. Paramedics are qualified to perform advanced life support (ALS) measures. Prehospital care providers are the first caregivers who help in transportation to the emergency department. Emergency medicine physicians receive specialized education and training in emergency client management. Which nursing intervention is the priority when the nurse notices that the client receiving a blood transfusion is having an acute hemolytic reaction? Stop the blood transfusion immediately. Report to the primary health care provider. Recheck identifying tags and numbers on the client. Maintain a patent intravenous (IV) line with saline solution. Rationale An incompatible blood transfusion can result in an acute hemolytic reaction in the client. During acute hemolytic reactions, the nurse would stop a blood transfusion as a priority nursing intervention. After stopping the blood transfusion, the nurse would report it to the primary health care provider. The nurse can then recheck the client’s identifying tags and numbers and maintain a patent IV line with saline solution. The nurse is caring for a client with a body surface burn injury of 55%. Which information will the nurse consider when planning care for this client? Is prone to poor healing because of a hypermetabolic state Has a decreased risk of infection when in a hypermetabolic state Needs a cool environment to decrease caloric need Will need 20 calories/kg during the healing process https://eaqng.elsevier.com/#/quizPerformance/29339070 10/23 9/20/22, 1:29 PM Elsevier Adaptive Quizzing - Quiz performance Rationale Burn injuries cause a hypermetabolic state. This results in lipid and protein catabolism, which in turn can inhibit wound healing. A hypermetabolic state increases the risk for slowed wound healing, increasing the chance for infection. Cooling the environment would cause an increase in caloric need as the body tries to warm to core temperature. Clients with burn injuries require increased calories and protein to promote wound healing. For an adult client, 20 calories/kg does not provide an adequate increase of calories or protein for the hypermetabolic state associated with burns. Which would be included in the plan of care for a preterm newborn who is given oxygen by way of a hood? Ensuring that the oxygen is continuously warmed and humidified Monitoring to see that the infant’s skin and mucous membranes are remaining bright pink Informing the parents that oxygen will be given at 4 L/min and that blindness is not a risk Checking the oxygen level in the hood every 4 hours and monitoring oxygen saturation continuously Rationale The oxygen must be warmed and humidified to help prevent hypothermia and drying of the mucous membranes. Bright-pink skin and mucous membranes may indicate an excessively high arterial oxygen level, which predisposes the infant to retinopathy of prematurity. Blindness develops with an excessive arterial oxygen level, which may occur with any percentage of oxygen. The oxygen level is checked every 1 to 2 hours and adjusted in response to the infant’s condition. Test-Taking Tip: Practicing a few relaxation techniques may prove helpful on the day of an examination. Relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, imagery, head rolling, shoulder shrugging, rotating and stretching of the neck, leg lifts, and heel lifts with feet flat on the floor can effectively reduce tension while causing little or no distraction https://eaqng.elsevier.com/#/quizPerformance/29339070 11/23 9/20/22, 1:29 PM Elsevier Adaptive Quizzing - Quiz performance to those around you. It is recommended that you practice one or two of these techniques intermittently to avoid becoming tense. The more anxious and tense you become, the longer it will take you to relax. Which is the focus of nursing care for a newborn with respiratory distress syndrome? Tapping the toes to stimulate respirations Turning the infant frequently to prevent apnea Maintaining oxygen concentration at 40% to support respiration Keeping the infant warm to maintain body temperature at 98°F (37°C) Rationale A warm environment is most important, because if the neonate has to maintain body temperature it will further compromise physical status by increasing metabolic activity and oxygen demand. Frequent turning and stimulation such as tapping the toes are both contraindicated, because increased activity increases oxygen demands. The oxygen percentage will vary with the neonate’s Po 2 values; the concentration of oxygen should never be set at a fixed amount. Test-Taking Tip: Pace yourself when taking practice quizzes. Because most nursing exams have specified time limits, you should pace yourself during the practice testing period accordingly. It is helpful to estimate the time that can be spent on each item and still complete the examination in the allotted time. You can obtain this figure by dividing the testing time by the number of items on the test. For example, a 1-hour (60-minute) testing period with 50 items averages 1.2 minutes per question. The NCLEX exam is not a timed test. Both the number of questions and the time to complete the test varies according to each candidate’s performance. However, if the test taker uses the maximum of 5 hours to answer the maximum of 265 questions, each question equals 1.3 minutes. https://eaqng.elsevier.com/#/quizPerformance/29339070 12/23 9/20/22, 1:29 PM Elsevier Adaptive Quizzing - Quiz performance Which action would the nurse anticipate taking when a client develops third degree atrioventricular block with a heart rate of 30 beats/minute? Assist with rapid defibrillation. Prepare for synchronized cardioversion. Obtain the transcutaneous pacemaker. Initiate cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Rationale Transcutaneous pacing is used for emergency treatment of bradycardia, because it is noninvasive and can be rapidly initiated. Defibrillation would be used for ventricular fibrillation. Synchronized cardioversion would be used as the treatment for rapid atrial or ventricular rhythms such as atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, and ventricular tachycardia. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation is used when the client has cardiac or respiratory arrest. A client who had extensive pelvic surgery 24 hours ago becomes cyanotic, is gasping for breath, and reports right-sided chest pain. Which action would the nurse take first? Obtain vital signs. Initiate a cardiac arrest code. Administer oxygen using a facemask. Encourage the use of an incentive spirometer. Rationale The client is exhibiting the classic signs and symptoms associated with the postoperative complication of pulmonary embolus. Initially oxygen should be administered to increase the amount of oxygen being delivered to the pulmonary https://eaqng.elsevier.com/#/quizPerformance/29339070 13/23 9/20/22, 1:29 PM Elsevier Adaptive Quizzing - Quiz performance capillary bed. Obtaining the vital signs should be done after oxygen therapy is instituted. The client is not yet experiencing a cardiac arrest, and a code should not be initiated. Although deep breathing (such as that used with an incentive spirometer) and coughing are important after surgery, they will not be effective in resolving hypoxemia caused by a pulmonary embolus. When a norepinephrine intravenous infusion is prescribed for a client in septic shock, which intravenous line would the nurse choose for the infusion? Implanted port Midline catheter 18-gauge peripheral venous catheter Peripherally inserted central catheter (PICC) line Rationale Norepinephrine is a vesicant and can cause tissue necrosis if it infiltrates into the intradermal or subcutaneous tissues. It is best infused through a central line, such as a PICC line. Implanted ports are also central lines, used mainly for chemotherapy, but require specialized needles and staff who are trained in accessing the port. Midline catheters are peripherally inserted in the antecubital area or upper arm and are not recommended for infusion of vesicants because large amounts of fluid may escape into the subcutaneous tissues before the infiltration is noted. Infiltration of fluids occurs more frequently when fluids are infused through the smaller and more fragile peripheral veins. Test-Taking Tip: Do not select answers that contain exceptions to the general rule, controversial material, or responses that appear to be degrading. Which diagnostic test result will the nurse review after noticing large U waves on the electrocardiogram (ECG) for a client who was just admitted https://eaqng.elsevier.com/#/quizPerformance/29339070 14/23 9/20/22, 1:29 PM Elsevier Adaptive Quizzing - Quiz performance to the cardiac unit? Troponin T Serum potassium Oxygen saturation C-reactive protein Rationale Large U waves suggest possible hypokalemia, which should be corrected to decrease dysrhythmia risk. The nurse may also review the other values, but these are unrelated to the presence of U waves. Troponin T levels increase with myocardial infarction. Oxygen saturation changes do not cause U waves. C-reactive protein elevations indicate inflammation but will not cause changes in the ECG. STUDY TIP: Rest is essential to the body and brain for good performance; think of it as recharging the battery. A run-down battery provides only substandard performance. For most students, it is better to spend 7 hours sleeping and 3 hours studying than to cut sleep to 6 hours and study 4 hours. The improvement in the rested mind's efficiency will balance out the difference in the time spent studying. Knowing your natural body rhythms is necessary when it comes to determining the amount of sleep needed for personal learning efficiency. When the chest x-ray for a client who has arrived at the emergency department with chest trauma shows multiple fractured ribs, which action will the nurse take next? Administer the prescribed morphine sulfate. Assist the client to take deep breaths and cough. Check for paradoxical movement of the chest wall. Teach the client about ways to manage rib pain. https://eaqng.elsevier.com/#/quizPerformance/29339070 15/23 9/20/22, 1:29 PM Elsevier Adaptive Quizzing - Quiz performance Rationale Flail chest can occur when multiple ribs are fractured and can compromise breathing efforts because of paradoxical movement during inspiration and expiration. Flail chest may require intubation and mechanical ventilation. Analgesic medication administration will be needed, because rib fractures make breathing painful, but further assessment of the client’s ventilatory effort is needed prior to giving narcotic pain medications. The client with fractured ribs will need to deep breathe and cough to prevent atelectasis and pneumonia, but assessing for possible flail chest would be done first. Education about management of pain is needed, but this would be done after assessing for possible respiratory distress caused by flail chest. STUDY TIP: Answer every question. A question without an answer is the same as a wrong answer. Go ahead and guess. You have studied for the test and you know the material well. You are not making a random guess based on no information. You are guessing based on what you have learned and your best assessment of the question. A client who had an infratentorial craniotomy is admitted to the intensive care unit after discharge from the postanesthesia care unit. Frequent assessments reveal that the client's intracranial pressure is increasing. Which action would the nurse take? Notify the health care provider. Elevate the head of the bed. Reduce the prescribed flow rate of intravenous (IV) fluid. Administer the next scheduled dose of osmotic diuretic early. Rationale Immediate corrective therapy based on current assessments must be implemented. After an infratentorial craniotomy the client is positioned flat on one side with the head on a small, firm pillow unless otherwise instructed by the health care provider. Administering medication or adjusting an IV rate is a dependent function of the nurse, https://eaqng.elsevier.com/#/quizPerformance/29339070 16/23 9/20/22, 1:29 PM Elsevier Adaptive Quizzing - Quiz performance and the prescription must be followed exactly. Changes to prescriptions may be received when the health care provider is notified. STUDY TIP: Remember that intelligence plays a vital role in your ability to learn. However, being smart involves more than just intelligence. Being practical and applying common sense are also part of the learning experience. A preschool-age child is about to be admitted to the pediatric intensive care unit after surgery for the removal of a brain tumor. Which nursing action would prompt the nurse manager to immediately intervene? Places a hypothermia blanket at the bedside Adjusts the bed to the Trendelenburg position Obtains electronic equipment for monitoring of vital signs Secures a pump to administer the prescribed intravenous fluids Rationale Raising the foot of the bed increases blood flow to the brain, thereby increasing intracranial pressure. An increase in temperature may occur after a craniotomy as a result of stimulation of the hypothalamus. A hypothermic blanket should be ready if the temperature climbs precipitously. Monitoring of vital signs is a critical component of postoperative care. Intravenous infusions must be regulated precisely to minimize the possibility of cerebral edema. Test-Taking Tip: If the question asks for an immediate action or response, all of the answers may be correct, so base your selection on identified priorities for action. Which physiologic responses to bronchiolitis would the nurse expect to observe in the pediatric intensive care unit? Select all that apply. One, some, or all responses may be correct. Wheezing https://eaqng.elsevier.com/#/quizPerformance/29339070 17/23 9/20/22, 1:29 PM Elsevier Adaptive Quizzing - Quiz performance Bradycardia Sternal retractions Nasal flaring Prolonged expiratory phase Rationale Bronchiolitis in most infants is caused by respiratory syncytial virus. Wheezing occurs as the air passages narrow, resulting in the typical whistling sound. As breathing becomes more difficult, the infant must expend more energy and use accessory muscles of respiration to breathe. Nasal flaring is a predominant characteristic of bronchiolitis. The infectious and inflammatory changes narrow the bronchial passage, making it difficult for air to leave the lungs. As a result of increased respiratory effort and decreased oxygen exchange, tachycardia, not bradycardia, develops. Breath sounds are diminished because of edema of the bronchiolar mucosa and filling of the lumina with mucus and exudate. Which action would the nurse anticipate implementing when caring for a client with acute respiratory distress syndrome who is intubated and on mechanical ventilation? Deflate the endotracheal tube cuff hourly. Schedule a change in ventilator tubing every 24 hours. Determine need for suctioning based on client assessments. Leave fraction of inspired oxygen (FiO 2) at the highest setting as the client oxygenation improves. Rationale Suction is likely to be needed and will be done based on assessment data such as client oxygen saturation, breath sounds, and activation of the high pressure alarm signifying https://eaqng.elsevier.com/#/quizPerformance/29339070 18/23 9/20/22, 1:29 PM Elsevier Adaptive Quizzing - Quiz performance endotracheal tube obstruction. The endotracheal tube cuff is kept inflated to protect the lower airways and improve delivery of breaths to the lungs. Research indicates that daily changes in ventilator tubing increase the risk for ventilator-associated pneumonia; the ventilator tubing should be changed only when soiled. Because high FiO 2 levels can cause damage to the lungs, the FiO 2 is reduced as the client’s oxygenation improves. Test-Taking Tip: Pace yourself while taking a quiz or exam. Read the entire question and all answer choices before answering the question. Do not assume that you know what the question is asking without reading it entirely. Which core temperature is the lowest temperature at which the nurse performing a rewarming procedure on a client with severe hypothermia by administering warmed intravenous fluids will stop the rewarming? 86°F (30°C) 91.4°F (33°C) 96.8°F (36°C) 100.4°F (38°C) Rationale A rewarming procedure should be performed carefully, because it places the client at risk for 'after drop,' a further drop in core temperature. This can lead to hypotension and dysrhythmias. So, active rewarming should be discontinued once the core temperature reaches 89.6°F to 93.2°F (32°C–34°C). Administering warmed intravenous fluids is a type of active rewarming. The nurse will stop this procedure when client’s core temperature reaches 92.4°F (33°C). A core temperature of 86°F (30°C) indicates that moderate to severe hypothermia is present. The nurse would continue the rewarming procedure at this temperature. A core temperature of 96.8°F (36°C) is outside the recommended range in which active rewarming should be performed. At this temperature, the client is mildly hypothermic, and an active rewarming procedure is not required. However, this is not the lowest temperature at which the nurse would https://eaqng.elsevier.com/#/quizPerformance/29339070 19/23 9/20/22, 1:29 PM Elsevier Adaptive Quizzing - Quiz performance the active rewarming procedure. A core temperature of 100.4°F (38°C) is in the normal range; the nurse would have stopped the active rewarming procedure long before this temperature is reached. Which client condition would the nurse keep in mind while performing a rewarming procedure in a client with severe hypothermia? The client is at risk for hypertension from rewarming shock. The client should be monitored for after drop during rewarming. The cold myocardium should be stimulated in a hypothermic client. The core of the client with severe hypothermia should be warmed after the extremities. Rationale Rewarming places the client at risk for after drop, a further drop in core temperature. This occurs when cold peripheral blood returns to the central circulation. So, the core temperature of the client should be monitored carefully during rewarming. Rewarming shock can produce hypotension, not hypertension. The cold myocardium is extremely irritable, making it vulnerable to dysrhythmias. Gentle handling is essential to prevent the myocardium from being stimulated. Clients with moderate to severe hypothermia should have the core warmed before the extremities to prevent rewarming shock. When the nurse initiates continuous cardiac monitoring and maintains oxygen saturation and end-tidal carbon dioxide on a client who survived a fire, which type of emergency assessment is being performed? Focused adjuncts Full set of vital signs Comfort measures Family presence https://eaqng.elsevier.com/#/quizPerformance/29339070 20/23 9/20/22, 1:29 PM Elsevier Adaptive Quizzing - Quiz performance Rationale Emergency assessment of focused adjuncts is used to determine the need for additional procedures in a secondary survey. Initiating a continuous electrocardiogram, maintaining oxygen saturation and end-tidal carbon dioxide, inserting a gastric tube, and obtaining blood for laboratory studies are some of the interventions performed during emergency assessment of focused adjuncts. Emergency assessment of the full set of vital signs is performed to obtain temperature, heart rate, and blood pressure. The nurse gives comfort measures to assess, treat, and reassess for pain and anxiety. Facilitating family presence involves determining the caregiver’s desire to be present during invasive procedures and/or cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Test-Taking Tip: Identify option components as correct or incorrect. This may help you identify a wrong answer. Example: If you are being asked to identify a diet that is specific to a certain condition, your knowledge about that condition would help you choose the correct response (e.g., cholecystectomy = low-fat, high-protein, low-calorie diet). Which nursing intervention would be of most benefit to the client with a compromised airway the nurse noticed while performing resuscitation during the primary survey? Preparing for chest decompression if needed Monitoring vital signs, especially blood pressure and pulse Preventing hypothermia using blankets and heating devices Preparing for endotracheal intubation and mechanical ventilation Rationale Preparing for endotracheal intubation and mechanical ventilation ensures airway patency during the primary survey to reduce the severity of airway compromise. Preparing for chest decompression is done during the primary survey when there are no breath sounds. Monitoring vital signs, especially blood pressure and pulse, is https://eaqng.elsevier.com/#/quizPerformance/29339070 21/23 9/20/22, 1:29 PM Elsevier Adaptive Quizzing - Quiz performance performed to assess circulatory disorders. Preventing hypothermia using blankets and heating devices is done during the exposure assessment. Which type of support provides immediate relief to the client with tongue occlusion, loss of gag reflex, alterations in level of consciousness, oxygen (O 2) saturation of 40 mm Hg, and carbon dioxide (CO 2) saturation of 75 mm Hg? Tracheotomy Laryngeal repair Abdominal thrust maneuver Autotitrating positive airway pressure Rationale Upper airway obstruction may occur with tongue occlusion, which is associated with loss of gag reflex and alterations in the level of consciousness. The client suffering from severe hypoxia (O 2 saturation of 40 mm Hg) and who is hypercapnic (CO 2 saturation of 75 mm Hg) requires an emergency tracheotomy for relief within 2 minutes. Laryngeal repair is performed to prevent laryngeal stenosis and cover exposed cartilage. The abdominal thrust maneuver clears upper airway obstruction caused by a foreign body. Autotitrating positive airway pressure resets the pressure throughout the breathing cycle in a client with severe sleep apnea. 1 topics covered Critical Care Proficient Specialty Area Novice https://eaqng.elsevier.com/#/quizPerformance/29339070 Intermed. Prof. Q's ans'd 22/23 9/20/22, 1:29 PM Elsevier Adaptive Quizzing - Quiz performance You Novice Intermed. Prof. Q's 152 ans'd 152 Quiz me on this topic https://eaqng.elsevier.com/#/quizPerformance/29339070 23/23



