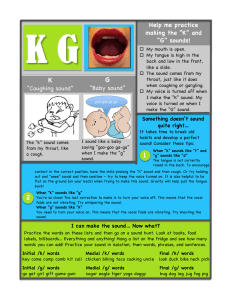
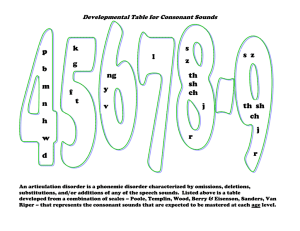
1. Speech or language impairment: difficulties with speech or language; trouble pronouncing words or making sounds with the voice; hard to understand words or express themselves. a. Speech Disorders: impairment of the articulation of speech sounds, fluency, and/or voice i. Apraxia: motor skills, hard say sounds and words due to a disconnect in brain communication. “Verbal dyspraxia” or “developmental apraxia” but children do not outgrow it. Don’t say words the same every time Stress on wrong syllable Distorts/changes sound Difficulty with fine motor skills Delayed language development Problems reading/writing Classroom challenges: understanding written directions, difficulty asking/answering questions and communicating Accommodations, a. supports, and interventions to support the student’s academic, social, and/or behavioral success in the classroom. b. Make movements with sounds, practice c. Transition supports - transitioning into or out of high school. ii. Dysarthria: face and mouth muscle weakness. ● Slur or mumble ● Slow or fast speech ● Speech too soft, robotic, or choppy ● Not moving tongue, lips, or jaw well ● Changes in voice sound ● Causes: stroke, Brian injury, tumors, muscle diseases ● Tips for listeners ○ Quiet area, pay attention, watch gestures, ask to repeat ● Classroom challenges ● Accommodations ○ SLP: Slowing speech, using more breath to make louder, strengthen muscles ● Transitions: iii. Orofacial Myofunction Disorders (OMD): abnormal movement pattern of face and mouth Interferes with normal face and mouth growth and development Problems eating, talking, breathing Tongue thrusting Breathless, difficulty breathing, breath with nose Limited tongue movement Messy eating Over/under bit Tongue pushing past teeth Difficulty says “s” and “j” sounds Drooling Difficulty closing lips to swallow Treatments a. Dentist, orthodontist, oral surgeon b. Change how chow or swallow c. Paying close attention to mouth movements Classroom challenges Accommodations: Transitions: iv. Speech sound disorders: trouble saying sounds clearly, “articulating disorder” or “phonological disorder” Not learn all sounds by age 4 (z, v, th) Starts as children, in adults after brain injury May sub one sound for another (w for r, w wabbit) Leave out or add or change sound (nana, banana) Causes a. Brain message delay (apraxia) b. Muscle weakness (dysarthria) c. Developmental disorder or genetic disorders d. Brain damage or healing loss v. Stuttering: getting stuck on certain sounds or words Disfluencies (adding sounds like uh, um) a. May have more or different disfluencies Repetitions-repeat word, phrase Prolongations-stretching a sound Blocks-not finishing a thought, pauses, stops in speech Changing a word Tension or negative feeling about talking, hide stuttering, availed words or situations Can change daily with stress or excitement Behaviors: head nodding, eye blinking, frustration vi. Voice disorders (short or long term) Chronic cough Paradoxical vocal fold movement (PVFM): hard to breath and talk Spasmodic dysphonia: long term vocal folds (inside larynx/voice box) harder time vibrating, vocal folds spasm or tighten a. Sounds jerky, shake your, hoarse Vocal fold nodules & polyps: growths in vocal folds that make vibration sound different a. Force voice wrong way the fold swell, swollen spots become hard a callus b. Scratchy, hoarse voice Vocal fold paralysis: one or both folds are not able to move a. Breathing or swallowing issues b. Language disorders: impaired comprehension and/or use of spoken, written, symbol systems i. Preschool language disorders: occur in age 3-5, problems following direction or understanding questions, learning new words or saying sentences Receptive language: understanding gestures, following directions, answering questions, pointing Expressive language: have trouble asking questions, naming objects, using gestures, put words together into sentences, learning songs and pronouns, covering, talking differently to different people Trouble reading and writing Holding a book right, turning pages Telling a story Naming letters and numbers, learning alphabet Cause: a. Family b. Born early or underweight c. Hearing d. Autism e. Developmental and genetic disorders f. Fetal alcohol syndrome g. Stroke or brain injury h. Nutrition Tips: a. Talk to, read to, point, listen and answer, get in ask questions, give time to answer, limit screen time ii. Learning disabilities: problems reading, writing, spelling Early speech and language issues can lead to LD Brain disorder Same signs as PLD Trouble remembering details Telling left from right Order of numbers and letters Memorizing Telling time and doing math iii. Selective mutism: more than just shy or not talking around new people until comfortable. Will NOT talk at certain times, no matter what Speaking at home but not school Last longer than 1 month Can speak the language but wont Does not have a speech or language problem that would cause it Causes: anxiety, fear, shy, want to be alone Treatment a. Stimulus fading: slowing adding a new person while talking to b. Shaping: praise and reward c. Self-modeling technique: watching videos of themselves talking in a comfortable situation, gain confidence 2. Medical and developmental conditions Medical and Developmental Conditions 3. Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder Autism (Autism Spectrum Disorders) Cleft Lip and Palate Right Hemisphere Brain Injury Traumatic Brain Injury