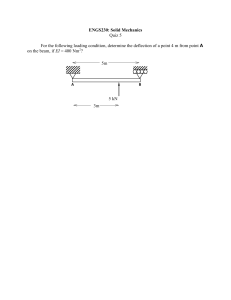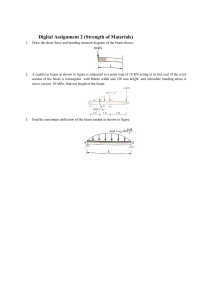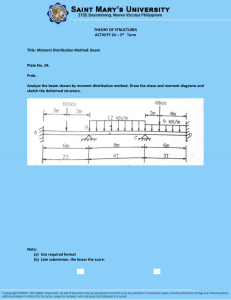
02A – Cantilever Load Cell 08/13/2022 08/16/22 Analaysis 21 Summary The following report presents various analyses for a cantilever load cell, summarized below. All elements are quadratic (beam and hexahedrals) with a global size of 0.0525”. The composite plate is E-Fiberglass/Epoxy, FVR = 67%. The contacting plates are rigid. The beam connections are low alloy steel. Deviations from beam theory are explained for each analysis. 1. 2D analysis of beam elements. 2. 3D analysis of solid composite plate bonded to rigid plates. 3. 3D analysis of solid composite plate with holes bonded to rigid plates. 4. 3D analysis of solid composite plate with holes connected to rigid plates via elastic beam connections (representing screws). 08/16/22 Analaysis 22 b Proximal Plate Reactions P over 2.05” 𝑃 = 180 𝑙𝑏𝑓 𝑎 = 2.83 𝑖𝑛 𝑏 = 1.415 𝑖𝑛 𝑅1 = 𝑃 𝑅1 = 180 𝑙𝑏𝑓 a 𝑀1 = 𝑃𝑏 𝑀1 = 254.7 𝑙𝑏𝑓 ∙ 𝑖𝑛 P over 2.05” M1 R1 over 0.04” 08/16/22 Analaysis 23 b Composite Reactions P over 2.05” 𝑃 = 180 𝑙𝑏𝑓 𝑎 = 2.83 𝑖𝑛 𝑏 = 1.415 𝑖𝑛 𝑅1 = 180 𝑙𝑏𝑓 𝑀1 = 254.7 𝑙𝑏𝑓 ∙ 𝑖𝑛 a 𝑅2 = 𝑅1 𝑅2 = 180 𝑙𝑏𝑓 R1 over 0.04” 𝑀𝑅2 = 𝑀2 − 𝑀1 + 𝑅1 𝑎 = 0 𝑀2 = −254.7 𝑙𝑏𝑓 ∙ 𝑖𝑛 M2 M1 R2 over 0.04” 08/16/22 Analaysis 24 Materials E-Fiberglass/Epoxy, FVR = 67% Low Alloy Steel 08/16/22 Analaysis 25 Beam Elements Shear Beam Width (into slide) = 2” Beam Height = 0.21” Moment Deflection 08/16/22 Analaysis 26 Discussion of Previous Slide • Beam geometry allows for Euler-Bernoulli deflection. • Though the material is orthotropic, the x-direction material properties are dominant and results are equivalent to isotropic bending. • All diagrams verified by hand calcs. 08/16/22 Analaysis 27 Solid Elements, Bonded Contacts y-axis direction Bonded Contact Surfaces x-axis direction 08/16/22 Analaysis 28 Discussion of Previous Slide • Deflection is very close to beam results • Minimum normal stress (maximum compressive bending stress) is a singularity due to contact with sharp corner of plates. • Maximum normal stress is ~14% less than beam results. Primarily due to the bonded contact where beam is supported by distributed load, thus there is a decrease in moment arm and a decrease in moment in the solid. 08/16/22 Analaysis 29 Solid Elements with Holes, Bonded Contacts y-axis direction Bonded Contact Surfaces x-axis direction 08/16/22 Analaysis 30 Discussion of Previous Slide • Deflection has increased compared to the previous analysis due to the decrease in stiffness at the hole locations. • Minimum normal stress (maximum compressive bending stress) is a singularity due to contact with sharp corner of plates. • The increase in maximum normal stress is local to the hole locations. The probed value of 16,077 psi away from the holes is more realistic, though is still lower than beam results due to the bonded contact and decrease in moment arm. 08/16/22 Analaysis 31 Solid Elements with Holes, Beam Connections Beam Connections y-axis direction No Separation Contact Surfaces x-axis direction 08/16/22 Analaysis 32 Discussion of Previous Slide • Deflection has grown compared to the previous analysis due to the elastic beam elements able to bend. • Minimum normal stress (maximum compressive bending stress) is a singularity due to contact with sharp corner of plates. • The increase in maximum normal stress compared to previous analysis is due to the increase in deflection. 08/16/22 Analaysis 33