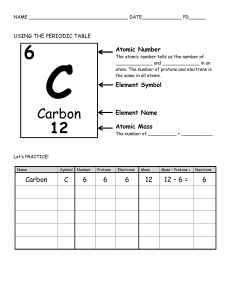
Periodic Table Scientists’ discoveries/theories: Davy: used electrochemical techniques for breaking down compounds into elements (Barium, Strontium, Calcium, Magnesium) Mosely: discovered positive charge in nucleus (atomic number) Dobreiner: suggested a Law of Triads, group of three elements of similar properties, where the weight of the 2nd is the average of the weights of the 1st and 3rd. Newlands: suggested a Law of Octaves; where elements are arranged in order of their atomic weight, properties repeated every 8th element. Robert Boyle: suggested that an element cannot be broken down into anything simpler Mendeleev: arranged elements in order of atomic weight, left gaps for undiscovered items, swapped iodine and tellurium because of their properties. Didn’t include noble gases. John Dalton: suggested that atoms are small and indivisible and make up all matter; atoms of given element are identical, atoms cannot be created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction William Crookes: accelerated cathode rays (beams of electrons with negligible mass and negative charge) in discharge tube. They cast a shadow by anode and moved the wheel. J.J Thomson: discovered electrons, measured e/m and suggested Plum Pudding Model: positive sphere with electrons embedded in it Johnstone Stoney: named the electron. Millikan: carried out oil drop experiment to determine charge on electron James Chadwick: discovered neutrons Modern atomic theory shows that electrons exhibit both wave and particle properties Rutherford: Gold Foil Experiment (observation conclusion) Bombarded gold foil with alpha particles (helium nuclei with 2 protons and 2 neutrons) A very large number of alpha particles were not deflected mostly empty space Many deflected at small angles positive mass repelling A few bounced straight back they collided with dense nucleus Isotopes: atoms with same number of protons but different number of neutrons Relative atomic mass: average mass of atoms of element relative to 1/12th of Carbon-12 Mass spectrometer processes in order: vaporisation, ionisation, acceleration, separation, detection. Principle of mass spectrometer: positively charged ions are separated according to their mass when moving in a magnetic field