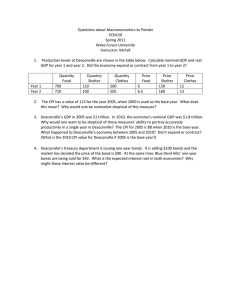
ECON 1220 A/B Introductory Macroeconomics Problem Set 1 [Due by 11pm on 5th Oct (Tue)] I. Multiple Choice Questions (20 points) 1) In 2013, an automobile dealership spent $20,000 on a new car lift for its repair shop, $2,000 on a new copy machine for its sales division, and $600,000 on Ford Motor company stock. Unsold cars and trucks were valued at $400,000 on January 1, 2013 and unsold cars and trucks were valued at $900,000 on December 31, 2013. What is the automobile dealership’s total investment spending in 2013? A) $22,000 B) $322,000 C) $522,000 D) $1,022,000 2) Emily is a writer. She buys pens and paper for $20 and writes a 500-page novel that she sells to a publishing company for $500,000. If the publisher prints 1 million copies that sell for $25 each, what is the contribution to GDP of Emily's novel? A) $25 million B) $20 million C) $500,000 D) $50,000 3) Which of the following could cause nominal GDP to increase, but real GDP to decrease? A) The price level rises and the quantity of final goods and services produced rises. B) The price level rises and the quantity of final goods and services produced falls. C) The price level falls and the quantity of final goods and services produced rises. D) The price level falls and the quantity of final goods and services produced falls. 4) A consumer price index of 160 in 1996 with a base year of 1982-1984 would mean that the cost of the market basket A) equaled $160 in 1996. B) equaled $160 in 1983. C) rose 160% from the cost of the market basket in the base year. D) rose 60% from the cost of the market basket in the base year. 5) You borrow $10,000 from a bank for one year at a nominal interest rate of 5%. The CPI over that year rises from 180 to 200. What is the real interest rate you are paying? A) 15% B) 5% C) -1.1% D) -6.1% II. True/False Questions (20 points) 1. 2. III. (10 points) Durable goods are most affected by the business cycle compared with nondurable goods. Explain. (10 points) Since real GDP is adjusted for inflation and nominal GDP is not, nominal GDP must always be higher than real GDP. Explain. Short-answer Questions (60 points) 1. (15 points) Consider the data above for a simple economy: Using 2009 as the base year, calculate nominal GDP, real GDP, and the GDP deflator for 2013. Show your work. 2009 2012 2013 Product Price Price Price Quantity Quantity Quantity MP3s 40 $250.00 45 $200.00 50 $150.00 Tacos 2,000 2.00 2,200 2.25 2,300 2.40 Coats 300 50.00 310 52.00 350 55.00 2. (15 points) Fill in the missing values in the table of data collected in the household survey for November, 2009. The working-age population, employment, unemployment, and labor force are measured in thousands. Show your work. Working-age population Employment Unemployment Unemployment rate Labor force Labor force participation rate 235,900 9.4% 65.5% 3. (20 points) The table below lists the actual minimum wage and CPI in 1974 and in 2012. Using the table below, calculate the real minimum wage for 1974 and 2012. Calculate the rate of growth of the real minimum wage from 1974 to 2012. Are workers better off in terms of the purchasing power of a dollar in 1974 or 2012? Explain why. Nominal CPI Year Minimum (1982-1984 =100) Wage 1974 $2.00 49.3 2012 7.25 224.9 4. (10 points) Use the equations for public and private saving to demonstrate how total saving equals investment plus net export in an open economy.