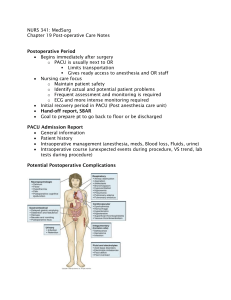
Care of the Surgical Client Phases of Perioperative Care • Perioperative: • Begins with decision to have surgery • Ends client is transferred to operating room or procedural bed • Intraoperative: • Begins when the client is transferred to the OR bed • Ends transfer to the post anesthesia care unit (PACU) • Postoperative: • Begins with admission to the PACU or other recovery area • Ends when complete recovery from surgery – follow up with MD Classification of Surgical Procedures • Urgency: Elective, urgent, emergency • Risk: Minor or major • Purpose: Diagnostic, curative, preventive, ablative, palliative, reconstructive, transplantation, constructive Anesthesia States • Loss of consciousness • Amnesia • Analgesia • Relaxed skeletal muscles • Depressed reflexes Types of Anesthesia • General: Administration of drugs by inhalation or intravenous route • Moderate sedation/analgesia (conscious sedation/analgesia): Used for short-term, minimally invasive procedures • Regional: Anesthetic agent injected near a nerve or nerve pathway or around operative site • Topical and local anesthesia: Used on mucous membranes, open skin, wounds, burns Phases of General Anesthesia • Induction: From administration of anesthesia to ready for incision • Maintenance: From incision to near completion of procedure • Emergence: Starts when client emerges from anesthesia and is ready to leave operating room Types of Regional Anesthesia • Nerve blocks • Spinal anesthesia • Epidural anesthesia Informed Consent • Description of procedure and alternative therapies • Underlying disease process and its natural course • Name and qualifications of person performing procedure • Explanation of risks and how often they occur • Explanation that the client has the right to refuse treatment or withdraw consent • Explanation of expected outcome, recovery, rehabilitation plan, and course of treatment Advanced Directives • Living wills • Durable power of attorney for health care • Nurses’responsibility with informed consent Nursing Process for Preoperative Care • Assessment • Health history • Medical history • Physical assessment • Diagnosis- NANDA • Impaired comfort • Risk for infection • Outcome identification and Planning • Implementing Client Risk Factors • Developmental level • Medical history • Medications • Previous surgeries • Nutrition • Use of alcohol, illicit drugs, or nicotine • Activities of daily living and occupation • Coping patterns and support systems • Sociocultural needs Surgical Risks of Medications • Anticoagulants: precipitate hemorrhage • Diuretics: electrolyte imbalances, respiratory depression from anesthesia • Tranquilizers: increase hypotensive effects of anesthetic agents • Adrenal steroids: abrupt withdrawal may cause cardiovascular collapse • Antibiotics in mycin group: respiratory paralysis when combined with certain muscle relaxants Pre-Surgical Screening Tests • Chest x-ray • Electrocardiography • Complete white blood cell count • Electrolyte levels • Urinalysis • Other screening dependent on client individual history Nurse’s Role in Pre-Surgical Testing • Ensure that tests are explained to the client. • Ensure that appropriate specimens are collected. • Ensure that results are recorded in client records before surgery. • Ensure that abnormal results are reported. Preparing the Client Through Teaching • Surgical events and sensations • Pain management • Physical activities • Deep breathing • Coughing • Incentive spirometry • Leg exercises • Turning in bed • Early ambulation Nursing Interventions to Meet Psychological Needs of Surgical Patients • Establish therapeutic relationship and allow client to verbalize fears and concerns. • Use active listening skills to identify anxiety and fear. • Use touch to demonstrate genuine empathy and caring. • Be prepared to respond to common client questions about surgery. • Leg Exercises to increase venous return Nursing Interventions: Preparing the Preoperative Client • Hygiene and skin preparation • Elimination • Nutrition and fluids • Rest and sleep • Preparation and safety the day of surgery Preoperative Medications • Sedatives • Anticholinergics • Narcotic analgesics • Neuroleptanalgesia agents • Histamine-2 receptor antihistamines Nursing Process for Intraoperative Care • Assessment • Pre-op completion • Marking site • Diagnosis- NANDA • Risk for imbalanced fluid volume • Risk for injury • Outcome identification /planning • Implementing • Documenting • Evaluating TJC Protocol to Prevent Wrong Site, Wrong Procedure, and Wrong Person Surgery • Preoperative client identification verification process • Marking the operative site • Final verification just prior to beginning the procedure, referred to as the time-out Post-Operative Nursing Care-PACU • Prevent complications from anesthesia • Prevent complications from surgery • Vital signs- level of consciousness- surgical site-color and skin temperatureintravenous fluids- other tubes- comfort- position and safety • Systematic assessments every 10-15 minutes • Ongoing postoperative assessment Return of Consciousness • Unconscious • Response to touch and sounds • Drowsiness • Awake but not oriented • Awake and oriented Nursing Process for Ongoing Postoperative Care • Assessment • Diagnosis • Acute pain • Risk for delayed surgical recovery • Outcome identification and planning • Implementing • Evaluation Postoperative Assessments and Interventions • Respiratory status (airway, pulse oximetry) • Cardiovascular status (blood pressure and heart rate) • Temperature • Central nervous system status (level of alertness, movement, shivering) • Fluid status • Wound status • Gastrointestinal status (nausea and vomiting) • General condition • Important: Note comparisons with preoperative baseline values Outcomes for the Surgical Client • Receive respectful and culturally and age-appropriate care • Be free from injury and adverse effects • Be free from infection and DVT • Maintain fluid and electrolyte balance, skin integrity, normal temperature • Have pain managed • Demonstrate understanding of physiologic and psychological responses to surgery • Participate in rehabilitation process Cardiovascular Complications • Hemorrhage • Shock • Thrombophlebitis • Pulmonary embolus Preventing Respiratory Complications • Incentive spirometer • Coughing/ deep breathing • Oral care • Understanding (client and staff education) • Getting out of bed at least three times a day • Per orders of HCP • Head of the bed (HOB) elevation Preventing Wound Complications • Interventions • Assess vital signs • Maintain hydration • Maintain nutritional status • Proper hygiene • Maintaining aseptic technique • Complications • Wound hemorrhage • Wound infection • Dehiscence • Evisceration • Keloids Discharge Planning • Client Education • Assisting the client to attain, maintain, retain optimal health. • Identify interventions as primary, secondary, tertiary. • Discharge Planning & Teaching • Medications • Wound care • Follow-up care • Activity • Nutrition • Support system