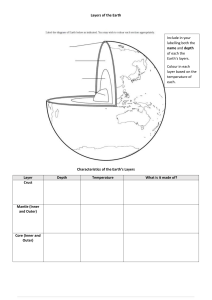
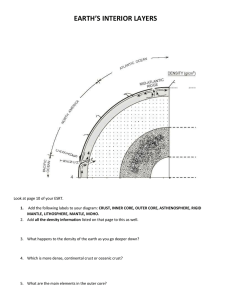
Name: Per: Date: Earth Layers Lab Introduction: Scientists who study the earth's layers are called geologists. Since they cannot see the inside of the earth, they use geographical clues to help them. These clues are gathered from activities such as volcanoes and earthquakes. From these clues, geologists make inferences about what the inside of the earth actually looks like. Crust Mantle Outer Core Inner Core is a made up of different layers known as the crust, mantle, and inner/outer core. These layers vary in depth, pressure, and temperature. Since pressure and temperature affect density, each layer has a different density as well. The Geologists believe the earth density of each layer determines its position in the earth, Earth La er Densi Crust 2.6 g/cm3 Mantle Outer Core Inner Core g/cm3 10.2 g/cm3 13.1 /cm3 .0 Analysis: crust 1) What layer of Earth is least dense? 2) What layer of Earth is most dense? 3) What is the relationship between the density and position of each Earth layer? the outer core the density of each layer determines its position in the earth. 4) If you were to make a model of Earth using the materials listed below, what should you use to represent the crust? Material marble clay the inner core? Densi Cla 2.0 A Marble 2.4 Aluminum Foil 1.2 /cm3 cm3 cm3 Models: A model is a tool used by scientists to represent another object that is either too large or too small to study on its own. For instance, since atoms are too small to see, use models to the structure of each atomic part. Similarly, since the on a much smaller scale. In this activity, you will help to create a model of Earth that is 22.2 million times smaller than the actual earth. scientists earth is illustrate so large, scientists construct models to represent the Earth Procedures: 1) Carefully, cut out your of the earth 'slice' 2) Put your name on the back 3) Use a calculator to determine the depth your slice of the earth. Actual De th Crust o km 2890 km 2260 km 1220 km 4) 5) (in centimeters) each layer should be on Record your data below. Earth La er Mantle Outer Core Inner Core model Scale Multi lier De th on Model (in cm) cm km cm km cm km 5 cm/km .00 5 .00 5 .00 .00 Use a ruler to mark off the location of each layer on your slice Use a pencil to label each layer of earth on your slice 6) Color your slice according to the following key: brown a. Crust- b. Mantle- yellow c. Outer Core- orange d, Inner Core- red Conclusion: The earth is made out of layers that separate according to their The density of each layer is amount of affected it is the . of the material and the by the under. The thinnest and least dense layer state of matter even though the nickel and iron are at such a high temperature. hand, the outer core remains in a state of matter On the other even though it is made out of the same material as the inner core since there is not enough it to a solid. known as The layer under the most pressure is known as the Such high amounts of pressure cause this layer to remain in a to change is Packet: Earth's Interior Inner Core - layer of Earth's interior Seismic waves in composed of iron velocity DENSITY (g!em3) 2.7 granit!c continental 3.0 basalttG oceanic cut MOHO 3.4-6.6 CASCADES TRENCH EARTH'S CENTEN us—I 2 7000 6000 5000 3000 2000 PARTIAL MELTING 1000 unanal 0 1000 2000 3000 4000 5000 6000 DEPTH (km) Leigh-ManueEl - 2 and nickel Packet: Earth's Interior PART QUESTIONS: MULTIPLE CHOICE i 1. 2. At 4,500 kilometers below the surface of the Earth, the pressure The a. 4 b. 2.0 million atmospheres c. 2.8 million atmospheres d, 3.1 million b. c. d. 4, In 7, is greatest layers of Earth's interior correctly arranged crust, mantle, inner core, outer core b, crust, mantle, outer core, inner core c. inner core, outer core, mantle, crust d. outer core, inner core, mantle, crust The temperature a. 200 oc d. 6. below the Earthls surface of rock located 1 is about and pressure decrease and pressure decrease b. density increases, but temperature c. density and temperature increase, but pressure decreases d. density, temperature, Which zone and pressure increase of the Earthis interior a. outer core br inner core c. crust d. mantle what 25000 c 50000 c 62000 c none of the above Inside Earth's interior, d. order of increasing density? within the Earthis interior increases, the density, temperature, c. in ,000 kilometers below the Eadh's surface a. b. of 2,100 oc 2,800 oc 3,200 oc As the depth a. between depths 3500 and 4000 km 250 and 500 km 1500 and 2500 km 2500 and 3500 km a. b. 5. atmospheres which group are the c. estimated to be atmospheres rate of temperature increase a. 3. million is is is inferred to have a density of 10.0 grams per cubic centimeter? the approximate temperature between the outer core Leigh-Manuell - 3 and inner core? Name: Earthquakes Date: Earth Science Period: Supplemental: Earth's Using the Earth Science Reference Tables, complete the chart by Interior and the Interior filling in the inferred properties of Earth's layers for the specific depths indicated. Depth Density [g/Cm3] 6,000 km 4,000 km 2,000 km Pressure [million Temperature Layer of Earth atmospheres) 500 km 0 km Lithosphere Leigh-Manuell - 1