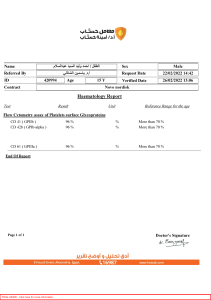
PRAIRIE VIEW A&M UNIVERSITY COLLEGE OF NURSING ASSESSMENT AND PLANNING GUIDE FOR USE IN THE HOSPITAL The following information should be included daily as it applies to your patient. Demographic Data G.C is a 67-year-old Hispanic female Height: 5’0 Weight: 121lbs 4.1 oz Date of Admission 04/07/2022 Vital Signs (D1) (D2) Day 1 Day 2 Significant Past Medical History Renal cyst (11/09/2016) Peripheral Arterial Disease (02/21/2013) Hyperlipidemia (05/27/2010) Osteoarthritis (05/27/2010) Diverticulosis (11/09/2016) Femoral-popliteal bypass (06/2013) Tubal ligation Foot surgery Pulse: 82 bpm RR: 12 bpm BP: 131/66 mmHg MAP: 87 mmHg Sp02: 95% on RA Temp: 99 F Pulse: RR: BP: MAP: Sp02: Temp: Allergies/Reactions Dexilant (diarrhea) Pneumovax 23 (nausea and vomiting) Gabapentin (palpitations) Eggs (No known reaction) Lactose intolerance (nausea and vomiting) Reason for Hospitalization and Current Diagnosis Patient came in with RLE claudication and occlusion of right femoropopliteal bypass graft. She also had limb ischemia s/p femoral-popliteal bypass surgery and vitamin b-12 deficiency. As well as presenting with GERD w/o esophagitis. She is also in acute renal failure stage. Describe the pathophysiology including signs, symptoms and incidence; and compare with patient findings: Peripheral Arterial Disease Patho/ Causes: is a common circulatory problem in which narrowed arteries reduce blood flow to your limbs and is commonly caused by atherosclerosis. The patient has prior history of hyperlipidemia, and she has hypertension which are major risk factors for atherosclerosis leading to PAD. Signs and Symptoms: includes painful cramping in one or both of your hips, thighs or calf muscles after certain activities, such as walking or climbing stairs (claudication), leg numbness or weakness, coldness in your lower leg or foot, especially when compared with the other side, sores on your toes, feet or legs that won't heal, a change in the color of your legs, hair loss or slower hair growth on your feet and legs, slower growth of your toenails, shiny skin on your legs, no pulse or a weak pulse in your legs or feet, erectile dysfunction in men, pain when using your arms, such as aching and cramping when knitting, writing or doing other manual tasks. My patient presented with claudication in her right leg and had weak pedal pulse in her right leg. She also had capillary refill of more than 3 secs in the right leg and had tissue ischemia around that leg which was brown. Complications: includes limb ischemia, stroke, and heart attack. My patient came in with ischemia on right lower leg which indicates a complication of PAD which has not been manage correctly. Diagnostic Labs: includes physical exam, Ankle-brachial index, ultrasound, angiography, and blood test. The patient had a blood test done as well as angiography was performed and physical exam which was found that the patient ischemia. Treatment: includes cholesterol-lowering medications, antihypertensives medications, medications to control blood sugar if that is the cause, blood thinners (anticoagulants) and symptom relief drugs. As well as Angioplasty, bypass surgery, and thrombolytic therapy. My patient’s treatment consists of atorvastatin, heparin, lisinopril, alteplase which are drugs used in treating PAD and accompanying symptoms. She also underwent bypass surgery and angioplasty as well to help resolve the problem. Medication Drug/Dose Acetaminophen (1000 mg oral q6h) Classification/Action Thought to produce analgesia by inhibiting prostaglandin and other substances that sensitize pain receptors. Drug may relieve fever through central action in the hypothalamic heatregulating center. (Analgesics) Purpose for use in this patient To relieve pain and high temp for the patient. Alteplase (20 mg in sodium chloride 1 mg/hr continuous) Atorvastatin (20 mg oral @bedtime) Converts plasminogen to plasmin by directly cleaving peptide bonds at two sites, causing fibrinolysis. (Thrombolytics) Inhibits HMG-CoA reductase, an early (and rate-limiting) step in cholesterol biosynthesis. (Antilipemic) To resolve the clots that is in her leg. To control high cholesterol levels Bisacodyl (10 mg rectal once) Stimulant laxative that increases peristalsis, probably by direct effect on smooth muscle of the intestine, by irritating the muscle or stimulating the colonic intramural plexus. Drug also promotes fluid accumulation in colon and small intestine. (Laxatives) To make her stool softer and easier for the stool to pass through the rectum and to prevent hemorrhoids since patient is at high risk for bleeding. Cyanocobalamin (1000 mcg oral daily) Heparin (1000 units injection continuous; 25,000 units 15 units/kg/hr intravenous) Prevent and treats low blood levels of vitamin B12. (Vitamins) To increase her vitamin B12 levels Accelerates formation of antithrombin III–thrombin complex and deactivates thrombin, preventing conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin. (Anticoagulants) To dissolve clots that may be present in her legs Lidocaine 5% ( 2 patch) Topical lidocaine stabilizes the neuronal membrane by inhibiting the ionic fluxes required for the initiation and conduction of impulses, thereby effecting local anesthetic action. (Analgesics) To help relieve any pain after her procedures Lisinopril (10 mg oral BID) Causes decreased production of angiotensin II and suppression of the RAAS. (Antihypertensives) To help decrease and or regulate her blood pressure to normal levels. Melatonin (5 mg oral @ bedtime) regulates the sleep-wake cycle by chemically causing drowsiness and lowering the body temperature. (Sedative) To help her sleep at night Methocarbamol (1,125 mg oral q8h) Action not established. Drug is a CNS depressant. It has no direct action on the contractile mechanism of striated muscle, the motor end plate, or the nerve fiber. (Muscle Relaxants) To help with RLE claudication and to relieve muscle stiffness or rigidity hence the patient has osteoporosis and osteoarthritis. Ondansetron (4 mg IV push q6h) May block 5-HT3 in the CNS in the chemoreceptor trigger zone and in the peripheral nervous system on nerve terminals of the vagus nerve. (Antiemetics) Helps relieve any nausea or vomiting patient may have. Polyethylene glycol (17 g oral 2 times daily) Causes water to be retained in stool. (Laxatives) Pregabalin (50 mg oral BID) May contribute to analgesic and anticonvulsant effects by binding to sites in CNS. (Anticonvulsants) To make her stool softer and easier for the stool to pass through the rectum and to prevent hemorrhoids since patient is at high risk for bleeding. To prevent seizures Sennosides-docusate sodium 8.6-50mg (2 tablet oral BID) Stool softener that reduces surface tension of interfacing liquid contents of the bowel. This detergent activity promotes incorporation of additional liquid into stools, thus forming a softer mass. (Laxatives) To make her stool softer and easier for the stool to pass through the rectum and to prevent hemorrhoids since patient is at high risk for bleeding. Tramadol (100 mg oral q8h) Unknown. Thought to bind to opioid receptors and inhibit reuptake of norepinephrine and serotonin. (Analgesics) To help relieve pain Intake/Output Diet__NPO_____ Enteral Feeding_NPO____ Drainage/Tubes__320 mL______ Intravenous Fluids/Flow/Rate: Alteplase 1 mg/hr Heparin 60 mL/hr Heparin 15 units/kg/hr Procedures/Surgery: (Describe). TPA: TPA is a naturally occurring protein found on endothelial cells, the cells that line blood vessels. It activates the conversion of plasminogen to plasmin, an enzyme responsible for the breakdown of clots, helping restore blood flow to the brain Angioplasty: is a procedure used to open blocked coronary arteries caused by coronary artery disease. It restores blood flow to the heart muscle without open-heart surgery. Pedal arterial access w/sheath left in place: used to gain arterial access and facilitate the insertion of catheters or other equipment for diagnostic and vascular interventions. Retrograde RLE angiogram through pedal access: allow the treatment of tibial occlusive lesions when standard endovascular techniques fail. Oxygen Therapy Room air Ventilator Setting:(if applicable) N/A Other Equipment/Lines applicable (eg PA catheters, A-lines, etc) Right tibial venous access sheath Urinary catheter Double lumen arterial sheath Diagnostic Studies/Lab Data (Identify abnormalities and describe their significance in the patient). RBC (4.20-5.40) - 2.48 Related to patient blood loss during the TPA procedure Hgb (12.0-16.0) – 6.5 Related to patient blood loss during the TPA procedure HCT (37.0-47.0) – 20.4 Related to patient blood loss during the TPA procedure MCH (27.0-32.0) – 26.2 Related to patient blood loss during the TPA procedure MCHC (32.0-36.0) – 31.9 Related to patient blood loss during the TPA procedure Platelets (150-400) – 97 Related to PAD makes it difficult for the patient to coagulation abilities and as well as blood loss PT (11.7-14.5/ 23.9-36.0) Due to the thrombolytic therapy INR – 2.9 Due to the thrombolytic therapy PTT- 60.0 secs Due to the thrombolytic therapy Treatments (Provide rational for use) Thrombolytic therapy (TPA, Heparin, Alteplase)- to help dissolve the blood clot in her leg Blood products- to help with blood less and anemia Antihypertensive (lisinopril)- to help manage her high blood pressure to prevent further complications Lipidemic (atorvastatin) - You may take a cholesterol-lowering drug called a statin to reduce your risk of heart attack and stroke Angioplasty of venous graft- reopen the artery while stretching the artery open to increase blood flow. Response to Illness and Hospitalization Patient’s anemia has not been corrected based on recent lab results. Patient is responding to thrombolytic therapy which has dissolve the clot. Patient has no questions or concerns regarding hospitalization. She says her nurse is doing a great job keeping her up to date with all procedures and medical information. Physical Assessment findings (ROS) General appearance: clean, has long black hair and wearing hospital scrubs. Neuro: Alert and orientated x 4 Resp: Clear breath sounds bilaterally Cardiovas: Regular S1 and S2 sounds heard, and flat jugular vein and normal sinus rhythm. GI: present bowel sounds in all four quadrants GU: patient has a urinary catheter in and has 320 mL output Muscul: patient has full ROM, but its muscle strength diminishes and lower legs Integumentary: skin is warm to touch, bruising around right knee, and brown discoloration of skin around the right lower leg. Other: Discharge Plans Educate patient regarding medication adherence pertaining to antihypertensives and lipidemic to help manage preexisting condition of hypertension and hyperlipidemia. Inform patient about the importance of keeping the bypass graft site sterile Inform the patient on signs and symptoms of thrombosis and decreased tissue perfusion so patient can immediately call 911 and notify her physician Inform patient regarding signs and symptoms of stroke or heart attack and if so to call 911 Educate patient on the importance to ambulating as tolerated to prevent further skin breakdown Teaching and Health Promotion Needs Knowledge Based Nursing Diagnosis Knowledge deficit r/t peripheral arterial disease management AMB: 1.) Patient developed ischemia of right lower leg Goals & Objectives Content By 03/14/2022 patient will verbalize understanding of selfcare measures required to treat and further prevent complications AEB: 1.) Patient will prevent further ischemia of the leg by ambulating a little and use of compression stockings 1) Instruct patient on further prevention of complications: a) Wear compression stockings to bed at night or as needed b) Hypertension management c) Lipid management d) Ambulate as tolerated daily 2) Provide a brochure on foot care 3) Provide a video that explains importance of ambulating and managing preexisting health conditions. 4) Have patient repeat back key points of our discussion to demonstrate understanding. Nursing Diagnoses (List top 7 in order of priority) Method 1.) One on One discussion 2.) Brochure 3.) Video 4.) Teach back Evaluation 1. Impaired peripheral tissue perfusion r/t blood clot in right lower leg AMB: patient’s right lower leg is becoming ischemic, patient’s Hgb levels is 6.5, patient’s HCT levels is 20.4, patient’s RBC is 2.48, and patient had weak pedal pulse in right lower leg, patient had low air loss bed in right foot. 2. Impaired tissue integrity r/t decreased peripheral tissue perfusion AMB: patient’s bruising of right knee, and patient had brown discoloration to the right lower leg. 3. Impaired physical mobility r/t musculoskeletal impairment AMB: patient has muscle wasting due to age, patient is lactose intolerant which explains low calcium and vitamin B12 levels, patient also was diagnosed with osteoarthritis, patient has claudication of right lower leg. 4. Ineffective health management r/t complexity of therapeutic regimen AMB: deterioration of peripheral perfusion in lower extremities, patient has ischemic tissue on right lower leg, patient has difficulty ambulating, patient develops a reocculsion of right femoropopliteal bypass graft, and patient has claudication. 5. Risk for infection 6. Risk for bleeding 7. Risk for falls Nursing Care Plan (Formulate nursing care plan on 3 of nursing problems (diagnoses) listed, Use nursing care plan forms) Nursing Diagnoses Nursing Diagnosis Human Response R/T Etiology Goals/ Outcome Criteria Interventions Specific & Individualized Rationales with references Evaluation Did the patient achieve the goal? Impaired peripheral tissue perfusion r/t blood clot in right lower leg AEB: 1.) patient’s right lower leg is becoming ischemic 2.) patient’s Hgb levels are 6.5 3.) patient’s HCT levels is 20.4 4.) patient’s RBC is 2.48 5.) patient had weak pedal pulse in right leg 6.) patient had capillary refill was more than 3 seconds in right foot. By 03/14/2022 patient will maintain optimal peripheral tissue perfusion AMB: 1.) patient’s right leg will not have further ischemic of tissue. 2.) Patient’s Hgb levels will be more than 12.0 3.) Patient’s HCT levels will be equal to or more than 37.0 4.) Patient’s RBC levels will be equal to or more than 4.20 5.) Patient will have strong pedal pulse in the right leg 6.) Patient’s capillary refill will be less than 3 seconds in right foot. 1.) Assess vital signs q4h 2.) Assess for signs of decreased tissue perfusion 3.) Monitor Hgb levels 4.) Administer alteplase 20 mg in sodium chloride 1 mg/hr intraarterial continuous as ordered by physician 5.) Administer Heparin 1,000 units in 0.9% NaCl 500 mL 60 mL/hr injection continuous as ordered by physician 6.) Administer lisinopril 10 mg oral Bid as ordered by physician 7.) Educate and instruct patient to inform nurse 1.) Vital signs provide baseline data (Gulanick, pg. 141, 2022) 2.) Specific clusters of signs and symptoms as listed in the supporting data are general indications of adequacy of tissue perfusion. Evaluation provides a baseline for future comparisons. Arterial thrombus at the puncture site may lead to occlusion of the artery or distal thrombosis in the extremity (Gulanick, pg. 142, 2022) 3.) Low levels reduce the uptake of oxygen at the alveolarcapillary membrane and reduce oxygen delivery to the tissues (Gulanick, pg.142, 2022) 4.) Used to reduce blood viscosity and coagulation (Gulanick, pg.143, 2022) 5.) Used to reduce blood viscosity and coagulation (Gulanick, pg.143, 2022) 6.) Used to reduce systemic vascular resistance and optimize cardiac output and perfusion (Gulanick, pg. 143, 2022) 7.) Early assessment facilitates of any signs of decreased tissue perfusion. prompt treatment (Gulanick, pg.144, 2022) Nursing Diagnoses Nursing Diagnosis Human Response R/T Etiology Impaired tissue integrity r/t decreased Goals/ Outcome Criteria By 03/14/2022 patient’s remaining skin will be intact Specific & Individualized Interventions Rationales with references 1.) Assess vital signs q4h 2.) Assess the 1.) Vital signs provide baseline data (Gulanick, pg. 140, 2022) 2.) These data provide information on Evaluation Did the patient achieve the goal? peripheral tissue perfusion AMB: 1.) patient’s bruising of right knee 2.) patient had brown discoloration to the right lower leg. without signs of injury, redness, or infection AEB: 1.) Patient’s bruise will decrease in size. 2.) Patient skin surrounding the ischemic tissue will remain free from discoloration. characteristics of the wound (color, size, odor, and drainage) 3.) Provide tissue care as ordered by physician 4.) Protect the skin from trauma and prolonged pressure 5.) Encourage a diet that meets nutritional needs extent of damage. Pale tissue color is an indication of decreased oxygenation. Odor may arise from infection present in the wound; it may also arise from necrotic tissue. Serous exudate from a wound is a normal part of inflammation and must be differentiated from pus or purulent drainage, which is an indication of infection (Gulanick, pg.140, 2022) 3.) Each type of wound is best treated based on its etiology. For example, skin wounds may be covered with wet or dry dressings, topical creams or lubricants, hydrocolloid dressings (e.g., DuoDerm) or vapor-permeable membrane dressings such as Tegaderm. An eye patch or hard, plastic shield may be worn for a corneal injury. The dressing replaces the protective function of the injured tissue during the healing process (Gulanick, pg. 140, 2022) 4.) The poor peripheral circulation of PAD combined with deceased sensation places the patient at high risk for injury. Attention to this nursing action minimizes the risk of harm to the patient (Gulanick, pg. 358, 2022) 5.) A high-protein, high-calorie diet may be needed to promote healing (Gulanick, pg. 141, 2022) Nursing Diagnoses Nursing Diagnosis Human Response R/T Etiology Impaired physical mobility r/t muscle strength AMB: Goals/ Outcome Criteria By 03/14/2022, patient will demonstrate use of adaptive techniques that Interventions Specific & Individualized 1.) Assess vital signs q4h 2.) Assess ROM of Rationales with references 1.) Vital signs provide baseline data (Gulanick, pg. 141, 2022) Evaluation Did the patient achieve the goal? 1.) patient has promote ambulation and muscle loss transferring AEB: due to age 1.) patient will seek 2.) patient is physical therapy lactose to help build intolerant muscle strength which explains low 2.) patient will take calcium and supplemental vitamin B12 substitutes for levels calcium and 3.) patient also vitamin B12 was nutrients diagnosed 3.) patient will seek with osteoarthritis physical therapy 4.) patient had to help relieve claudication osteoarthritis of right symptoms lower leg. 4.) patient will display no signs of claudication of right lower leg. 3.) 4.) 5.) 6.) all joints as needed Evaluate the need for ambulatory aids Provide a safe environment: a) Bed rails up b) Bed in down position c) Necessary items close by Institute measures to prevent skin breakdown Administer tramadol 100 mg oral q8h as ordered by physician. 2.) This assessment provides data on extent of any physical problems and guides therapy. Testing by a physical therapist may be needed (Gulanick, pg. 90, 2022) 3.) Proper use of canes and walkers and other assistance can promote activity and reduce dangers of falls. The specific aid required depends on the amount of weight bearing that is tolerated, and the ability of the patient to balance safely (Gulanick, pg. 91, 2022) 4.) These measures promote a safe, secure environment and may reduce risk for falls (Gulanick, pg. 91, 2022) 5.) These measures reduce skin breakdown, and the compression devices promote increased venous return to prevent venous stasis and possible thrombophlebitis in the legs (Gulanick, pg. 93, 2022) 6.) Analgesics may reduce pain that impedes movement (Gulanick, pg.92, 2022) Include References: Gulanick, M., & Myers, J. L. (2022). Nursing care plans: Diagnoses, interventions, and outcomes. Elsevier. Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research. (2021, January 14). Peripheral artery disease (PAD). Mayo Clinic. Retrieved April 14, 2022, from https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/peripheral-artery-disease/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20350563 SKIDMORE-ROTH, L. I. N. D. A. (2022). Mosby's Drug Guide for Nursing Students. CHURCHILL LIVINGSTONE.





![The Power of NOW[3741]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/025690828_1-687eebfb243c6979cdc2ac319fc077fd-300x300.png)