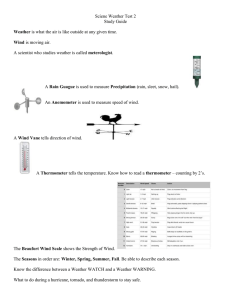
WORKSHEET #3: Matter and Its Temperature Elaborating Key Concepts Discussion Questions 1. How do you measure temperature using a thermometer? What does temperature show? 2. Why is using a thermometer useful in your daily life? 3. Based on the activity in Part 4, is there a difference between the temperature of tap water and tap water with ice? Explain. Concept Discussion Temperature can help us to determine how hot or cold an object is. The unit of measurement for temperature is degrees Celsius (°C). We can use thermometer to measure the temperature of an object. The parts of thermometer are bulb, mercury, stem, Celcius scale and capillary tube. Bulb holds the mercury, a silvery colored heavy metal. Mercury will flow in capillary tube, a long cylindrical tube that is connected to the bulb. As the mercury arise, you can read the temperature on Celcius scale. While stem allows us to hold the glass securely without our hand on the actual bowl. The proper way of reading the thermometer is by positioning your eye at the same level as the liquid in the thermometer and observing where the lower meniscus is. The thermometers that we usually use are made up of mercury which measures body temperature by placing the metallic tip under the armpit and read based on the level where the mercury stops after a minute or two. There are two types of thermometers: medical thermometer and digital thermometer. Medical thermometer is the kind of thermometer that has a bulb on its tip and has a chemical content called mercury. Extra caution is needed when using this because when this device is broken its chemical content could be fatal when consumed by a human person. Digital thermometers are most commonly used and is safest type of thermometer because it uses digital analog to detect your temperature through the bulb itself. Measuring temperature is important especially when monitoring body temperature to determine whether you have a fever or not. This method can also be used when cooking food so that you would avoid having overcook food or raw food. Weather humidity or the amount of water vapor in the air is also measured so that weather agency would be able to determine whether a low-pressure area would be form due to too much amount of heat in the atmosphere. LET US PRACTICE A. Which of this temperature is cooler? 1. 19 oC or 91 oC = ___________ 2. 100 oC or 10 oC = __________ 3. 37 oC or 35 oC = __________ B. Arrange the following temperature in order, the coldest first. 1. 100 oC, 15 oC, 33 oC, 76 oC,= ________________________________ 2. 75 oC, 38 oC, 2 oC, 89 oC, = __________________________________ 3. 0 oC, 11 oC, 4 oC, 6 oC, = __________________________________________________________________ __________ WORKSHEET #4: Heating vs. Cooling ELABORATING KEY CONCEPTS Concept Discussion The state of matter can be changed when we heat or cool it. This process is called phase changes. Usually, the change occurs when adding or removing heat at a particular temperature. After an object gets hotter, they lose energy and move it to another thing that is colder. The hotter object will cool down, and the colder object will warm up. The transfer of energy will keep going until both objects are at the same temperature at the same time. When you heat something, the molecules move faster. Cooling down a substance makes the molecules move more slowly. When a matter changes its state, it also changes its appearance, but it remains the same matter. If we heat a solid object, it becomes a liquid substance. This process is called melting. The common examples of this are the melting of ice, chocolate, butter or ice cream. On the other hand, when we cool a liquid, it becomes a solid. This process is called freezing. Freezing of water to form ice in an ice cube, formation of snow, are some examples of this process. WORKSHEET #6: Sublimation vs. Deposition EXPLORE AND INVESTIGATE PART 3. Encircle the picture that shows an example of sublimation and box the picture that shows an example of deposition. ELABORATING KEY CONCEPTS Discussion Questions 1. Why did the mothball gradually disappear over time after placing under the sun? 2. Based on the experiment, what happened to the coin after placing it under the sun? 3. How is the process of sublimation different from deposition? WORKSHEET #7: Safety First! ELABORATING KEY CONCEPTS Concept Discussion Many products and materials at home and in school are useful to us but they can also be harmful if they are not handled, stored, or used properly which may lead to injuries or death. In order to prevent accidents, it is important to know the name and uses of the products and materials we use at home and in school. One of the common products and materials that we usually find at home and in school are cleaning materials such as bleach and detergent. These products are commonly used to wash our clothes. We should keep these products out of children’s sight because they contain chemicals that can cause heavy vomiting and stomach pain or even poisoning when swallowed. Aside from the cleaning agents, products such as gasoline or LPG tank, lighter, mosquito coil, and battery are also commonly found at home and in school. Gasoline or LPG tank is used as fuel for cooking. Lighter serves as the source of fire. Mosquito coil is used to keep the bugs away. Battery provides power for electrical products such as remote control, clock, and flashlight. These products are also harmful because they can cause fire when not used or stored properly. Paint is used for decorating and protecting materials from rusting. Other materials that are also harmful are mothballs, mosquito spray, rat poison and nail polish. All of these materials may cause poisoning when swallowed. The following are some reminders on how to properly handle or use harmful products and materials at home and in school: 1. Always read the labels and check for expiration dates. 2. Do not try to swallow products like bleach, detergent, and rat poison. 3. Wash your hands after using products and materials with harmful chemicals. 4. All harmful products and materials should be kept away from children’ sight especially the flammable materials such as LPG tank and lighter. 5. Place the flammable materials away from any source of heat so they cannot catch fire easily. 6. Wear gloves or masks when using products that contain smelly chemicals such as paint and mosquito spray. 7. Have a designated area at home and in school for harmful products and materials. It should be out of reach of children. 8. Expired products should be disposed properly.