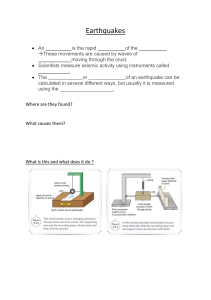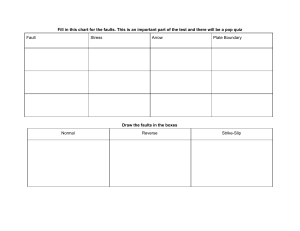
Module 1 Quarter 2 E A RT H Q U A K E S A N D FA U LT S Review • Directions: Read and analyze the statements below about safety at home in using electrical devices. Say the word TADASHI (✓) if it is correct and MACHIGAI (X) if it is not. • _____1. The proper way to unplug your electrical appliances from a power strip is by using your hand in removing the plug and being careful not pulling the cord. • _____2. If a friend receives a severe electric shock from an electrical appliance at home, the best thing to do is to grab the appliance and throw it aside. • _____3. One is more likely to experience an electric shock if he/she touches an electrical object with wet hands. • _____4. It is safe to run an extension cord under a carpet or along a baseboard for permanent use. • _____5. It is not advisable to overload electric outlets with too many items. • Start Game Are you Ready? Okay Let Start the game… Continue RTHAEUQKEA HINT: shaking of the ground…” ANSWER: EARTHQUAKE 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 00 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 Start Timer Show Answer Scoreboard Next Jumble LUATF HINT: Fractures between two blocks of rocks ANSWER: FAULT 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 00 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 Start Timer Show Answer Scoreboard Next Jumble OOALVCN HINT: Often found when tectonic plates are diverging ANSWER: VOLCANO 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 00 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 Start Timer Show Answer Scoreboard Next Jumble PLSI HINT: Movement of geological features on either side of a fault plane. ANSWER: SLIP 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 00 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 Start Timer Show Answer Scoreboard Next Jumble CKRO HINT: Dwayne Johnson ANSWER: ROCK 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 00 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 Start Timer Show Answer Scoreboard Next Jumble Objective • Explain how movements along faults generate earthquakes. Some of the countries located in the Pacific Ring of Fire include the Philippines, Japan, Taiwan, New Zealand, Russia, Antarctica, Indonesia, Canada, Mexico, Chile, United States, Peru, Canada and Papa New Guinea. An earthquake is the sudden shaking of the ground which lasts for seconds. It causes destruction anywhere it occurs, and no one knows exactly when and where it is going to happen. Sometimes, it could lead to a tsunami, or a large ocean wave created by undersea earthquakes or volcanic eruptions. An earthquake wave is also known as seismic wave. Do you Know? • An earthquake somewhere every Seventy-five Earth’s happens single percent day. of volcanoes—more than 450 volcanoes—are located along the Pacific Ninety Ring percent of of Fire. Earth’s earthquakes occur along its path. That is why the Philippines is frequented by volcanic activities. seismic and July 16, 1990 • Faults are fractures in the Earth’s crust where rocks on either side of the crack have slid past each other. Just like in the experiment, a break was formed in the clay, which represents the soil, as movement occurs and the parallel lines are displaced. Layers of rocks may experience several types of stress. Stress is a force that acts on rocks to change its shape or volume. Tension is a type of stress that pulls on the crust stretching the rock from opposite directions. Compression is a force that squeezes rocks until they fold or break. Shearing is a force that pushes masses of rock in different directions. • Strike-Slip Faults • are rocks sliding past one another on a horizontal plane, with little to no vertical movement. Examples to these are the San Andreas Fault and the Anatolian Fault Normal Faults • are two blocks of crust layer pulling apart, extending the crust into a valley thus, creating a space. A normal fault has the upper side or hanging wall appears to have moved downward with respect to the footwall. The Basin and Range Province in North America and the East African Rift Zone are two notable districts where normal fault is spreading apart Earth's crust Reverse Fault • are also known as thrust faults, the slide one block of crust on top of another. These faults are normally found in collision zones where tectonic plates push up mountain ranges, for example, the Himalayas and Rocky Mountains. • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=x52LiTS9urc • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PHSVXXQVMrQ Survival Kit Emergency Survival Kit For your assessment Answer Your Module 1