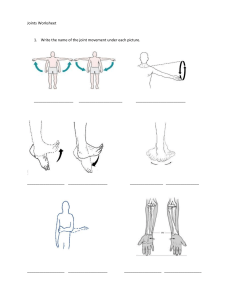
Chapter 8 Joints: Study Guide Vocabulary: Review Questions: How are joints classified? Movement of skeleton at points of articulation (joints) where two or more bones meet. Structural: whether a joint cavity is present Fibrous Cartilaginous Synovial Functional: the amount of movement Synarthroses: immoveable Amphiarthroses: slightly moveable Diarthroses: freely moveable joints List and describe the three classes of fibrous joints, include an example of where each type is found. Sutures Seams between bones (e.g. skull)/ bones are held together with very short interconnecting fibers, and bone edges interlock. Syndesmoses Bones connected by a ligament, with little movement Gomphoses Peg-in-socket connection, found in teeth Name and describe the two types of cartilaginous joints. Give an example of where each type is found. Which joint type is the most common in the body? Diarthroses List and explain the characteristics of synovial joints. Articular cartilage: hyaline cartilage covering of opposing bone surfaces Joint (synovial) cavity: space with synovial fluid Articular capsule: Fibrous capsule with a synovial membrane; adds strength to bones, keeping them from being pulled apart Synovial fluid: slippery fluid in cavity, composed primarily of water and hyaluronic acid Reinforcing ligaments: reinforce joint Describe the structure of synovial joints. How is friction reduced in synovial joints? Bursae and tendon sheaths associated, but not part of the joint Bursae flattened fibrous sacs with synovial fluid Tendon sheath elongated bursa that wraps around a tendon (like a hot dog bun) What factors influence the stability of synovial joints? How? Articular surfaces Shape determines movement, but NOT stability Ball and socket is an example of a stable, articular joint Ligaments Prevent undesirable movement, with more increasing the strength (most important factor) Muscle tone Good increases stability, holding the tendons tense List the four types of movement based on planes. List and describe the synovial joint movements discussed in class. Plane: flat, gliding Hinge: cylinder and trough Pivot: rounded end into sleeve Condyloid: oval surfaces in depressions Saddle: similar to condyloid; more movement with concave and convex surfaces Ball-and-socket: spherical head with cuplike socket