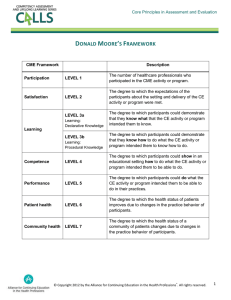
Vision: Provides personnel with the information needed to perform their daily tasks and processes and ensuring both the juniors and the seniors know their respective work processes and related procedure so that the laboratory can deliver high-quality services. GOAL: Ensure personnel performance results in consistent, predictable and high-quality outcomes Ensure performance of assigned job tasks remains constant Verify that personnel have and can demonstrate the necessary knowledge, skills and behaviors to perform their respective duties Support all the laboratory’s path of work flow and laboratory disciplines including the preexamination, examination and post examination Adding the post-training assessment verifies that the training was effective A laboratory’s best assurance of contributing to patient safety is developing and sustaining a staff with: 1. A clear understanding of the sequence of work activities 2. The instructions for completing the activities at the right time and in the right way 3. The ability to put their understanding and instructions into practice when presented with typical and atypical situations 1. Training needs are identified 4. Training pragram is evaluated Training Processes 3. Training is conducted 2. Training Plan is developed 1. Training needs are identified: a. Work processes performed in a given job including all phases of testing (LABORATORY PATH WORK FLOW) b. Procedure performed in each work process (flow charts) c. Rules that apply to work processes and procedures d. Technical and non technical tasks based on the technologist responsibility Training needs may identified as a result of audit observation, competence assessment outcomes, updates in current testing platforms, ISO accreditation requirements, Change in organization, technology, methodology, supplies, customer requirements, posttraining evaluation, Repeated performance problems, problem-prone procedure, customer feedback. NOTE: Training does not consist of a new person reading SOPs and signing off on a checklist Training subjects will be designed as per technologists level: 1. Newly joined/Junior 2. Senior/In charged 3. For all technologist 4. Laboratory co-worker Training will cover laboratory PATH OF WORKFLOW: PRE EXAMINATION • Order • Sample Transport • Sample collection • Receive and Process 2. Training plan is developed : EXAMINATION • Analysis • Review and Interpretation POSTEXAMINATION • Report Release • Sample management This involve systematic planning to ensure uniform and consistent transfer of knowledge, skills, and attitudes throughout the laboratory and to increase the efficiency of training activities. Planning the training session include: a. b. c. d. Identifying the training purpose Assessing the learner’s needs Determining available resources Developing and documenting the training event plan On Each Training session the Training plan should be developed and documented including the information needed to prepare, conduct, and complete the training. The training plan should be approved and signed by Laboratory Quality /Medical leader. Training Plan Purpose •Goal •objective and the outcome expected Learner Needs •who need training and names •location •skills & knowledge •Method Resources •External resourses if needed •material used for the session •administrative support Methods Evaluation •Training methods to be used •instruction •Checklists •Competence assesment methods •Competence assesment methods •Training experience •Trainer performance 3. Training is Conducted: Training can be conducted as individual level for new workers, group level for new process or procedure and as annual review of the current process. Training will be conducted in the work environment that provides information and knowledge needed for a specific position. Training Record will include the following: Training schedule Training material Training instruction Training checklist Witten Quiz Training evaluation for the learner Training attendance sheet 4. Training Program is evaluated: Evaluation done for the training session and for the training program. The outcomes analyzed and recorded for the improvement process. The records can demonstrate when remediation training took place, processes that had repeated errors and problems, and common questions that may point to a need for changes in the process, procedure or training event. Trainer will prepare a checklist for Direct observation of the learners during the training. Structure of Training module PHCG as per laboratory work flow: Training in PHCG will be designed in Three categories: Inhouse training, External training and CME External Training Laboratory personnel will be sended to attend external training when ever there is a chance. Some example to these trainings: Roche consulting training, MOH training program and MedLab conference and exhibition CME Five CME will be conducted per year. Topics, presentation and the conduction will be done by laboratory personnel of PHCG. It will be conducted in PDC and Prime hospital. Each laboratory personnel need to collect minimum 10 CME hrs yearly. These CME hours will be added to the laboratory personnel record and designation upgrading. •< 1 yr Jounio •10 CME r hrs •< 4 yrs Lab Techn •20 CME ologist hrs •4 yrs Senior •40 CME hrs •> 6 yrs Incharg •80 CME e hrs Inhouse Training 1. Training will be conducted on the same work place of laboratory personnel 2. Training will be given according to laboratory work flow. It will be designed to cover each phase of processing; pre examination, examination and post examination. Topics for each phase will be planed and designed according to the target’s learner level and needs and will be supported with training documents. 3. Training will be developed to cover different personnel levels: 1. For all laboratory personnel despite their level 2. For Newly joined 3. For juniors 4. For seniors 5. For In-charge technologists 6. Laboratory co-workers 4. Training sessions will be designed using different methods and resources: 1. Power point presentation 2. Known/blind samples 3. Equipment engineer support 4. Workshops 5. The training session will end with written exam. Laboratory personnel will be graded as “ A” , “B”, “C” & “D” . Any Laboratory personnel who will have grad “D” need to go for retraining session. IF he/She got Garde “D” in technical related subject, the retraining session should designed within one week followed the assessment result. IF He/She got Grade “ D” in nontechnical related subject, the retraining session should designed after one/Two month period followed the assessment result. 6. Newly joined laboratory personnel Training: When new laboratory personnel joined the PHCG, He/She will undergo a training schedule. This schedule should be completed before he/she engaged alone with routine laboratory work flow. The Schedule designed to be completed in three stages: First month followed the joining period. After the one month period , written exam will be conducted. According the performance in this period and the assessment result, the laboratory personnel will be evaluated for the eligibility to perform the routine work process. o Tools and methods: awareness checklist, SOPs, test witnessing, observation checklist, written exam Six month followed the joining and the eligibility to perform the work process. Competency assessment will be conducted. Surprise visit for the performance observation will be conducted. Blind sample will be given to the laboratory personnel and His/Her processing end result will be evaluated. o Blind samples, competence assessment, written exam, surprise visit and performance observation checklist One year followed the joining. A summary of the laboratory personnel performance and evaluation with a complete feedback report will be given to him/Her. Transition from a joiner level to laboratory technologist level will be announced with new responsibilities to be added to the laboratory personnel achievement requirements. o Feedback report, competence assessment final evaluation, responsibilities document. The training will be held in PDC as initial then the laboratory personnel will rotate in different branches to cover the training schedule, techniques and instruments applied in PHCG laboratories. Specimen processing flow chart Prime Deira Premier Satellite Labs Main sheet Request form Messenger Messenger Sample receiving Returned to the lab Verification Inadequate Adequate Accept In LIS Samples For Processing Rejected Interfaced tests Non interfaced tests LIS Manual Entry Approval Accepted EMR Printing Dispatch to Branch& Internal Drs Result With signature Main sheet for verification Specimen Collection Flow Chart- OP Receiving Patients Hospital ID card/ Verify Photo ID / Invoice test details Identification Pediatrics Three ID 1) MRN# 2)Mother Name 3)DOB Adult Two ID 1)MRN # 2)Full Name Instruction about the test given / Appointment Not ready State of patient Eg Fasting Ready Comes prepared Accepting in LIS / Bar-code generating & Shown to the patient Specimen Collection Sample to Lab ( Pneumatic Transfer ) Page 2 Stat Sample will be separately send for immediate processing Receiving Specimens in lab Sample Accession Area Pneumatic Sample Acknowledgement Form /Register – Signed & send IP Porters OP OP Generate Barcode IP Generate Barcode Sample Receiving In LIS Non Serum / Other Samples Serum / Plasma Centrifugations Sample Rejection Record Informed to Doctors/ Nurses Rejected Sample Accepted Analytical Page 3 Sample Acknowledgement Form /Register – Signed & send Analytical Process Type Of Specimen If Trop T in Request Sample goes Serum / Plasma EDTA/ Whole Blood Urine / Stool /Body Fluids / Semen Swabs Electrolyte Analyser CBC Sysmex Processing in Clinical Pathology Rapid tests Biochemistry Analyser (Integra 400) HBA1C (Integra 400) Immunology analyzer (Cobas E411) Blood Bank OSSR Register Refferal Lab ( If aay ) PRIME HEALTHCARE GROUP LABORATORIES PHCG/LAB/TP VER1.0 DATE0 1.01.2019 Training Plan Page 11 of 36 Training Subject:---------------------------------------------------------------------------Training Location:-----------------Training Date:-------------------------------------------------------------------------------Trainer: ------------------------------ Who are the Trainee--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Training objectives:-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Expected Outcome from the training:-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Skills and knowledge will be given in this training session:----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Materials will be used for this training session:------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Methods & training structure:-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------External resources needed for this training session ( if any):--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Training references : Checklist handbook/handout Training session evaluation Attendance sheet Trainer evaluation Competence assessment Method:------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Done By: Approved by: PRIME HEALTHCARE GROUP LABORATORIES PHCG/LAB/TI VER1.0 DATE0 1.01.2019 Training Instruction Page 12 of 36 Date & Signature: Date & Signature: Learner Responsibilities for ( NAME of the training session) OBJECTIVE At the conclusion of the training session, you must be able to: Explain the process and describe your role within the process Perform the procedures in the correct sequence Perform the procedures as written and without direct supervision Perform all required safety precautions Methods and Material Complete any prerequisite reading - Processes - References - Procedures - Package inserts - Manuals Observe any demonstrations Obtain practical material Perform procedures on practical material Receiving Training Receive the training according to the schedule Ask questions if anything is unclear Learner Evaluation To demonstrate that you have learned the material, you will be asked to do one or more of the following: Test unknown, if applicable Perform the procedure for the Trainer Complete and pass the written Quiz Answer any oral questions Obtain the trainer’s sign-off on the training checklist PRIME HEALTHCARE GROUP LABORATORIES PHCG/LAB/TOCL VER1.0 DATE0 1.01.2019 Training Orientation Checklist 2 Trainer : Started Date: Staff name : Staff employee no.: Designation: Branch: NO Topic 1 General awareness Sub Topics Prime Medical center branches structure Branch Lab orientation Branch timing /Lab timing Branch Doctors & department Branch Phone numbers & extention Duty rota/ duty request/ Duty exchange Branch lab Scope of services In-house tests Send-out tests Send-out preparation & result follow up Branch – PDC send out policy /schedule Not invoice samples policy Sample receiving from nurses policy Endorsement protocol Stock & consumables Positive results releasing Critical alert policy Add on policy External QC programm Documentation protocol Contingency plan policy Complaint management policy Quality team coordination Branch pathologist Store coordinator Key role area Authorization matrix Branch code blue 2 ISO 15189 Requirements Branch SOPs Checks Date of completion Remarks 3 / Documentation Branch Non conformity Branch Quality indicator Forms / Work registers/ Records Equipment Records Routine Clinical Pathology Type of urine samples Tests performed by urine sample Collection of urine sample Not invoice urine samples Receiving urine sample The workflow of an urgent urine Accepting the urine sample Urine analysis SOP Processing the urine sample Mix the urine well before pouring into the centrifuge tube for centrifuging. Label the centrifuge tubes Dispatch and refer culture testing on the same sample How to manually use, and read the dipsticks Understand the importance of timing the tests such as Glucose Urine sample microscopy Identify different cellular elements in a normal urine Identify different cellular elements in an abnormal urine What to do if the dipstick and the microscopy don’t appear to match Urine- reporting on LIS How to change a result What to do if the dipstick results are missing How to enter a comment How to check the final report Rejection urine sample Add on tests on urine sample policy Send out preparation for urine sample Where to put the urines at the end of shift Where the finished urines are stored Urine retention policy Type of stool samples Tests performed by stool sample Collection of stool sample Not invoice stool samples What to do with if sample is contaminated with urine Receiving stool sample Accepting the stool sample What to do with mislabeled specimens Processing the stool sample Stool analysis SOP evaluate stool macroscopy : color and consistency Stool sample microscopy How to prepare a wet mount slide How to use the microscope Identify different cellular elements in a normal stool Identify different cellular elements in an abnormal stool Identify different stool parasite Identify different stages of parasite if applicable Stool – reporting on LIS Stool positive reporting policy How to change a result What to do if the either macro or microscopic results are missing How to enter a comment How to check the final report What to do if the macroscopy and the microscopy don’t appear to match Rejection stool sample Add on tests on stool sample policy Send out preparation for stool sample Where to put the stool at the end of shift and are due for endorsement Where the finished stool are stored Where and when to discard processed stool samples Collection of Semen sample Receiving Semen sample Accepting the Semen sample Processing the Semen sample Semen analysis SOP Semen microscopy Semen - Reporting Repeat semen sample Rejection semen sample ( body fluid) 4 Clinical chemistry Instrument -Daily, Weekly, Monthly Maintenance Calibration and Quality Control EQAS Rout cause analysis Equipment history record Instrument handling training Asset plus management Monthly CV Reagents Type of samples Critical alert policy Sample Rejection policy SOPs Lot validation Kit in use Kit insert Stock register Add on policy Pending tests follow-up Send-out sample preparation Sample archiving Sample storage 5 Hematology Instrument -Daily, Weekly, Monthly Maintenance Calibration and Quality Control MLE Rout cause analysis Equipment history record Instrument handling training Asset plus management Monthly CV Sample Rejection policy SOPs Peripheral smear preparation Peripheral smear staining Differential count AEC Manual PLT count correction Malaria Screening Abnormal cells identification Corrected WBC count Critical alert policy Lot validation Kit in use Kit insert Stock register Add on policy Pending tests follow-up Send-out sample preparation Sample archiving Sample storage ESR QC Manual/ Automation ESR daily validation 6 Coagulation Instrument -Daily, Weekly, Monthly Maintenance Calibration and Quality Control MLE Rout cause analysis Equipment history record Instrument handling training Asset plus management Monthly CV Sample Rejection policy SOPs Critical alert policy Lot validation Kit in use Kit insert Stock register Add on policy Pending tests follow-up Send-out sample preparation Sample archiving Sample storage 7 Rapid tests Rapit test kits Lot validation QC management Kit insert WDI Work Register Documentation Critical alert policy Scope of tests Sample collection Test reporting Stock management 8 Analyzers Cobas Integra 400 PLUS Cobas e 411 Sysmex XS 2000 i Cobas U 411 Roche 9180 electrolytes analyser Verify ISTAT - POCT Cobas H232 Cardiac analyser - POCT Nihon Kohden Ortho Bio vue set up - Blood Group ESR ACL Elite Pro Mini Vidas Indiko Randox Olympics U411 Urisys Vitros350 9 General instruments & Maintaince Micro Pipettes Water Baths Roller Mixers / Shaker Centrifuges Refrigerators Microscopes Deep Freezers Plasma Thawer Platelet shaker Datalogger Comments: ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… Trainer signature: Date: Trainee signature: Date: PRIME HEALTHCARE GROUP LABORATORIES PHCG/LAB/TOCL VER1.0 DATE0 1.01.2019 Training Orientation Checklist 1 Trainer : Started Date: Staff name : Staff employee no.: Designation: Branch: NO Topic 1 General awareness Sub Topics Prime health care Group & Prime Hospital Prime Medical center branches structure Premier Diagnostic laboratory Commitees Staffs, Designations( level) & management team job description &responsibility Performance improvement & Appraisal Training protocol Competencies process Departments policies Central lab store Duty rota/ duty request/ Duty exchange Attendance & Biometric fingerprint Comp-off policy Leave plan Phone numbers & extention ( branch) Stakeholders Insurance / Contracts 2 Universal Precautions Patient safety goals Safety Manual Using of PPE ( Gloves , Masks & Aprons) Handwashing protocol Handling of Sharps , Spill management Segregation of Medical & Nonmedical Wastes Checks Date of completion Remarks Management of spillage-Chemical / Biological Management of needle stick injury First Aid Fire safety Shower / Eye Wash stations HSE guideline Emergency codes Complaint management 3 ISO 15189 Requirements / Documentation JCI Standards ISO 15189: 2012 Standard Internal Policies Quality manual SOPs Non-Conformity & OVR Quality indicators Forms / Work registers/ Records Equipment Records 4 Laboratory Information System General Awarness on handeling LIS Generation of bar codes Cross check bar code identity with specimen label Sample Acceptance sample Collection Urgent Samples, Prioritize on entry and distribution Sample receiving Sample rejection o Recognition of sample rejection (cause of rejection) o Update in LIS o Discard in LIS o Write in Rejection register & notify the source result entry Send-out test identification PDC tests Critical/Stat request & reporting TAT Rerun Pending tests Report notes 5 Beginning of the Shift General authorization protocol/ Delta check- up Disinfect workbench Disinfect centrifuge Refrigerator temperature monitoring Arrange reagents, and pending stock Disposal of retained specimen as per retention policy (1 week) Endorsment protocol, Check endorsement logbook 6 Reception & Receiving Scope of services PDC requirerments Branch sample preparation & trasportation Batchs timing Segregation of samples: Serum o Biochemistry o Special Chemistry o Serology o Immunology o Send out EDTA whole blood o Hematology o Biochemistry o Blood Bank o Send out Citrate whole blood o Coagulation o Send out Stool o Clinical Pathology o Microbiology o Special Chemistry o Send out Urine o Clinical Pathology o Microbiology o Special Chemistry o Send out Swabs o Rapid tests o Microbiology o Send out samples & request verification Sample receiving Referral samples preparations Basic Transcription Receiving of samples from courier representatives Receiving of samples from in house collection Verification of sample referred based on : Identification on both sample and requisition Patient detail in computer generated label Temperature upon handover Spillage and sample integrity Sample adequacy and appropriateness to requisition Number of samples received based on consignment Check sample type: Volume Correct sample type Number of tubes Stability o Blood o Urine Mid stream o Urine 24 hour o Stool o Semen o Swabs o Sputum o Histology samples o Cytology samples o Urea Breath test Doctors and Departments Patient Registration work flow ( OP, ER and IP ) 7 Phlebotomy/Preanalytical Greets patient, states procedure to be done Properly identifies patient Examine requisition form. Puts on gloves Select tubes and equipment for procedure Assembles and conveniently places equipment Positions patient’s arm Applies tourniquet Identifies vein by palpation Releases tourniquet Cleanses site and allows it to air dry. Reapplies tourniquet. Does NOT touch puncture site with unclean finger. Checks plunger movement and ensures all air expelled Anchor vein below puncture site. Smoothly enters vein at 15o angle with without contamination. Collects appropriate amount of blood Matches filled tubes to request form Releases/removes tourniquet Maintains needle firmly positioned while drawing Removes needle smoothly/safely and applies pressure Covers puncture site with gauze/dry cotton Fills tubes in the correct order and gently (on the side) Mixes anti-coagulated tubes promptly Disposes of all used supplies and butterfly properly Labels tubes properly Examines puncture site, makes sure that the patient is feeling all right & advises the patient NOT to exercise arm immediately. Applies bandage / Band-Aid. Removes gloves and washes hands. Thanks the patient. Converses appropriately with patient during the procedure. Appearance and Personal Hygiene Professionalism In-house & referral tests Laboratory tests profiles Not approved/ pending invoice samples handleing Faint management Patient pre- preparation Order of draw Vacuatte colour code Sample volume Pediatric blood collection Blood culture collection Nasal & Throat Swabs collection Special tests requirement Consumables management samples transportation 8 Post analytical/Dispatch Sample Storage & Discard Add on tests management Reports Releasing& Emailing Infectious/ Notified Diseases 9 End of Shift Disinfection of workbench All samples received during shift are entered Samples not entered or not distributed due to certain issues like insurance, non compliant on sample type, extra tubes must be placed refrigerated or frozen depending on the tests requested Hand over communication. Remittance of attached payments to Accounts Department 10 Purchase / Stock Major Distributors / Purchase system Stock Manintance Reorder level ,Receiving stocks / Consignments 11 QC & Calibration Daily runs Reconstitution Warning & rejection rules LJ chart Corrective action Rout cause analysis & Documentation External QC programms Comments: ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… I certify by my initials above and by my following signature that I have been shown/discussed, reviewed and understood the information summarized in the above Employee Orientation checklist. I have been made aware of who to ask and/or where to look should future questions arise. I understand that violation of any safety, fire prevention, health or health system security rule, department/division or PHD policy or practice is unacceptable, requiring corrective & progressive disciplinary action per Prime Healthcare Diagnostic Laboratories policy. ___________________________ Employee Name ___________________________ Training Coordinator __________________________ Laboratory Manager ___________ Date ___________ Date ___________ Date ___________________ Signature ___________________ Signature ___________________ Signature PRIME HEALTHCARE GROUP LABORATORIES PHCG/LAB/DOT VER1.0 DATE0 1.01.2019 Direct Observation of Technologists Page 28 of 36 Department Employee Name Skill or Assay Observed Task 1. Application and adherence to al elements of assay method/instrument/ procedure - Follows procedures - Acesses reference instrument user manual as needed 2. Sample handling and processing - Identifies sample type and storage requirments - Understands sample acceptance criteria - Maintain positive sample ID throughout all phases of analysis 3. Preparation/assesment of reagents and control materials -Varifies lot number and expiration date - Ensures correct labeling 4. Interpretation and acceptance of test reactions and results - Reviews and assesses test results; judges acceptability( ie, varifies and confirms test resultd are within the reference range) Date Score Overall competence result Satisfactory should be >=80% S U Satisfactory Unsatisfactory Comments 5. Documentation of results - Documents and notifies appropriate personnel about clinically significant or unusual test results - Call and documents critical value results 6. Review of QC - Understands, uses, and adheres to QC acceptance criteria - Review QC charts 7. Instrument operation, function checks, monitoring, and maintenance - Performs daily, weekly, and monthly instrument monitoring and maintenance - Operates and calibrates instruments according to manufactureres' requirements - Understands instrument software/ operating error messages; follows troubleshooting instructions 8. Use and demonstration of appropriate laboratory skills and practices - Reads meniscus - Performs accurate assessment - Demonstrates manual dexterity 9. Adherence to safety requirements - Wears appropriate PPE - Disposes of wastes properly (biohazardous, chemical, sharps, nonhazardous) - Follows safe laboratory practices 10. LIS knowledge and abilities - Tracks samples - Looks up test and patient information - Logging and releasing critical results - Reviews and varifies patient results Comments/Corrective Action/Follow-up: Competence Asseement Performed By: Date & Signeture: Competence Asseement Approved By: Date & Signeture: Scoring Key # Category Satisfied 10 9 8 7 Scoring 100% 90% 80% 70% Overall Competence Result Able to work independently Needs additional training Needs additional training Unsatisfactory Competence assessment: Competence assessment is an evaluation of a person’s ability to apply his or her skill, knowledge and experience to perform assigned laboratory duties correctly. Competence assessment verifies that the knowledge and skills gained from training are applied by technologists. It is assessed : Following the training to determine the effectiveness of the training Periodically to verify the individual’s continued demonstration of necessary knowledge, skills and correct practice of the work processes and procedures When retraining needs are identified When there are new or changed in procedures 1. CA needs are identified 4. Personnel competence is evaluated Competence Assessment Processes 2. CA Plan is developed 3. CA is conducted 1. Competence Needs to be assessed at the following times: a. Initial assessment after completion of the training and before a person works independently b. Periodically (QM requirement ) c. When demonstrated competence does not meet criteria that determine competence or a technologist returning from an extended medical or long leave of absence 2. Competence Assessment Plan is developed A comprehensive competence assessment plan needs to be based on the job responsibilities and all activities related to the Pre-examination, examination and post-examination in addition to quality management activities for which a personnel responsible. The flow chart of the process can be used for the basis of the assessment method chosen. Assessment Methods: Competence can be assessed by using any combination or all of the following methods: Direct observation of routine work processes and procedures Direct observation of equipment maintenance and function checks Monitoring examination result recording and reporting Review of work records Examination of samples including add on, PT and QC material. Assessment of problem- solving skills The types of assessment methods selected are influenced by the learning objectives developed for the work process or procedure Blind test samples: Blind test samples are one type of specially provided material for competence assessment. The advantages of blind samples include more reliable assessment of routine performance and the identification of problems within all phases of the path of workflow. The personnel should be unaware when the blind samples are entered into the workflow. Previously analyzed material: Replicate testing of previously analyzed material is another type of competence assessment. The new results are compared for concordance.. Sample questions: Assessment of a person’s knowledge with respect to particular process, procedure, or test system can be determined by written quizzes or tests. 3. Competence assessment is Conducted Ongoing assessments need to take place periodically on a scheduled basis. By developing an assessment schedule it will be integrated as laboratory routine The schedule will include define: Times for direct observations of the work processes of the person regular work. Visit for assessment blind samples in equal difficulty manner Time for low volume examination and high volume examination assessment Each phase work flow direct assessment Competence record should be created after completion of the assessment. The record will be retained in the personnel file. Record will include: Direct observation document. Any written assessment Outcomes and reviews of reports Results of any blind or other sample testing Periodic review document for all the competence assessment records for all personnel in a given work discipline. 4. Personnel competence is Evaluated When performance is unacceptable, retraining personnel is the follow-up action. If after retraining the personnel still not competent, reassessment criteria should be established, documented and communicate to the person. Staff Joiner General Tech Joining Yearly competency final evaluation Orientation Summary General Branch Identify training needs ( 1 week) Departments checklists Annual Training plan prepared (one month) Monthly training Competency for eligibility Training Post Pre Training needs identified department distributed monthly Assessment orientation checklist/ Assessment Training sessions 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 ( Per training topic) Per 1 2 3 Assessment after completion B R H Q S P S M H C P After sex month competency end of the year staff covered all ` At the departments Identify training needs Yearly final eval Training sessions Identify training needs Assessment after completion After one year competency Evaluation summary record for the staff Senior & incharges will follow the same process flow of the general tech, however the topics will be different Training needs will be grouped in two level: o First level : Staff level = they will be grouped to follow the training needs topics o Second level: Branch level= per branch needs & instruments Training Plan will have both level of training needs Juniors training needs when it will be identified based on competency & assessments cycles , emergency training plan will be implemented Type of Competency we will follow: 1. Cycle competency ( yearly) 2. Department competency ( each month one department to be assess all group, like January is a hematology month). Here we will increase distribution of knowledge, article , & pre training orientation checklist/assessment 3. Un planed surprised competency : to asses staff performance in random selection of a staff : a. Surprise visit b. Any tech in the duty c. Blind samples to be used d. Direct performance observation checklist e. Report will be generated and hand over to the tech & supervisor & will be attached to the yearly summary report f. Will be used to identify training needs for the annual training plans Training Calendar : If we can follow LQMS email notification once we grouped the staff and identified the topics for each list . Then we will include their name in the calendar with the training topic & the timing , so like a MEETING CALENDER WE WILL GENERATE THE TOPIC WITH TRHE ATTENDEES AND A REMINDER.