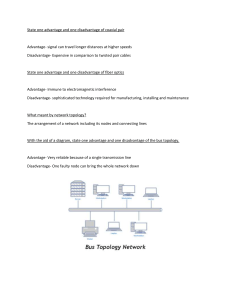
DATA COMMUNICATIONS AND NETWORKS 1 QUESTION 1 Multicasting in computer network is a group communication, where a sender(s) send data to multiple receivers simultaneously. Broadcasting in computer network is a group communication, where a sender sends data to receivers simultaneously. This is an all − to − all communication model where each sending device transmits data to all other devices in the network domain. unicast is a one-to-one transmission from one point in the network to another point; that is, one sender and one receiver, each identified by a network address. A firewall is a network security device that monitors incoming and outgoing network traffic and decides whether to allow or block specific traffic based on a defined set of security rules. Multiplexing is a technique by which different analog and digital streams of transmission can be simultaneously processed over a shared link. Modem stands for Modulation Demodulation. A modem converts the digital data signals into analogue data signals In Full duplex mode, the communication is bi-directional, i.e., the data flow in both the directions. Both the stations can send and receive the message simultaneously. Half-duplex data transmission means that data can be transmitted in both directions on a signal carrier, but not at the same time. Simplex mode is a type of transmission mode; where data can be sent only in one direction i.e. communication is unidirectional. QUESTION 2 Hub works at physical layer and is responsible to transmit the signal to port to respond where the signal was received whereas Switch enable connection setting and terminating based on need. Whereas Switch is a network device which is used to enable the connection establishment and connection termination on the basis of need. Switch is operated on Data link layer. Logical Address is generated by CPU while a program is running. Whereas Physical Address identifies a physical location of required data in a memory. A thin client is a computer system that runs on a server based computing environment. Whereas A thick client is a system which can be connected to the server even without the network. QUESTION 4 File sharing - you can easily share data between different users, or access it remotely if you keep it on other connected devices. Resource sharing - using network-connected peripheral devices like printers, scanners and copiers, or sharing software between multiple users, saves money. Sharing a single internet connection - it is cost-efficient and can help protect your systems if you properly secure the network. Increasing storage capacity - you can access files and multimedia, such as images and music, which you store remotely on other machines or network-attached storage devices. Faster Problem-solving – Since an extensive procedure is disintegrated into a few littler procedures and each is taken care of by all the associated gadgets, an explicit issue can be settled in lesser time. Security through Authorization – Security and protection of information are additionally settled through the system. Reduced cost: Cost is one of the crucial factors that one needs to consider while evaluating the pros and cons of a particular technology. QUESTION 5 The Internet is a vast network that connects computers all over the world. Through the Internet, people can share information and communicate from anywhere with an Internet connection. An Intranet is a private, secured online network where employees can create content, communicate, collaborate, manage tasks and events, and develop the company culture. An Extranet is a private network similar to an intranet, but typically open to external parties, such as business partners, suppliers, key customers, etc. The main purpose of an extranet is to allow users to exchange data and applications, and share information. In a P2P network, the "peers" are computer systems which are connected to each other via the Internet. Files can be shared directly between systems on the network without the need of a central server. A local area network (LAN) is a collection of devices connected together in one physical location, such as a building, office, or home. A LAN can be small or large, ranging from a home network with one user to an enterprise network with thousands of users and devices in an office or school. QUESTION 3 i. Bus topology is a network setup where each computer and network device is connected to a single cable or backbone. Depending on the type of computer network card, a coaxial cable or an RJ-45 network cable is used to connect them together. Advantage It works well when you have a small network. Disadvantage Bus topology is not great for large networks ii. Star topology is one of the most common network setups. In this configuration, every node connects to a central network device, like a hub, switch, or computer. Advantage Easy to add another computer to the network. Disadvantage The central network device determines the performance and number of nodes the network can handle. iii. A ring topology is a network configuration where device connections create a circular data path. Each networked device is connected to two others, like points on a circle. Advantage Data can transfer between workstations at high speeds. Disadvantage The entire network will be impacted if one workstation shuts down. iv. Serial Transmission is the type of transmission in which a single communication link is used to transfer the data from an end to another. Advantage More reliable Disadvantage Data transmission rate is low. v. Parallel Transmission is the transmission in which multiple parallel links are used that transmit each bit of data simultaneously. Advantage It is easier to program. Disadvantage It is a costly transmission system.