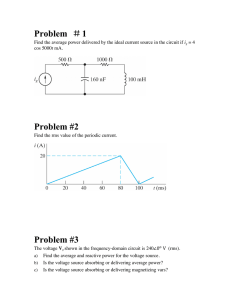
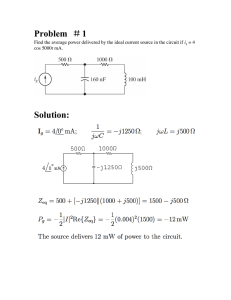
RC Circuit Part 04 Special Topics Course instructor Dr. Maryam Liaqat Group Members Group #3 1.Naeem 2.Shahzaib 3.H.M.Ayyan 4.Shahid Ali 5.Ayesha Qudrat 6.Noor ul Ain 7.Javeed Iqbal Objectives Explain true, reactive, and apparent power. Describe power triangle. Define Power Factor Significance of Apparent power Rc Circuit as a Filter Discuss About Ac Coupling. Power in RC Circuits When there is both resistance and capacitance, some of the energy is alternately stored and returned by the capacitance and some is dissipated by the resistance. The amount of energy converted to heat is determined by the relative values of the resistance and the capacitive reactance. The Power in the resistor is true power: Ptrue = I2R Power in RC Circuits Unit of true power is Watt The Power in the capacitor is reactive power: Pr = I2XC Unit of reactive power is VAR(Volt-ampere reactive). Power Triangle for RC Circuits The apparent power (Pa) is the resultant of the average power (Ptrue) and the reactive power (PR). Pa = I2totZ Ptrue = PacosΘ Power Factor The term cos , in the previous slide, is called the power factor: PF = cos The power factor can vary from 0 for a purely reactive circuit to 1 for a purely resistive circuit. In an RC circuit, the power factor is referred to as a leading power factor because the current leads the voltage. Significance of Apparent Power Apparent power is the power that appears to be transferred between the source and the load. Apparent power consists of two components; a true power component, that does the work, and a reactive power component, that is simply power shuttled back and forth between source and load. Apparent power is expressed in Volt-amperes (VA). Basic Applications RC series circuit Used for filtering Low Pass Filter High Pass Filter Low-Pass RC Filter A capacitor acts as an open to dc. As the frequency is increased, the capacitive reactance decreases. As capacitive reactance decreases, output voltage across the capacitor decreases. A series RC circuit, where output is taken across the capacitor, finds application as a low-pass filter. Low Pass Filter (frequency cutoff) 1 1 fc 2 2RC = Time Constant = RC fc = frequency cutoff Vout Attenuation Gain 20 log Vin (dB) High-Pass RC Filter For the case when output voltage is measured across the resistor. At dc, the capacitor acts an open, so the output voltage is zero. As frequency increases, the capacitive reactance decreases, resulting in more voltage being dropped across the resistor. The result is a high-pass filter. High Pass Filter (Frequency cutoff) 1 1 fc 2 2RC = Time Constant = RC fc = frequency cutoff Vout Attenuation Gain 20 log Vin (dB) AC Coupling An RC network can be used to create a dc voltage level with an ac signal superimposed on it. This is often found in amplifiers, where the dc voltage is required to bias the amplifier. Summary In an RC circuit, part of the power is resistive and part is reactive. The phasor combination of resistive power and reactive power is called apparent power. Apparent power is expressed in volt-amperes (VA). The power factor indicates how much of the apparent power is true power. Summary A power factor of 1 indicates a purely resistive circuit, and a power factor of 0 indicates a purely reactive circuit. A filter passes certain frequencies and rejects others. An RC network can be used to create a dc voltage level with an ac signal superimposed on it. Trouble shooting Effect of an Open Capacitor When the capacitor is open. • There is no current. • Thus, the resistor or voltage remains at zero. • The total source voltage is across the open capacitor. Effect of shorted capacitor Capacitors rarely short; but when a capacitor does short out, the voltage across it is zero, the current equals ViR, and the total voltage appears across the resistor, as shown in Figure